AP BIO FINAL
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is the classification system?
domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species
What are the properties of water?
surface tension, adhesion/cohesion, polarity, capillary action, high specific heat, density (997kg/m)
What are macromolecules?
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
What are monomers and polymers?
monomers- a chemical subunit
polymers- a chain of chemical subunits
What is the most likely pathway taken by a newly synthesized protein that will be secreted by a cell?
ER to Golgi to vesicles that fuse with plasma membrane
Prokaryotes are classified as belonging to two different domains. What are the domains?
Bacteria and Archaea
What are the protein folding structures?
primary- peptide bond
secondary- alpha helix and beta pleated sheet
tertiary- bonds between R groups (ionic, disulfide bridges, hydrophobic, and hydrogen bonds)
quaternary- multiple polypeptide chains
Explain the characteristics of a cell in an isotonic environment.
A cell in a isotonic environment is one that is in an environment where it neither gains no loses water. Thus meaning the environment is neutral.
What are the nitrogen bases for both DNA & RNA?
DNA: C,G,T,A
RNA: C,G,U,A
In order for a protein to be an integral membrane protein it would have to be
amphipathic, with at least one hydrophobic region
Water passes quickly through cell membranes because
it moves through aquaporins in the membrane
What is diffusion?
It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
Which of the following is a characteristic feature of a carrier protein in a plasma membrane?
It exhibits a specificity for a particular type of molecule.
The difference between pinocytosis and receptor-mediated endocytosis is that
pinocytosis is nonselective in the molecules it brings into the cell, whereas receptor-mediated endocytosis offers more selectivity.
A form of endocytosis in which a one-celled organism takes in a large food particle
phagocytosis
A cell secreting large molecules by the fusion of vesicles with the plasma membrane
exocytosis
A form of endocytosis that is specific for a substance in the extracellular fluid
receptor-mediated
Water moving out of a plant cell causes the cell membrane to pull away from the cell wall, this is _____ .
plasmolysis
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
catabolism
Which term refers to the sum total of all the chemical reactions that occur in an organism?
metabolism
What is true for anabolic pathways?
They consume energy to build up polymers from monomers.
Which of the following types of reactions would decrease the entropy within a cell?
anabolic reactions
A chemical reaction that has a positive deltaG is best described as
endergonic
The active site of an enzyme is the region that
is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme (where the reaction takes place.).
Allosteric enzyme regulation is usually associated with
an enzyme with more than one subunit
Which of the following is a term that refers to a metabolic pathway that is switched off by the inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway.
negative feedback
What term refers to describe any case in which a protein's function at one site is affected by the binding of a regulatory molecule to a separate site.
allosteric regulation
In plant cells in photosynthesis, the electron transport chain is located in the
thylakoid membrane
In prokaryotes, the respiratory electron transport chain is located
plasma membrane
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen is present or absent?
glycolysis
Why is glycolysis described as having an investment phase and a payoff phase?
It uses stored ATP and then forms a net increase in ATP.
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytosol
Carbon dioxide is released during which of the following stages of cellular respiration?
oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
Which of the following produces the most ATP when glucose is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
Most carbon dioxide from catabolism is released during
the citric acid cycle
What is the molecule that enters the citric acid cycle(Kreb's cycle)?
acetyl CoA
Which process is anaerobic?
glycolysis
Where is the lowest pH due to hydrogen ions found in the plant cell?
thylakoid space
What is the primary function of the Calvin cycle?
synthesize simple sugars in the form of G3P molecules from carbon dioxide
Which of the following does the Calvin cycle need to continue to run?
carbon dioxide, ATP, NADH, and Rubisco phosphate (RuBP)
Which is NOT part of the nonspecific immune defense?
antibodies
What white blood cell that recognizes a particular antigen will remain alive and will react rapidly if the antigen ever comes along again?
memory B cells
Where do B cells mature?
bone marrow
Which of the following are not part of the immune system?
red blood cells
Antibodies are what macromolecule?
proteins
What is responsible for humoral immunity?
B cells
An antigen-presenting cell that is also part of innate immunity
macrophages
Which cell specifically attacks a cell that contains a virus?
cytoxic T cells
Where are most T and B cells found?
bone marrow
What are two of the most common second messengers in transduction?
calcium ions and cAMP
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
-70mV
What is the threshold of the action potential of a neuron?
-55mV
A neuron works because there is a membrane potential due to what?
Na+ and K+ ions
REMEMBER
this :)
What are two characteristics of a dendrite?
contains sensory endings and carries an electrical impulse toward the cell body
What releases the neurotransmitter into the synapse?
the action potential opens voltage-gated channels that allow Ca++ across the membrane into the neuron
What type of channel does the neurotransmitter bind to?
ligand-gated ion channel
the ligand and the G-protein-couple receptor activate this
G protein
Which of the following is characterized by a cell releasing a signal molecule into the environment, followed by a number of cells in the immediate vicinity responding?
paracrine signaling
What organism would use quorum sensing?
prokaryotic cell
Many signal transduction pathways use second messengers to
relay the message from the inside of the membrane throughout the cytoplasm
What is a G protein?
a protein on the cytoplasmic side of a membrane that becomes activated by a receptor protein
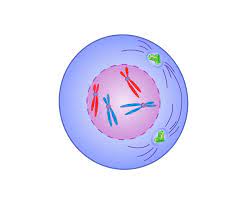
What phase is this?
prophase
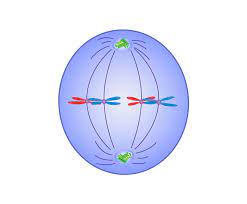
What phase is this?
metaphase
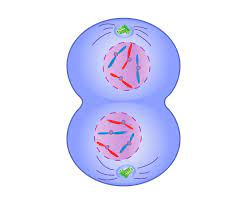
What phase is this?
telophase
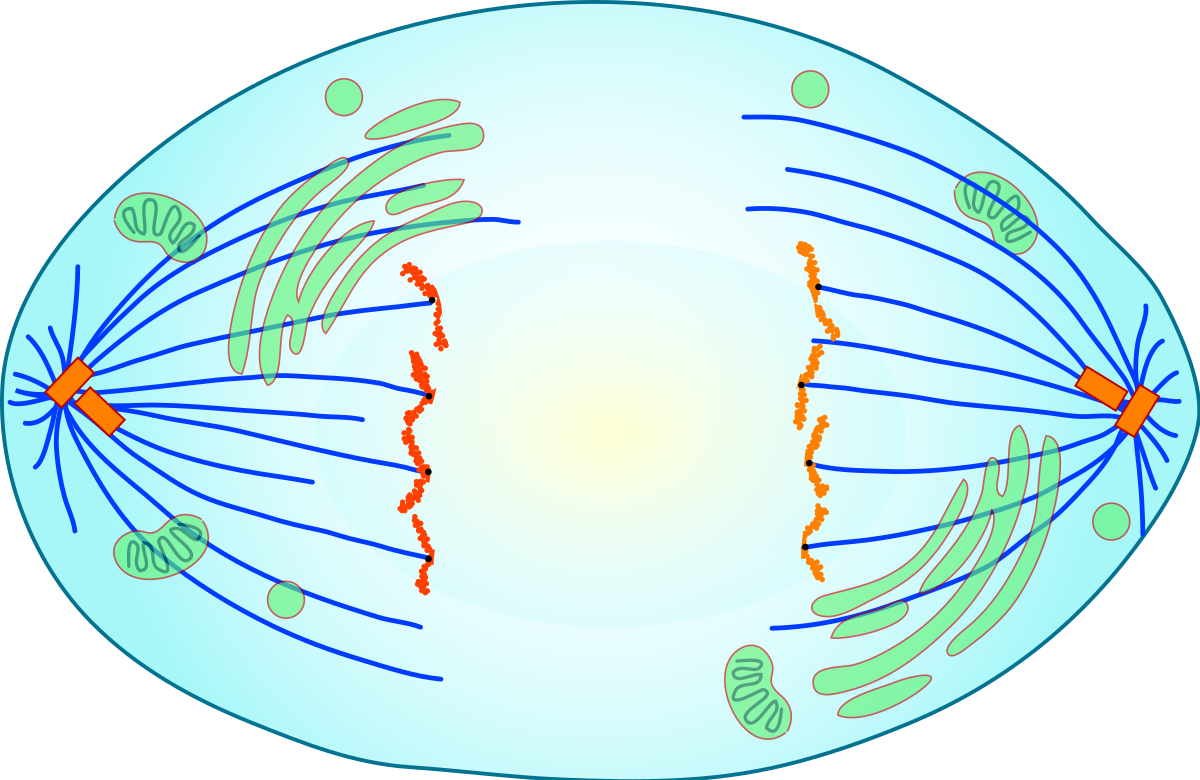
What phase is this?
anaphase
Name of chromosomes that have a replicated copy held together by a centromere.
sister chromatids
All of the DNA of a cell is referred to as the
genome
Normal cells that must be attached to a substratum like the extracellular matrix of a tissue.
anchorage dependency
Human have 46 chromosomes. That number of chromosomes will be found
somatic cells