MKT220 Craig Martin Exam 3 - Chaps 11 & 12
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
2 classifications of products
Consumer products and Business Products
Consumer products are used for...
Personal use
Product
Everything both tangible and intangible that a buyer receives in exchange.
Product Examples
Good, service, or an idea
Business products are used for...
organizations to produce other products or resell
The 4 types of Consumer products
convenience, shopping, specialty, and unsought products
Convenience Products characteristics
Inexpensive, Frequently purchased, minimal mental effort, available at numerous locations. (Hint) Routinized Behavior
Convenience Products in class Example
Poptarts, you love poptarts and you get them every time you go to the store when you run out
Shopping Products characteristics
Expensive, Infrequently purchased, Comparison Shopping, Available at few locations. (Hint) Higher Per Unit Gross Margin
Shopping Products in class Example
TV, can only get one at BestBuy, Walmart, Sams, or Target; its not cheap and takes a bit of mental effort to compare and decide
Specialty Products characteristics
Has 1 or more unique characteristics, Buyers are willing to go out of their way to get, and they are less likely to accept substitutes. (Hint) only available at specific locations or some kind of seasonal product
Specialty Products in class Examples
Pumpkin Spice Latte and Local Restuarant from your hometown that people travel a ways from to get
Unsought Products Characteristics
Costumers either don't see a need for it, are unaware of it, or its only Aggressively personally sold.
Unsought Products in class Examples
Insurance or Funeral Agency :(
3 Types of Business Products
Installations, Component Parts, MRO Supplies
Installations def
Large machines and tools used for production purposes
Component Parts def
Finished items that become part of the final physical product
EX: Car manufacturing
MRO Supplies def
Items that facilitate organization operations and DONT become part of the product.
EX: office supplies
3 ways of Classifying Products via Organizational Strategy
Product Mix, Product Line, Product Item
Product Mix def
All products offered by a firm
Product Line
a group of closely related product items that have similar end use
Product Item
a specific brand of a product line
Order of the Product Life Cycle
introduction, growth, maturity, decline
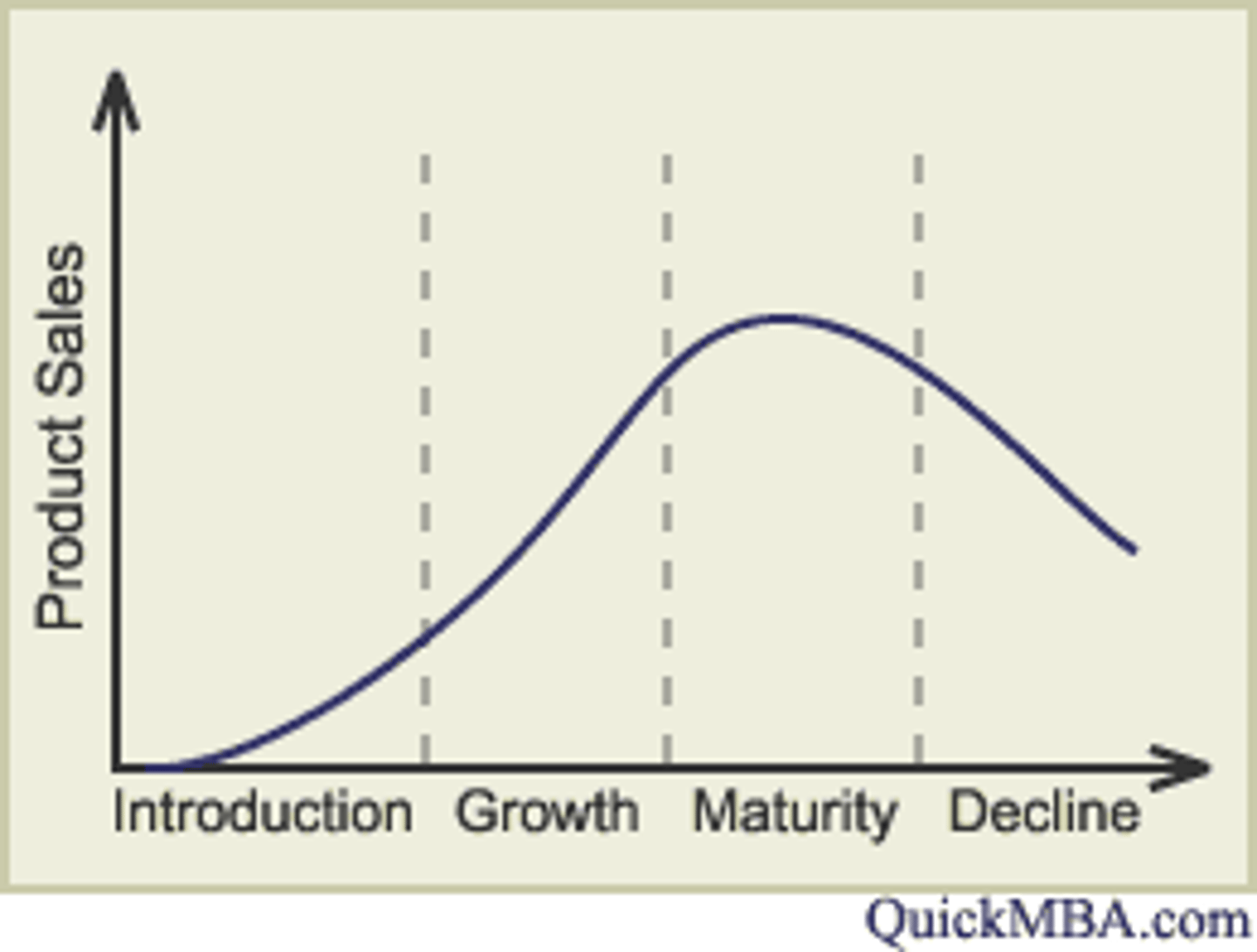
Introduction Example
Meta Sunglasses
Growth Example
Tesla
Maturity Example
PlayStation 5 console
Decline Example
Home phones and Fidget Spinners
Brand
a name, term, symbol, design, or combination thereof that identifies a seller's products and differentiates them from competitors' products
Brand Name
that part of a brand that can be spoken, including letters, words, and numbers
Brand Mark
the symbol associated with the brand
EX: Nike's Swoosh
Brand Loyalty
Costumers favorable attitude towards a specific brand
3 types of Brand Loyalty
brand recognition, brand preference, brand insistence
Brand Recognition
Costumer is aware brand exists and views it as an alternative
(Weakest)
Brand Preference
Costumers prefers one brand but if it is not available, they will settle for a substitute (Popular)
Brand Insistence
Costumer strongly prefers one brand and will make significant effort to get it (Extreme)
Brand Equity
the marketing and financial value associated with a brand's strength in a market
3 Types of Brands
manufacturer, private distributor, generic
Manufacture Brands
Initiated by the producer and the producer is Identified at the point of purchase (Name Brands)
EX: Nike
Private Distributor Brands
Initiated and owned by reseller, Producer not identified on product; typically cheaper than alternatives (Store Brands)
EX: Walmart's Great Value and Costco's Kirkland
Generic Products
Indicates only product category, no brand; very unpopular today
2 types of Branding Policies
Individual Branding and Family Branding
Individual branding
a firm uses a different brand for each of its products
EX: Proctor and Gamble's Tide and Gain brands
Family Branding
All of firms products are branded with same name
EX: Green Giant canned food and Automobiles like Ford
4 Things to Packaging
Packaging Functions, Packaging & Marketing Strategy, Criticisms of Packaging, and Labeling
Packaging Functions
protect and maintain functional form, offers convenience, and Promotes product
Packaging and Marketing Strategy
--Altering the package: Doritos changing the look
--Secondary-Use Packaging: Resealable packaging
--Innovative Packaging: Ketchup from glass to plastic
--Multiple Packaging: Variety pack of chips
Criticisms of Packaging
Functional Problems: Salt and sugar in paper bags
Safety Issues: glass breaking
Deceptive Packaging: Chip bags with 90% air
Cost: expensive
Labeling
Identifies, Promotes product, and informs costumers
Federal requirements: Nutrition, textiles, hazards
Universal Product Code (UPC): the bar code
Managing/Expanding Existing Products
line extension; product modification
Line Extension
development of a product that is closely related to existing products in the line but is designed specifically to meet different customer needs (ADD or KEEP)
EX: Gatorade
Product Modification
changing 1 or more characteristics from existing product and removing the original product from production (Remove)
EX: Automobile Brands like the Ford Bronco
3 Types of Modification
Quality, Functional, and Aesthetic
Quality Modification
change in a product's dependability or durability
Functional Modification
change in a product's versatility, effectiveness, convenience, or safety
Aesthetic Modification
changes to the sensory appeal of a product
(Subjective and Hardest to do)
7 steps of new product development process
1. idea generation
2. screening
3. concept testing
4. business analysis
5. product development
6. test marketing
7. commercialization
Screening
Where most product ideas are eliminated
Concept Testing
Gather feedback on new Product Idea from Costumers and employees
Business Analysis
evaluating the potential of the product's sales, costs, and profits
Product Development
Develops BASIC working model or Prototype
Test Marketing
Sample launching of entire Marketing Mix (product, price, promotion, and distribution)
Commercialization
Full $cale marketing and production; Most Expensive step
The Adoption Process' 5 categories
Innovators, Early adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards
Innovators
High income and Education, mostly male, don't know how to use product but have a psychological drive to own it. (2.5%)
Early Adopters
Opinion Leaders, Higher income and Education, 50:50 Gender ratio, Know how to use product (13.5%)
Early Majority
White collars, General public adoption, Higher income level
Late Majority
Blue Collars, lower income level
Laggards
Mainly Elderly, only adopt when forced too