SCUHS Neuro Lecture Final (Nolte Ch. 1-23) created by troubleZZ edited by me
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
A. Fight or Flight
The sympathetic nervous system is commonly referred to as the system that governs the ___________________________ response.
A. Fight or Flight
B. Read and Feed
C. Fight and Sleep
D. Rest and Digest
3 multiple choice options
C. 12
How many cranial nerves are there?
A. 7
B. 22
C. 12
D. 2
3 multiple choice options
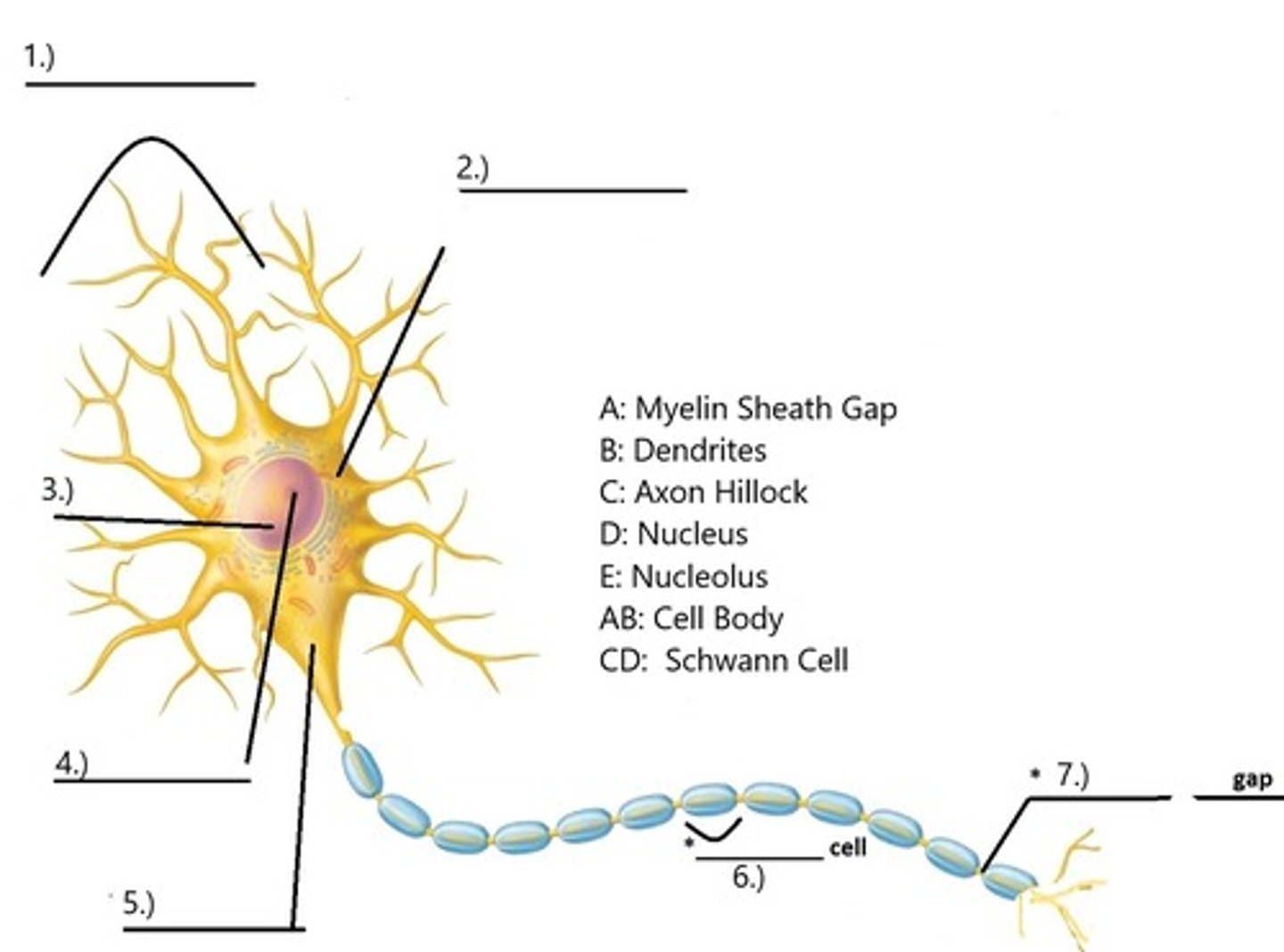
A. Dendrites
The receptive region of a neuron shown here as #1 is called:
A. Dendrites
B. Schwann Cell
C. Axon
D. Myelin Sheath Gap
3 multiple choice options
A. Multipolar
The most common type of neuron in the CNS is:
A. Multipolar
B. Unipolar
C. Non-Polar
D. Bipolar
3 multiple choice options
A. Myelin
The nervous system is made up of white matter and gray matter. What makes white matter appear white?
A. Myelin
B. Cell Bodies
C. Nissl Substance
C. Chromatin
3 multiple choice options
C. Cell Bodies
What is NOT considered to be a subdivision of white matter:
A. Funiculus
B. Fasciculus
C. Cell Bodies
D. Tract
3 multiple choice options
C. Wallerian Degeneration
_________________is an active process of degeneration that results to the axon distal to the injury when a nerve fiber is cut or crushed.
A. Demyelination
B. Parkinson's Disease
C. Wallerian Degeneration
D. Alzheimer's Disease
3 multiple choice options
B. False
True or False? Peripheral nerves are not capable of regenerating.
A. True
B. False
1 multiple choice option
C. NSAIDs
What substances are known to block VEG-F?
A. Vitamin B12
B. Vitamin C
C. NSAIDs
D. CBD
3 multiple choice options
C. Oligodendrocytes
What cell type makes myelin sheath in the Central Nervous System?
A. Schwann Cells
B. Astrocytes
C. Oligodendrocytes
D. Satellite Cells
3 multiple choice options
C. Hippocampus
Which of the following is NOT a part of the diencephalon?
A. Thalamus
B. Subthalmic Nuclei
C. Hippocampus
D. Hypothalamus
3 multiple choice options
C. Ectoderm
The nervous system is made from what embryological structure?
A. Mesoderm
B. Endoderm
C. Ectoderm
2 multiple choice options
B. Neutroderm
What is NOT a primary germ layer?
A. Endoderm
B. Neutroderm
C. Ectoderm
D. Mesoderm
3 multiple choice options
D. Mesencephalon
The cerebral aqueduct is derived from ____________________
A. Telencephalon
B. Rhombencephalon
C. Diencephalon
D. Mesencephalon
3 multiple choice options
C. Sulcus Limitans
_____________ separates sensory & motor areas of the spinal cord & brain stem.
A. Lateral Sulcus
B. median Sulcus
C. Sulcus Limitans
D. Central Sulcus
3 multiple choice options
C. Metencephalon
The cerebellum is derived from the:
A. Telencephalon
B. Mesencephalon
C. Metencephalon
D. Diencephalon
3 multiple choice options
D. Mesencephalon
Which of the following is both a named primary vesicle and secondary vesicle in Neuroembryology?
A. Diencephalon
B. Rhombencephalon
C. Metencephalon
D. Mesencephalon
3 multiple choice options
B. Neural Crest Cells
Which of the following differentiates into the peripheral nervous system?
A. Neural Groove
B. Neural Crest Cells
C. Neural Fold
D. Neural Tube
3 multiple choice options
D. Telencephalon
Which of the following is NOT a primary vesicle?
A. Rhombencephalon
B. Prosencephalon
C. Mesencephalon
D. Telencephalon
3 multiple choice options
B. Meningocele
An outpouching of the dura mater, CSF but NOT the spinal cord is known as:
A. Spina Bifida
B. Meningocele
C. Meningitis
D. Myelomeningocele
3 multiple choice options
D. Medulla Oblongata
Pyramids and Olives are landmarks on what structure?
A. Midbrain
B. Cerebellum
C. Pons
D. Medulla Oblongata
3 multiple choice options
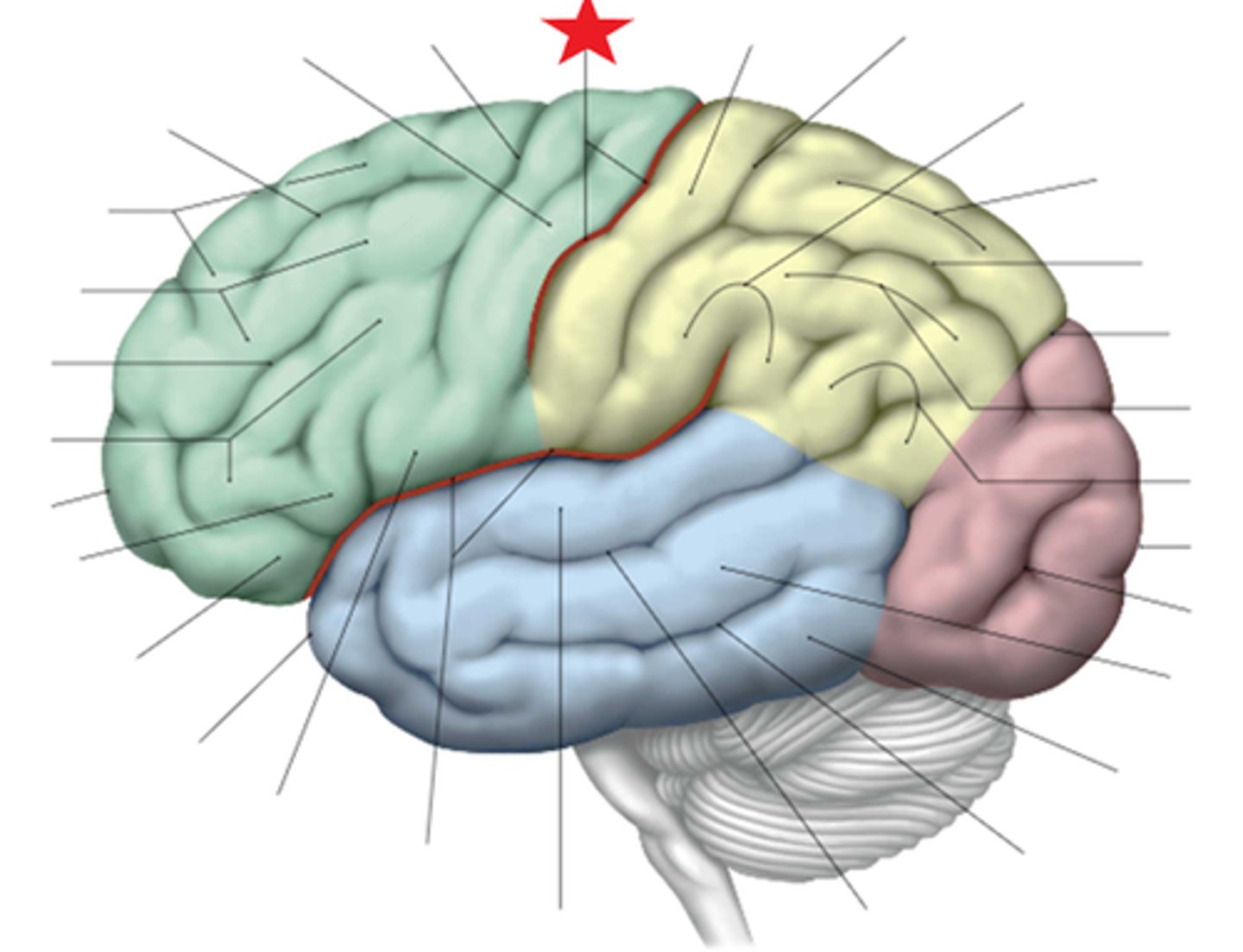
C. Central Sulcus
The redline in the center between the frontal and parietal lobes traditionally known as the separating line between motor from sensory function shown with a star here is called the:
A. Lateral Sulcus
B. Cingulate Sulcus
C. Central Sulcus
D. Calcimine Sulcus
3 multiple choice options
C. Serotonin
Electrical Stimulation of the periaqueductal gray has been shown to cause the release of norepinephrine, glycine and this pain modulating substance:
A. Substance P
B. Glutamate
C. Serotonin
D. TNF
3 multiple choice options
C. Homunculus
The word "_________________" means little man in Latin. But in neuroanatomy, the cortical _____________________represents either the motor or the sensory distribution along the cerebral cortex of the brain. The motor homunculus is a topographic representation of the body parts and its correspondents along the precentral gyrus of the frontal lobe. While the sensory homunculus is a topographic representation of the body parts along the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe.
A. Hypothalamus
B. Parietal
C. Homunculus
D. Hippocampus
3 multiple choice options
A. Brainstem
Most of the cranial nerves are attached to the:
A. Brainstem
B. Parietal Lobe
C. Frontal Lobe
D. Spinal Cord
3 multiple choice options
A. Medulla, Pons, Midbrain
Identify the correct order of the structures of the brain stem from inferior to superior (caudal to cephalad).
A. Medulla, Pons, Midbrain
B. Pons, Midbrain. Medulla
C. Medulla, Midbrain, Pons
D. Midbrain, Pons, Medulla
3 multiple choice options
B. Kinesthesia
The medical terminology for awareness of movement/ the ability to discriminate joint position, relative weight of body parts, and joint movement, including speed, direction, and amplitude is:
A. Two Point Discrimination
B. Kinesthesia
C. Stereognosis
D. Proprioception
3 multiple choice options
C. Cerebellum
Which of the following structures is most associated with balance:
A. Inferior Colliculus
B. Superior Colliculus
C. Cerebellum
D. Red Nucleus
3 multiple choice options
C. Flexion Protection Reflex
The red nucleus and rubrospinal tract is known for:
A. Extensor Reflex
B. Gag Reflex
C. Flexion Protection Reflex
D. Blink Reflex
3 multiple choice options
D. Superior Colliculus
Which of the following structures mediates the visual startle reflex?
A. Tegmentum
B. Substantia Nigra
C. Inferior Colliculus
D. Superior Colliculus
3 multiple choice options
A. Ependymal Cells
What cell type makes cerebral spinal fluid?
A. Ependymal Cells
B. Astrocytes
C. Oligodendrocytes
D. Schwann Cells
3 multiple choice options
B. Pia Mater, Arachnoid Mater, Dura Mater
Place the meninges in proper order from deep to superficial:
A. Dura Mater, Pia Mater, Arachnoid Mater
B. Pia Mater, Arachnoid Mater, Dura Mater
C. Pia Mater, Dura Mater, Arachnoid Mater
D, Dura Mater, Arachnoid Mater, Pia Mater
3 multiple choice options
B. 8 hours
Normal adult CSF volume of ~150 ml is replaced every___________
A. 3 days
B. 8 hours
C. 24 hours
D. 7 days
3 multiple choice options
A. Choroid Plexus
______________________ is/are a cluster of capillaries that hangs from roof of each ventricle, enclosed by pia mater and surrounding layer of ependymal cells
A. Choroid Plexus
B. Brachial Plexus
C. Cervical Plexus
D. Cysterna Chyli
3 multiple choice options
A. Subarachnoid Space
This space in the skull is normally present and filled with CSF.
A. Subarachnoid Space
B. Epidural Space
C. Subpial Space
D. Subdural Space
3 multiple choice options
B. Pia and Arachnoid
Which of the following are known as the Leptomeninges?
A. Arachnoid and Dura
B. Pia and Arachnoid
C. Dura and Pia
D. Dura, Arachnoid, and Pia
3 multiple choice options
B. Dura Mater
Which of the meninges is known as the pachymeninge/pachymeninx?
A. Arachnoid Mater
B. Dura Mater
C. Pia Mater
2 multiple choice options
D. Cerebral Aqueduct
The third and fourth ventricle are connected by the __________________________________.
A. Lateral Aperature
B. Lateral Ventricle
C. Medial Aperature
D. Cerebral Aqueduct
3 multiple choice options
B. Falx Cerebri
The______________________ is the largest of the folds of dura mater. It attaches anteriorly to the crista galli. In its upper edge, it divides to form the superior sagittal sinus, and its lower edge is where it divides to form the inferior sagittal sinus.
A. Tentorium Cerebelli
B. Falx Cerebri
C. FalxCerebelli
D. Transverse Sinus
3 multiple choice options
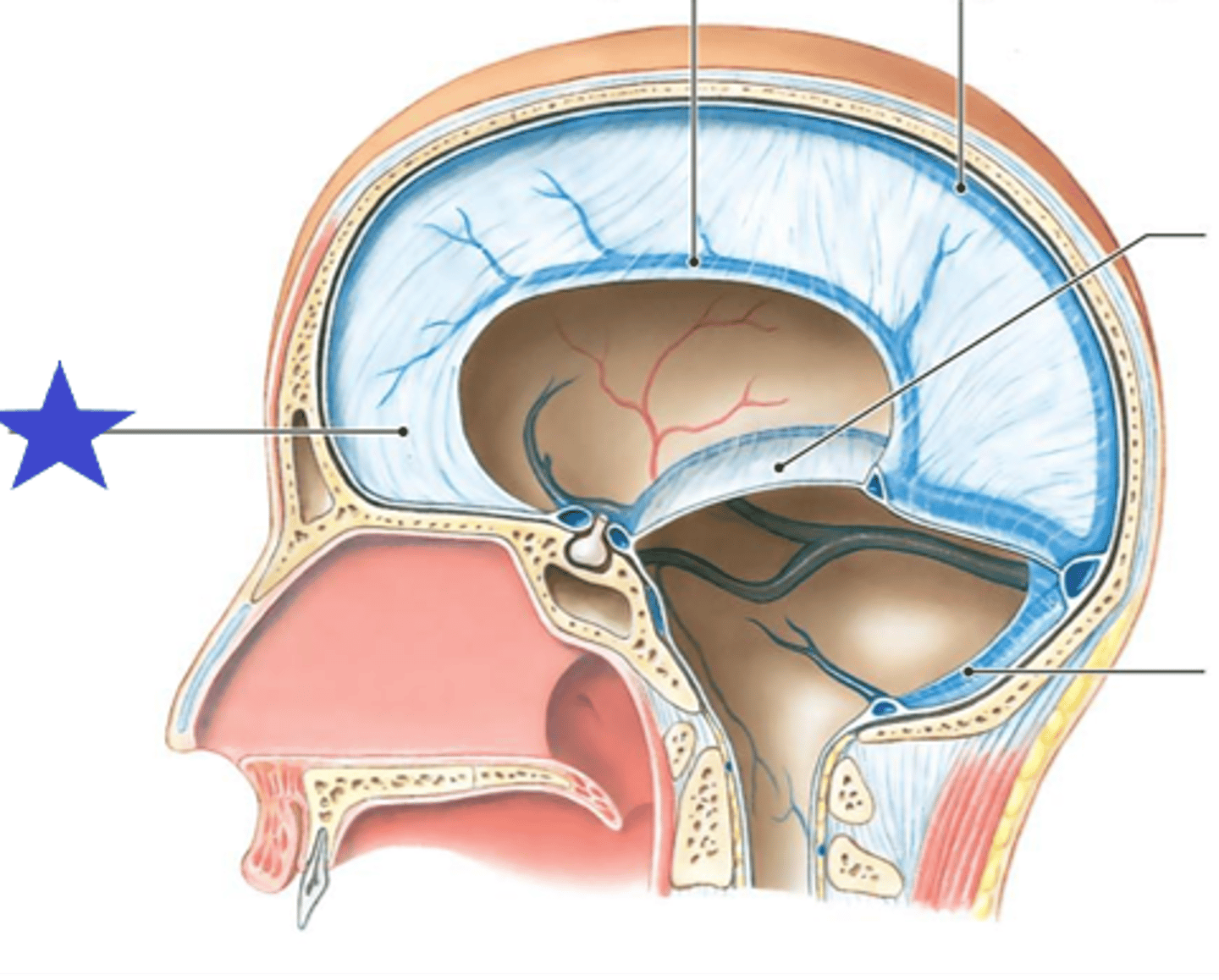
B. Area Postrema
The blood brain barrier is absent in some areas, such as vomiting center and hypothalamus. What is the name of the "vomiting center"?
A. Baroreceptor
B. Area Postrema
C. Carotid Body
D. Cingulate Gyrus
3 multiple choice options
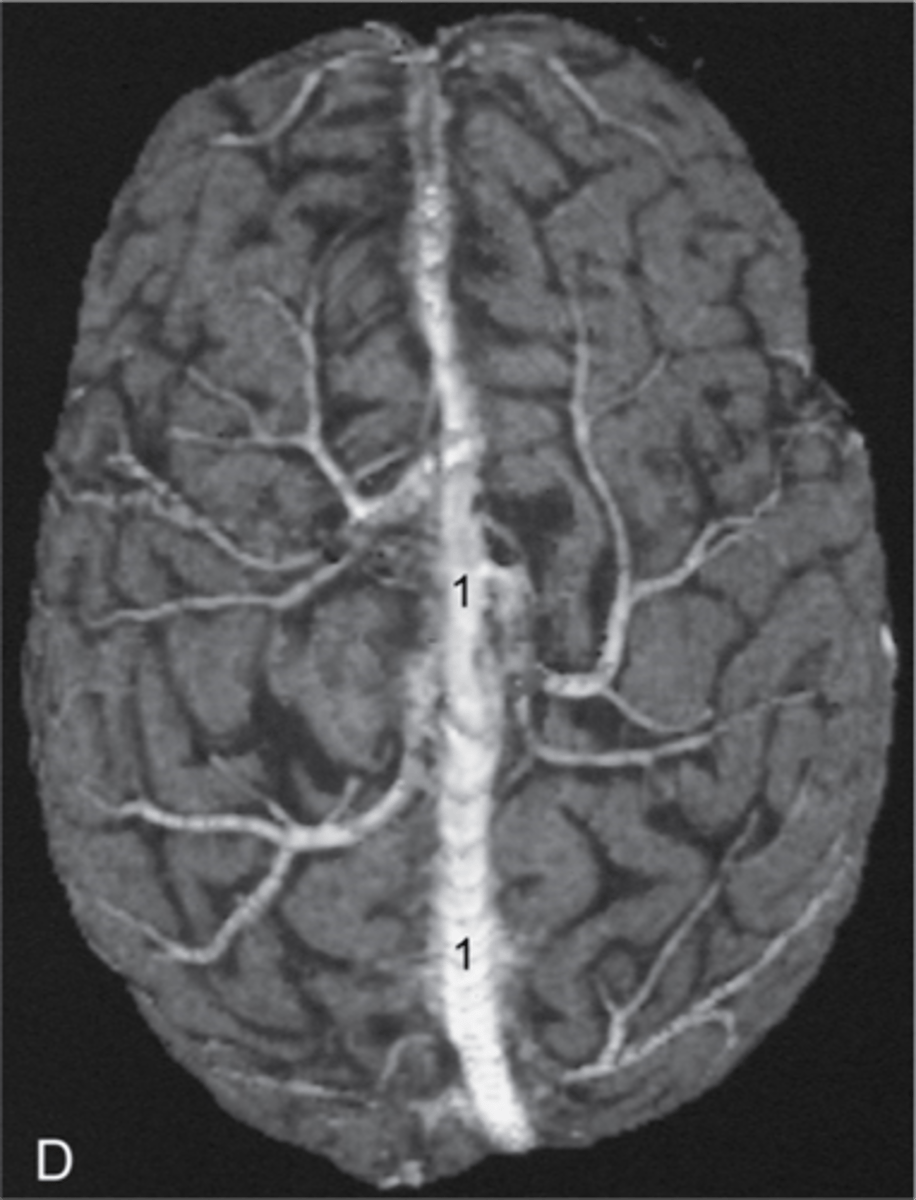
A. Superior Sagittal Sinus
What is the name of the structure here indicated by the #1:
A. Superior Sagittal Sinus
B. Transverse Sinus
C. Confluence of Sinuses
D. Middle Cerebral Artery
3 multiple choice options
A. Posterior Cerebral Artery
The artery labeled #11 here is responsible for midbrain structures including cranial nerve 3 & 4 nuclei.
A. Posterior Cerebral Artery
B. Anterior Cerebral Artery
C. Anterior Communicating Artery
D. Vertebral Artery
3 multiple choice options

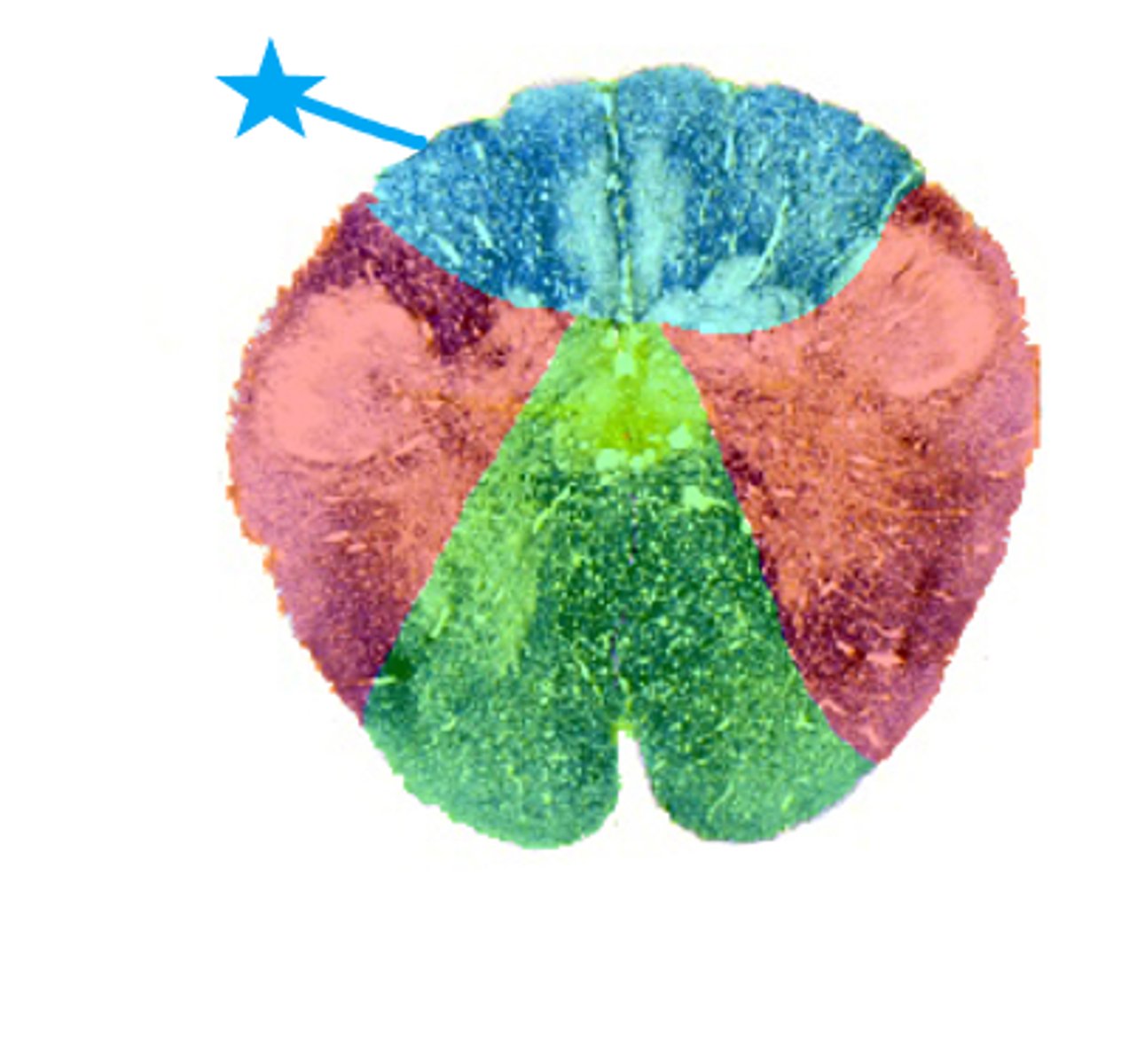
A. Posterior Spinal Artery
The dorsal columns of the spinal cord is primarily served by what blood vessel labeled with the blue star seen here?
A. Posterior Spinal Artery
B. Posterior Cerebral Artery
C. Anterior Spinal Artery
D. Vertebral Artery
3 multiple choice options
A. Myocardial Infarction
What is NOT one of the three types of Stroke?
A. Myocardial Infarction
B. Hemorrhagic
C. Ischemic
D. Transient Ischemic Attach
3 multiple choice options
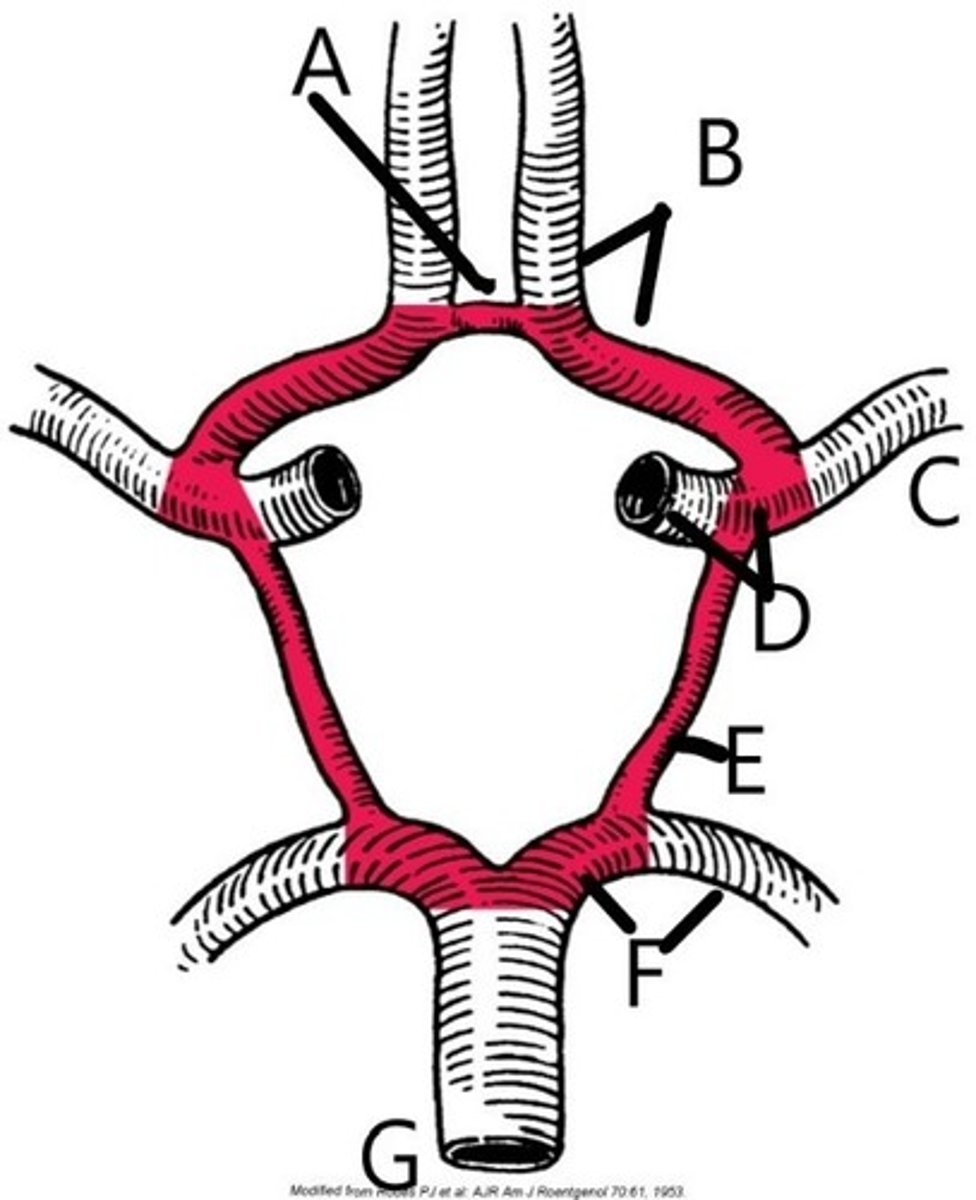
A. Anterior Cerebral Artery
The structure labeled "B" is:
A. Anterior Cerebral Artery
B. Posterior Cerebral Artery
C. Posterior Communicating Artery
D. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
3 multiple choice options
A. Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
This blood vessel supplies the lateral medulla oblongata:
A. Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
B. Posterior Cerebral Artery
C. Anterior Cerebral Artery
D. Posterior Communicating Artery
3 multiple choice options
A. Basilar
The 2 Vertebral Arteries combine to immediately become the ____________at the level of the pons.
A. Basilar
B. AICA
C. ACA
D. PCA
3 multiple choice options
A. Vertebral
The cervical vertebra are unique in the fact they have transverse foramina that contain the _______________________ artery
A. Vertebral
B. Basilar
C. Anterior Communicating Artery
D. Anterior Cerebral Artery
3 multiple choice options
A. FAST
The Acronym that is useful in diagnosing a stroke is:
A. FAST
B. RICE
C. FOOSH
D. TIA
3 multiple choice options
A. Towards
In a medullary stroke the tongue deviates ________________________ the lesion.
A. Towards
B. Away
C. In no relationship to
2 multiple choice options
B. Higher
Extracellular fluid has a ____________________concentration of Na+ than ICF
A. Lower
B. Higher
1 multiple choice option
C. Nerve Cell Bodies
Neurotransmitters are synthesized in the ___________________or Pre Synaptic Endings
A. Dendrites
B. Axons
C. Nerve Cell Bodies
D. Synaptic Clefts
3 multiple choice options
B. Dopamine
“What is NOT considered a small molecule neurotransmitter? Small molecules are stored in small vesicles and are transported from the cell body to the pre synaptic ending by SLOW AXONAL TRANSPORT:
A. GABA
B. Dopamine
C. Glycine
D. Ach
3 multiple choice options
C. Hyperpolarize
The Inhibitory PostSynaptic Potential (IPSP) will ________________ the Post Synaptic Membrane.
A. Depolarize
B. Have no effect
C. Hyperpolarize
2 multiple choice options
A. Repolarization
During this phase of generating an action potential; the Na+ channels are inactivating, and K+ channels open
A. Repolarization
B. Hyperpolarization
C. Depolarization
3 multiple choice options
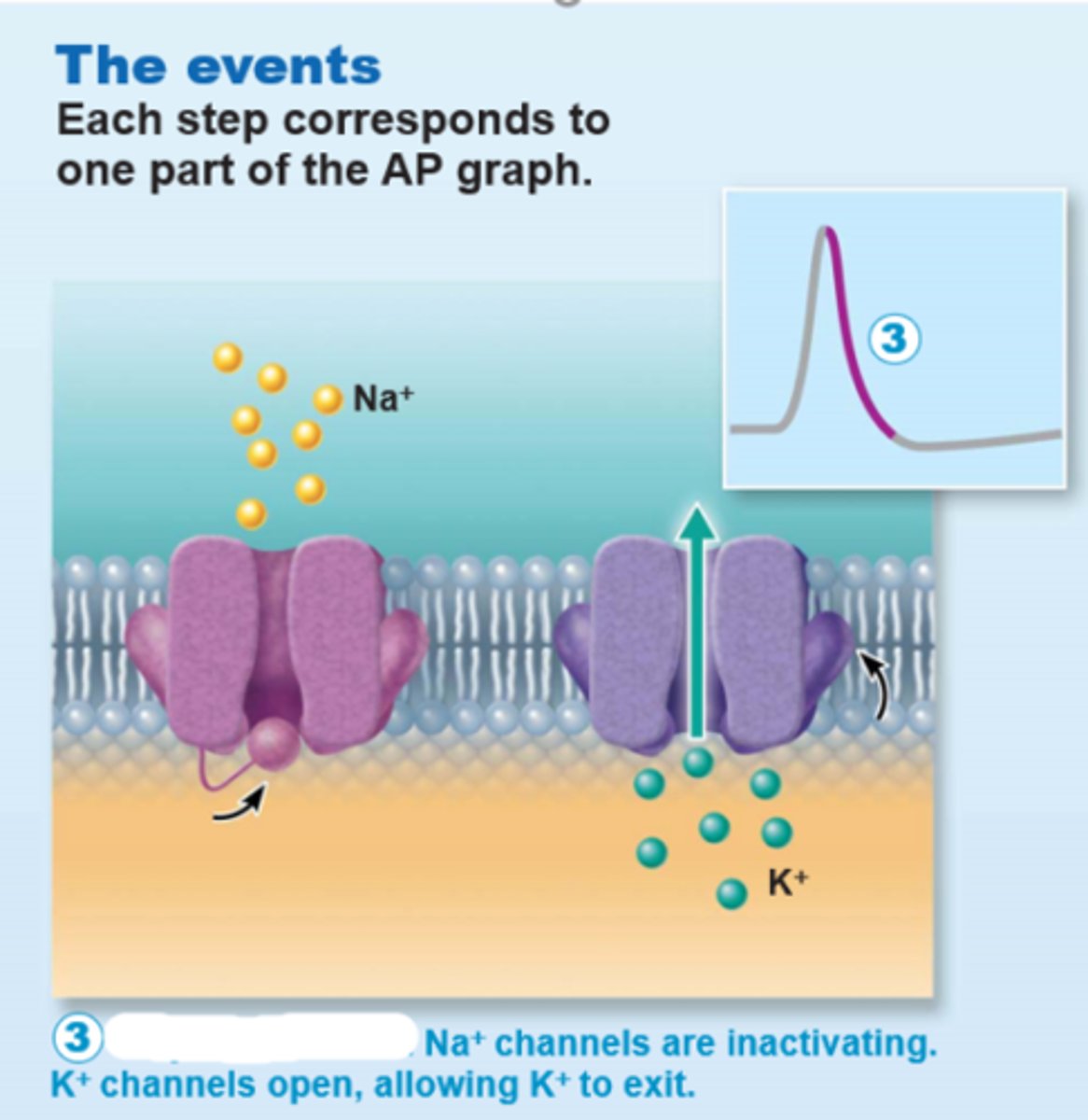
C. Action Potentials
In neurons, _______________________ is also referred to as a nerve impulse. It is the principal way neurons send signals and is a means of long-distance neural communication. It occurs only in muscle cells and axons of neurons
They also do not decay over distance.
A. Graded Potentials
B. Resting Membrane Potential
C. Action Potentials
2 multiple choice options
A. Mechanically gated channels
These channels open and close in response to physical deformation of receptors, as in sensory receptors:
A. Mechanically gated channels
B. Chemically gated channels
C. Ligand-gated channels
D. Voltage-gated channels
3 multiple choice options
D. Ohm's Law
This law gives the relationship of voltage, current, resistance in the equation:
Current (I) = voltage (V)/resistance (R)
A. Starling Law
B. Hilton's Law
C. Boyle's Law
D. Ohm's Law
3 multiple choice options
A. Potassium
The sodium-potassium pump (Na+/K+ ATPase) stabilizes resting membrane potential to have more ____________________ on the inside of the cell.
A. Potassium
B. Calcium
C. Oxygen
D. Sodium
3 multiple choice options
A. Depolarization
______________________________ is a decrease in membrane potential (moves toward zero and above). Whereas, the inside of membrane becomes less negative than resting membrane potential and the probability of producing impulse increases
A. Depolarization
B. Isometric Contraction
C. Hyperpolarization
D. Latency period
3 multiple choice options
A. Sensory
Nerves that are afferent in nature and are usually structurally more on the dorsal aspect of the body are associated more with:
A. Sensory
B. Parasympathetic
C. Sympathetic
D. Motor
3 multiple choice options
D. Spatial Discrimination
Two point discrimination test would be an example of:
A. Magnitude Estimation
B. Quality Discrimination
C. Pattern Recognition
D. Spatial Discrimination
3 multiple choice options
B. Nociceptors
These receptors are sensitive to pain-causing stimuli:
A. Pacinian Corpuscles
B. Nociceptors
C. Thermoreceptors
D. Meissner's Corpuscles
3 multiple choice options
A. Epineurium
__________________________ is the tough fibrous sheath around all fascicles to form the nerve
A. Epineurium
B. Endoneurium
C. Exoneurium
D. Perineurium
3 multiple choice options
D. 1A
Muscle Spindles are innervated by what classification of nerve fibers?
A. 1B
B. C
C. B
D. 1A
3 multiple choice options
D. Hyperalgesia
Inappropriate excessive pain perception or pain amplification is also known as:
A. Analgesia
B. Hypoalgesia
C. Subalgesia
D. Hyperalgesia
3 multiple choice options
D. C Fibers
The slowest nerve conducting fibers of the body are the:
A. A delta
B. A beta
C. B
D. C fibers
3 multiple choice options
B. Tolerance
"Sensitive to pain" means low pain _____________________
A. Threshold
B. Tolerance
1 multiple choice option
B. Slow
Some examples of tonic receptors are nociceptors and most proprioceptors. These are know to be ____________ adapters.
A. Fast
B. Slow
1 multiple choice option
D. Merkel Discs
What is NOT an encapsulated nerve ending?
A. Meissner's Corpuscles
B. Pacinian Corpuscles
C. Ruffini Endings
D. Merkel Discs
3 multiple choice options
Fasiculus Gracilis
Which of the following is responsible for vibration sense of the lower limbs?
3 multiple choice options
Closer
The parasympathetic ganglia are _____________________ to the organ they serve in comparison to the sympathetic ganglia.
2 multiple choice options
23
There are ____ paravertebral ganglia in the sympathetic trunk (chain)
3 multiple choice options
Rubrospinal Tract
This tract is responsible for flexion protection of the upper extremity:
3 multiple choice options
8, 12
There are __ Cervical Nerves and ___ Cranial Nerves
3 multiple choice options
Sympathetic Nervous System
The aspect of the nervous system that will increase heart rate, blood pressure and blood sugar in response to stressors is the:
3 multiple choice options
Spinothalamic Tract
Which of the following tracts is responsible for touch, pain and temperature sensations of the body
3 multiple choice options
Sudoriferous
Almost all sympathetic postganglionic axons release norepinephrine as their neurotransmitter. Most notable exception to this is _______________glands which release ACh.
3 multiple choice options
Spinothalamic Tract
Which of the following is an Ascending Tract?
3 multiple choice options
T6-T9
Location of the pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons for the gall bladder are located at the spinal levels:
3 multiple choice options
CN 5 & Medulla Oblongata
Which of the following Cranial nerve nuclei is improperly matched with the area of origin of the brainstem?
3 multiple choice options
Medulla
What level of the brain/brainstem do the corticospinal tracts decussate?
3 multiple choice options
4
Which of the following is the only cranial nerve to exit from the dorsal surface?
3 multiple choice options
lateral
Sensory nuclei will be _____________to sulcus limitans
3 multiple choice options
Superior cerebellar artery
Which of the following blood vessels does not normally supply the Medulla?
3 multiple choice options
Olives
Which of the following structures is not a midbrain structure?
3 multiple choice options
Medulla, Pons, Midbrain
Put the brainstem in proper order from inferior to superior (caudad to cephalic).
3 multiple choice options
Midbrain
The PAG/periaqueductal grey is generally associated with what level of the brainstem?
2 multiple choice options
Edinger-Westphal Nucleus
Which of the following nuclei are associated with the midbrain?
3 multiple choice options
CN 9
Which of the following structures are not found in the midline area of the brainstem/which structure is most lateral?
3 multiple choice options
Trigeminal Nerve Mandibular Division
Which of the following does not go through the cavernous sinus?
3 multiple choice options
5
Tic Douloureux is associated with what cranial nerve??
3 multiple choice options
9 & 10
Nucleus Ambiguus is known to be where some cell bodies of what nerves are located?
3 multiple choice options
5
Which of the following cranial nerves is not involved in eye movements?
3 multiple choice options
4
Which of the following nerves is least associated with the parasympathetic nervous system?
3 multiple choice options
Trochlear
Which of the following cranial nerves is NOT considered a primarily sensory nerve?
3 multiple choice options
Trigeminal
What cranial nerve is responsible for the muscles of mastication?
1 multiple choice option
Facial
Sweet, sour, salty taste are associated with what cranial nerve?
3 multiple choice options
7,9,10
Nucleus Solitarius is associated with what cranial nerves?
3 multiple choice options
5 & 7
The blink reflex/corneal reflex involves what nerve(s)
3 multiple choice options