Lab Exam 2 Review Flashcards
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Orbicularis oris
lip muscles
Orbicularis oculi
muscle that closes the eyelids
Zygomaticus major
cheek muscles
Risorius
assits Zygomaticus major in creating a smile or grin
Epicranius
muscle that helps creating facial expressions, such as the raising eyebrow
Platysma
collarbone to jaw muscle
sternocleidomastoid
muscles that connect the sternum, clavicle, and mastoid
Temporalis
muscle involved in closing the mouth or chewing
Buccinator
thin muscle wall of the cheek
Erector Spinae
muscles located on each side of the vertebral column
External/internal intercostalis
rib muscles
Diaphragm
muscle that helps you breathe
Latissimus dorsi
muscle covering lower part of back; triangular-shaped
Serratus anterior
muscle that helps stablize shoulder blade
Trapezoid
muscle that extends from skull to back
Rhomboideus major
muscle that connects shoulder blade to spine
Levator scapulae
muscle in the lower back/neck that elevates shoulder blade
Pectoralis major
muscle in chest that helps move the arm
Rectus abdominis
top layer of abdominal muscles
External oblique
lateral side of anterior side of the abdomen
Internal oblique
lateral side of posterior side of the abdomen
Transverse abdominal
deepest of the abdominal muscles
Deltoid
muscle that helps with the glenohumeral joint
Supraspinatus
back on shoulder; forms part of rotator cuff
Infraspinatus
stablize henoglumeral joint
Biceps brachii
makes itself visble when flexing arm muscles
Brachialis
provides elbow flexion
Brachioradialis
muscle at lateral side of forearm
Triceps brachii
Flexor carpi radialis
lies in first layer of the anterior muscle of the arm
Palmaris longus
small tendon between flexor muscles
Extensor carpi ulnaris
skeletal muscle at ulna side of forearm
Extensor digitorum
extends the four fingers of the metacarpals
Oppenens pollicis
extends the thumb
Illiacus
curved surface of pelvic bone
Psoas major
muscle at posterior abdominal wall
Sartorius
longest muscle in human body; spanning both knee and hip joints
Adductor group
Quadriceps
rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius
Hamstrings
Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, and Semimembranous
Gluteus maximus
main exterior muscle of the hip
Gluteus minimus
medial radiator of the hip
Tensor fascia latae
muscle outside of hip, allowing hip flexion
Gastrocnemius
main muscle of the back leg
Soleus
located below the gastrocnemius
Tibialis anterior
Largest leg muscle
Fibularis longus
attached to the outside/lateral side of leg and allows for foot and ankle movement
Dendrites
Receive signals from other neurons
Axon
Elongated portion of neuron
axon hillock
Controls where electrical impulses are sent that are also dependent of the actions of other neurons
Neurilemma
thin sheath around the axon
Myelin Sheath
insulating layer or “blanket” around neurons
Central sulcus
seperates frontal and parietal lobes

Pineal gland
regulates circadian rythm
Cerebral aqueduct
small tube that connects third and fourth ventricles of the brain
Pitituary gland
produces hormones
third ventricle
connects ventricles
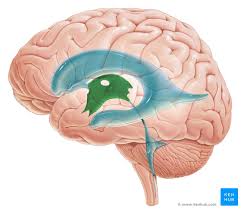
fourth ventricle
connects ventricles
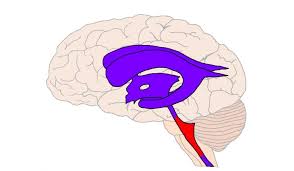
Arbor vita
brings sensory information to the cerebellum; “white tree-like”
Longitudinal fissure
midline of the brain
Dura mater
layers of connective tissue that protect the brain and spinal cord (outermost layer)
Arachnoid mater
layers of connective tissue that protect the brain and spinal cord (middle layer)
Pia meter
layers of connective tissue that protect the brain and spinal cord (innermost layer)
Spinal nerve
interacts with spinal cord to deliver sensory and motor information to the roots of the spinal cord.
Ventral root
anterior root of spinal cord
Dorsal root
posterior root of spinal cord
Dorsal root ganglion
cluster of neurons in the dorsal root
Dorsal/ventral/lateral horn
grey matter within spinal cord
dorsal/ventral/lateral funiculus
white matter within spinal cord
I
Olfactory
II
Optic
III
Oculomotor
IV
Trochlear
V
Trigeminal
VI
Abdecens
VII
Facial
VIII
Vestibulocochlear
IX
Glossopharyngeal
X
Vagus
XI
Accessory
XII
Hypoglossal
Epineurium
surrounds nerve’s internal environment
Perineurium
surrounds the fascicles
Endoneurium
surrounds muscle fibers
Fasicle
bundle of nerves or muscle fibers
Nerve FIber
nerve cell
Myelin sheath
Wrapped around each nerve cell
Axon
long cordlike part of a nerve cell