Unit 4.1 - Skin, Hair, and Nails
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Skin
Epidermis: very thin, tough outer layer of the skin
Dermis: thicker inside layer of skin
Epidermis
Stratum Corneum: exposed top portion; constantly shed
Stratum Germinativum: innermost layer; constantly reproducing
Dermis
Contains:
collagen for strength and elastic fibres for flexibility.
blood vessels, nerves, sensory receptors, lymphatics.
accessory organs (hair, sweat and sebaceous glands).
Subcutaneous
Hypodermis (adipose tissue)
Stabilizes skin in relation to underlying tissues.
Hair
Velus Hairs: peach fuzz found mostly everywhere
Terminal Hairs: thicker hair found on certain areas of the body
Glands
Sebaceous Glands: oil glands that lubricate the hair and skin
Sweat Glands: excretes waste, cools skin, provides protection
Eccrine: “everywhere”
Apocrine: active after puberty where there are terminal hairs
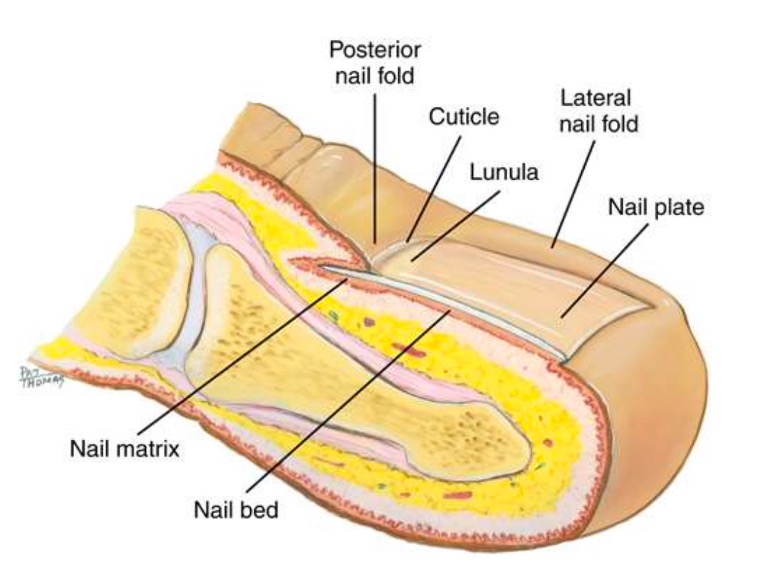
Nails
Protects tip of fingers/toes.
Nail plate can alter with diseases.
Assess Skin
Skin should be even across the body.
Colour: pallor, erythema (fever), cyanosis (late sign of little oxygen), jaundice (breakdown of blood cells).
Moisture: diaphoresis (profuse sweating), dehydration (leads to dry skin).
Texture and Thickness: should be smooth, firm, and uniformly thin.
Mobility and Turgor: pinch back of hand, if skin remains upright (tenting) sign of dehydration.
Lesions: Asymmetry, Border, Colour, Diameter, Elevation and Evolution.
Concerning if lesion is asymmetrical, has an irregular or indistinct border, has multiple colours, is greater than 6mm, or is raised/uneven.
Assess Nails
Profile Sign: hold up index finger and see if angle of nail sticks straight out (angle greater than 180° indicates clubbing)
Consistency: note any pits or grooves.
Colours: should be pink in colour.
Capillary Refill: how long it takes colour to return to nail bed.