Psychodynamic approach (part 1)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
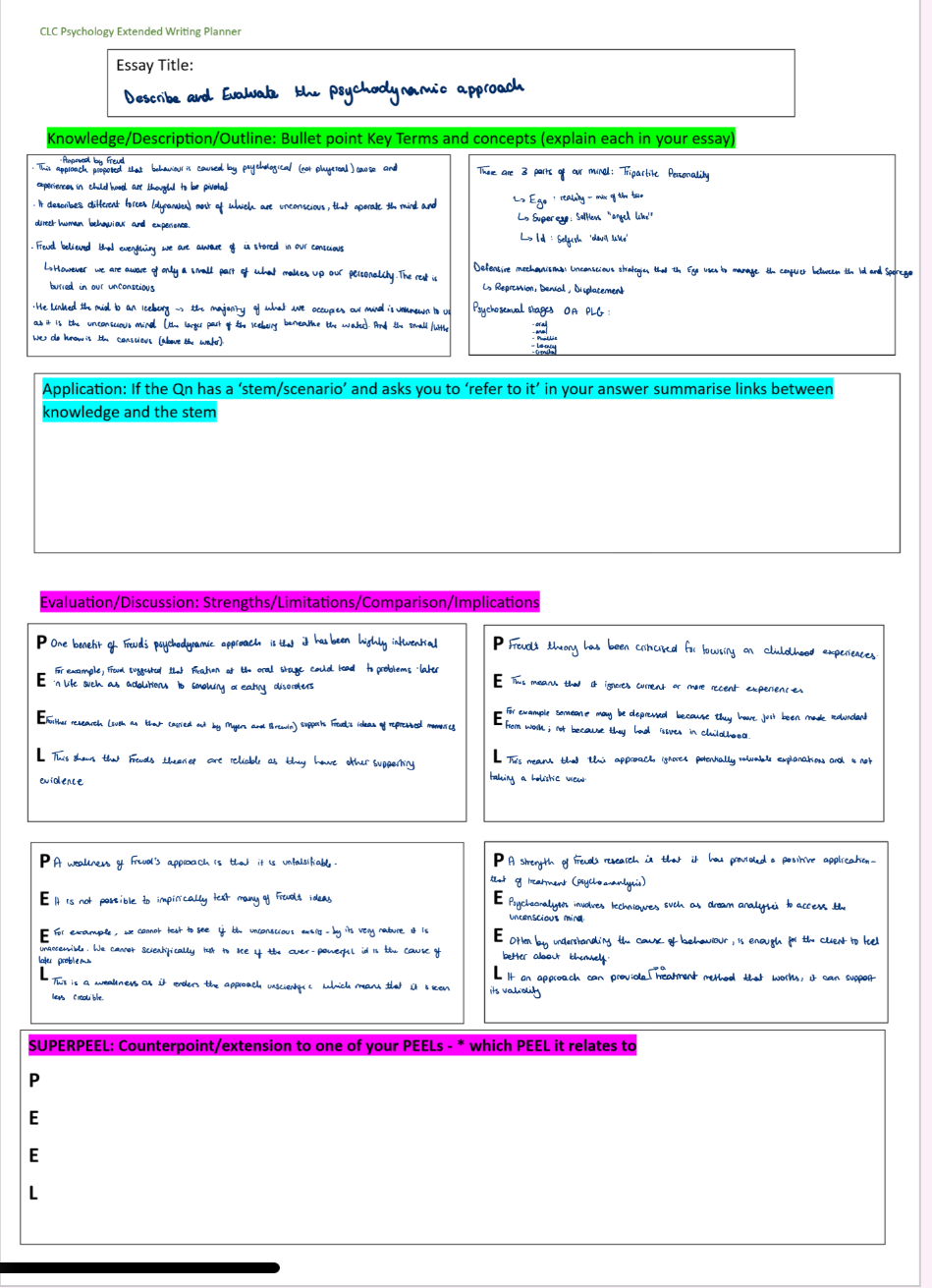
What does the psychodynamic approach focus on?
It focuses on unconscious forces that influence behaviour and personality.
Define the psychodynamic approach.
A perspective that describes unconscious forces that operate in the mind and direct human behaviour and experience.
According to Freud
what causes behaviour?
Which period of life is thought to have the biggest impact on behaviour?
Early childhood. (The environment does have an impact but only in the very early childhood)
Define the unconscious mind.
The part of the mind we are unaware of but which influences behaviour
How did Freud describe the mind?
As an iceberg – most of it (the unconscious) lies below the surface.
What is stored in the unconscious mind?
Fears
Define the conscious mind.
The small part of our mind we are aware of – includes thoughts and perceptions.
Define the preconscious mind.
Contains thoughts and memories not currently conscious but accessible.
What are the three parts of the personality according to Freud?
The id
Define the Id.
The primitive part of personality
Define the Ego.
The rational part of personality that mediates between the id and the superego (reality principle).
Define the Superego.
The moral conscience that internalises societal and parental values (morality principle).
What happens if the ego cannot control the id or superego?
One dominates
Define defence mechanisms.
Unconscious strategies used by the ego to manage conflict between the id and the superego.
Name three common defence mechanisms.
Repression
Define repression.
Forcing distressing memories into the unconscious.
Define denial.
Refusing to accept reality or acknowledge an unpleasant truth.
Define displacement.
Redirecting emotions from the true source onto a substitute target.
According to Freud what are the five psychosexual stages?
Oral, Anal, Phallic, Latency, Genital
What is a way of the 5 psychodynamic stages in order?
Oranges And pineapples Love Gardens
Describe the oral stage.
Pleasure focused on the mouth (sucking) mothers breast can be the object of desire
Describe the anal stage.
Focuses of pleasure is the Anus. Child gains pleasure from withholding or expelling faeces; conflict = toilet training.
Describe the phallic stage.
Pleasure from genital area; development of Oedipus/Electra complex.
Describe the latency stage.
Sexual urges are repressed; focus on friendships and social skills.
Describe the genital stage.
Sexual desires become conscious; formation of adult relationships.
What happens if a psychosexual stage is not resolved?
The individual becomes fixated and may show behaviours linked to that stage in adulthood.
What are the consequences of unresolved conflict in the oral stage?
Oral fixation - smoking, biting nails, sarcastic, critical
What are the consequences of unresolved conflict in the anal stage?
Anal retentive- perfectionist - obsessive
Anal expulsive - thoughtless, messy
What are the consequences of unresolved conflict in the phallic stage?
Phallic personality - narcissistic, reckless
What are the consequences of unresolved conflict in the latency stage?
What are the consequences of unresolved conflict in the genital stage?
Difficulty forming heterosexual relationships
What is a key criticism of Freud’s research?
It is androcentric – focused mainly on males.
Why is the psychodynamic approach criticised scientifically?
Because it is not very scientific – many concepts cannot be tested or measured empirically.
What are two strengths of the psychodynamic approach?
Highlights importance of early childhood experiences and recognises unconscious influences on behaviour.
What are the Oedipus and Electra complexes?
Oedipus complex = boys’ unconscious desire for their mother; Electra complex = girls’ unconscious desire for their father.
Here is a 16 marker plan of the psychodynamic approach