Lipids study guide
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
What does cholesterol do in the body, what is it used for?
Cholesterol is essential for maintaining cell membrane integrity, synthesizing steroid hormones, bile acids, and vitamin D, and aiding in nerve transmission by forming myelin.
Cholesterol is made from
acetyl coA
how much of the cholesterol is esterified in the body
70%
ACAT is cholesterol acyltransferase where
intracellular
LCAT is cholesterol acyltransferase where
in circulation
fatty acids are made of what
a chain hydrocarbons with a terminal carboxyl group at one end and a methyl group at the other
fatty acids determine what in a compound
if the compound will be solid or liquid
What are the three essential fatty acids
linoleic
linolenic
arachidonic
what do fecal fatty acids help detect
malabsorbtion or pancreatic disorder
why do we produce ketones
Ketones are produced from fatty acids in the liver and serve as an alternative energy source for the brain and body when glucose levels are low. causes acidification of blood tho
What are three ketone bodies
acetone
acetoacetate
BHOB
what transports triglycerides
by chylomicrons
what are phospholipids made of
diglyceride esterified with phosphoric acid bound to an alcohol
Amphipathic
containing hydrophilic head groups and hydrophobic fatty acid side chains
Phospholipids act as
detergents and surfactants
Whata are the two fatty acids used for fetal lung maturity testing
phosphatidylcholine
phosphatidylglycerol
cardiolipin
a component of the inner mitochondrial membrane that generates electrochemical potential for substrate transport and ATP synthesis
Shingomyelin
the only phospholipid that doesnt contain a glycerol back bone from a sphingosine
What ratio is used for maturity of an inutero baby
Lecithin: shpingomyelin (more lecithin the more mature)
Prostaglandins
A group of lipids that have a hormone like action, they modulate inflammatory responses
Terpenes
Polymers of different isoprene units
What vitamin is a terpene
Vitamin A
What are the lipid soluble vitamins
ADEK
how is lipids digested and absorbed
lipase in the stomach starts breaking down lipids
bile is produced in the liver and aids in the digestion and absorbtion
the pancreatic lipase breaks down fatty acids
micelle is formed and is diffused into the mucosal cells
lipids are transported by chylomicrons
fat is absorbed by the small intestine
What is the order of density for lipoproteins
(most dense) HDL
LDL
IDL
VLDL
Chylomicrons (least dense)
What percentages make up chilomicrons
90% triglyceride
5% cholesterol
4%phospholipids
1% protein
What percentages make up VLDL
65% triglyceride
20% cholesterol
10% phospholipids
5%proteins
What percentages make up IDL
30% triglyceride
35% cholesterol
20% phospholipid
15% protein
What percentages make up LDL
10% triglycerides
50% cholesterol
20% phospholipids
15% protein
What percentages make up HDL
5% triglycerides
15% cholesterol
25% phospholipids
55% protein
chylomicrons are major carriers of _____ triglycerides
exogenous
VLDL carries ____ triglycerides synthesis in the liver
endogenous
VLDL creates ____ in spun spcimens
turbidity
What is IDL made from
is formed from the metabolism of Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL) as VLDL is broken down by lipoprotein lipase and loses triglycerides.
APoE ‘s role with IDL
ApoE requir eleed for liver uptake and continues degredation of IDL to LDL
APOE deficiency will result in elevation of chylomicron remnants and IDL
What does LDL transport?
transports cholesterol and triglycerides from the liver to peripheral tissues. It is often referred to as 'bad cholesterol' due to its association with plaque buildup in arteries.
LDL is a major risk facto for
CHD
HDL increased levels means
decreased risk of accelerated atgherosclerosis
Apolipid proteins function as
enzyme cofactors
structural integrity agents
receptor ligands
Apolipoprotein A1
the major constituent of HDL
What does ApoA1 activate and what does this cause
LCAT, removing free cholesterol from extrahepatic tissues
Apolipidprotein B 48
associated with clearing of chylomicrons, binding VLDL to LDL
Apolipidprotein B 100 is a
recognition site for LDL to bind to cell membranes
Apolipidprotein C
slows clearance of trig rich lipoproteins
Apolipid C1 inhibits and activates what
inhibits- lipoprotein binding to LDL and VLDL receptors
Activates- lipoprotein lipase for breakdown of triglycerides in the cell
Apo C-II activates
lipoprotein lipase
APO C-III is an inhibitor of
LPL activity
Apolipidprotein E functions to
regulate lipid levels in plasma by promoting binding of lipoproteins to the LDL receptor and a specific chylomicron remnant receptor
LpA functions to
homolog of plasminogen and may compete for binding site thereby slowing the rate of clot lysis
LPA is a contributor to
CVD, atherosclerosis and heart attacks
What are the risks of increasing atherosclerosis
smoking
diabetes
obesity
hypertension
What test detects small amounts of inflammation
HsCRP
Homocysteine
an amino acid that can accumulate and promote endothelial injury
elevated levels of homocysteine are associated with
cardiovascular disease
stroke
alzheimers
osteroporosis
nutritional deficiency of B6, B12, and folic acid
What is the ideal time to fast before a test
12 hrs
If someone is not fasting for the lipid testing then
the serum will become turbid w/ a layer of CM and have an increase of triglycerides
desirable level of HDL
>60mg/dl
desirable level of LDL
<100mg/dl
desirable levels of triglycerides
<150mg/dl
desirable total cholesterol
<200mg/dL
What is the method used now for cholesterol testing
enzymic cholesterol oxidase testing
triglycerides testing method has lipase liberating
glycerol
lipid testing methods interferance:Glycerol contamination from stoppers of evacuation tubes or ingestion of glycerol-coated medication can falsely _______ results
increase
Hisotric method of HDL measurements would have removed
CM, VLDL, LDL by pcpt and analyze supernatant for HDL
Most known assays for HDL dont need
pre-treatment
Friedewald equation
LDL=[total chol.-HDL] -[trigly/5]
What is the limiting factor of friewald equation
its an estimate and the higher the triglyceride the more likely LDL will be udnerestimated
in the friedewald equation the total cholesterol and HDL must be
measured by the same chemical procedure
Primary hyperlipedemia is due to…
genetic
Secondary hyperlipedemia
secondary condiion
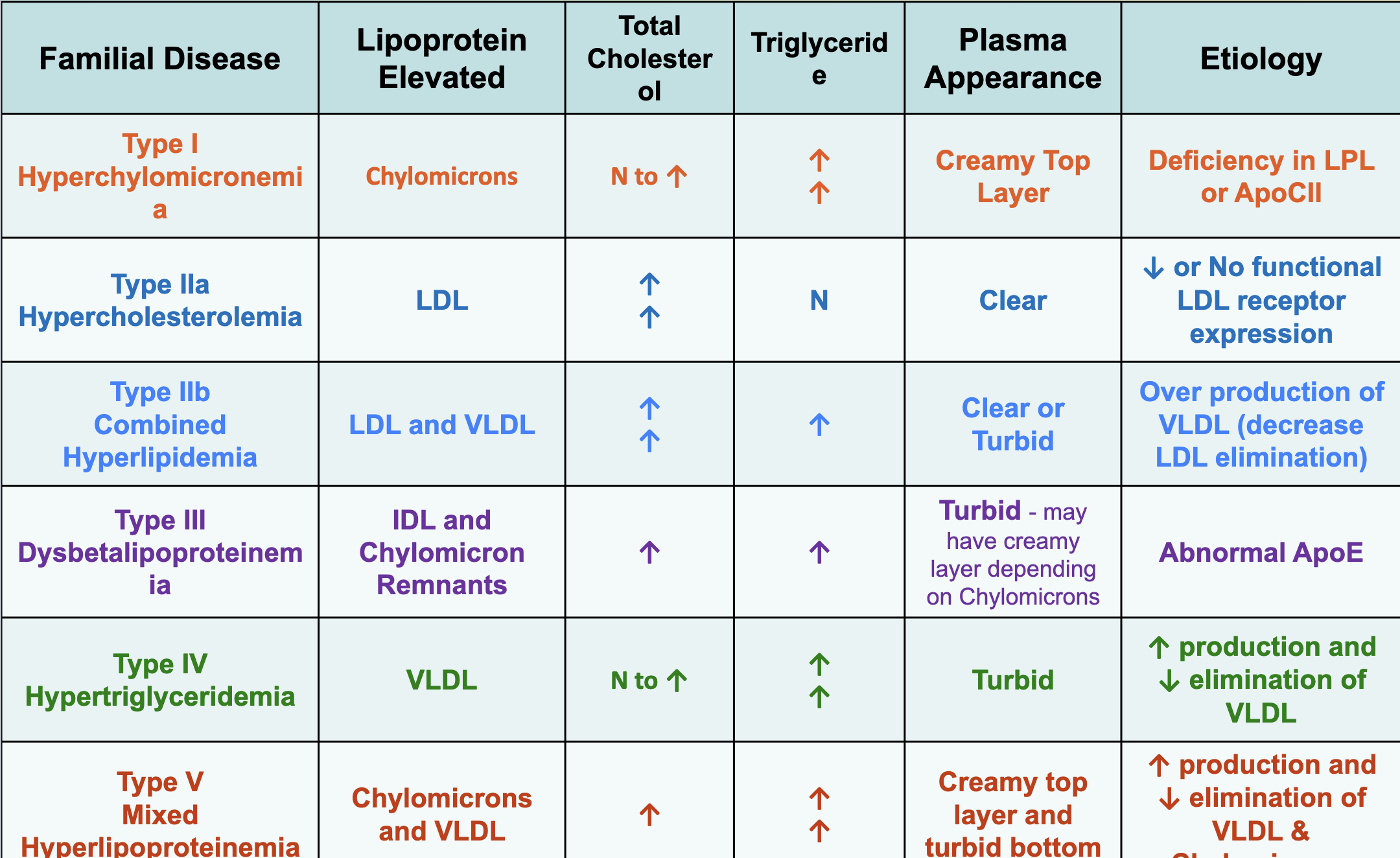
Frederickson classification of lipid disorders
What does defective ApoB100 result in
results in increased LDL
hypoalphalipoproteinemia has low ____ and ____ deficiency associated
HDL-C and LCAT
Tangier disease characteristics
absent HDL which means low Apo AI and Apo AII
clinical signs of Tangier disease
hyperplastic orange tonsils
splenomegaly
peripheral neuropathy
Gauchers disease
deficency in Beta glucocerebrosidase, leading to acculmination of glucocerebroside in bone marrow, liver, and spleen
What are clinical signs of gauchers
normocytic, hypochromic anemia
thrombocytopenia
leukopenia
bone pain
hepatosplenomegaly
skin pigmentation
gaucher cells
Niemann pick disease is caused by a deficiency in what
sphingomyelinase
clinical signs of niemannpick disease
loss of appetite
loss of early motor skills
enlarged spleen and liver
jaundice at birth
irregular speech
For Niemann pick what would you see on a blood smear
macrophages loaded with sphingomyelin
Taysachs disease is from what ancestry
ashkenazi jews
tay sachs is due to a deficiency in
hexosamidase A
What are the clinical signs of taysachs
psychomotor deterioration and dementia
blindness with a cherry spot in the retina
Type 1 familial hyperchylomicronemia
elevated chylomicrons
Type IIA familial hypercholesterolemia
increased LDL-C
Type III dysbetalipoproteinemia
increased VLDL with increased chylomicrons
creamy layer w/ turbid infranate
Type IV hypertriglyceridemia
Overproduction of VLDL
turbid
Type V hyperlipoprotenemia
mixed hyperlipidemia
-creamy and turbid
Which type of hyperlipidemia would be present if there was a deficiency in lipoprotein lipase or apoCII?
Dysbetalipoproteinemia