Skeletal System III
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Why Calcium Homeostasis Matters
Muscle contraction (including heart)
Nerve Impulse transmission
Blood Clotting
Enzyme function and second-messenger systems
Bone Mineralization
Normal blood Calium Range
Typical range: ~ 9-11mg/dL (2.2-2.7mmol/L)
Homeostasis maintained by a balance between dietary intake, urinary excretion, and bone storage
Regulated by the Endocrine System
What is the Endocrine System?
Glands that secrete hormones into the blood stream
Hormones: Chemical messengers that affect distant organs
Parathyroid Gland
Thyroid Gland
Endocrine Glands are often Control Center
Bone as Calcium Reservoir
99% of body calcium stored as hydroxyapatite in bone
Bone constantly remodeled by
Osteoblasts → Build bone, deposit calcium
Osteoclasts → Break down bone, Releases calcium
Balance between them keeps both bone and blood healthy
If Osteoclasts are too active, what happen to blood calcium levels?
Calcium will be rise
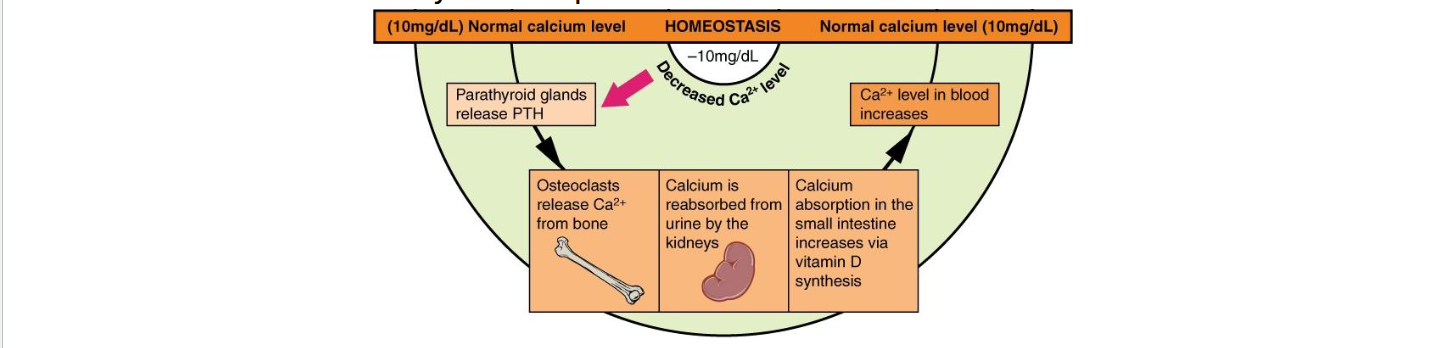
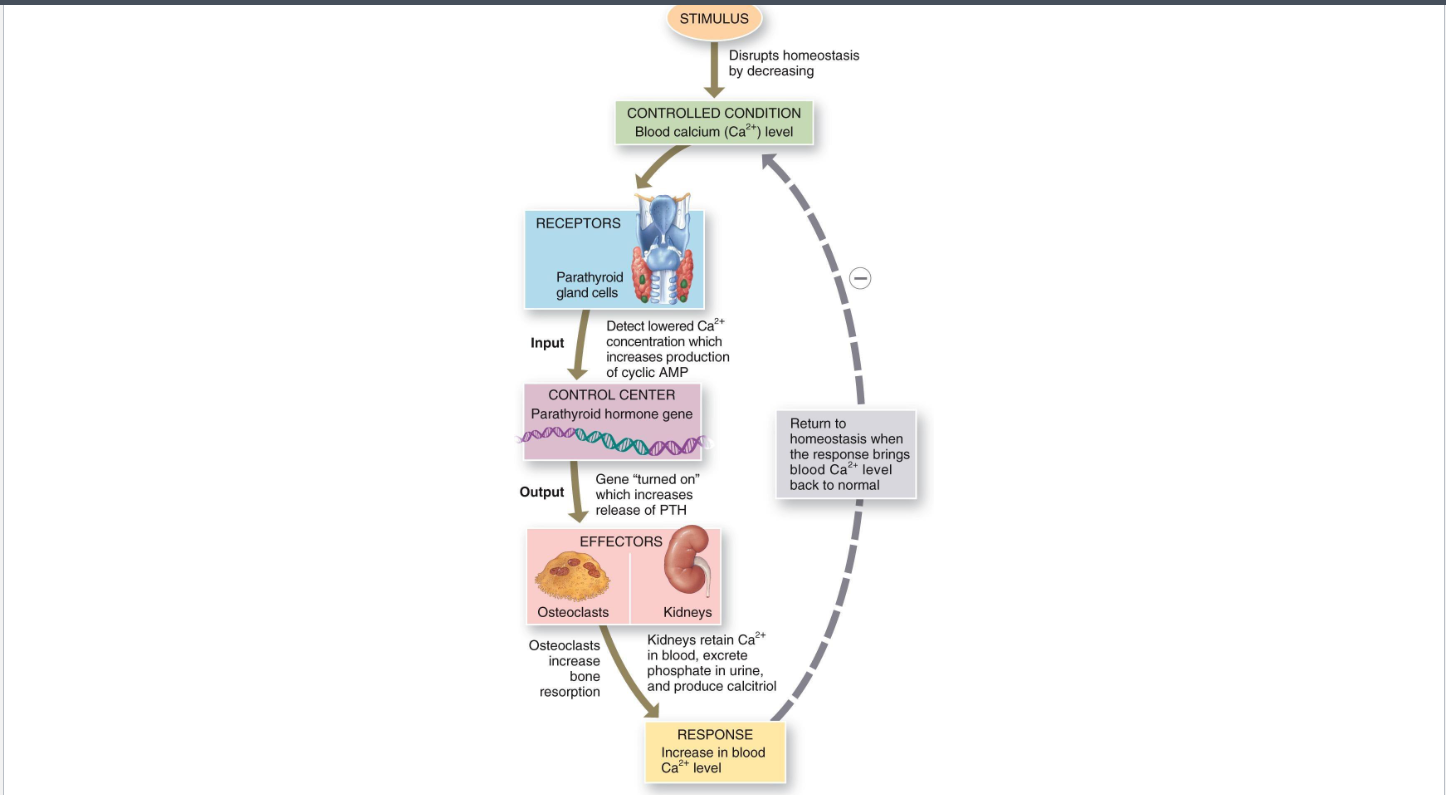
Parathyroid Hormone (PTH)
Secreted by parathyroid glands when blood Ca2+ is low (hypocalcemia)
Actions
Bone: Stimulates osteoclast activity (via osteoblast signaling) → releases Ca2+
Kidney: Increases Ca2+ reabsorption, stimulates calcitriol synthesis
Intestine: Indirectly up absorption via calcitriol
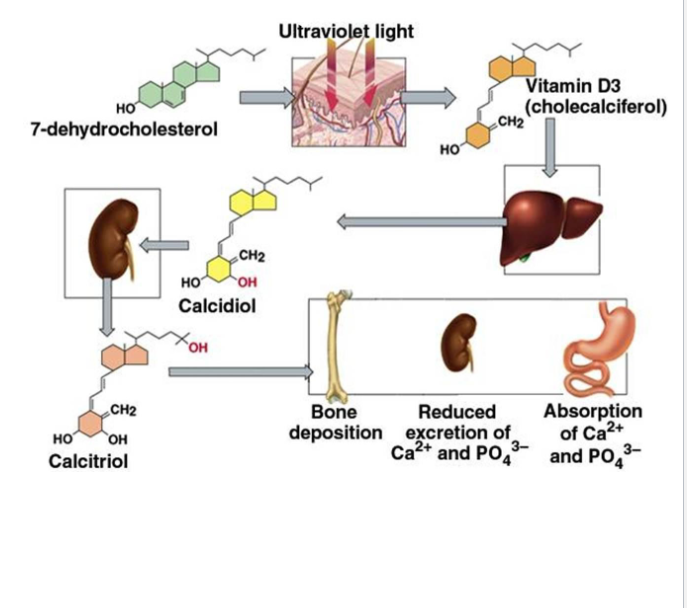
Calcitriol (Active Vitamin D3)
Formed from vitamin D after liver & kidney activation (PTH stimulates final step)
Increases intestinal Ca2+ absorption
Works with PTH to raise blood Ca2+
Promotes bone deposition
PTH and Calcitriol work together … Sorta
Both work to increase blood calcium
PTH causes it to be released from bone
Calcitriol causes it to be absorbed from the gut and retained in blood by action on kidneys
Same goal, different effect at bone level
PTH causes bone breakdown, Calcitriol causes bone deposition
PTH quickly raises blood calcium
Calcitriol maintains long term blood-calcium levels
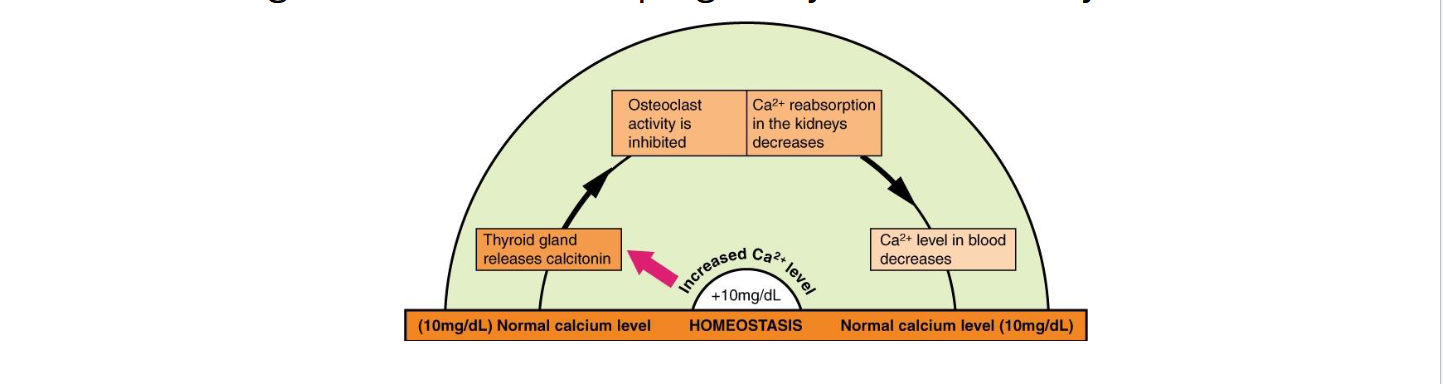
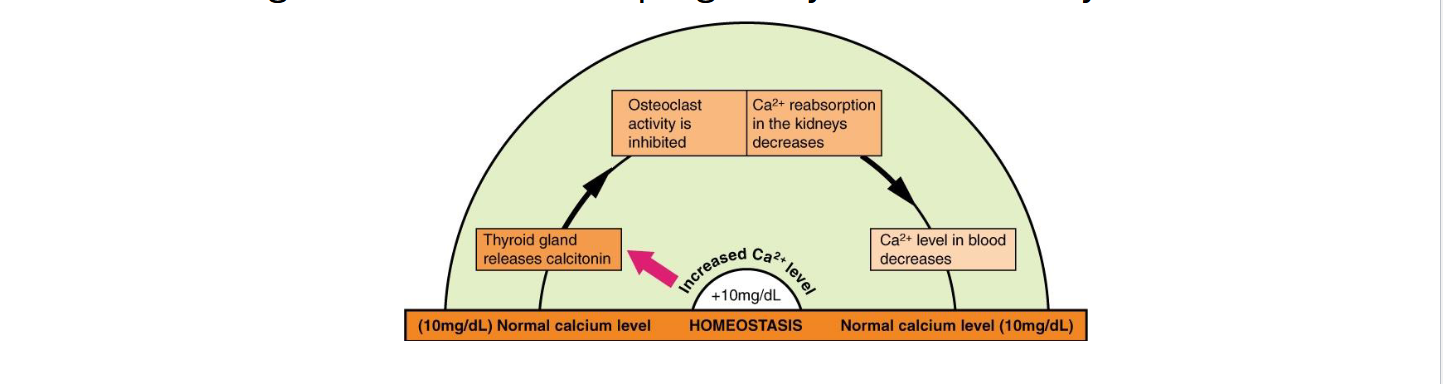
Calcitonin
Secreted by thyroid ( parafollicular (C) cells) gland when blood Ca2+ is high (hypercalcemia)
Inhibits osteoclasts (directly) → lowers blood Ca2+
More significant in children/pregnancy than in healthy adults
When blood calcium level decrease ____ gland releases ______, which acts to ______ blood calcium by stimulating _____ activity and enhancing calcium reabsorption in the kidneys and intestines.
Parathyroid, PTH, Rise Ca2+, Osteoclast
When blood calcium levels increase, the ____ gland releases ____, which acts to ______ blood calcium by inhibiting _____ activity
Parathyroid, calcitonin, dump, osteoblast
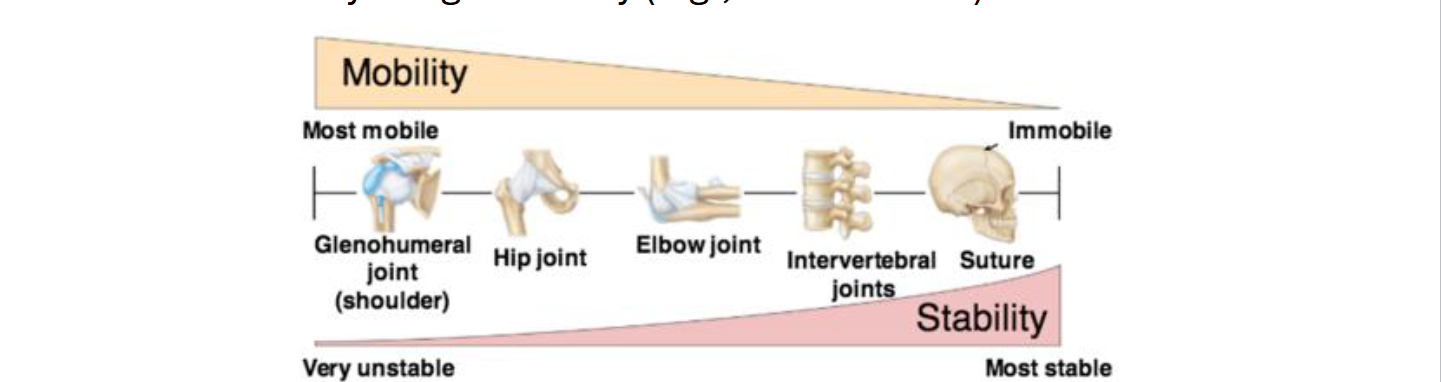
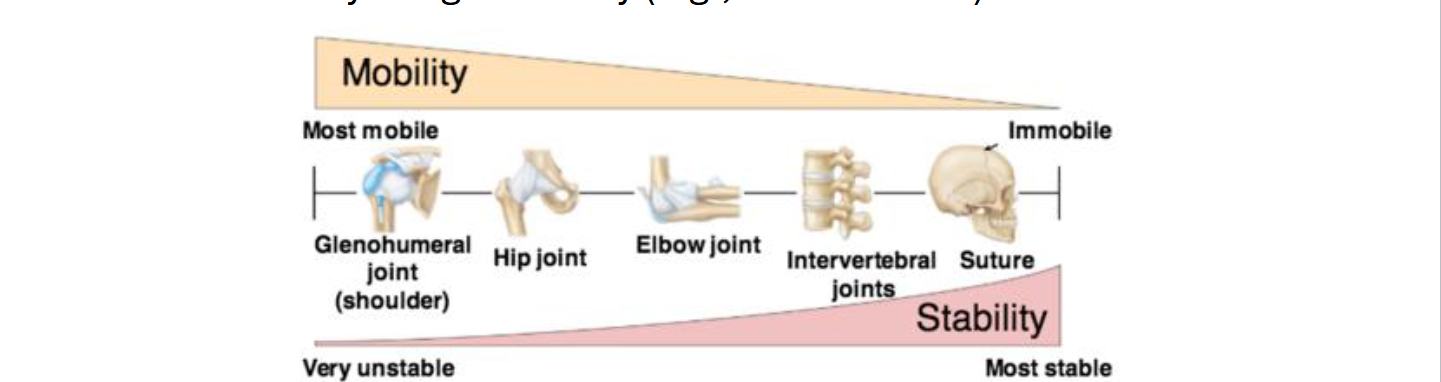
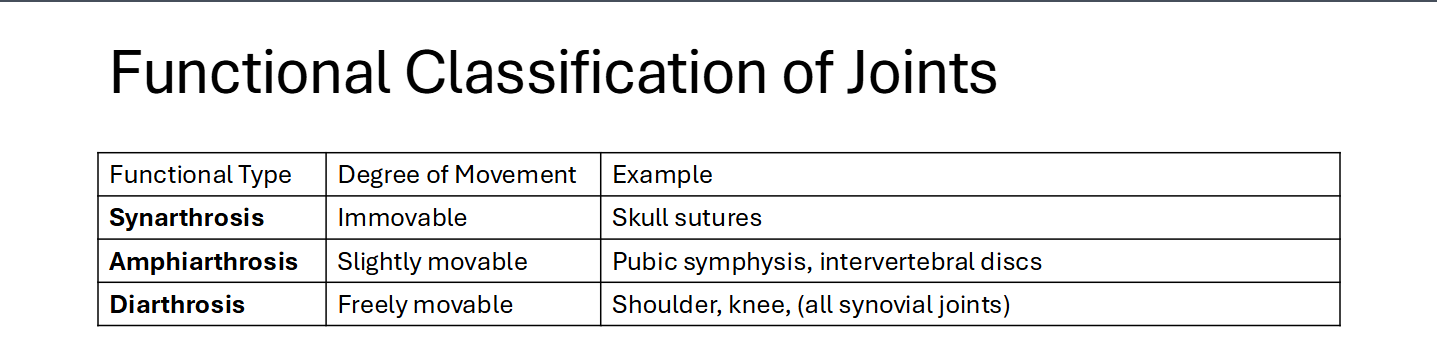
What is a Joint?
A Joint (articulation) = where two or more bones meet
Functions: allow movement and provide stability
Mobility vs Stability tradeoff:
High mobility → low stability (ex: Shoulder)
Low Mobility: high stability (ex: Skull sutures)
Structural Classification of Joints
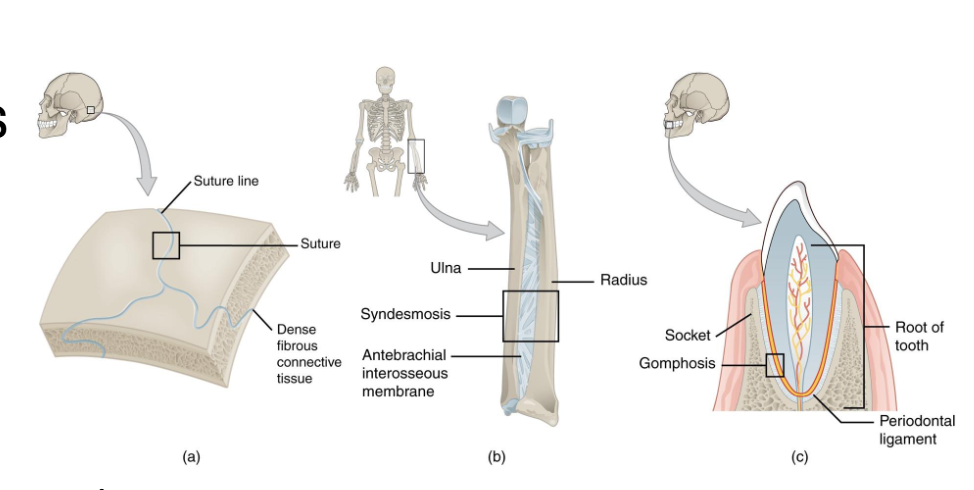
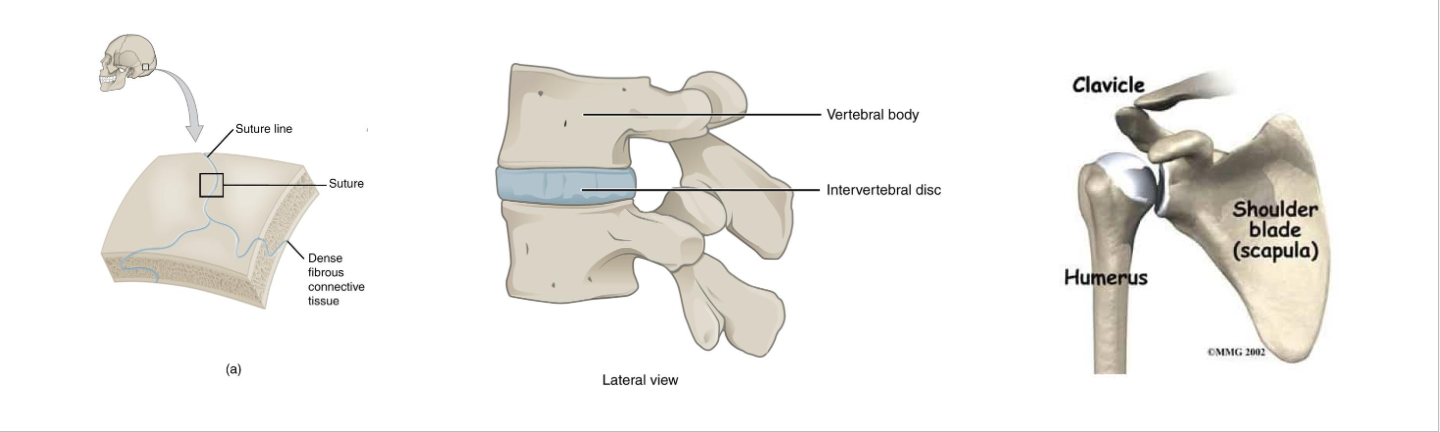
Fibrous Joints
Sutures: Interlocking bones of skull
Syndesmoses: Connected by ligaments (connect bone to bone) (ex: tibia-fibula)
Gomphoses: Teeth anchored in socket
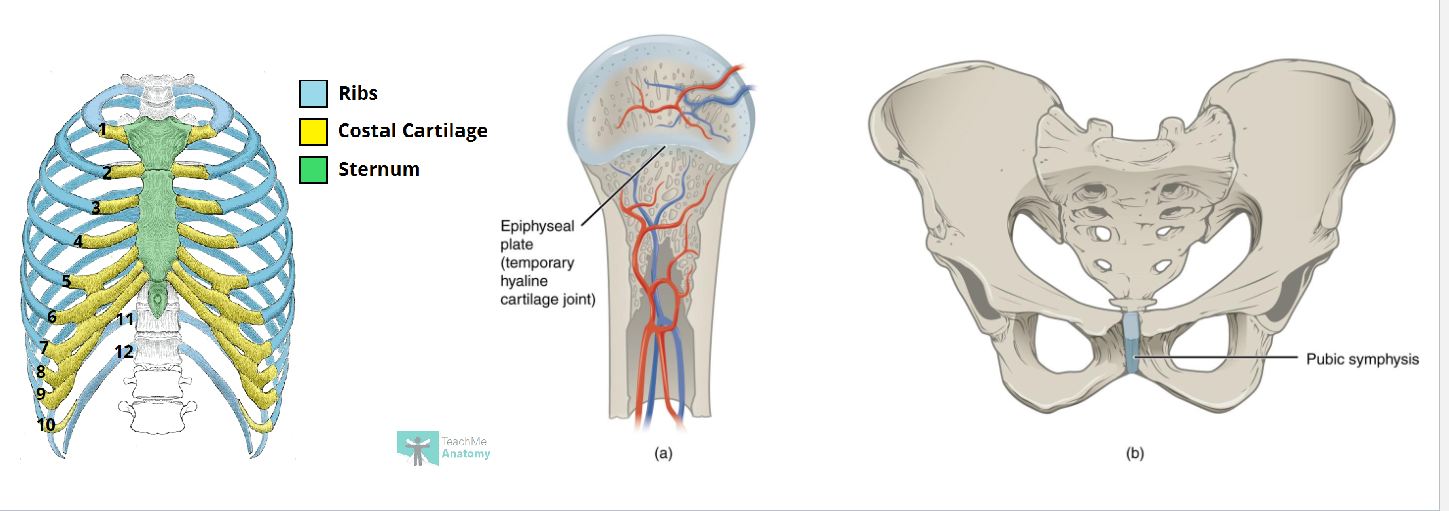
Cartilaginous Joints
Synchondroses: Bones joined by hyaline cartilage (ex: epiphyseal plate)
Symphyses: Fibrocartilage pad (ex: intervertebral disc, pubic symphysis)
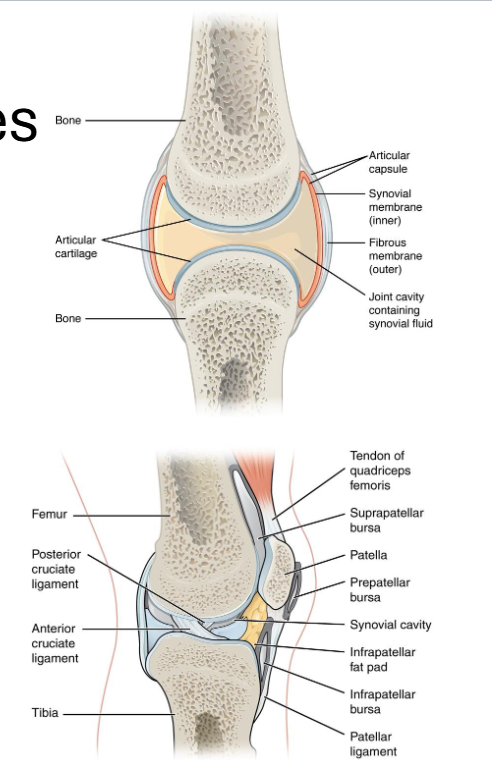
Synovial Joints: General Geatures
Articular Cartilage: Covers bone ends
Joint cavity filled with synovial fluid
Joint capsule (fibrous + synovial membrane)
Ligaments and Tendons reinforce stability
Bursae/Menisci reduce friction and absorb shock
What feature make synovial joints more vulnerable to injury but allow greater motion?
A: Fibrous connective tissue
B: Joint cavity
C: Articular cartilage
D : Menisci
B: Joint cavity
Functional classification of Joints
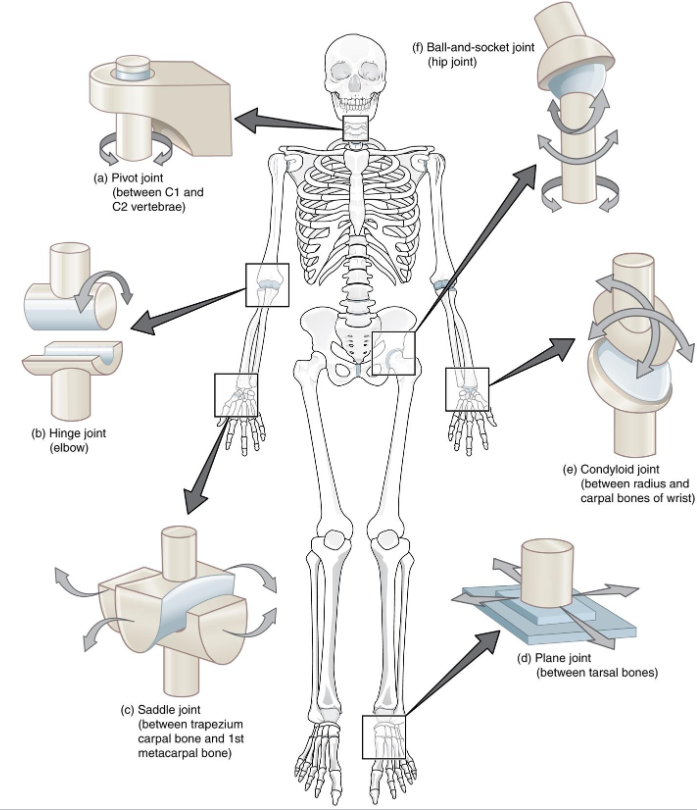
Types of Synovial Joints
Plane (gliding)
Hinge
Pivot
Condylar (ellipsoid)
Saddle
Ball-and-Socket
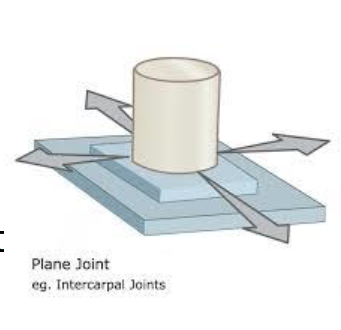
Plane Joints
Plane (Gliding): Intercarpal joints → Sliding movement
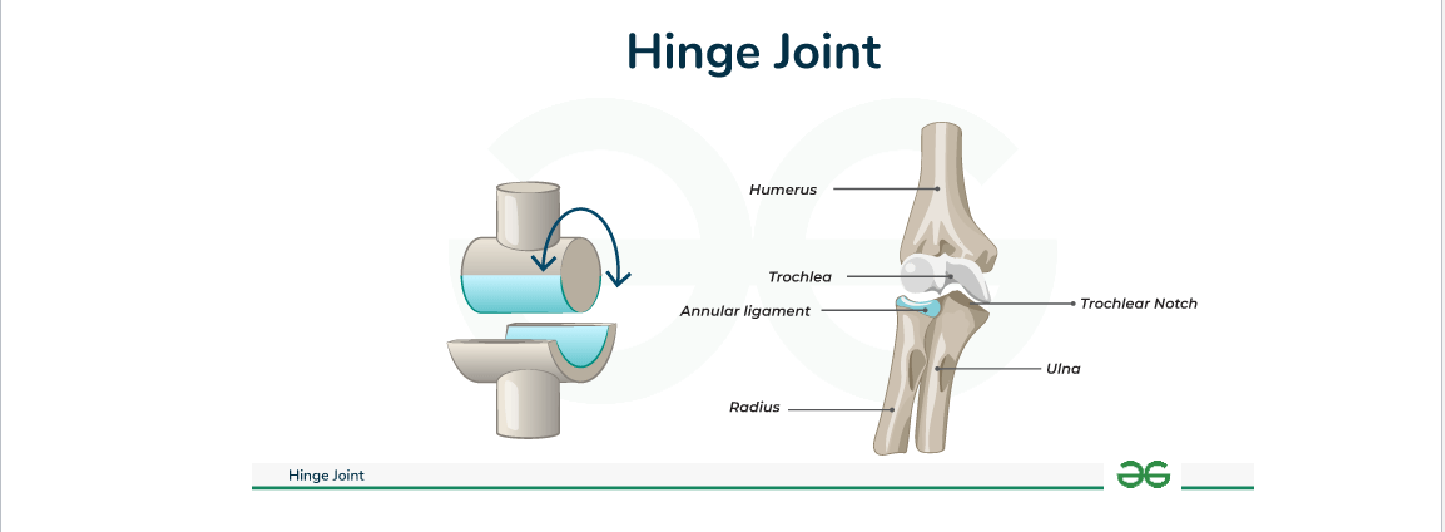
Hinge Joints
Hinge: Elbow, Knee → Flexion/Extension only
Pivot Joints
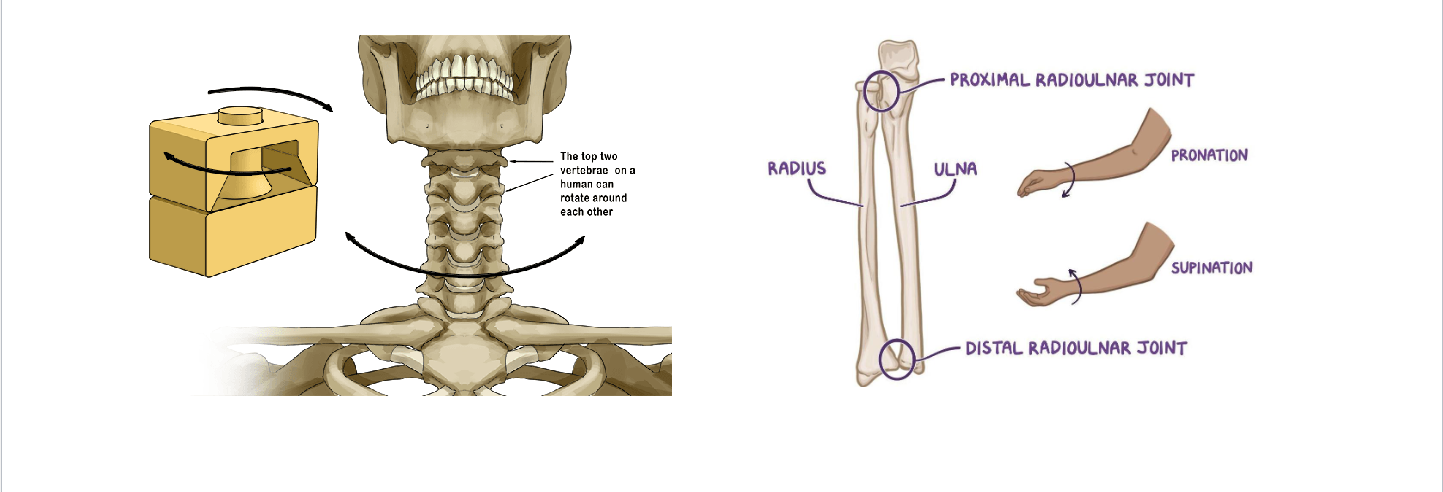
Pivot: Rotation around a single axis (atlas/axis, proximal radioulnar)
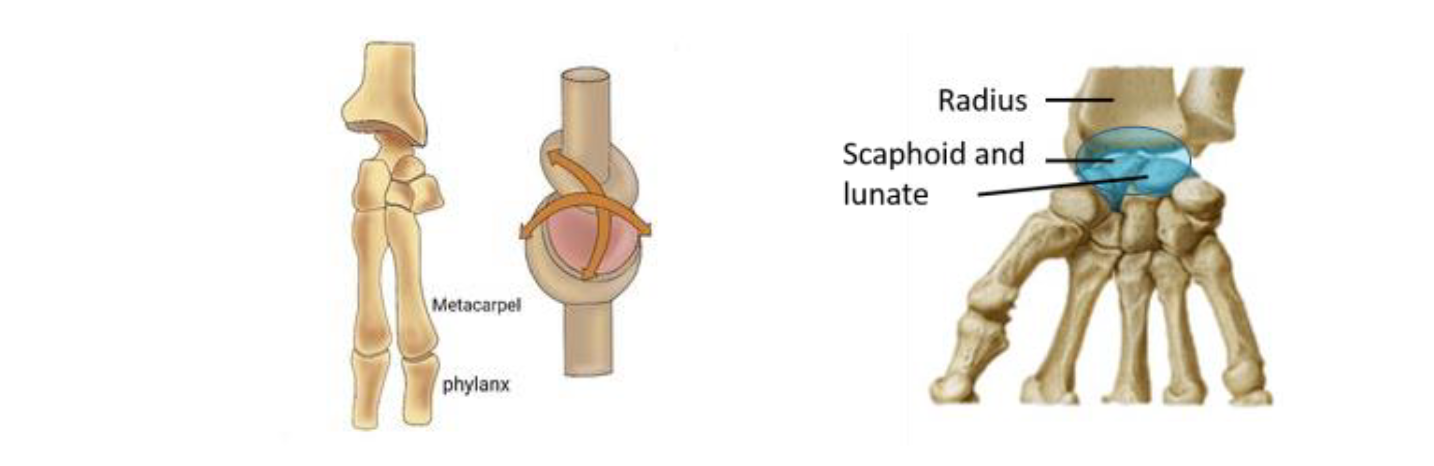
Condylar Joints
Condylar: Oval-shaped condyle of one bone fits into the elliptical cavity of another bone (wrist, knuckle joints)
Movement in two planes
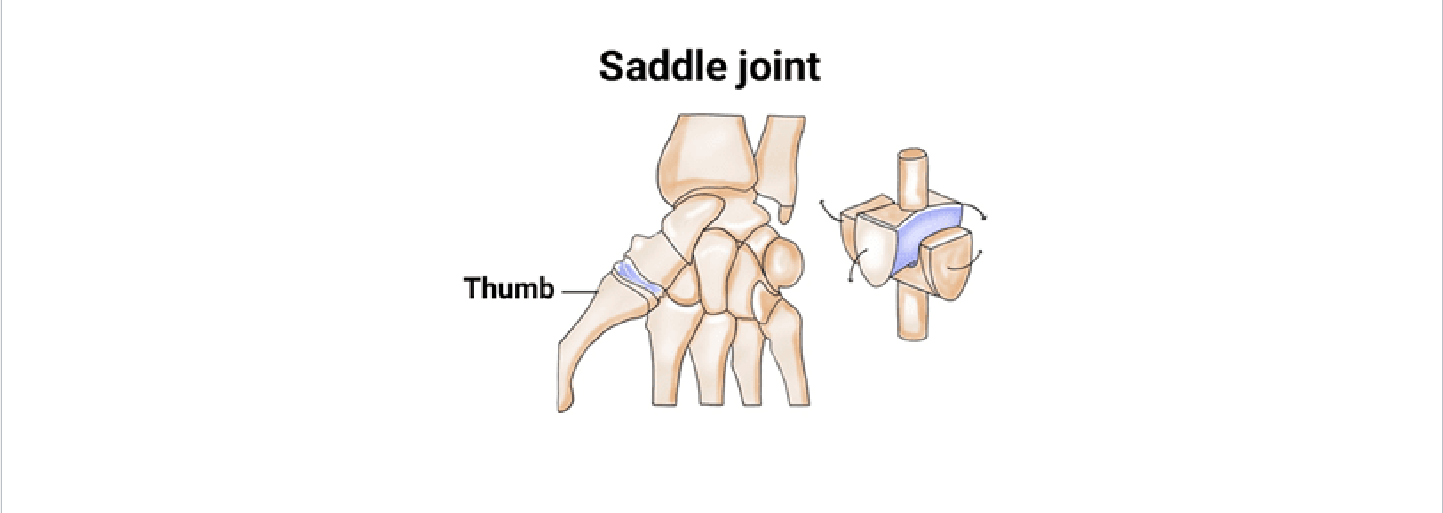
Saddle Joints
Saddle: Thumb (1st carpometacarpal) - allow opposition
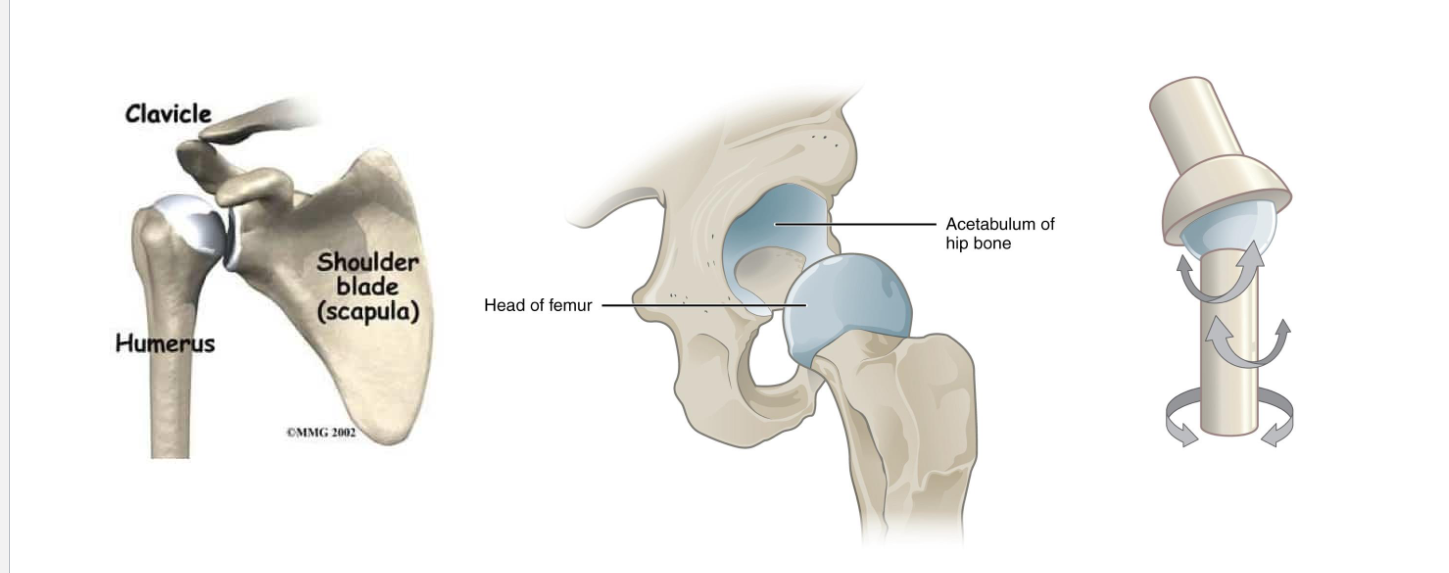
Ball-and-Socket Joints
Ball-and-Socket: shoulder, hip-widest range of motion
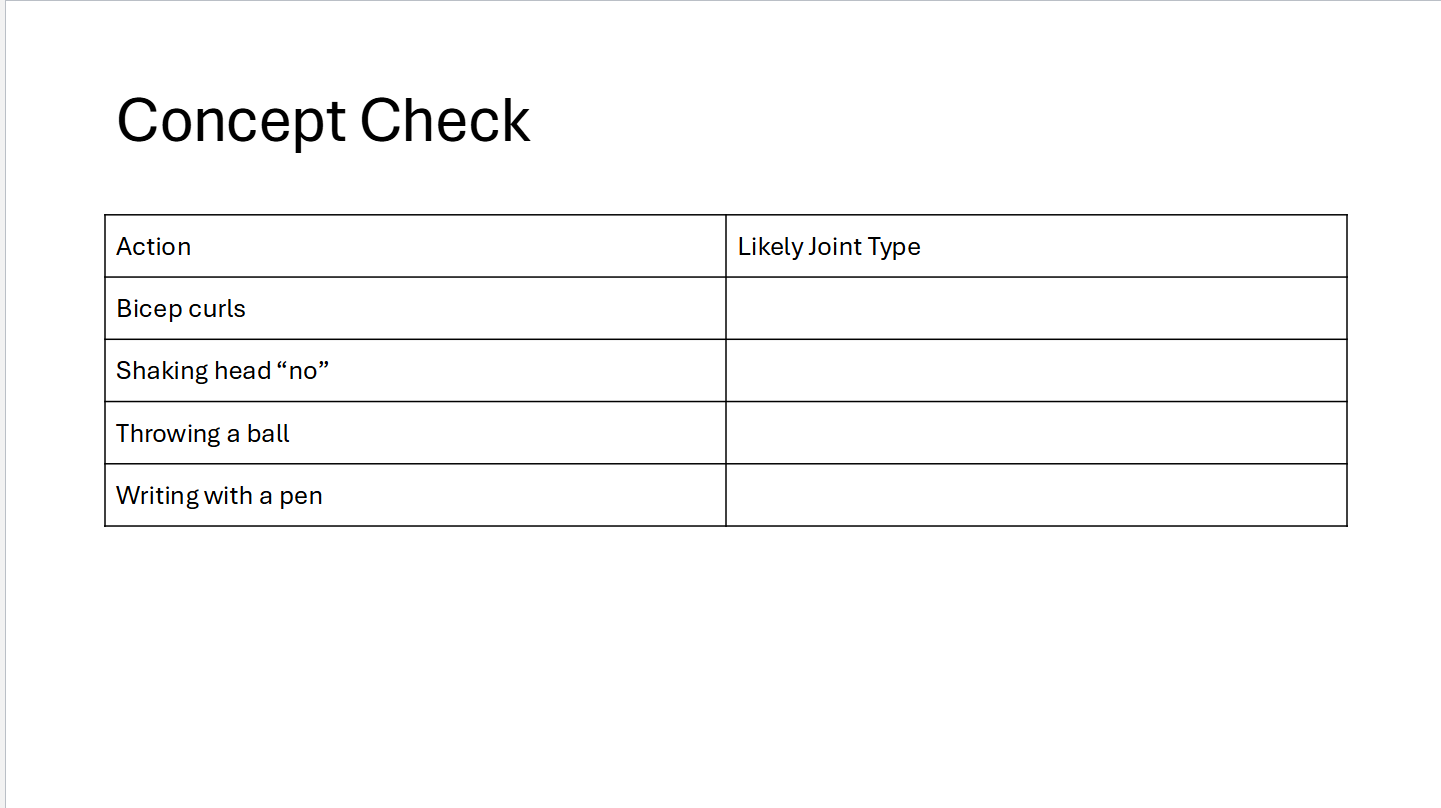
Concept check
Hinge
Pivot
Ball-and-Socket
Saddle
Fractures
Joints and bones work together
When bones are stressed beyond capacity → Fractures
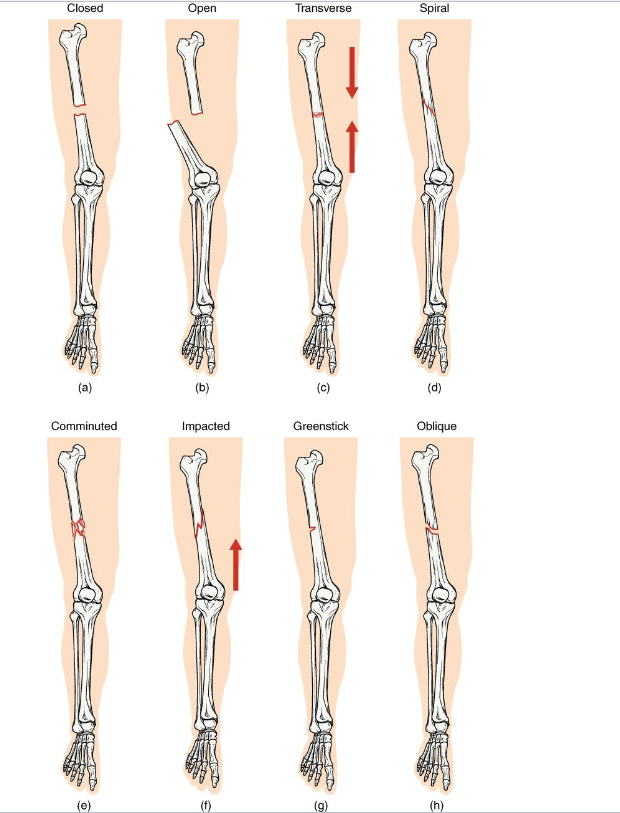
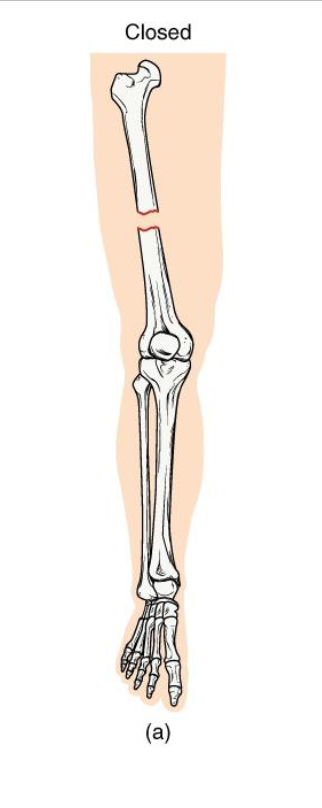
Closed Fracture
Definition: Bone breaks but does not penetrate the skin
Mechanism: Usually caused by a direct blow or bending stress
Clinical note: Lower infection risk; easier to manage if aligned
Key Concept: Skin remains intact → internal healing environment protected
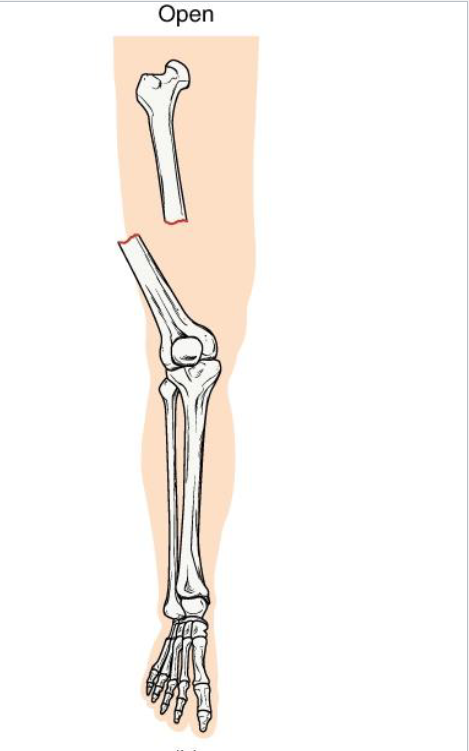
Open Fracture
Definition: Bone breaks through the skin (or skin is broken, exposing bone)
Mechanism: High-energy trauma (ex: motor vehicle accident, gunshot)
Clinical note: High infection risk and delayed healing.
Key concept: Requires surgical cleaning and fixation
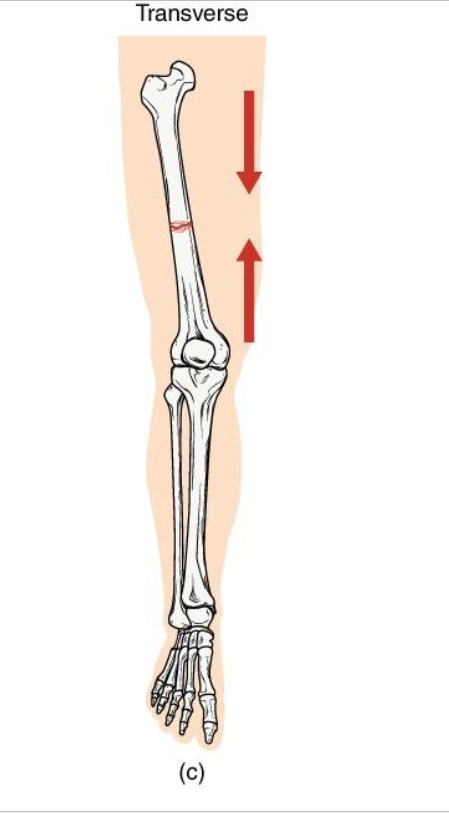
Transverse Fracture
Definition: Straight horizontal break across the bone shaft
Mechanism: Perpendicular force to long axis (ex: direct impact)
Clinical note: Often stable if bone ends align well: heals predictably with immobilizaton.
Key Concept: compression or bending directly across bone.
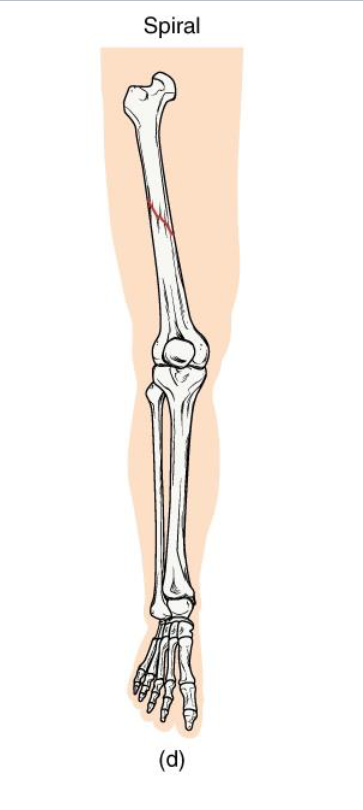
Spiral Fracture
Definition: Twisting or rotational fracture line around the bone
Mechanism: Rotational force (ex: skiing, twisting fall, child abuse case)
Clinical note: Jagged edges → difficult reduction; may damage surrounding soft tissue.
Key Concept: Indicates torque forces; look for rotational injury pattern
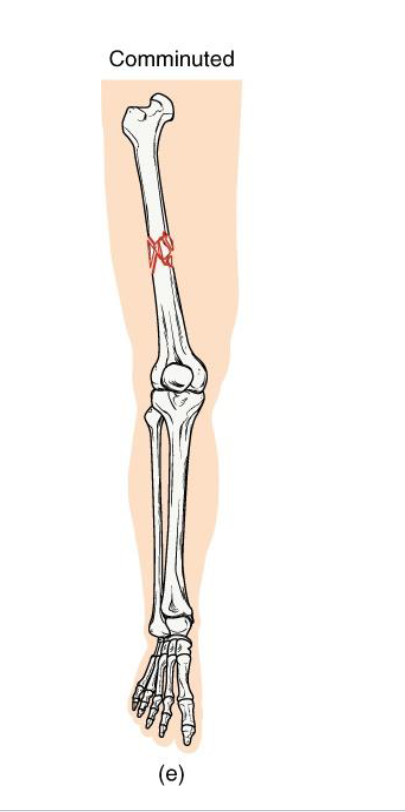
Comminuted Fracture
Definition: Bone is shattered into three or more fragments.
Mechanism: high impact trauma (ex: car accidents, falls from height)
Clinical note: Complex repair; may require surgical plates/pins; slow healing.
Key concept: represents severe energy transfer → bone fragmentation
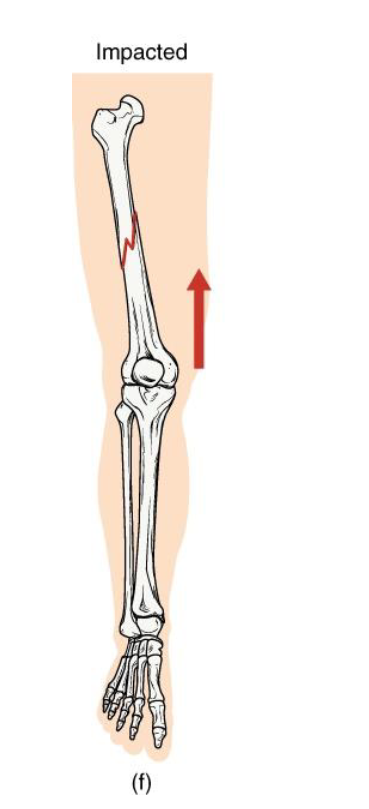
Impacted fracture
Definition: One fragment is driven into another within the same bone
Mechanism: Axial loading (ex: landing hard on extended arm/leg)
Clinical note: Bone ends jammed together; limb may apper shortened
Key concept: common in falls - the bone compresses itself
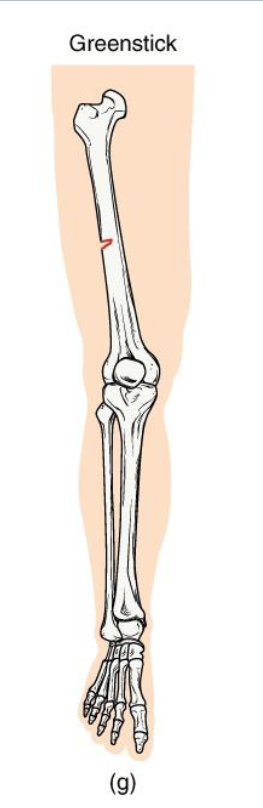
Greenstick Fracture
Definition: Incomplete break - bone bends and cracks on one side
Mechanism: common in children (softer, more flexible bone)
Clinical note: Often associated with forearm fractures in pediatrics.
Key concept: compare to bending a green twig - it splinters but doesnt snap
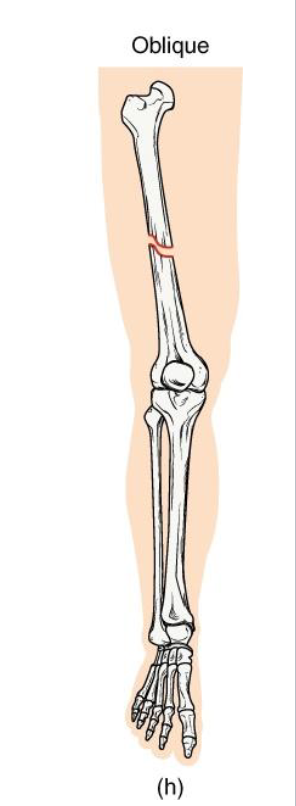
Oblique Fracture
Definition: Diagonal fracture line across the bone shaft.
Mechanism: angles force applied along the long axis.
Clinical note: Sharp ends may lead to displacement; requires stabilization.
Key concept: often confused with spiral fractures - but lacks twist pattern
One fracture but Many types

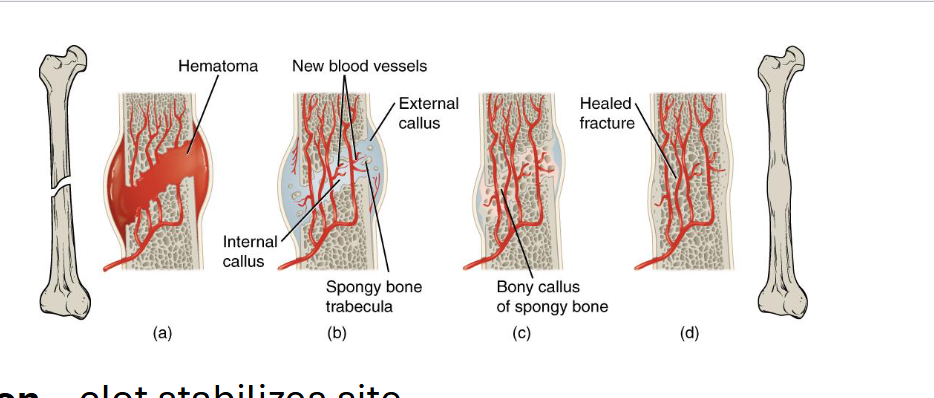
Bone Healing
Hematoma Formation - Clot stabilizes site
Fibrocartilaginous callus - connective tissue bridge
Bony callus formation - spongy bone replaces cartilage
Remodeling - Compact bone restores original shape
Factors Affecting Healing
Adequate blood supply & stabilization are critical
Age, nutrition, and hormones affect repair rate
Possible complications
Malunion / nonunion
Infection (especially open fractures)
Epiphyseal damage in children