marine bio test #1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
what are the three layers of the earth?
core, mantle, crust (aka lithosphere) which is where plates are!
what are the two types of plates?
oceanic, which is made of basalt
continental, above ground and made of thicker granite
why do plates move?
plates move because of convection currents (hot air rises, cold air sinks, cycle repeat) as a result plates separate
3 boundary types
diverging/constructive - oceanic plates separate because of convection currents, new material from an underwater volcano fills the gap, creating a mountain
converging - oceanic plate and continental plate push together, oceanic plate is heavier and gets pushed under and melts
transform - two continental plates are sliding past each other
what is sediment?
accumulation of loose material (sand, mud, gravel, etc)
how do we measure the age of sediment
we use sediment cores (long cylinders of sediment brought up by ocean floor drilling) which can help us understand the earth’s past
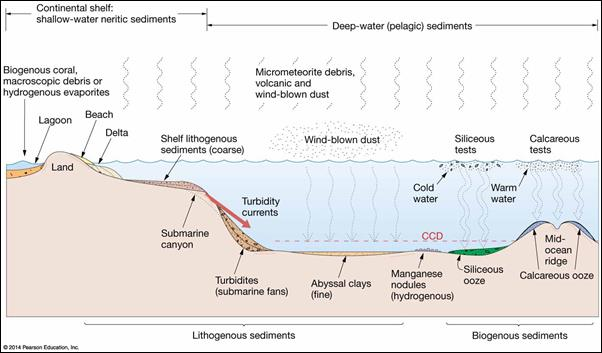
lithogenous sediment
tells us about changing plate tectonic activity, come from erosion of rocks
typically accumlate along continental margins, but sometimes small particles move out to sea and form a sediment called abyssal clay
biogenous sediments
tell us about environmental conditions in ocean surface waters
made up of skeletal remains of once-living organisms, including shells of microscopic organisms (tests), coral fragments, etc.
includes ooze (separate flashcard)
hydrogenous sediment
give us substances for money, created from chemical reactions in seawater
evaporites: sediment that comes from evaporated seawater that crystalize and group together
manganese nodules: lumps of iron and manganese oxide all over the seafloor

what is ooze? what are the two types?
when tests make up more than 30% of the particles in a sediment, it is called an ooze, typically found in the open ocean
calcareous ooze: calcium carbonate, made of the tests of foraminifers and coccolithophores, harden into chalk as they get low into the ocean
siliceous ooze: made of radiolarians and diatoms, found in polar regions, and open ocean areas. sometimes, the silica that makes up siliceous ooze is combined with calcareous ooze to made hard lumps called chert nodules
what do grain size/rounding mean?
they indicate the energy of the environment in which they are from (applies best to lithogenous sediments). a beach is high energy, with big grains that become smooth, the ocean floor is the opposite
neritic vs pelagic
neritic — found close to land
pelagic — biogenous, found farther away (see image)
how does wave erosion work, what are some examples
depositional features
east coast vs west coast features
The east coast has depositional features
Reason: east coast has sinking shoreline and a passive margin (no real activity happening except for sediment growth)
The west coast has erosional features
Reason: west coast has rising shoreline, coast has subduction zones
lagoons
Lagoons form when dunes separate water completely from the ocean

eustatic sea level change/sea level rise
Eustatic sea level change: global changes to sea level (seen in the East Coast because the areas near the ocean are in danger of sinking because the sea levels are rising)
What causes sea level to drop: expanding glaciers, cooling ocean temperatures, and increasing ocean basin size
Sea level has increased a lot recently because of US!!!! Currently rate of sea level is 3.4 mm/yr
how do scientists gather data on past sea levels
deep-sea sediments, ice cores, coastal caves, and lagoon sediments
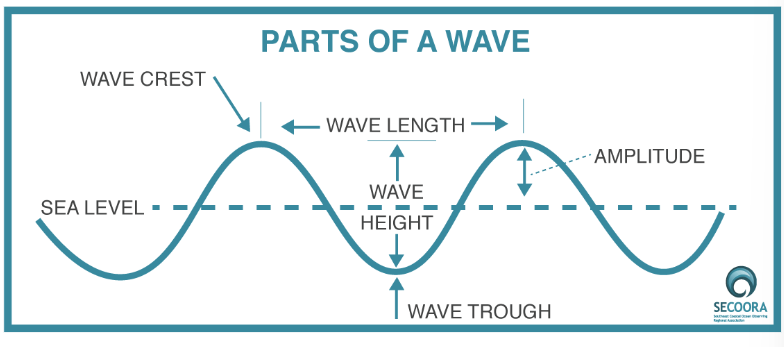
parts of a wave
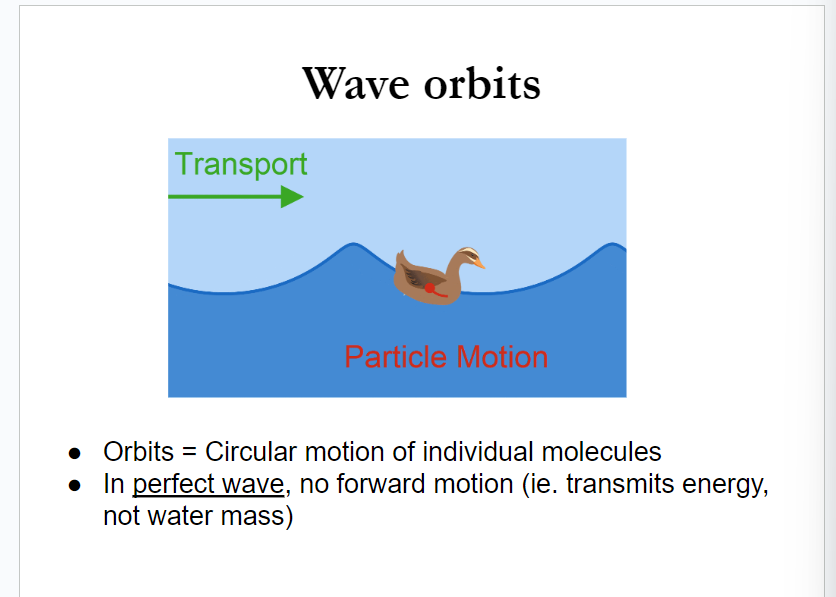
wave orbins
basically, the object never really moves (in a perfect world) because the ENERGY is what’s moving
what causes waves?
wind
tides (caused by gravity)
tsunamis (tectonic activity causes them)
wind-specific waves
waves are affected by: wind strength, wind duration, and fetch
what is difference between seas and swells?
seas are where the generating force is, swells are where there is no generating force!
seas are super chaotic and diverse, swells are consistent and have long periods, fast
this is because of wave sorting. long periods have a greater speed so they move ahead of shorter waves (kind of like in a marathon)
wave orbits
waves transfer energy through orbits (little circles) which decrease as these go down
if orbits touch the bottom, you have a shallow water wave
the bottom of the wave orbits is the wave base, orbits reach depth of ½ wave length
so why do waves break?
crest is moving wayyy faster and it creates an angle
spilling breaker
shallow sloping/flat bottom
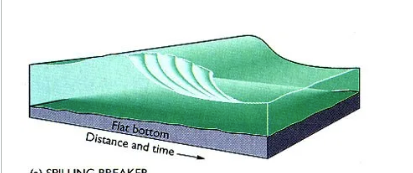
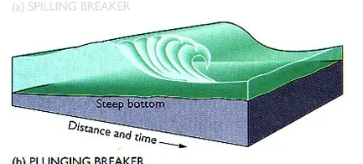
plunging breaker
steep bottom, quickly loses energy
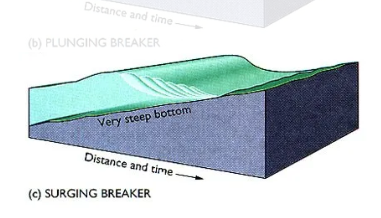
surging breaker
steep bottom, abrupt shore
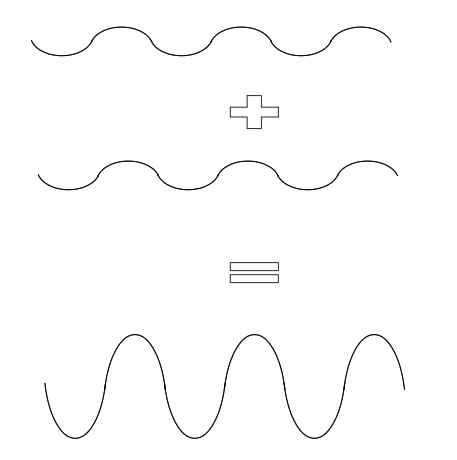
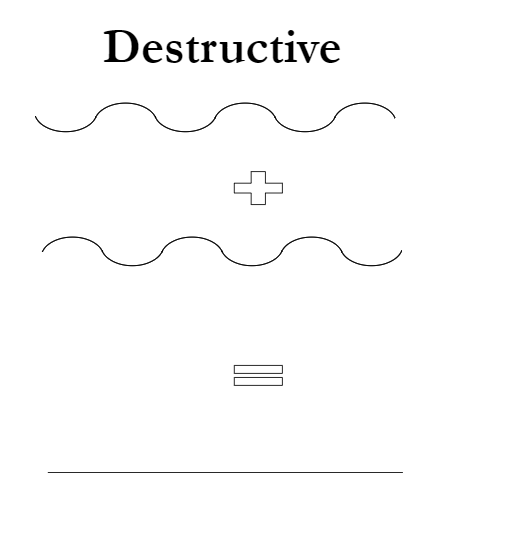
constructive vs destructive
refraction
reflection
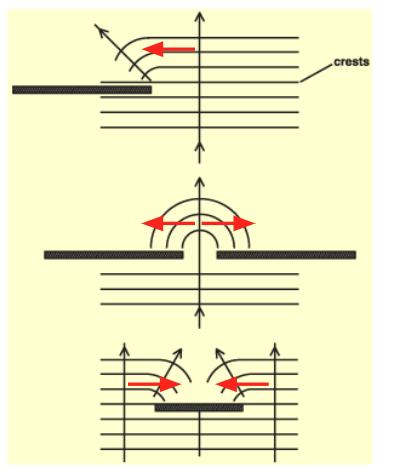
diffraction
spread of wave energy sideways to the direction of wave travel, around/through an obstacle or gap