Ornithology Lec 18: Reproductive System
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What are the alleles that determine sex in birds?
ZZ= male
ZW= female
What is an adaptation for sex determination selection?
Selective release of one ova occurs in the female Seychelles Warbler. This allows them to release an ova with Z or W depending on current territory quality (they do cooperative breeding in which the females help raise young).
What is gynandromorphism?
When an organism displays characters of both males and females of their species due to cell division errors early in embryonic development.
What are the two different versions of gynandromorphism?
Mosaic gynandromorphism and bilateral gynandromorphism
What are the stages of egg formation in the female reproductive system?
Mature ovum in ovary, surrounded by yolk—> ovulated
Fertilized in infundibulum
Goes down the magnum (duct) where albumin is added
In the isthmus section soft shell is added
In the glandular section, covered in papillae, where lime is, the hard shell is added and pigment is added
Out the urovaginal junction
Out the cloaca
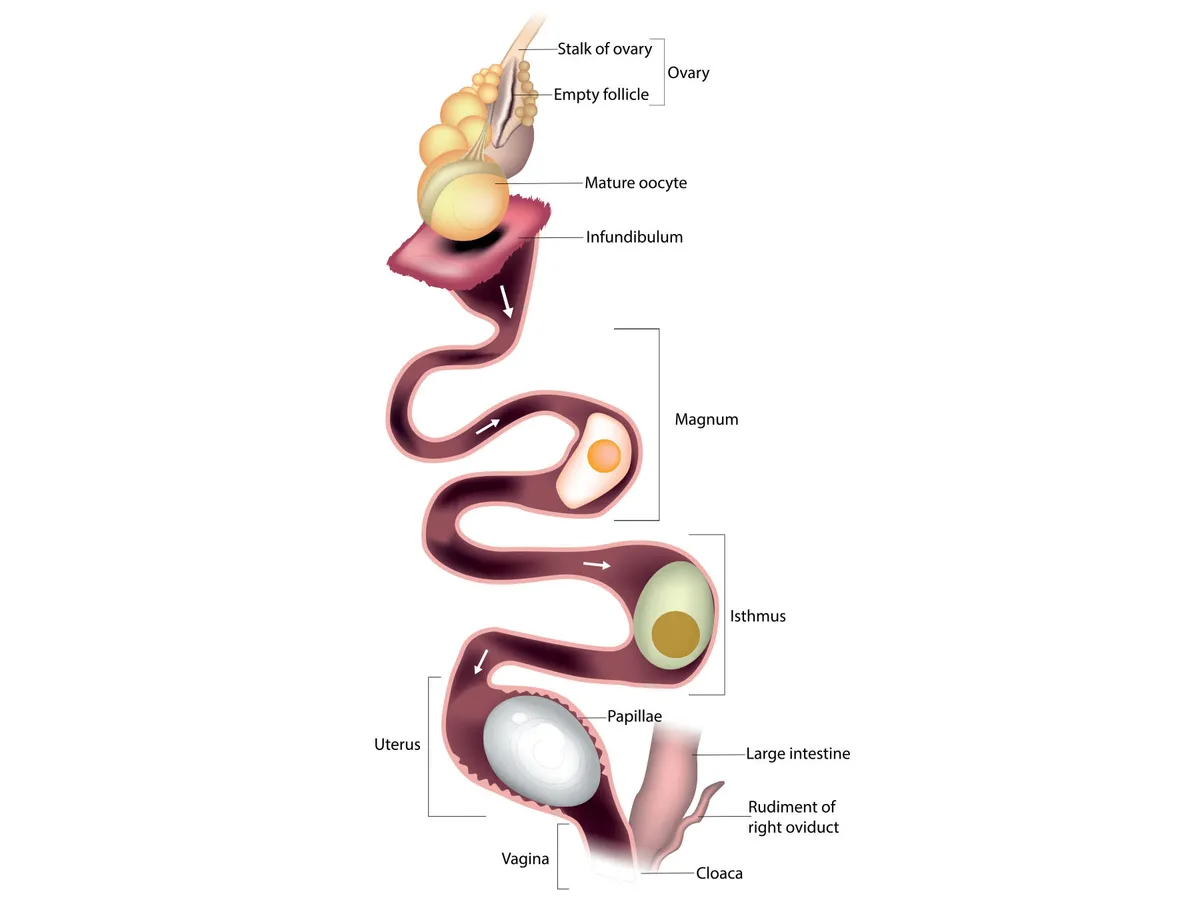
What birds have both ovaries (one is not ruptured)?
Raptors, kiwis
What are the components of the male reproductive system?
testes
vas defrens
What are some adaptations to ensure paternity?
copulate frequently after separation
cloacal protuberances in males for more sperm storage
larger testes and larger sperm stores
mate guarding
pecking female cloaca to remove other male’s sperm (ex: Dunnocks)
long cloacas in ducks (ex: Mallard)
Why have some species of ducks adapted long cloacas? Examples
Arms race between female vaginas and male elongated cloacas due to forced copulation. Restricts species that copulate together. Lymphatic swelling in the cloaca creates phallus structure, it does not contain the urethra.
ex: Mallard, Long tailed duck
What is the ranking of testes mass among different mating systems from most to least?
polyandry
colonial monogamy
solitary monogamy
lek promiscuity
result of decreasing sperm competition among these mating types and of diverging sperm morphologies
What is a fertilization adaptation among females to increase of clutch?
In Japanese quail sperm storage vesicles sperm can stay viable for days to months that can be used to fertilize different eggs.
What adaptations does post copulatory sexual selection promote in males?
Divergence of sperm morphology: midpiece length, flagellum length, total length
Influences: sperm ability to swim faster, live longer, displace other sperm form female storage tubules
How does sperm morphology change with female sperm storage tubules?
increasing sperm storage tubule length—> increases sperm length
increasing sperm storage tubule number—> decreases sperm length
longer sperm are selected for if there are few sperm storage tubules because sperm long enough to fill sperm storage tubules prevent access of other sperm
What is the increasing length of sperm primarily due to?
Disproportionately due to increase in midpiece size, because the midpiece is where ATP is stored (mitochondria is wrapped around the midpiece), increases energy
How does increased levels of of sperm competition affect sperm length?
There is an optimum length, so sperm length will stabilize as they approach the optimum in order to be competitive