Comprehensive Drama and Theatre Concepts: Play-Events, Genres, and Aristotle's Components
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
play-events
Performances that happen in time and at a specific place.
conventions
A sort of group agreement about some basics of how something will unfold.
genre
Derived from the French word for 'kind.'
tragedy
A profoundly serious play that almost always ends in the death of one or more of its main characters.
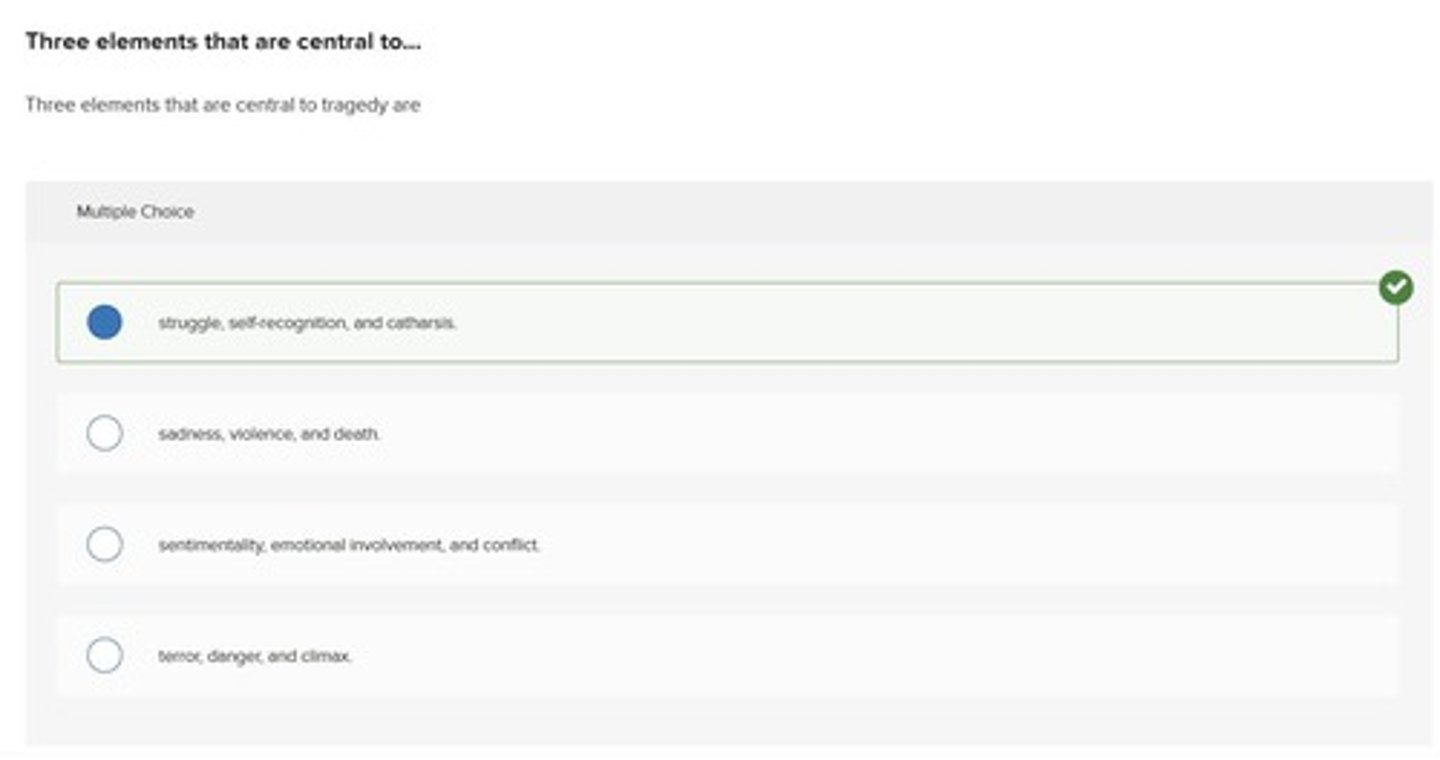
elements of tragedy
Struggle, self-recognition, and catharsis.
comedy
A play that exhibits ordinary life through devices such as mistaken identities and sexual puns.
dramaturgy
Term derived from Greek words 'drama' and 'ergos'.
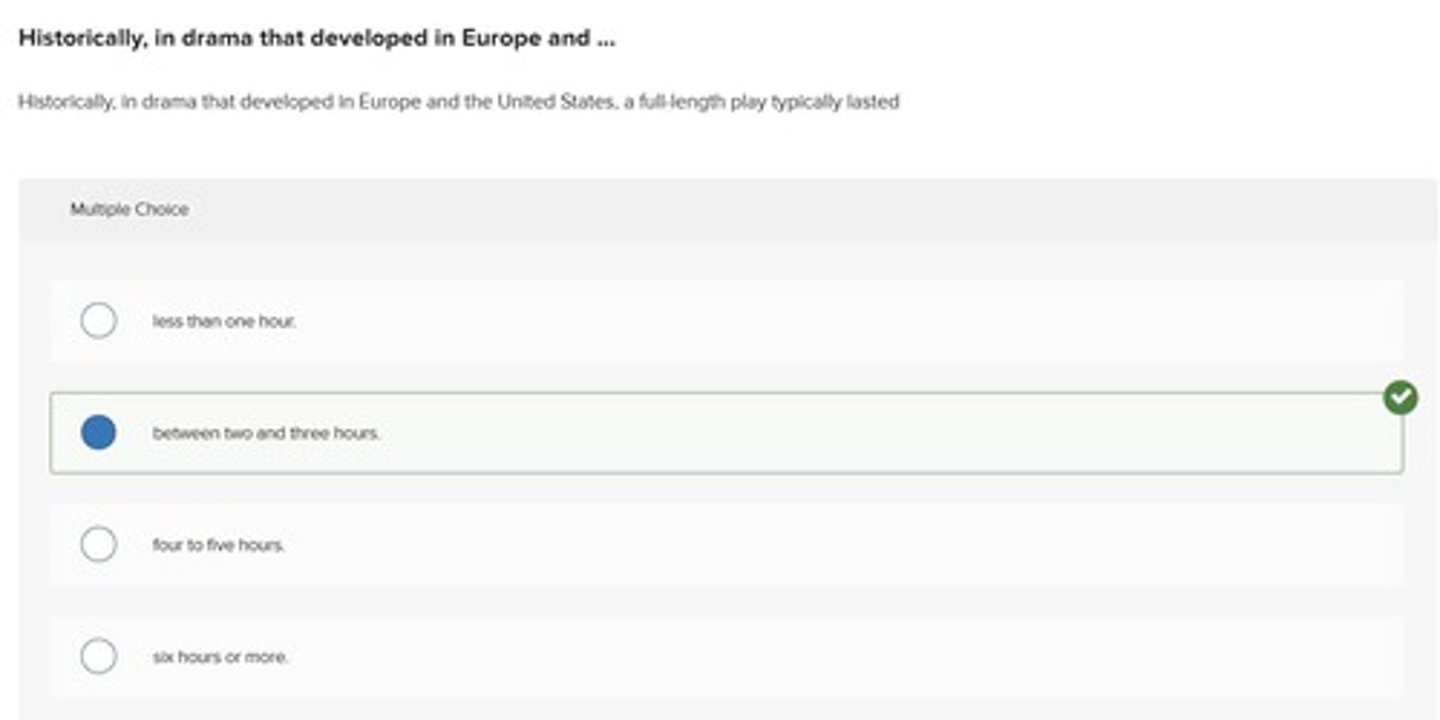
historical play duration
A full-length play typically lasted between two and three hours.
struggle
One of the three central elements to tragedy.
self-recognition
One of the three central elements to tragedy.
catharsis
One of the three central elements to tragedy.
narrative
Simply the narrative of what happens in the play.
repeated elements
The repeated elements of a play that come to define our experience of the play, text, or performance.
quality of language
Used to describe the quality of a play's language.
sixteenth century genres
Genres that first came to popularity in the sixteenth century when William Shakespeare wrote plays.
ordinary life
A play that exhibits ordinary life through devices such as mistaken identities and sexual puns.
historical drama
Drama that developed in Europe and the United States.
full-length play
Typically lasted between two and three hours.
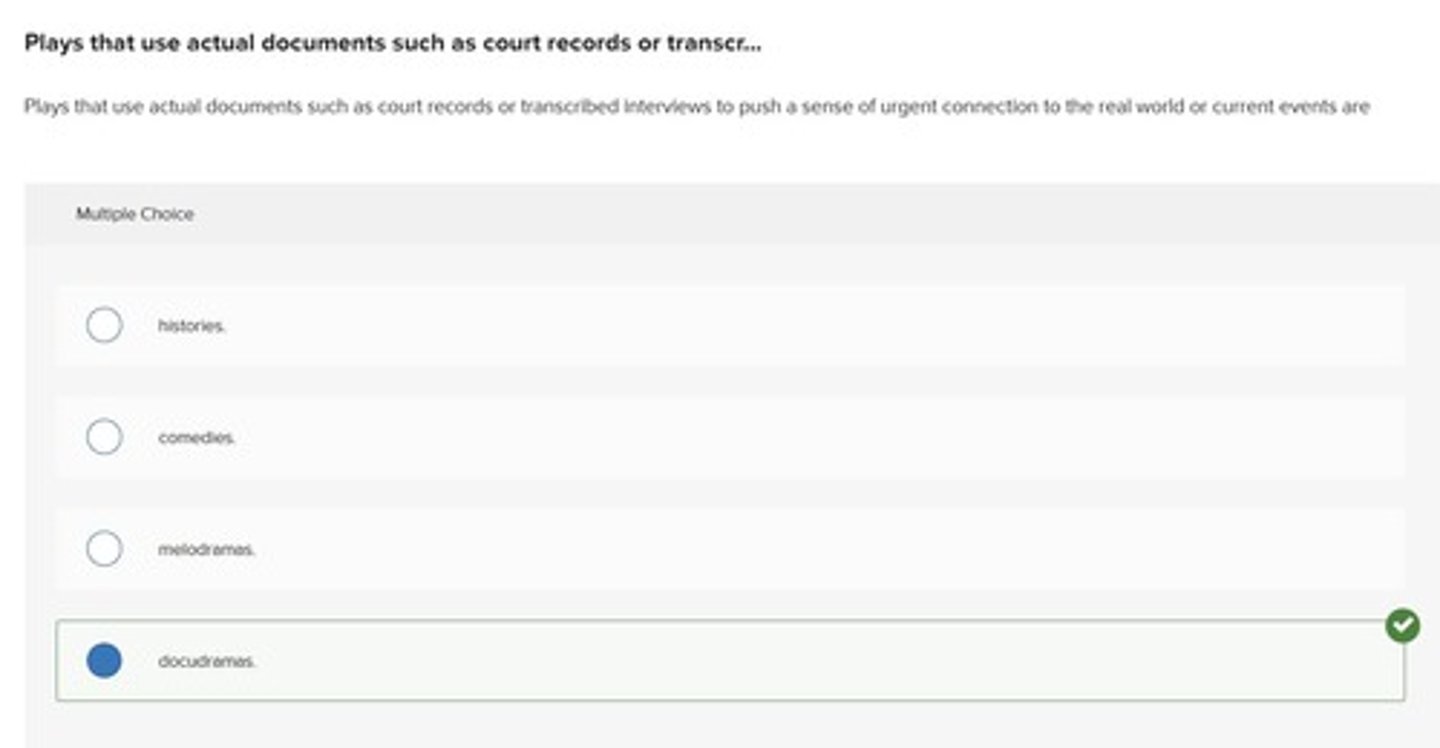
docudramas
Plays that use actual documents such as court records or transcribed interviews to push a sense of urgent connection to the real world or current events.
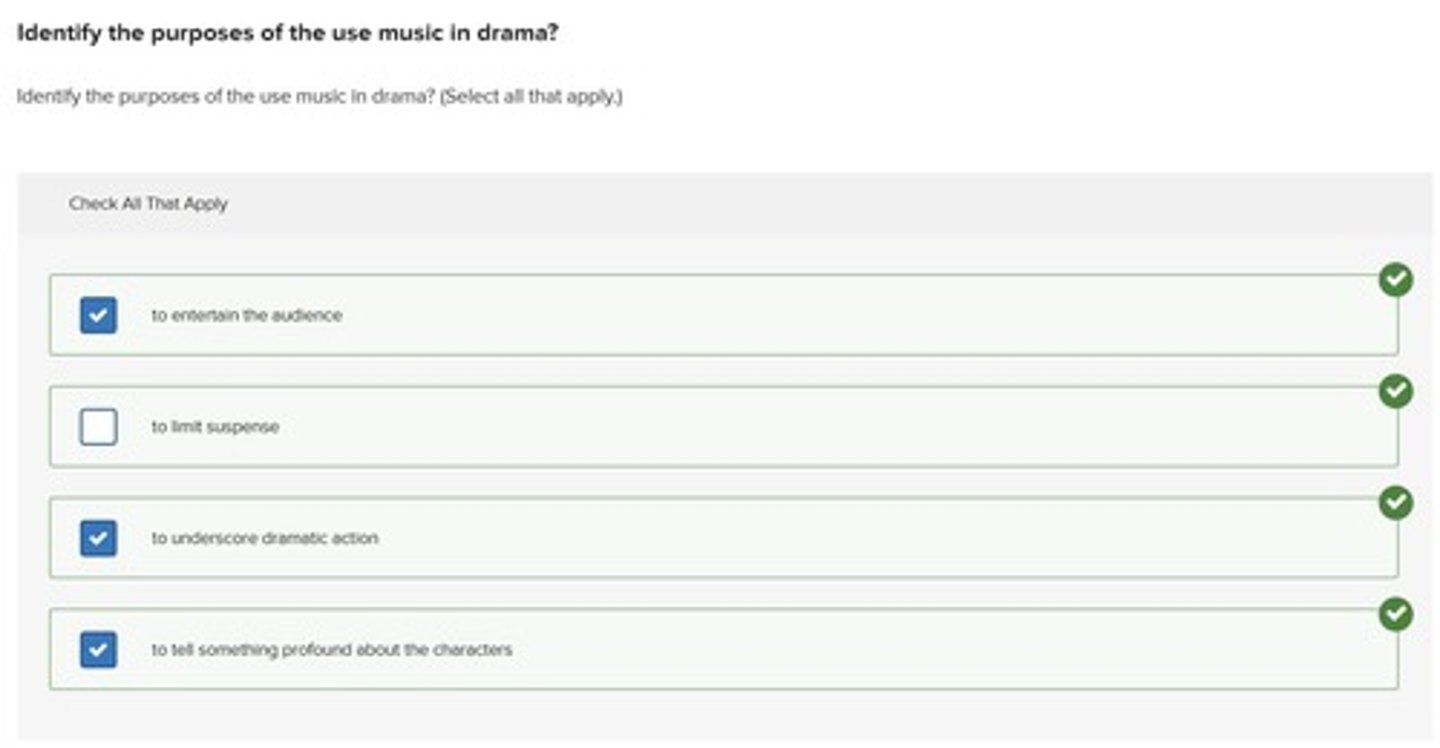
music
A component of drama that serves various purposes, including entertainment and underscoring dramatic action.
plot
The sequence of events in a play, including the order of characters' entrances and exits, actions that take place onstage, and the reasons behind events.
character
The individuals who take part in the action of a play, defined by their traits and roles.
thought
Aristotle's concept that is consistent with what we might think of as a play's theme.
diction
The quality of a play's language.
spectacle
The visual aspects of production such as scenery, costumes, lighting, makeup, properties, and the overall look of the theatre and stage.
the rehearsal process
An element of the pre-play that involves practicing the performance before the actual presentation.
advertising the production
An element of the pre-play that involves promoting the play to attract an audience.
ushers that provide the audience with programs
An element of the pre-play that involves assisting the audience by distributing information about the performance.
an announcement asking the audience to silence their cell phones
An element of the pre-play that ensures minimal distractions during the performance.
conflict
A key feature in the orderly plot sequencing of a conventionally Aristotelian dramatic experience.
conversation
A key feature in the orderly plot sequencing of a conventionally Aristotelian dramatic experience.
climax
The point in a play where the conflicts reach their peak.
circumstance
A key feature in the orderly plot sequencing of a conventionally Aristotelian dramatic experience.
exposition
The introduction of background information within a play.
post-play
The events or activities that occur after the main action of the play has concluded.