Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply (CH.12)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
aggregate demand
The total quantity of goods and services demanded in the economy, measured in terms of their market value
aggregate demand curve
a curve that shows the relationship between the overall price level in the economy and total demand
Why does the aggregate demand curve slope downwards?
It can be caused by 3 main factors:
The real balance effect
The interest rate effect
The exchange rate effect
Real Balance Effect
When the price level rises, the purchasing power of people's fixed money holdings (cash, checking accounts, savings) decreases, meaning their dollars buy less goods and services.
Interest Rate Effect
When prices rise, the cost of borrowing also rises, which makes it more expensive for consumers and firms to borrow money. Firms will invest less in factories and working capital, while consumers will spend less on big-ticket purchases like a house or a car.
Exchange rate effect
Higher domestic prices make your country's goods less competitive internationally, leading to lower net exports and reduced aggregate demand.
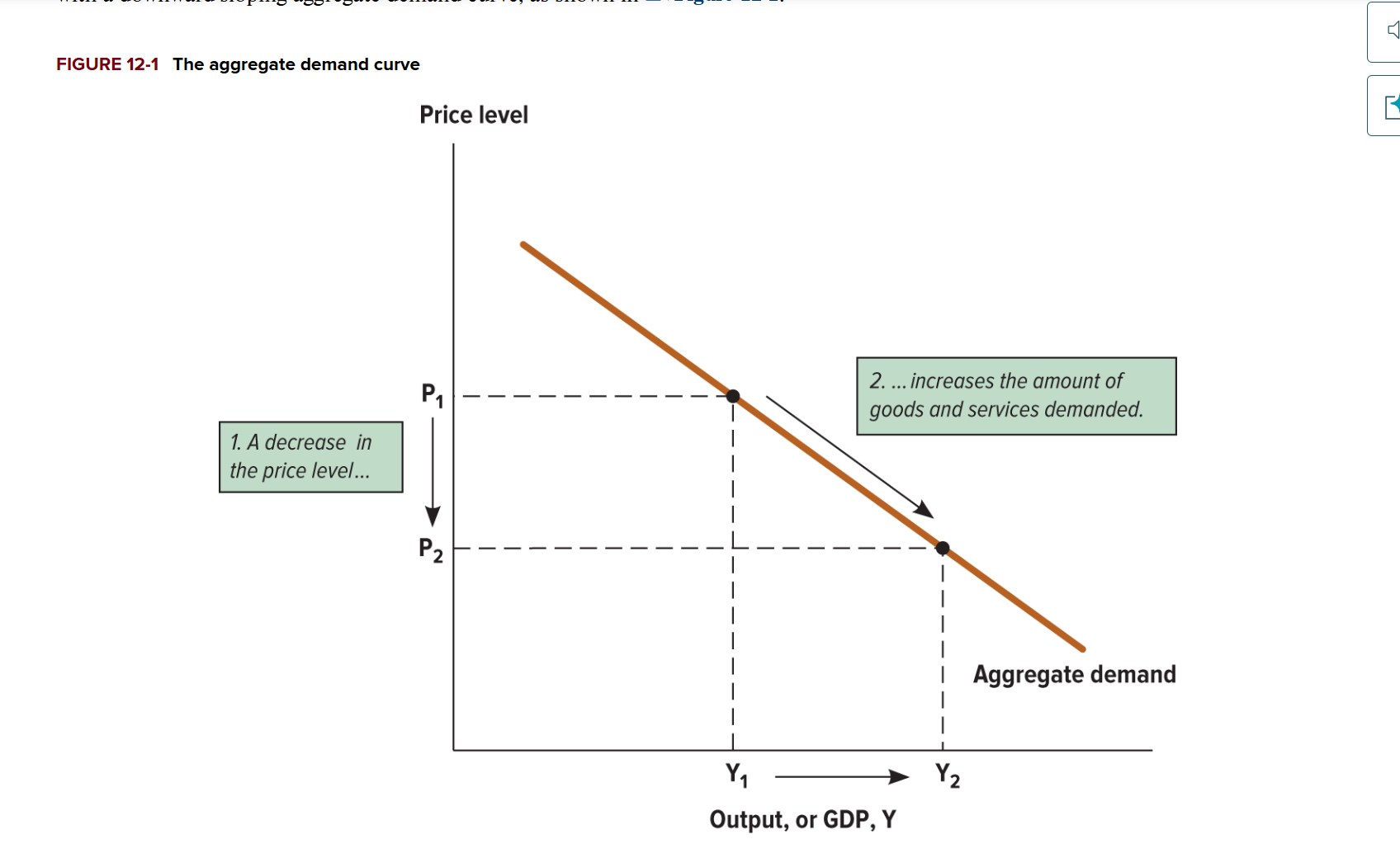
What does the aggregate demand show us?
As price decreases, the quantity of aggregate output demanded increases
aggregate supply
the sum total of the production of all the firms in the economy, measured in terms of their market value
aggregate supply curve
a curve that shows the relationship between the overall price level in the economy and total production by firms
long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve
a curve that shows the relationship between the overall price level in the economy and total production by firms in the long run
short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) curve
a curve that shows the relationship between the overall price level in the economy and total production by firms in the short run
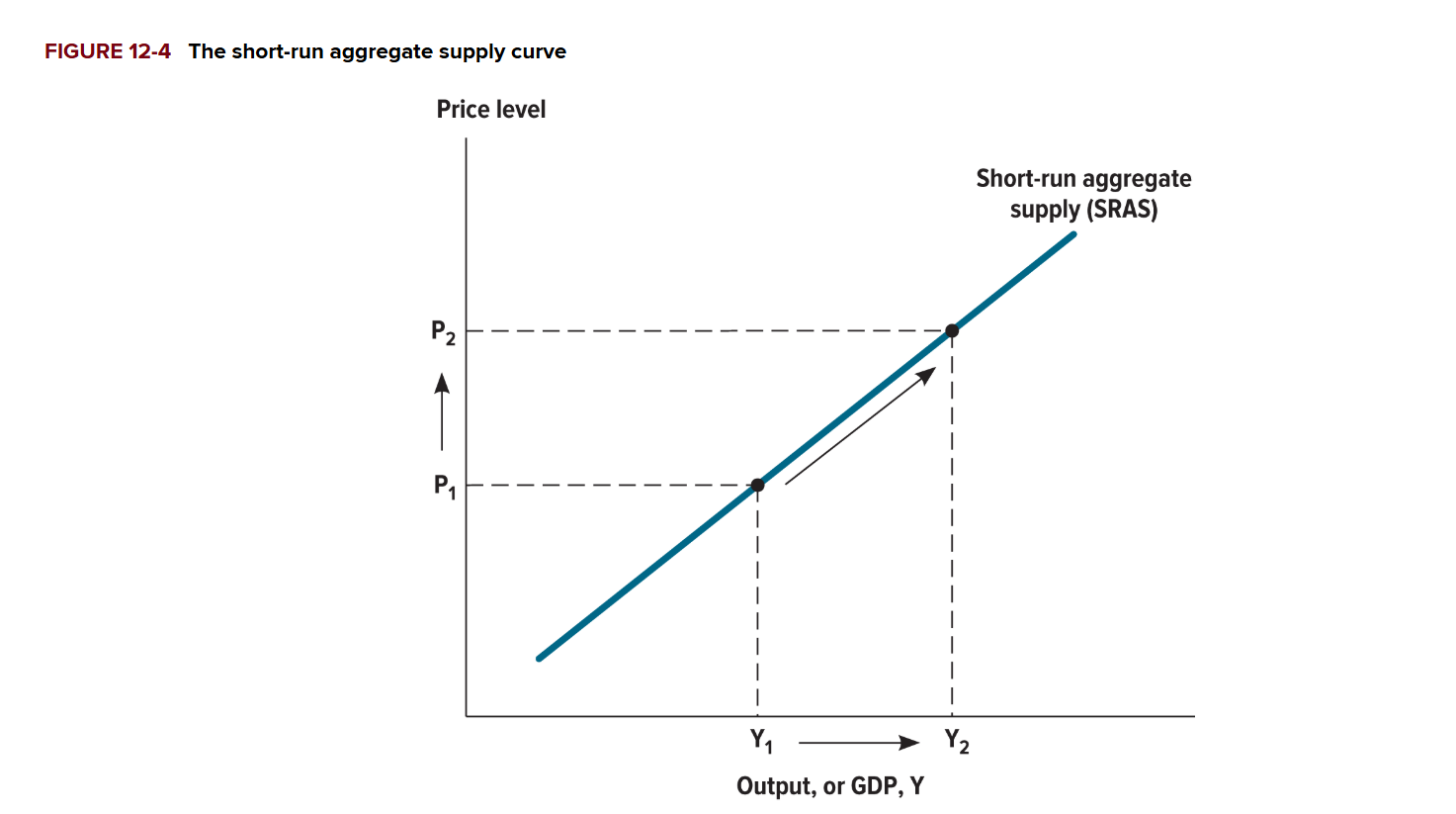
Why is aggregate supply sloping upwards in the short run?
As prices go up, firms produce more, giving them more profit
What does it mean if prices are sticky?
Prices adjusts slowly in response to changes in the economy
Why do sticky wages cause short run aggregate supply (SRAS) to slope upwards?
Even though the price of the firm’s products is higher, the wages don’t adjust right away, allowing the firm to earn more revenue, higher new staff, and produce more output.
Why are input prices sticky, while the prices of final goods and services can change so quickly?
Input prices are often locked into contracts that can only be changed periodically, while final goods prices can be adjusted quickly by simply changing the menu or price tag.
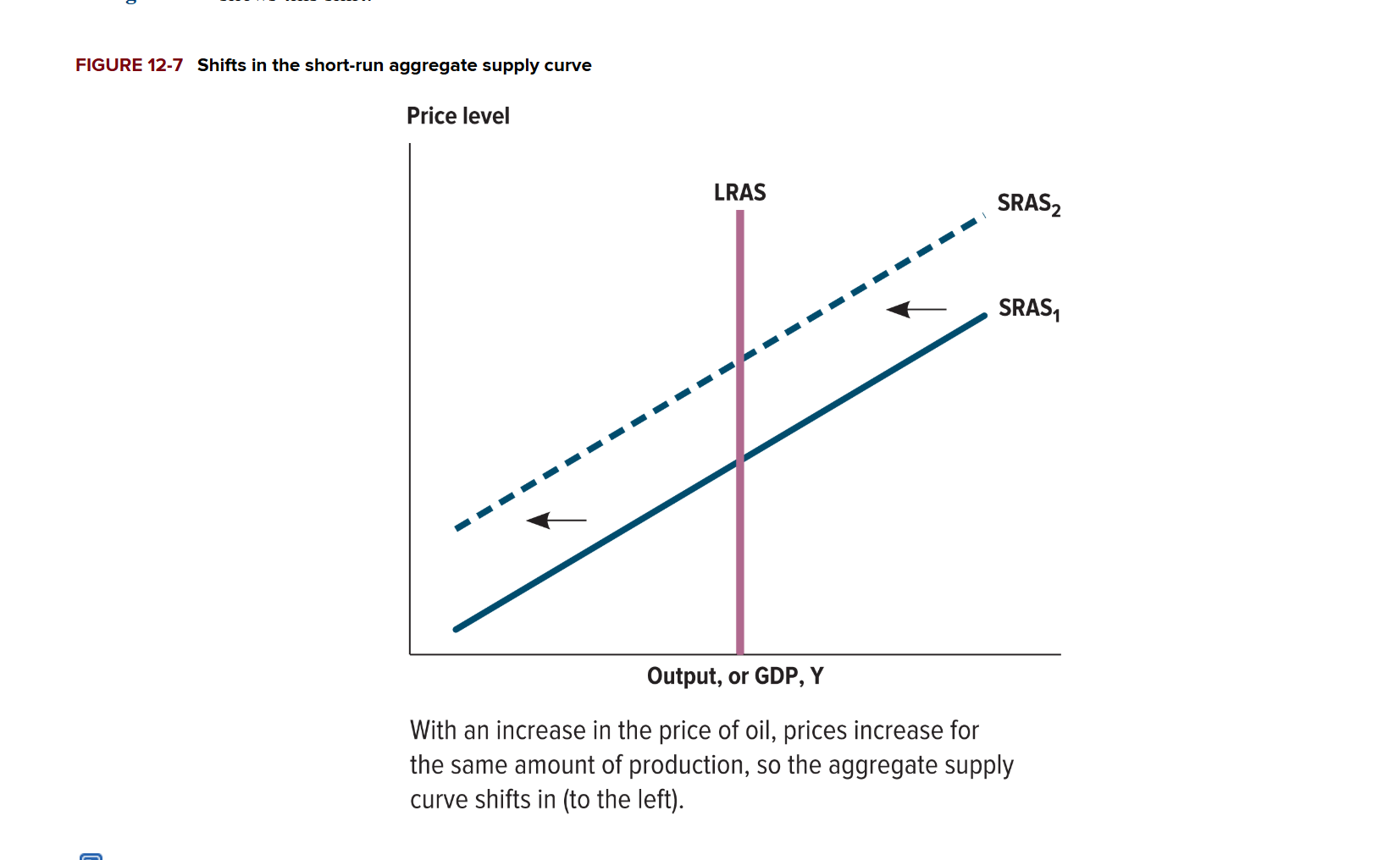
When does the Short Run Aggregate Supply (SRAS) shift?
Changes in input prices (Labor costs, raw materials, energy)
Productivity
Government Policies (Regulations, Taxes, and Subsidies)
Expectations of Future Inflation
Supply Shocks (Natural disasters, Wars, Geopolitical events, etc)
What factors can cause the LRAS to shift?
Changes in Capital Stock: Factories, Machinery, and Infrastructure
Technological Developments
The rise or depletion of natural resources
Government policies or institutions that affect productivity for better or worse
Changes in the quality and quantity of the labor force
When does AD (Aggregate Demand) shift?
When there are changes in:
Consumption
Investment
Government Spending
Net Exports
Long Run Aggregate Supply
Measures how long it takes for input prices to adjust to changes in the economy
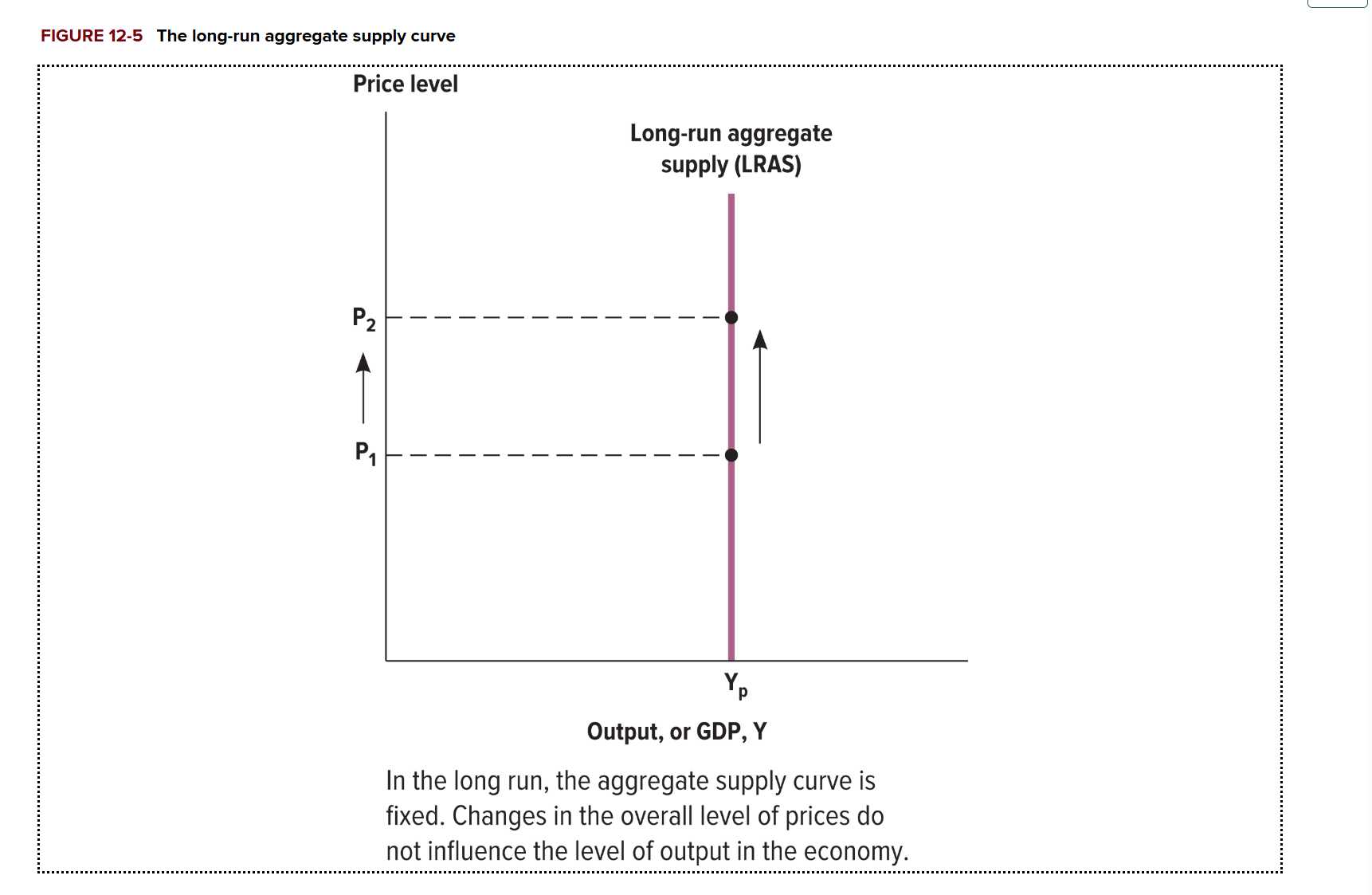
What does the long run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve show us?
Changes in the price of goods and services do not affect the aggregate supply in the long run. Shows us the potential output of the economy if the economy were at its full capacity.
business cycle
Fluctuations of output around the level of potential output in the economy
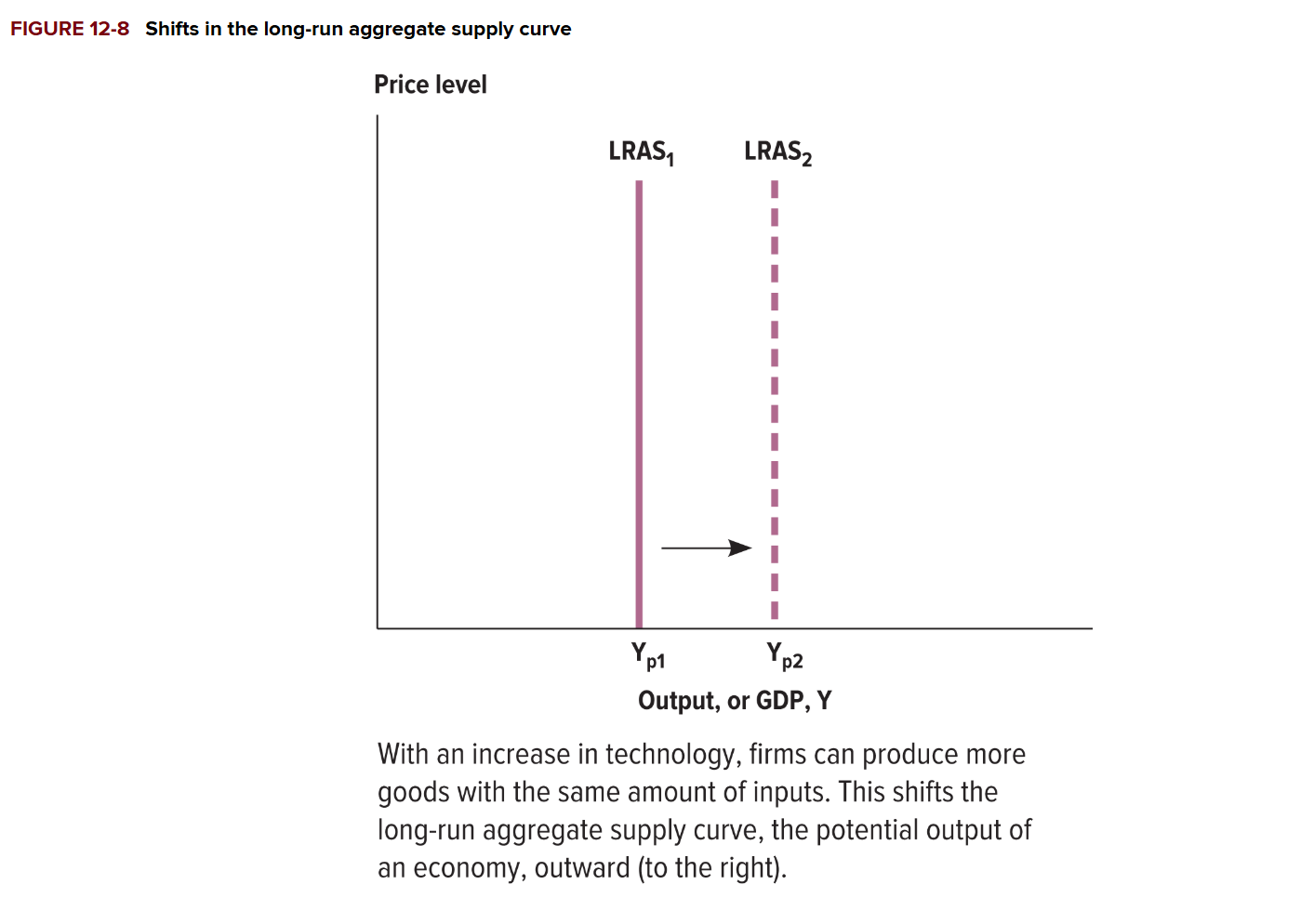
When does the LRAS curve shift to the right?
When the potential output of the economy expands
When does the LRAS curve shift to the left?
If the economy loses productive capacity
Everything that shifts the LRAS curve will also shift the SRAS curve, Why is this the case?
Avalible factors of production and technology that determine the position the LRAS will also drive short run supply.

What does the equillibrium of the macroeconomy model show us?
A stable level of prices and output
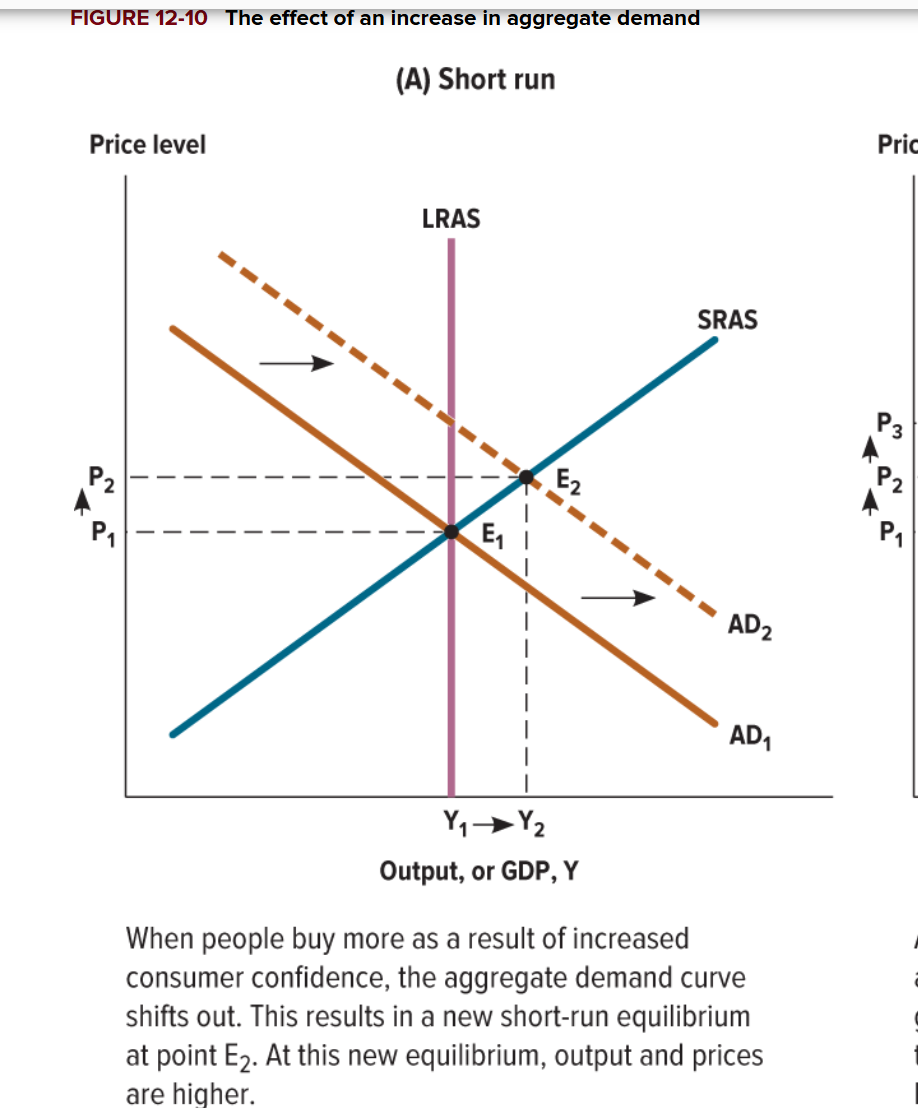
What happens in the short run when there is an increase in aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand shifts to the right, as the prices and output are higher in the new equilibrium
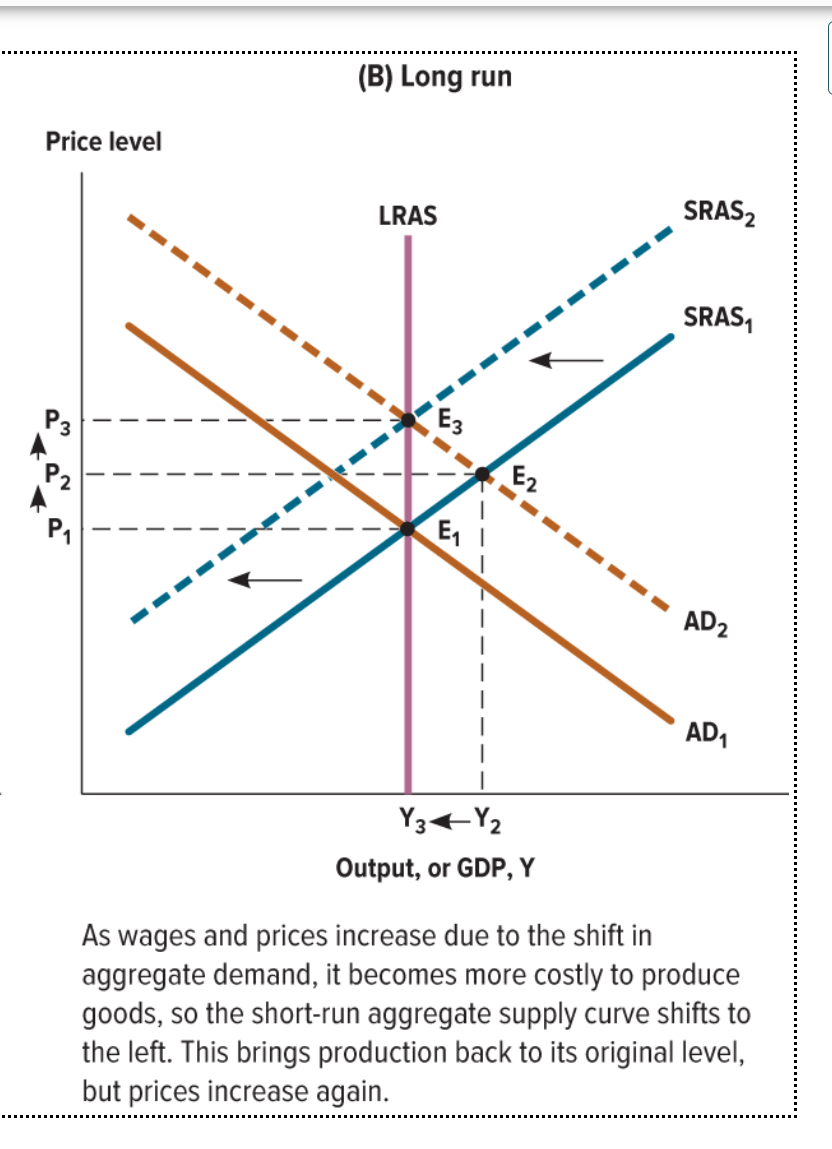
What happens in the long run when the aggregate demand shifts to the right?
The SRAS shifts to the left as wages and prices increase in AD, it becomes more costly to produce goods.
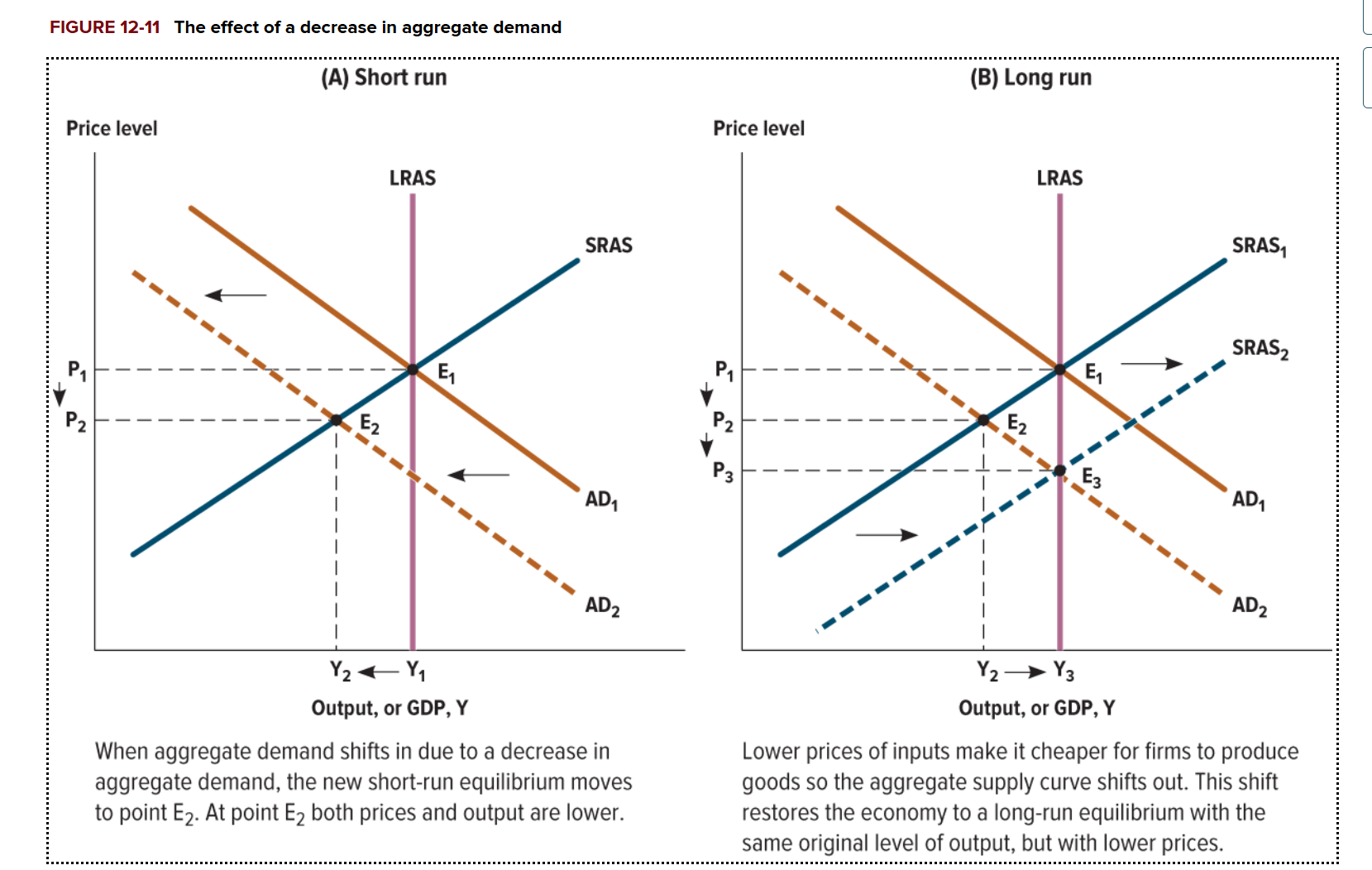
What happens in the long run when the aggregate demand shifts to the left?
The SRAS shifts to the right b/c input prices decreases during this period, with the same level of output,