Full Economics Flashcards
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
168 Terms
Behavioural economics
Adds elements of psychology to traditional models in an attempt to understand decision making by the consumers
Ceteris paribus
All things being equal
Circular economy
Economic system that focuses on society wide benefits. Based on design out waste, keep products/materials in use, regenerate natural systems
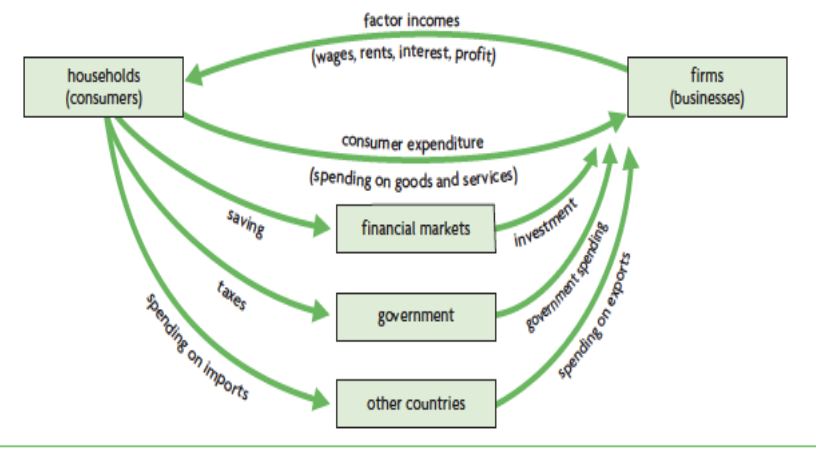
Circular flow of income
Simplified model of the economy that shows the f,ow of money through the economy
Consumer surplus
The additional benefit/utility received by consumers by paying a price that is lower than the maximum price they are willing to pay.
Consumption
Spending by households on consumer goods and services over a period of time
Demand
The willingess and ability of consumers to purchase a quantity of a good or service
Demand curve
Shows the relationship between the price of a good/service and the quantity demanded
Demerit goods
Goods/services considered to be harmful to people
Economic development
A broad concept involving improvement in standards of living etc
Elasticity
A measure of responsiveness of something to a change in one of its determinants
Engel curve
Curve that shows the relationship between income and quantity demanded
Equilibrium
Quantity supply = Quantity demand and there is no tendency for the price to change. When in equilibrium, every unit that is produced is consumed. Market clearing price and quantity where there is no excess demand or supply
Excess demand
Shortage. Price of a good is lower than the equilibrium price such that the quantity demanded is greater than the quantity supplied
Excess supply
Surplus. Where the price of a good is higher than the equilibrium price, such that the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded
Exports
Goods/services produced in one country and purchased by consumers in another country
Externalities
External costs or benefits to a third party when a good or service is produced or consumed
Factors or production
Land, labour, capital, entrepreneurship
Labour
Wages
Capital
Interest
Entrepreneurship
Profit
Free market economy
Means of production are privately held by individuals and firms. Supply/demand determine what,how much, how and for whom to produce.
Imports
Goods/services purchased by consumers in one country that have been produced in another country
Income elasticity of demand (YED)
A measure in the responsiveness of the demand for a good or a service to a change in incomeI
Indirect taxes
Added to the selling price of a good or a service
Inflation
a sustained increase in the average price level of goods and service
Inflation rate
Percentage change of a price index over a certain time period
Injections
Investment, government expenditure and export revenues that add spending to the circuclar flow of income
Interest rate
The price of borrowing money
Law of demand
As the price of a good falls, the quantity demanded will normally increase
Law of supply
As the price of a good rises, the quantity supplied will normally rise
Leakages
Savings, taxes and import expenditure that remove spending from the circular flow of income
Marginal costs
The additional costs of producing more than one unit of input
Marginal utility
Extra utility derived from consuming one or more unit of a good or a service
Market
Where buyers and sellers come together to carry out an economic transaction
Market demand
Horizontal sum of the individual demand curves for a product of all the consumers in a market
Market failure
A failure of markets to produce at the point where community surplus is maximised (consumer surplus + producer surplus)
Merit goods
Goods/services considered to be beneficial for people
Negative externalities of consumption
Negative effects suffered by a third party when a good/service is consumed
Normal goods
Demand for it increases as income increases
Normative economics
Areas of economics that are open to personal opinion and belief
Opportunity cost
Next best alternative when an economic decision is made
Perfectly elastic demand
Increase in price of a G/S leads to a fall in the QD of the G/S to zero
Perfectly elastic supply
Where a change in the price of a G/S leads to a fall in the QS of the G/S to zero
Perfectly inelastic demand
Where a change in the price of a G/S leads to no change in the QD of the G/S
Perfectly inelastic supply
Where a change in the price of a G/S leads to nochange in the QS of the G/S
Positive economics
Deals with areas of the subject that are capable of proven to be correct or not
Positive externalities of consumption
Benefits that are enjoyed by a third party when G/S are consumed
Positive externalities of production
Benefits that are enjoyed by a third party when a G/S is prpdiced
Price ceiling
Imposed by an authority and set below the equilibrium price, prices cannot rise above this set price
Price controls
Imposed by authority, set above or below the market equilibrium price
Price floor
Imposed by an authority and set above market price, proces cannot fall below this set price
(Price) Elastic demand
Change in the price of a G/S leads to a proportionally larger change in the QD of it
(Price) Elastic supply
Change in price of a G/S leads to a proportionally smaller change in the QD of the G/S
(Price) Inelastic demand
Change in the price of a G/S leads to a proportionally smaller change in the QD of the G/S
(Price) Inelastic supply
Change in the price of a G/S leads to a proportionally smaller change in hte QS of the G/S
PED stands for…
Price elasticity of demand
Definition of PED
Measure of the responsiveness of the QD of a G/S when there is a change in its price
PES stands for…
Price elasticity of supply
Definition of PES
Measure of responsiveness of the QS of a G/S when there is a change in its price
Producer surplus
Additional benefit received by producers by receiving a price that is higher than the price they were willing to receive
PPC
Production possibilities curve
Quantity demanded
Willingness and ability to purchase a quantity of a G/S at a certain price over a given time period
Quantity supplied
Willingness and ability to produce a quantity of a good or service at a given price over a given time period
GDP Meaning
Total monetary value of all final goods/services produced within an economy in a year
GNI
Total income that is earned by a country’s factors of production regardless of where the assets are located
GDP Formula
C + I + G + (X-M)
GDP Formula WORDS
Consumer spending + investment spending + government spending + export spending - import spending
GNI Formula
GDP + Net income from abroad
GDP Deflator formula
Nominal GDP / Real GDP / 100
rGDP with deflator formula
Nominal GDP / GDP deflator * 100
GDP / GNI per capital formula
rGDP or GNI / population
Nominal prices
GDP measured at current prices
Real GDP
GDP measured at constant prices and adjusted for inflation
Inflation
The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, leading to a decrease in purchasing power.
Business cycle phases
Expansion → Peak → Contraction → Trough → Expansion + Potential output & Actual output
Inferior good
A good whose demand falls as income rises, has negative income elasticity
Substitute goods
Goods which can be used in place of each other (f.eg Apple juice and orange juice)
Complementary goods
Goods used/purchased together (f.eg a phone and a phone case)
Supply
The amount of a good or service that producers are willing and able to provide at a given price
Supply curve
A curve, or line, showing the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity supplied over a range of prices
Joint supply
Goods which are produced together, or where the production of one good involves the production of another product e.g. Meat and leather (a by-product)
Resource allocation
Examine the way that scarce factors of production are allocated to meet unlimited demand
Signalling
Conveying of information by one party to another to indicate their intentions or qualities, often used in markets where there is asymmetric information
Public good
A product which is non-rivalrous and non-excludable and so would not be provided at all in a purely free market economy (f.eg healthcare or education)
Merit goods
Considered to be beneficial for people that would be under-consumed in a purely free market economy
Demerit goods
Considered to be harmful for people that would be over-consumed in a purely free market economy
Sustainability
Implies an ability to sustain the worlds' resources over time
Short run
The period of time in which at least one factor of production (usually capital) is fixed
Long run
The period of time in which all factors are variable
Formula: Price elasticity of demand
% ∆ Quantity Demanded
÷
% ∆ Price
Formula: Price elasticity of supply
% ∆ Quantity Supplied
÷
% ∆ Price
Formula: Income elasticity of demand
% ∆ Quantity Demanded
÷
% ∆ Income
Formula: Nominal GDP
Quantity of goods + services produced × Current Prices
Formula: Real GDP
Nominal GDP
÷
Price Index* ×10
*Any price index: CPI, RPI, GDP Deflator
Formula: Aggregate demand
C + I + G + (X-M)
Formula: Unemployment rate
(# Of unemployed ÷ labor force) * 100
Formula: Percentage change
Actual - Original
÷
Original
× 100
Tradable permits
Market based policy where government sets an amount of permits that can be bought and sol by polluters
Market based policy
“You have a permit to fish 100 fish. If you do not do this, you can sell the permit to someone else to fish 100 fish.”
SPLAT
Substitutes
Proportion
Luxury
Addictive
Time