Stagecraft chapter 5
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
choosing wood
1)look for straight grain and even texture
2) should be straight, not warped, strong and rigid
3) inexpensive and available in sufficient quantities
grading quality
A - D
A grading
used for all practical purposes
B grading
difficult to acquire and is expensive
C grading
top grade for use in construction, has small blemishes and deflects but do not physically detract from it
D grading
there are more surface blemishes but none so great that significantly detracts the property of the material
common grades
1 - 5
grades 1-2
generally considered structurally sound and used for scenery framing or where appearance is NOT a factor
grades 3-5
are increasingly difficult to use with out considering amount of waste due to knotholes and other defects that must be avoided
board lumber
referenced by its thickness, width, and sold by its board foot
1 × 12
1” thick and 12” wide
12 × 12 × 1
1” thick, 12” wide, 12” long
1 inch in lumber sizes
Actual size: 3/4 “
2 - 6 inches in lumber sizes
Actual sizes: 1” 1/2 , 2” 1/2 , 3” 1/2 , 5” 1/2
8 - 10 inches in lumber sizes
Actual sizes: 7” 1/4, 9” 1/4, 11” 1/4
Use of 1 × 2
used for small framing members
Use of 1 × 3
used for standard framing
Use of 1 × 4
used for battens or large framed units
1 × 6 and 8
used for door, window casings, and framing and achitectural trim
1 × 10 and 12
used for properties, furniture, and architectural trim
3/4” x 3 and 4
used for light platform, framing and large framed units
2 × 4, 6, 8, 10, 12
used for weight bearing structures and trusses
Sheet goods
aka paneling, are manufactured products created from the by products of wood
plywood
used for flooring surfaces and it is composed of layers of wood w/ grains that lay adjacent from another
lauan
type of hardwood plywood and used to cover hard covered flats, very smooth but not environmentally friendly
particle board
composed of small wood chips, saw dust, and glue (costs considerably less than plywood but is heavier and weaker) however is hard to work with and is often used for cabinets and cabinets
MDF (medium density fiberpine)
fine grain version of the particle board and is very easy to use in machines and routing
OSB (Oriented strand board)
composed of compressed strands arranged in layers oriented right angles to one another. . . can be used similar to plywood if finish is not important
Masonite
aka hardboard/pressboard, used for nonstructural flooring and facing. . . can come tempered (very hard) or non tempered
Homosote
works well for sound deadening as part of the decking of a floor or platform and can be used as the top surface of a deck for a sculpted or heavily textured finish
Celotex
less expensive and readily available than homosote, softer and requires greater care to prevent compression when used in flooring applications
Quarter Round Moulding
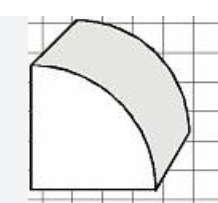
Half Round Moulding
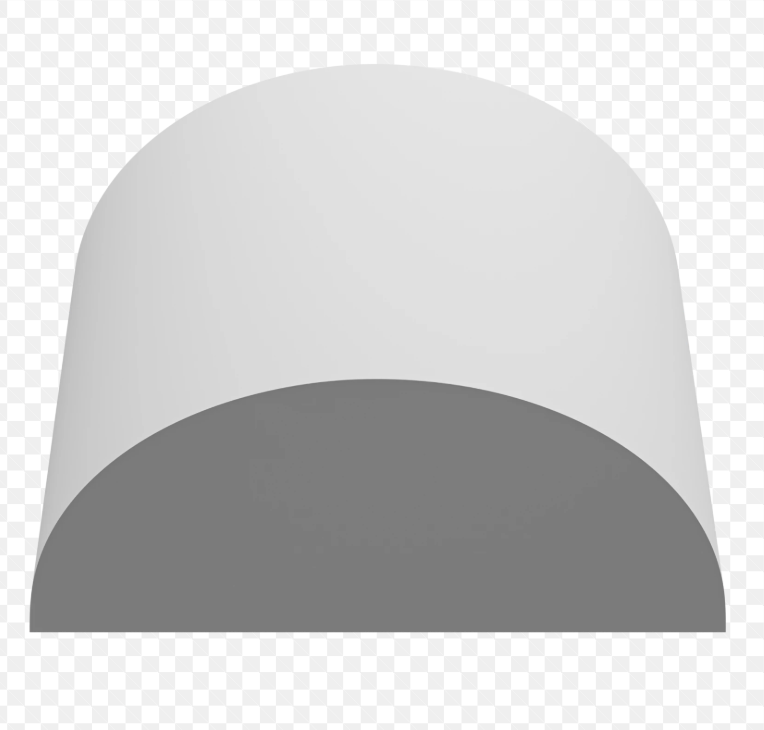

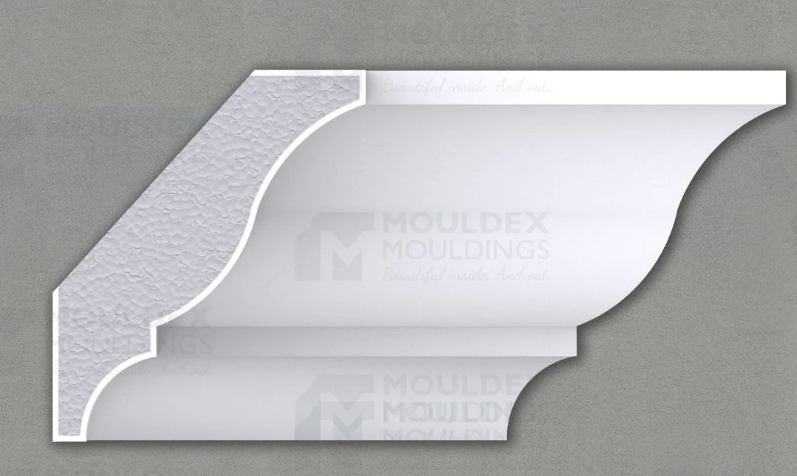
Cove moulding
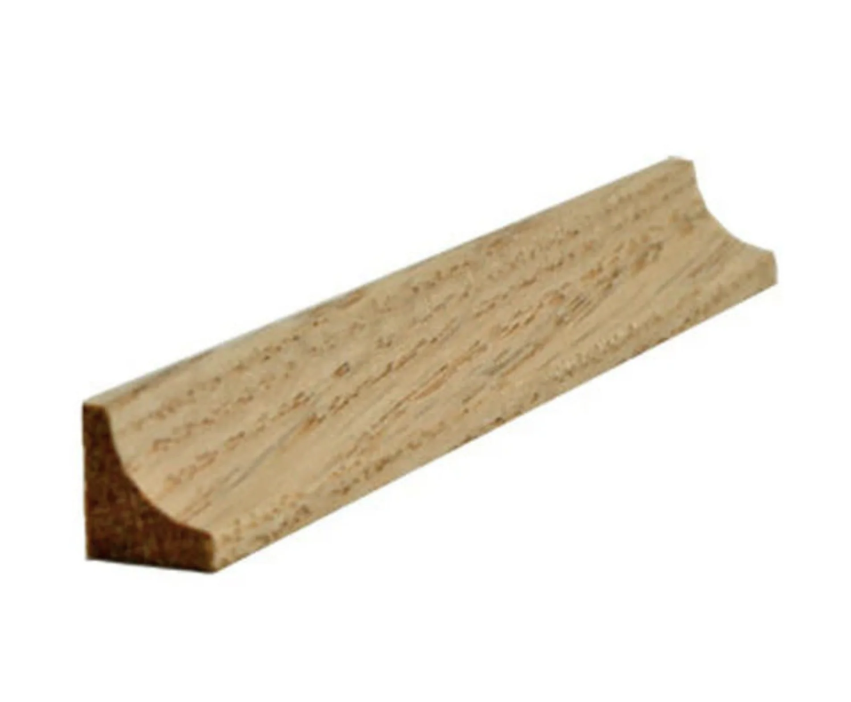

Ogee Moulding
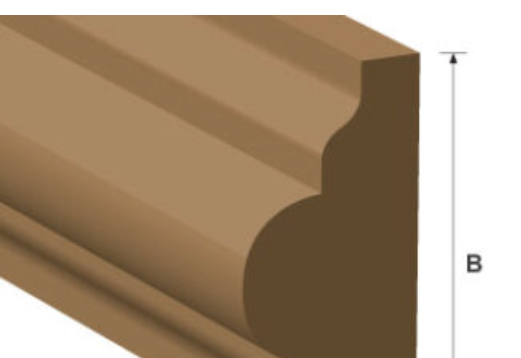
Picture Rail Moulding
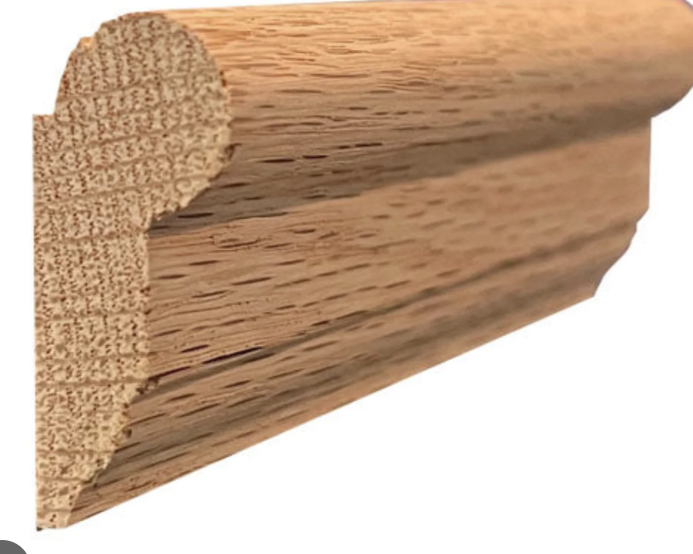

Crown moulding
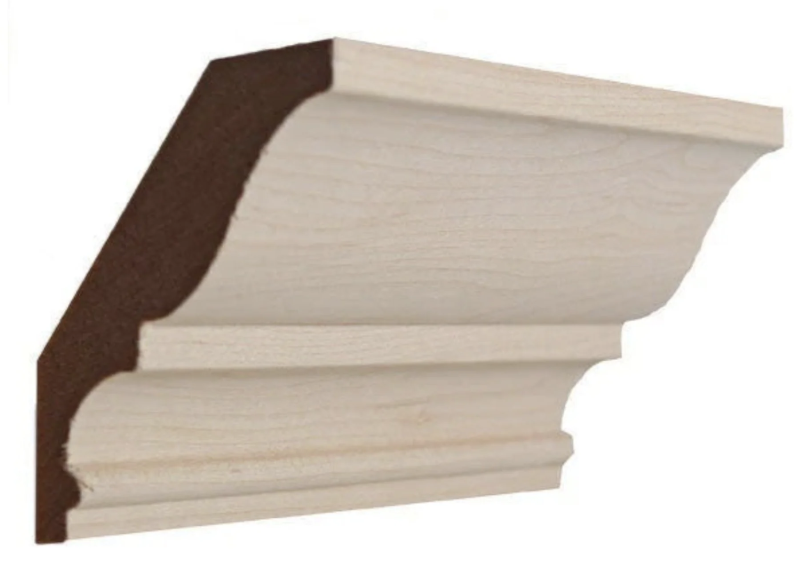

Cornice moulding
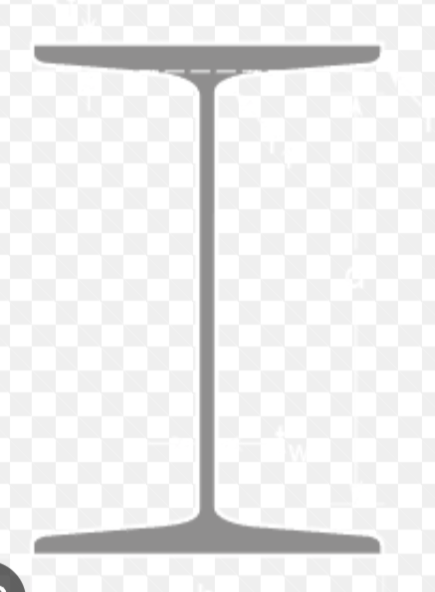
“W” Wide Flange Beam
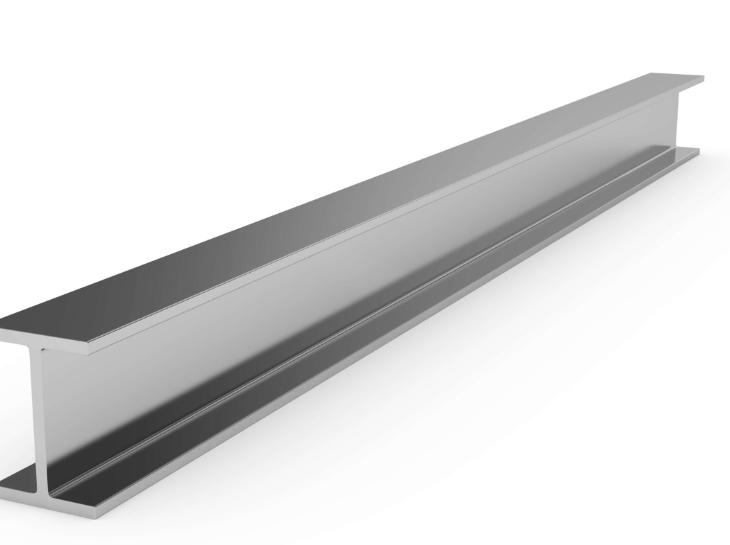
“S” Standard Beam

Moulding
variety of shapes for door and window casings, baseboards, chair rails, picture rails and cornic mouldings
Metal
an alternative to traditional wood construction, the structural characteristics meet demands of modern scenic design
structural steel
used scenery applications with with a plain oxide finish
Tubing
round, rectangular, square steel tubing is useful in steel construction for scenery, alternative to board lumber
plastics
synthetic or organic materials that can be shaped when soft and hardened, capable of being moulded
styrofoam
most prevalent form of plastic and available in varying densities
beadboard
manufactured from expandable polystyrene beads, most often found formed into sheets for use by the building trades as insulation
Acrylic
commonly known as plexiglass and comes in sheets, rods, bars as well as a variety of textures and colors
Lexan
is highly resistant to impact, kind of similar to acrylic and is ideally suited for transparent weight-bearing surfaces
Ethafoam
low density, flexible material available in sheets and rods. Particularly useful in number of moulding and trim applications on curved surfaces
Polyurethane foam
two part liquid that when mixed together expands and hardens into a rigid polysterene like material. Once hard, the material can be carved very easily
PVC (polyvinyl chloride)
commonly used in the theater as pipe but can be available in rods and sheets
fabric
used in theatrical scenery construction and general stage use fall into three basic categories: scenery fabrics, stage draperies and speciality fabrics
scenery fabrics
used in scenic construction with the goal of representing something else. These fabrics are typically meant to be painted
Muslin
a plain weave cotton fabric is the most common material in this category and is used primarily for drops and soft covered flats, and to provide a quality painting surface on hard covered scenic units (comes with limited color assortment)
canvas
a very strong and durable, closely woven cotton fabric used primarily for ground cloths and to provide a quality point surface for false doors and platforms. . . also used in covering for scenic units that are very large or expected to withstand heavy use or rough treatment
Sharkstooth scrim
used extensively for theatrical application requiring a bleedthrough effect
(when the front line is removed and the scene behind the scrim is lit, the scrim and its painting appear to dissolve, revealing the scene behind)
Leno Skilled Scrim
an opaque, densely knit fabric will no render a bleed through effect. . . very elastic, making it virtually wrinkle free and an excellent choice for cycloramas or full stage backings
cotton scrim
open weave fabric made of very fine threads, can be used like sharkstooth scrim in smaller and less demanding applications
theatrical gauze
coarser and a larger weave than cotton scrim
Bobbinet
larger open weave than sharkstooth and cannot be lit to appear opaque
scenic netting
used to support cut out drops, borders, and legs
opera netting
similar to sharkstooth but with a more open weave
cheesecloth
commonly used to cover foam and plastic
Burlap
a very coarse, heavy, plain weave fabric made of cotton jute or hemp. . . used to provide a textured surface
stage draperies
these fabrics are used primarily for stage curtains such as front drapes, travelers, masking legs, borders, and backdrops. They are also used to cover constructed pieces such as portals and hard legs, and as general purpose masking fabric.
Velour
first choice for stage draperies. . . has a long, thick nap, which gives the fabric a rich texture and absorbs light well, making it an excellent fabric for masking drapes.
Velveteen
a lightweight velour available
Wool Serge
used in england in place of velour for stage draperies. . .it is extremely dense, brushed-weave fabric with excellent light absorption properties
duvetyn
is a soft felted fabric used extensively for masking and blackout drapes.
commando cloth
another name for duvetyn. Refers to heavy weight devetyn.
other stage draperies
fabrics of assorted colors. . . with textures and patterns woven.
box nails
have a large flat head and a thinner diameter shank than common nails, and come in a smaller range of sizes
Finish Nails
used to secure moulding or in any application where exposed nail heads would be obtrusive. . .have a very small head so it’s not so visible
Duplex nails
known as double head or scaffolding nails. . . used for temporary fastening
roofing nails
have wide, flat heads, which makes them useful in holding soft and easily compressible materials like Homosote or Celotex. Can be used in pneumatic nailers
Clout Nails
designed to penetrate through the wood, strike a metal plate placed under the material and curl back into the wood fibers. . . this creates a secure joint
corrugated fasteners
used to temporarily. hold a corner joint together until a permanent fastening can be completed.
wood screws
are most useful when a joint needs to be taken apart at a later date, to fasten hardware to scenic units, and on occasions when the clamping force and holding power of a screw can be used to advantage
Drywall Screws
useful for certain applications. . . they are tempered which causes them to shatter under certain conditions
lag screws
large, heavy duty wood screws. . . come with a square or hex head are are sometimes called lag bolts
Sheet metal screws
designed to fasten metal to metal
Self drilling screws
aka tek screws, combine a drill and screw into a single efficient unit to save time and labor costs. . . terrific fastener to use when applying wood coverings to steel frames
Machine bolts
have square or haxagonal heads and are threaded over approximately the first 1 1/2” shank
Stove bolts
have flat or round slotted heads and are threaded over the entire length of the bolt shank
machine screws
like stove bolts, but with finer threads
carriage bolts
have a round head and a square portion of shank just below the head. . . designed to refrain the bolt from turning
Yellow Glue
aka carpenter’s glue used for most wood on wood applications. . . it dries one to two hours and should NOT be used to adhere muslin to flat frames because it discolors fabric
White glue
is more flexible, and suitible for use with fabrics, wood, and paper. It can be diluted and cleaned with water before it dries
Epoxy
used when a waterproof adhesive is required. . . it generally comes in two parts. . . they are very strong and fast drying
contact cement
most commonly used to adhere nonporous materials. . . .its advantage is that it holds on contact, which can be very useful for some theater applications
Glue sticks
hot glue sticks are used with a glue gun for applications that do no require strength
The back flap hinge
available with a tight pin or loose pin. . . the pin is easily inserted and removed to faciliated the quick scene shift and the tight pin back is used for longer lasting unions
The butt hinge
is most commonly found on doors, and is designed to be mortised into the edge of the door and the door jamb
Piano Hinge
aka continuous hinge
Strap hinges
can also be either tight pin or loose pin
latches
used to secure doors, cupboards, and windows as well as for a variety of creative uses.
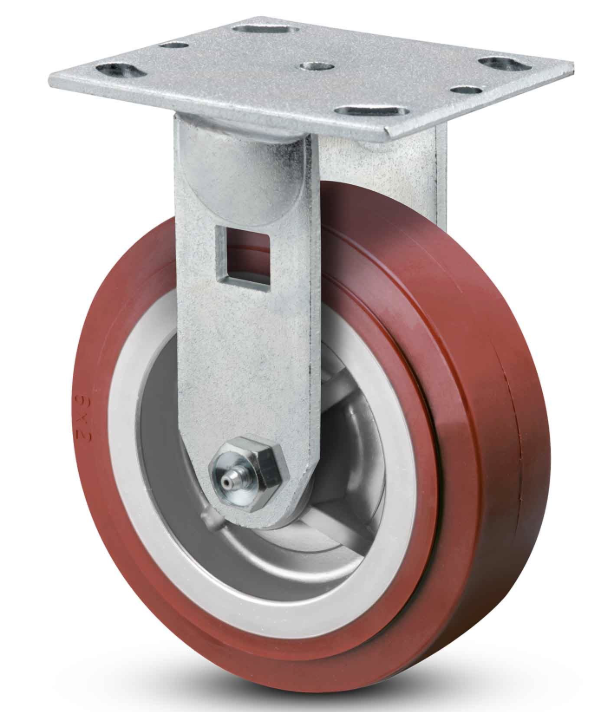
Rigid casters
fixed, straight, or stationary casters that move along a single line

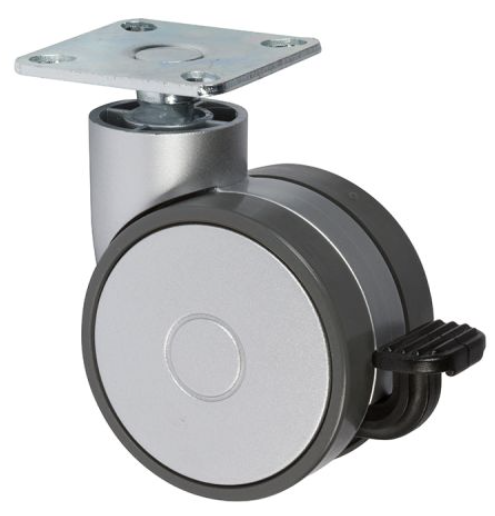
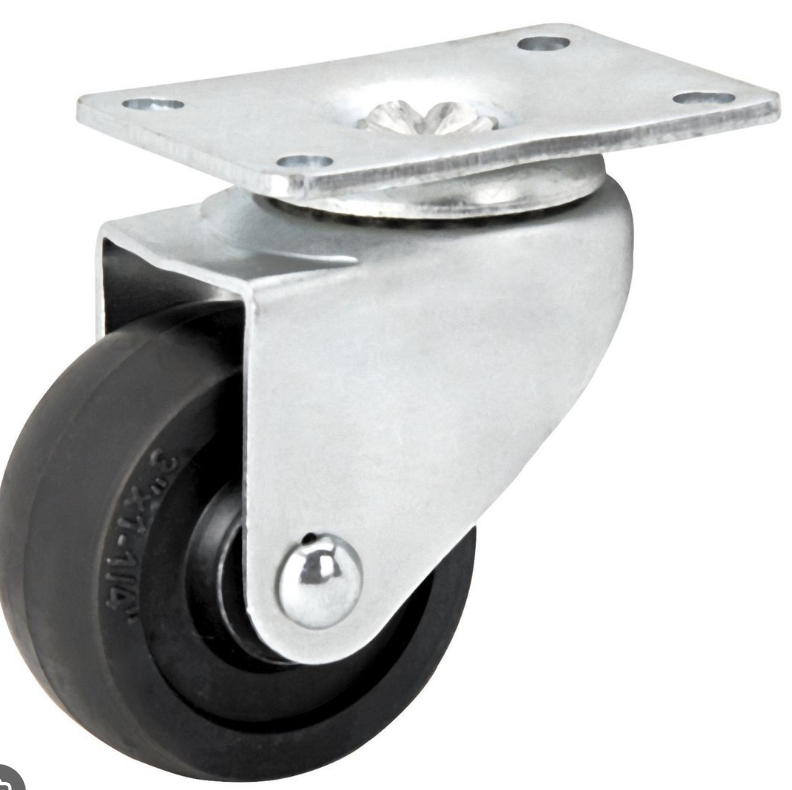
Swivel casters
allow for movement in any direction. . . some casters are equipped with a locking mechanism that turns them rigid

furniture caster
may employ a ball or roller in place of the wheel
