Lesson 12: Chordata (Cephalochordata and Tunicates)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Chordata & Invertebrates Similarities
bilateral symmetry
anterioposterior axis
coelom
tube-within-a-tube body plan
metamerism
cephalization
5 Classic Chordate Characteristics
dorsal hollow nerve cord
notochord
first 2 only true synapomorphies
pharyngeal pouches/slits
endostyle/thyroid gland
muscular, postanal tail
DNM EP (do not move elvis presley)
Notochord
rodlike, semirigid tissue enclosed in a sheath
extends the length of the body, lying between the gut and the nervous system
main purpose is to stiffen the body
providing skeletal scaffolding for the attachment of swimming muscles
support
always found at some embryonic stage
1st part of the endoskeleton to appear in the embryo
in non vertebrate and jawless chordates it persists throughout life
however, it is displaced by the vertebrae in most vertebrates. remains as a disc
Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord
dorsal to digestive tract
anterior end= brain
via neurulation
passes through the neural arches of vertebrae
or just runs dorsal to notochord if no vertebrae
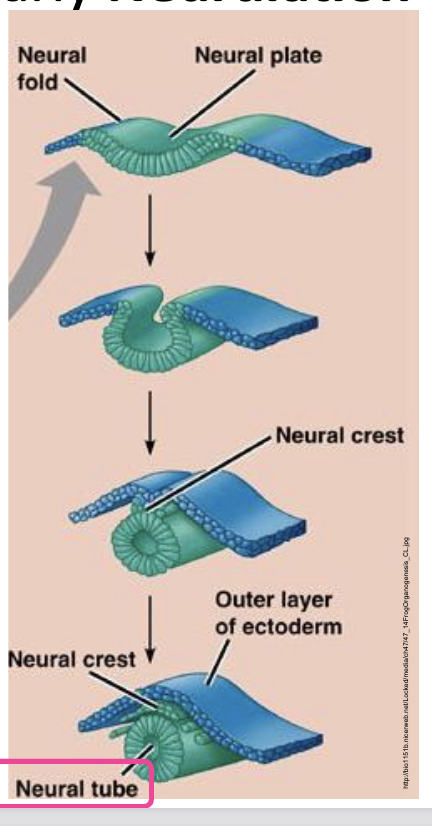
Neurulation
the process in early vertebrate development where the neural plate, a flat sheet of cells on the back of the embryo, folds to form the neural tube
ectodermal origin
Pharyngeal Pouches/Slits
from the in pocketing of the ectoderm and envagination of endoderm of pharynx
perforated pharynx function as filter-feeding apparatus in non-vertebrate chordates
post embryonic secondary development in some vertebrates
auditory tube, middle ear, glands, larynx…
fishes added a capillary network with thin gas-permeable walls
leads to the evolution of gills
Endostyle/Thyroid Gland
longitudinal ciliated groove ventral to pharynx
some cells in endostyle secrete iodinated proteins homologous with iodonated hormone-secreting thyroid gland in vertebrates
secretes mucous for food capture in the filter-feeding non vertebrate chordates
Postanal Tail
postanal tail + musculature = motility
mainly for larval tunicates and amphioxus to swim
efficiency increased in fishes, but became smaller or vestigial in later lineages
Earliest Known Chordate
Pikaia
510 million years ago
remnants found in burgess shale, BC
similar to living cephalochordate
though originally classified as a polychaete
Cephalochordata
the poster chordate (lancelets)
amphioxus
pointy at both ends
burrow in porous mud and sand
seldom swim
expose mouth to seawater, and filter out particles
water enters the mouth driven by cilia in the buccal cavity and pharynx
passes through pharyngeal slits, where food is trapped in mucus secreted by the endostyle
branchiostoma: gill mouth
closed circulatory system
but no heart
only moderate cephalization
no distinct brain or cranium
body surface respiration
Urochordata
tunicates
named after the cellulose tunic layer
most sessile as adults
but some are free living
two classes
ascidiacea
appendicularia
no cephalization
two-directional heart
Ascidiacea
sea squirts
class of tunicates
may be compound, colonial, or solitary
one of aquacultures worst enemies
common in atlantic canada, and wreck havoc on aquaculture sites via biofouling
includes the thaliacea (salps)
Thaliacea
the salps
apart of the class ascidiacea, tunicates
free swimming
can be solitary or colonial
use water current for both feeding and gas exchange, as well as for locomotion
form of jet propulsion
feed using a mucus net
Appendicularia
“small appendage”
larvaceans; ghost larva
pelagic, free-swimming, tiny larva
show all 5 chordate characters in the adult form
secrete a mucous house to suspension feed
Chordata Organization
Chordata Symmetry
Chordata Body Cavity
Chordata Development
Chordata Segmentation