BYU EXSC 602 Graduate AT Exam 1 Study
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
4 Step Problem Solving Process
Understand the problem
need to look at whole problem (and sometimes BEYOND)
Look beyond heuristics if it isn’t working. (can be helpful short term, test them and then put them away and test it all)
Devise a plan (Translate)
Carry out the Plan (Solve)
Look Back (Check and Interpret
Heuristics
Heuristics
Anchoring
Availability
Representativeness
using these is LAZY
Cognitive Biases
Bandwagon Effect
confirmation bias
framing effect
Over confidence
Foundation of Problem Solving
Think
Meaningful questions
Problem solving
Novice clinician
rigid adherence to taught rules
little situational perception
no discretionary judgement
Competent Clinicians
sees actions in terms of long-terms or wide spread conceptual framework
follows standardized and routinised procedures
should be here AFTER BOC
Expert clinicians
no longer relies explicitly on rules/guidelines
has intuitive grasp on situations
doesn’t let the expectations cloud the available data
uses funnel approach
does not come from getting certified, takes lifetime of learning
PRO-ACT-IVE
Problem
Reframe the problem
Objectives
Alternatives
Consequences
Trade-offs
Integration of
Values
Exploration
REMEMBER (Problem Solving)
don’t make assumptions
have all data been considered?
do all the data fit the problem?
have you continued to collect data and make adjustments?
keep differential diagnoses/treatments in mind don’t settle on your first thought
Training vs. Conditioning
10 principles of conditioning
warm up/cool down
motivation
overload
consistency
progression
intensity
specificity
individuality
minimize stress
safety
SAID principle
Specific Adaptation to Imposed Demands
when is this applicable?
Systems affected by Stress/Load
enhance heart muscle
increase the bone density
calm the nervous system
reduce the body weight
fresh air is better for health
boost the brain function
strengthen the respiratory system
raise the immunity
Warm-Up
injury prevention
performance enhancement
general and specific
time period???
temperature of muscle
blood flow
elasticity
nervous system - secret weapon, can manipulate to help us
pumps and channels are much more efficient
Cool Down
Blood pooling following activity
important to get blood back centrally from peripheral
clears debris from working muscle
slows re-oxygenation
increases HR - stress on heart
Same activity as warm-up?
combine with stretch
Flexibility/Stretching
ROM possible around joint or series of joints
maybe get it through proposed activity and not necessarily stretching
warm up first can be helpful
ROM can be limited due to injury and scar tissue on connective tissue
injury prevention ?? - not really (in those with normal ROM, population is 50/50 that has less ROM)
Performance enhancement?? - not really
Stretching Techniques
Ballistic
bouncing (like a warm up) primes nervous system for activity
Static
Holding tension
PNF
passive stretches with active muscle contractions
** Ballistic and static have same effectiveness
Strength
maximum force that can be applied by a muscle during a single contraction
determines strength
size
neuromuscular efficiency
biomechanical factors
Strength Terms
Hypertrophy - increase size of muscle (fiber)
Atrophy - Decreased size of muscle (fiber)
Reversibility - if strength training is discontinued or interrupted, the muscle with atrophy
Length/Tension Relationship
optimal resting sacromere length is when the protein heads line up with each other (on sarcomere)
Types of muscle contraction
Isometric - generates force with changing length
Isokinetic - at a consistent speed
Plyometric - involves all 3 types of contractions
Isotonic
Concentric - shortening
Eccentric - lengthening
Progressive Resistive Exercise
work muscles against increasing resistance to build strength and size
Plyometric Training
power exercise
uses stretch shortening cycle
high injury rate
cardiorespiratory fitness
ability of circulatory and respiratory systems to deliver oxygen to skeletal muscle during exercise
very important part of physical fitness
cardiovascular endurance is inversely related to cardiovascular disease
reduces relative risk of dying prematurely due to CVD
Cardiovascular Endurance
normative values based on VO2 max test
VO2 max indicates how well the heart and lungs work together to deliver oxygen and nutrients to working muscles and how well those muscles can utilize them
aerobic training adaptations
type I fibers 7-22% increase
capillary increase 5-15%
fatty acid oxidation 30% increase
VO2 improvement 15-20%
mitochondrial enzymes 2.5x more
mitochondria 15% more and 35% bigger
myoglobin increase 75-80%
Grains Guideline
make ½ of your grains whole
women 19-30: 6oz
men 19-30: 8oz
eat at least 3oz of whole grain
Vegetable guidelines
Vary your veggies
women 19-30: 2.5 cups
men 19-30: 3 cups
eat more dark green veggies, orange veggies, dry beans, and pasta
Fruit Guidelines
focus on fruits
2 cups for both men and women 19-30
eat variety (fresh, frozen, canned, dried)
go easy on fruit juices
Milk guidelines
get calcium-rich foods
men and women 19-30: 3 cups
go low fat or fat-free
if not milk, chose lactose free or other calcium sources
Meat and Beans Guidelines
Go lean on protein
Women 19-30: 5.5oz
Men 19-30: 6.5oz
choose low-fat or lean meats and poultry
bake it, broil, or grill
vary choices - fish, beans, peas, nuts, and seeds
Oil Guidelines
Know your fats
Women 19-30: 6 tsp
Men 19-30: 7 tsp
make most fat sources from fish, nuts, and vegetable oils
avoid butter, margarine, shortening and lard
general guidelines for eating healthy
Carbs 55-70% of caloric intake
Fat 20-25% of caloric intake
Protein 12-25% of daily caloric intake
needs depend on sport, level of training, and nutritional goals
Supplementation
Vitamins and minerals
iron and calcium tend to be low (in females)
sodium and potassium can be replenished via sports drinks or diets
protein
daily needs usually exceeded in a normal diet
performance - enhancing substances
creatine and caffeine
Determining Protein Needs
0.8g/kg for average individual
1.1-1.4g/kg for recreational athletes
1.2-1.4 g/kg for endurance athletes
1.2-1.7g/kg for strength and power athletes
hydration guidelines
pre-exercise: 1.5-2.5 cups 2-3 hours before
during exercise: 1 cup ever 15-20 min
post exercise: 2-3 cups of fluid for every pound lost during exercise
use sports drinks during if it exceeds an hour
Female Athlete Triad
low energy availability
excessive reduction of dietary energy intake
excessive increase in energy expenditure
eating disorders are usually the first step in
menstrual disorders
when too little energy is available after exercise, a female athlete’s body reduces energy expenditure in other processes, in part by suppressing menstrual function
weak bone
when too little energy is available after exercise, the female athlete’s body also reduces energy expenditure by slowing the turnover of bone tissue
the loss of regular menstrual cycles often reduces the body’s production of estrogen, which normally restrains the rate of bone resorption
Eating Disorders
affect both males and females and often strike during adolescence
8 million americans with eating disorder
50% of americans know someone with an ED
10-15% of people with anorexia or bulemia are males
95% of people with ED are 15-25
18-20% of anorexics die within 20 yrs of contracting the disease
Healthy Eating
don’t restrict food servings below suggested guidelines of food guide pyramid
eat frequently, include healthy snacks between meals
establish a reasonable weight goal based on healthy body composition and a reasonable time to achieve the goal
refer athlete for help in dealing with ED
Body Temp Affected by
affected by
metabolic heat production (ATP)
conductive heat exchange (needs contact)
convective heat exchange (though mediation)
radiant heat (sun)
evaporative heat loss (sweat)
increase blood flow to periphery
water loss through sweat glands
water evaporates takes heat with it
Heat Illnesses
heat syncope
heat cramps
heat exhaustion
heat stroke
Heat Syncope
peripheral pooling of blood
symptoms: dizziness, fainting, and nausea
tx: place in cool environment, lay down (feet up), replace fluids
Heat Cramps
water loss / electrolyte osmotic imbalance
energy fuel depletion
tx: hydrate and stretch
Heat Exhaustion
Causes: Hot, humid weather, outside temp of 90+* & humidity 70%+ = danger. prolonged sweating, inadequate fluid replacement
Symptoms: sweat profusely, cold & clammy, pale face, excessive thirst, fatigue/weakness, mental dullness, weak, rapid pulse, shallow breathing
TX: treat for shock, ventilate area, remove excess clothes, increase fluid intake, sponge with ice water
Heat Stroke
Causes: hot humid weather, thermoregularity failure
Symptoms: no sweat, nausea & headache, flushed skin, hot & dry, temp 106-112*, strong & rapid pulse, increased respiration, chest pain, loss of consciousness
TX: call 911, cool athlete in ice water
Prevention of heat injury
hydration
acclimatization
identify susceptible athletes
monitor temperature and humidity
ACSM Hydration Recommendations
Nutritionally balanced diet and maintain normal hydration in 24 hrs prior to event
consume 500 ml of fluid 2hrs before event
consume enough fluid during the event to equal loss or to tolerance
fluid should be cool and accessible
activiti4es lasting 50 min or more - use sports drinks to help replace glycogen stores
activities of an hour or more - include sodium to enhance fluid retention and prevent hyponatremia
Acclimization
attain adequate fitness in cool environment before attempting to heat acclimatize
exercise at intensities >50% VO2max and gradually increase the duration and intensity of sessions during the 1st 2 weeks
perform the highest intensity workouts in morning and evening
monitor body weight to ensure proper hydration
monitor body temp
Identify Susceptible Athletes
age, alcohol use, creatine use, drug abuse, obesity, skin condition, previous heat illness
hypothermia
complicating factors:
uniforms, interval competition, moisture, hydration
physiological response:
body shuts down between 77-85*F
shivering - sympathetic response
Heat Index
DBT - dry bulb temp
WBT - wet bulb temp
DBT - WBT = relative humidity
GT - global temp
WBGT - universal wet bulb globe temp
=0.1 x DBT + .07 + WBT + GT x 0.2
hyponytremia
loss of salts, presents similar to heat illness, need to check core temp
Stress
Everything we need for adaptation
Physiological responses:
alarm - fight or flight
resistance - body prepares for coping and directs stress to particular body site
exhaustion - organ or organ system becomes diseased as a result of chronic stress
Negative stress results in
muscle tension, reduction of flexibility, problems in coordination, decrease in movement efficiency
Integrated model of Physiological Response to Injury
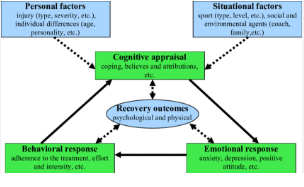
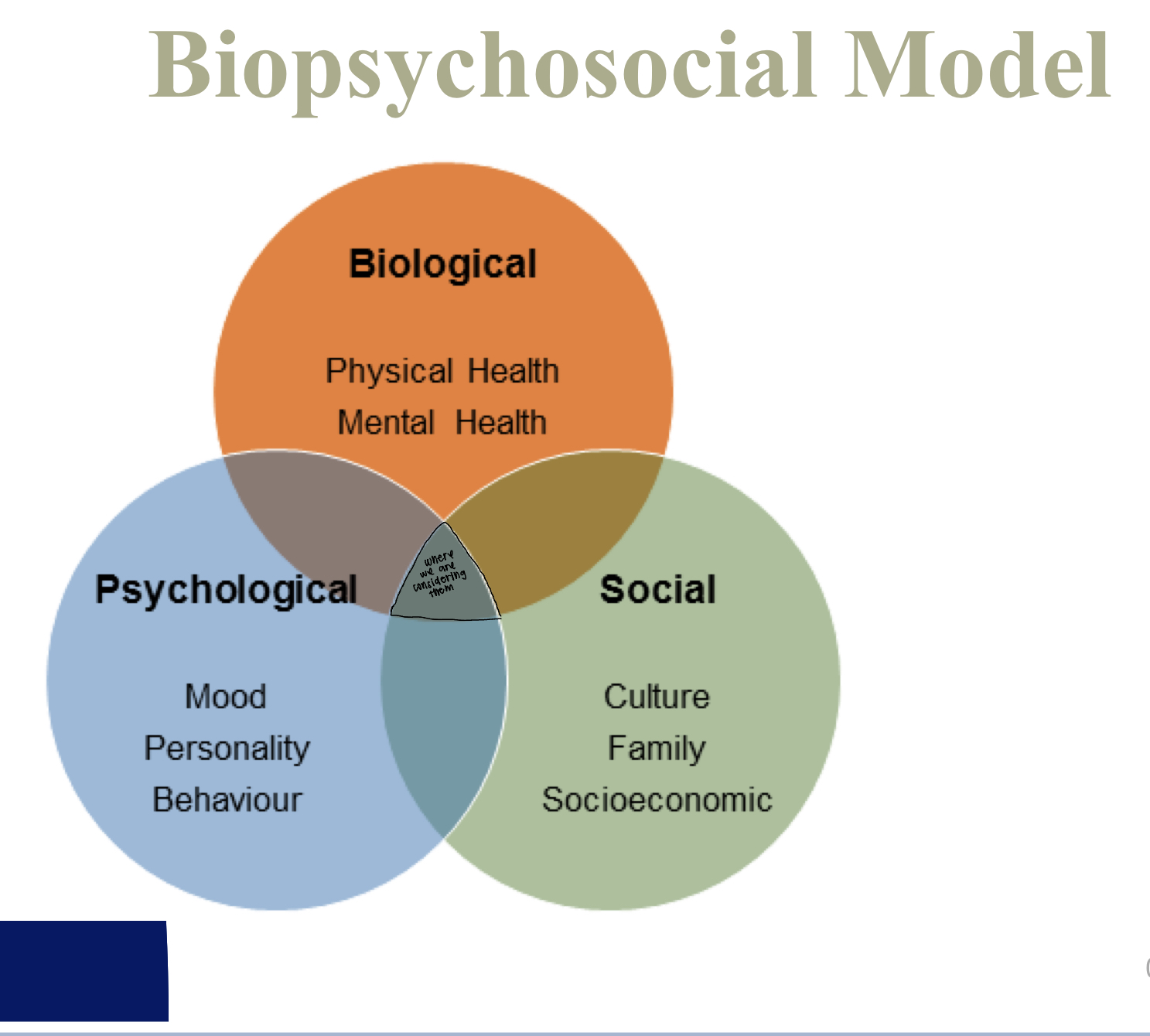
Biopsyhosocial Model
Psychology of Loss
Kubler-Ross Model
denial
anger
bargaining
depression
acceptance
Psych / personality factors that may predispose the athlete to injury
low confidence / self esteem
tense, restless, nervous
anxiety
attention seeking
Burnout - causes/sign/symptoms
Long seasons
not enough breaks
constant negative feedback
decreased performance levels
difficulty concentrating
loss of appetite
difficulty falling asleep
prone to sickness
restlessH
how to prevent burnout
reaction to injured athletes
DO - be calm, reassuring, allow venting of emotion, show empathy, encourage them to talk to you
DONT - pity them, tell them they are abnormal, be abrupt
give every injury a fair look
don’t be condescending
psychology of rehab
rapport, give a sense of cooperation, make the experience an educational process, build competitive confidence
psychology of returning to competition
small, progressive steps
mental training techniques
meditation
progressive relaxation
imagery
it is up to them how they’ll go back mentally
reactions to injury and early reactions to rehab
anger, anxiety, apprehension, bitterness, confusion, depression, disappointment, dispiritedness, devastation, fear, frustration, helplessness, relief, resentment, shock
Reactions to Rehab
shift towards more positive emotion: enthusiasm and excitement
evidence of periodic episodes of: depression, frustration, sadness
reactions to return to participation
myriad of mixed positive and negative emotions:
apprehension, anticipation, anxiety, confidence, depression, encouragement, fear of reinjury, frustration, reinjury anxiety
Injury Process
Primary: tissue destruction directly associated with traumatic force; can’t change amount of initial damage
Secondary: occurs from cell death caused by a blockage of O2 supply; can assist to keep minimum damage to other tissues
injury response cycle = pain - spasm - pain cycle
(chemicals stimulates free N endings & cause pain which causes M spasm & triggers body’s protective mechanisms)
Healing Process
Inflammatory / Acute phase
Fibroblastic / repair phase
Maturation / Remodeling phase
Signs of Inflammation
redness, swelling, pain, heat, loss of function
Acute inflammation
recognition of injury
vascular changes (vasodilation and permeability)
activation of endothelial cells
migration of leukocytes (primarily neutrophils) through vessel wall
accumulation of leukocytes at injury site
activation of leukocytes
phagocytosis and removal of debris
monocyte/macrophage infiltration
signaling of regenerative response
acute phase vascular response
experiences immediate platelet plug (vasoconstriction 5-10 min) [ first thing that happens so that we don’t bleed out
THEN histamine induced vasodilation 24-36 hours
Permeability happens because of capillary budding
Acute Phase Cellular response
Leukocyte (neutrophil) migration
1st to arrive, not big enough to make a difference that they are not specialized
monocytes mature into macrophages
macrophages are very specific
can tell difference between debris and live cells
when doesn’t develop, turns into chronic inflammation
Acute phase chemical mediators
Cell-derived histamines and prostaglandins
goals of the acute phase
clean up the debris (from injury and pathogen)
localize the injury/infection
isolate the site and make sure everything else around it is okay
Fibroblastic/repair phase
2 days - 6 weeks
2 parts
fibroplasia - scar tissue formation
capillary budding - “feeds” the scar tissue
regenerative tissues
do not repair
liver
nervous system
muscle
repair phase - fibroplasia
break down fibrin clot
replace fibrin clot with granulation tissue (with extracellular matrix)
formation of scar tissue
random network of connective tissue
tensile strength of matrix increases with the line of stress
capillary budding
factors that impede healing
extent of injury
edema
hemorrhage
poor vascular supply
separation of tissue
muscle spasm
atrophy
corticosteroids
keloids and hypertrophic scars
infection
humidity, climate, oxygen tension
health, age, and nutrition
Maturation / Remodeling phase
3 mo - 2 years
balance between blast/clast activity
rehab must focus on strengthening
organizes as it matures
type 1 fibers phase out as stress is introduced and type 3 influxes
we help control this stress as ATs
chronic inflammation
Load: time, tissue, what’s been done in the past
repeated trauma
macrophage proliferation (instead of neutrophil)
increase in prostaglandin and bradykinin activity
>1 month = subacute
months to years = chronic
itis vs. osis
itis = inflammation
osis = degeneration
improved healing
PRESSUES
Oncotic vs> Hydrostatic
POLICE
Prevention
Optimal
Loading
Ice
vasoconstriction, less volume, blood flow slowed upstream
Compression
manipulates, goes to lymphatic system
Elevation