Demographics
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is the dependency ratio?
An age-based measurement that takes people younger than 14 and older than 65 who are not in the labor force, and compares that to the number of people who are
What is the life course theory?
Aging is a social, psychological, and biological process that begins from the time you are born until the time you die
What is the age stratification theory?
Suggests that age is a way of regulating behavior of a generation
What is activity theory?
Looks at how the older generation looks at themselves
What is disengagement theory?
Older adults are society separate, assumes they become more self-absorbed as they age
What is continuity theory?
People try to maintain same basic structure throughout their lives overtime
What is the racial formation theory?
Looks at the social/economic/political forces that result in racially constructed identities
What is race?
A socially defined category based on physical differences between groups of people
What is ethnicity?
Socially defined, not defined by physical characteristics like race, but these groups are defined by shared language, religion, nationality, history, or some other cultural factor
What is pluralism?
Encourages racial and ethnic variation
What is gender?
A social construction theory that states that gender is not a fixed or innate fact, but instead it varies across time and place
What are gender roles?
A set of societal norms dictating what types of behaviors are generally considered acceptable, appropriate, or desirable for a person based on their actual or perceived sex
What is gender schema theory?
Theory that explains how individuals should be gendered in society
What is gender script?
What we expect men and females to do
What is urbanization?
The movement of people from rural to urban area
What are rural areas?
Anywhere with <1000 people per square mile
What are urban areas?
Cities/towns with >1000 people per square mile
What is metropolis?
Cities with over 500,000 people
What is a megalopolis?
Many metropolises connected together
What is suburbanization?
Movement away from cities to get a larger home, but commute to work can be long and harder to get medical help
What is urban decline?
As people move out of city centers, the city can fall into disrepair
What are exurbs?
Beyond suburbs; prosperous areas outside of the city where people live and commute to city work
What is urban renewal?
Revamping old parts of cities to become better
What is gentrification?
Redesign of city parts in the hopes of targeting a wealthier community, which increases property value
What is rural rebound?
People getting sick of cities and moving back out to rural areas
What is a slum?
A heavily populated urban informal settlement characterized by substandard housing and squalor
What are ghettoes?
Areas where specific racial, ethnic, or religious minorities are concentrated, usually due to social or economic inequalities
What 3 factors contribute to total growth rate?
Fertility, migration, and mortality
What is fecundity?
The potential reproductive capacity of a female
What is immigration?
Movement of a person into a country
What is birth rate?
The number of births per 1000 people per year
What is fertility rate?
The number of births a woman is expected to give birth to in her child bearing years
What is emigration?
Movement of a person out of a country
What is a population pyramid?
Graphs the age and sex distribution of a population
What is a stationary/constrictive pyramid?
Indicates low birth and death rates in a population
What is an expansive population pyramid?
High birth rate and high death rates
What is a life-table/mortality table?
When you break mortality rate by age, tells the probability someone will die given their age
What is internal migration?
Moving within the same country
What is growth rate?
How much a population of a country grows or shrinks over a period of time
What is demographic transition?
A model that changes a country’s population
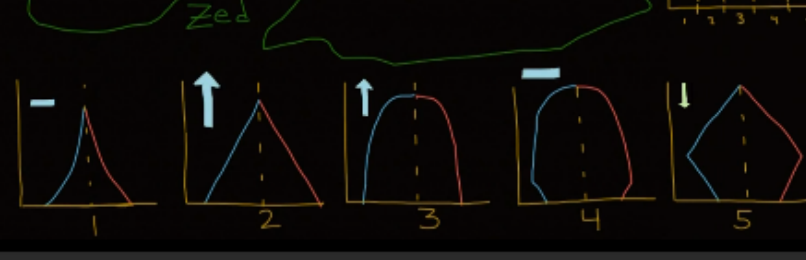
What is the first stage in the demographic transition model?
High birth rates due to limited birth control, economic advantage for more workers, and higher death rate due to disease/poor nutrition; large young population and small old population; overall population remains fairly stable
What is the second stage in the demographic transition model?
Population rises as death rate decreases/lower death rate, but high birth rates remain; overall population growth
What is the third stage in the demographic transition model?
Death rates continue to drop and birth rates begin to fall; access to birth control and social trend towards smaller families; more industrialized and children no longer need to work
What is the fourth stage in the demographic transition model?
Both birth rates and death rates are low and balance each other out, longer life expectancy
What is the fifth stage in the demographic transition model?
Speculation, the world population will be forced to stabilize; lack of resources will lead to public health disaster and force population to stabilize
What is the Malthusian theory?
We won’t be able to maintain natural resources for everyone on the planet
What is anti-Malthusian theory?
Couples only want to have one child or have children later in life
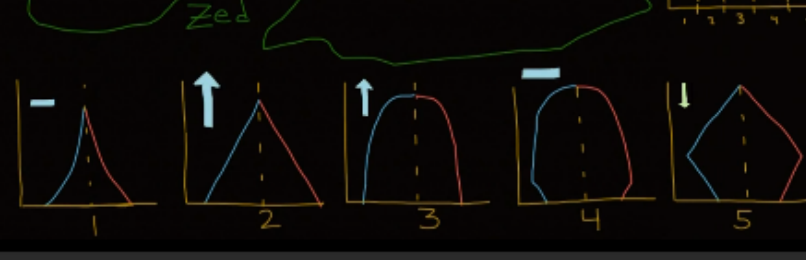
Demographic transition model
What is globalization?
The sharing of culture, money, and products between countries due to international trade and advancements in transportation and communication
What is the world-systems theory?
Importance of the world as a unit, rather than individual countries
What is a core country?
Economically diversified, industrialized, and independent of outside control
What is a periphery country?
Relatively weak government, greatly influenced by and depend on core countries and transnational corporations; focuses on on economic activity like extracting a raw material
What is a semi-periphery country?
Not dominant in international trade, but diversified/developed economy. Middle-ground between core and periphery
What is modernization theory?
All countries follow a similar path of development from traditional to modern society
What is dependency theory?
Periphery countries export resources to core countries; they will remain poor and dependent on core countries
What is the hyperglobalist perspective?
Sees globalization as a new age in human history; countries become interdependent and nation states themselves are less important
What is the skeptical perspective?
Critical of globalization and considers it as being regionalized instead of globalized
What is the transformationalist perspective?
Believe national governments are changing, perhaps becoming less important but difficult to explain change so simply
What is globalization?
We live in a global community not limited by physical boundaries
What are activist movements?
Aim to change some aspect of society
What are regressive/reactionary movements?
Resist change
What is mass society theory?
Social movements would only form for people seeking refuge from main society
What is the relative deprivation theory?
Actions of groups oppressed/deprived of rights that others in society enjoy
What are the 3 things needed for social movement to form?
Relative deprivation, feeling of deserving better, and conventional means are useless
What is resource mobilization theory?
Focuses on factors that help/hinder a social movement like access to resources
What is rational choice theory?
People compare the pros and cons or different courses of actions and choose the one they think is best for themselves
What is the incipient stage of social movement?
Public takes notice of the situation that they consider to be a problem