Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Assessment
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Microscopes, Anatomical Terminology, and Feedback Loops - assume eyepiece power is 10 for every problem related to such
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Superior
A part that is above another part (also called cranial)
Inferior
A part that is below another part (also called caudal)
Anterior/Ventral
Toward the front
Posterior/Dorsal
Toward the back
Medial
A position that is closer to the imaginary midline
Lateral
A position further from the imaginary midline
Proximal
Nearer to trunk or point of attachment
Distal
Away from trunk or point of attachment
Longitudinal
Along the long axis
Cross/transverse
Across long axis
Sagittal
Divides left/right
Frontal/Coronal
Middle of body, anterior and posterior separated
Transverse
Cuts at torso-ish area
Midsagittal
Divides into fairly equal parts
Liver Quadrant
Right upper quadrant
Stomach Quadrant
Left upper quadrant
Spleen Quadrant
Left upper quadrant
Appendix quadrant
right lower quadrant
Small intestine quadrant
right lower quadrant & left lower quadrant
Pancreas quadrant
left upper quadrant

Frontal

Orbital

Nasal

Cervical

Brachial

Carpal

Digital

Thoracic

Abdominal

Femoral

Crural

Pedal

Digital

Dorsal

Popliteal

Femoral

Calcaneal
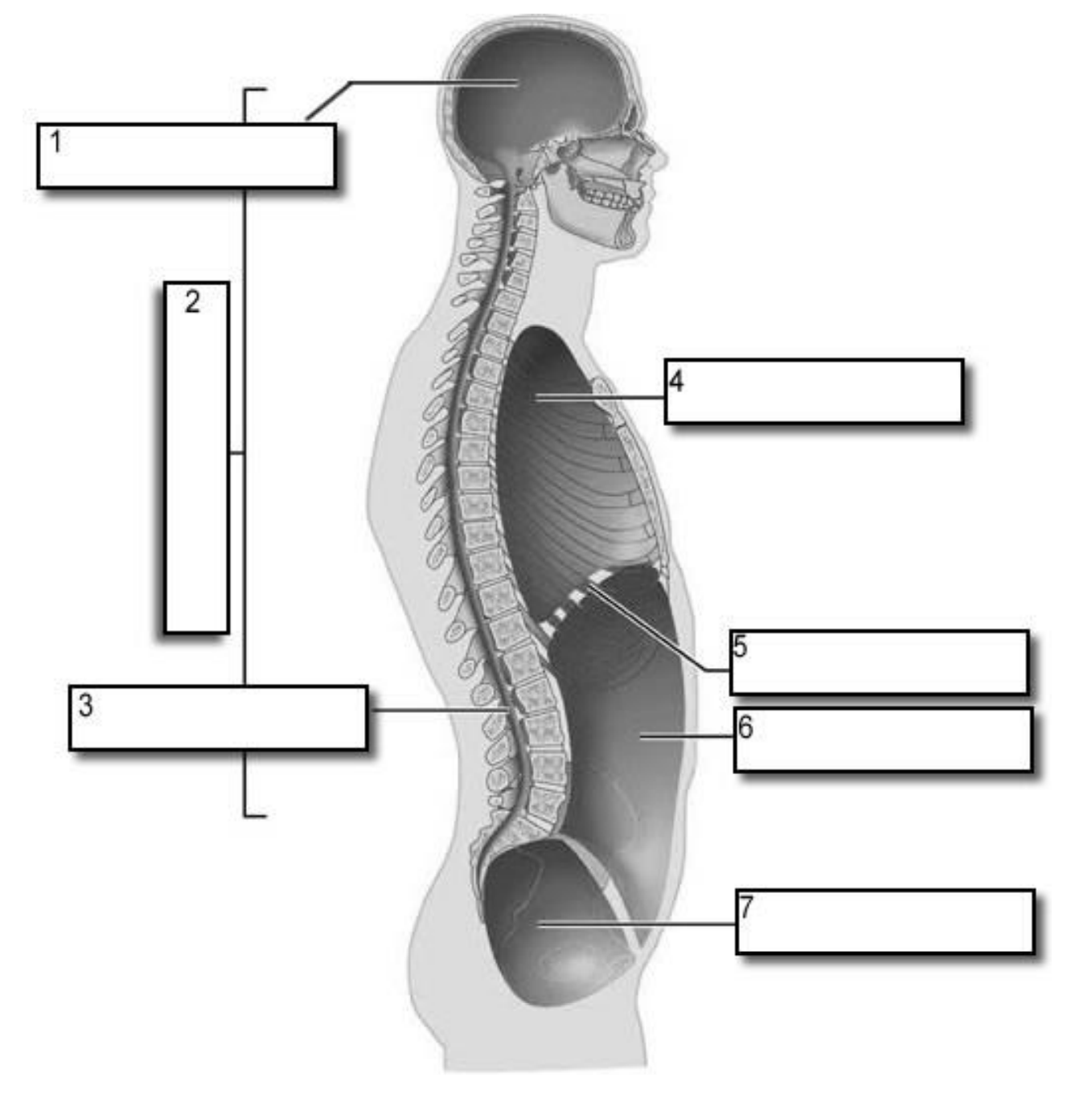
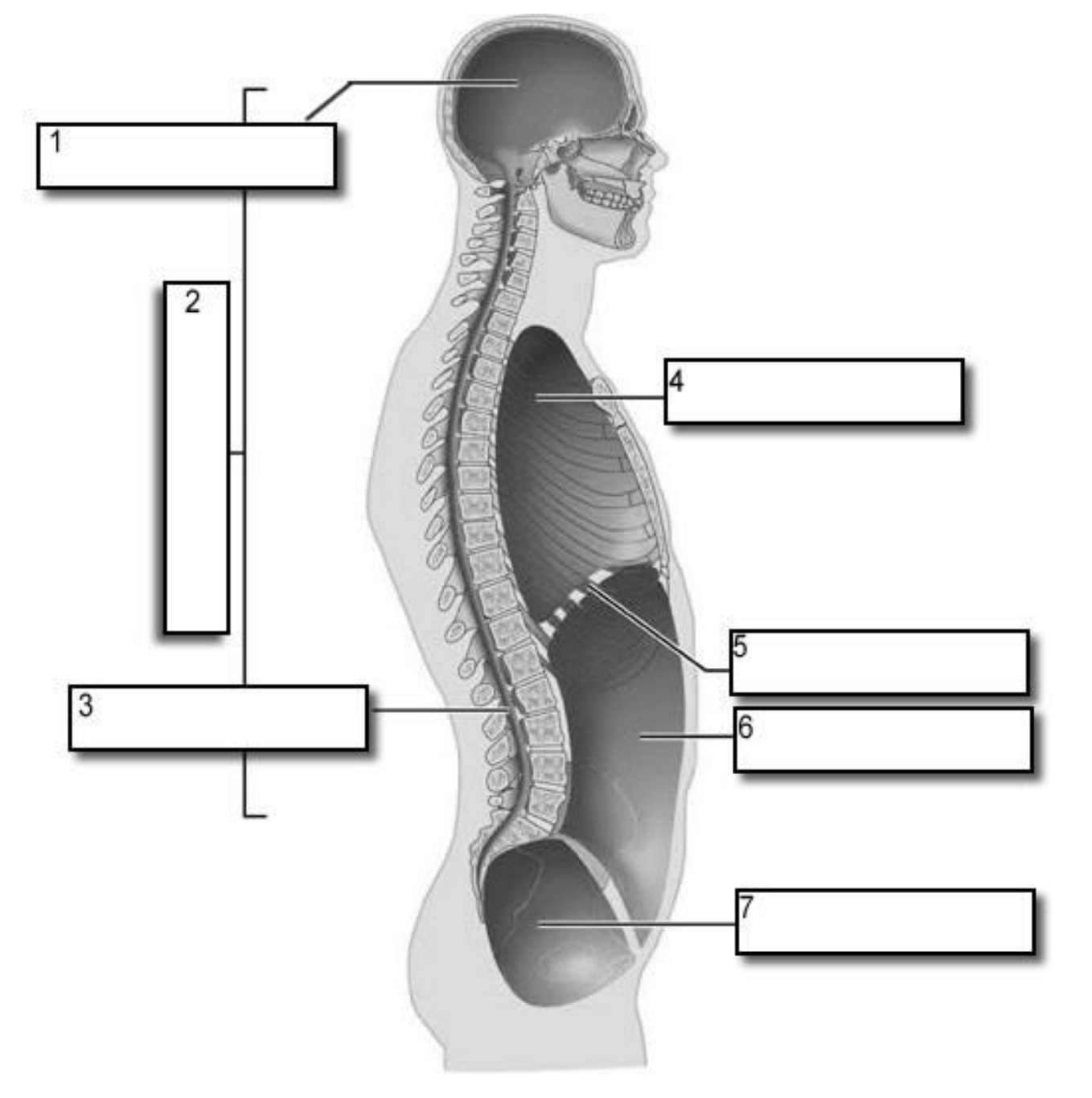
1?
Cranial Cavity
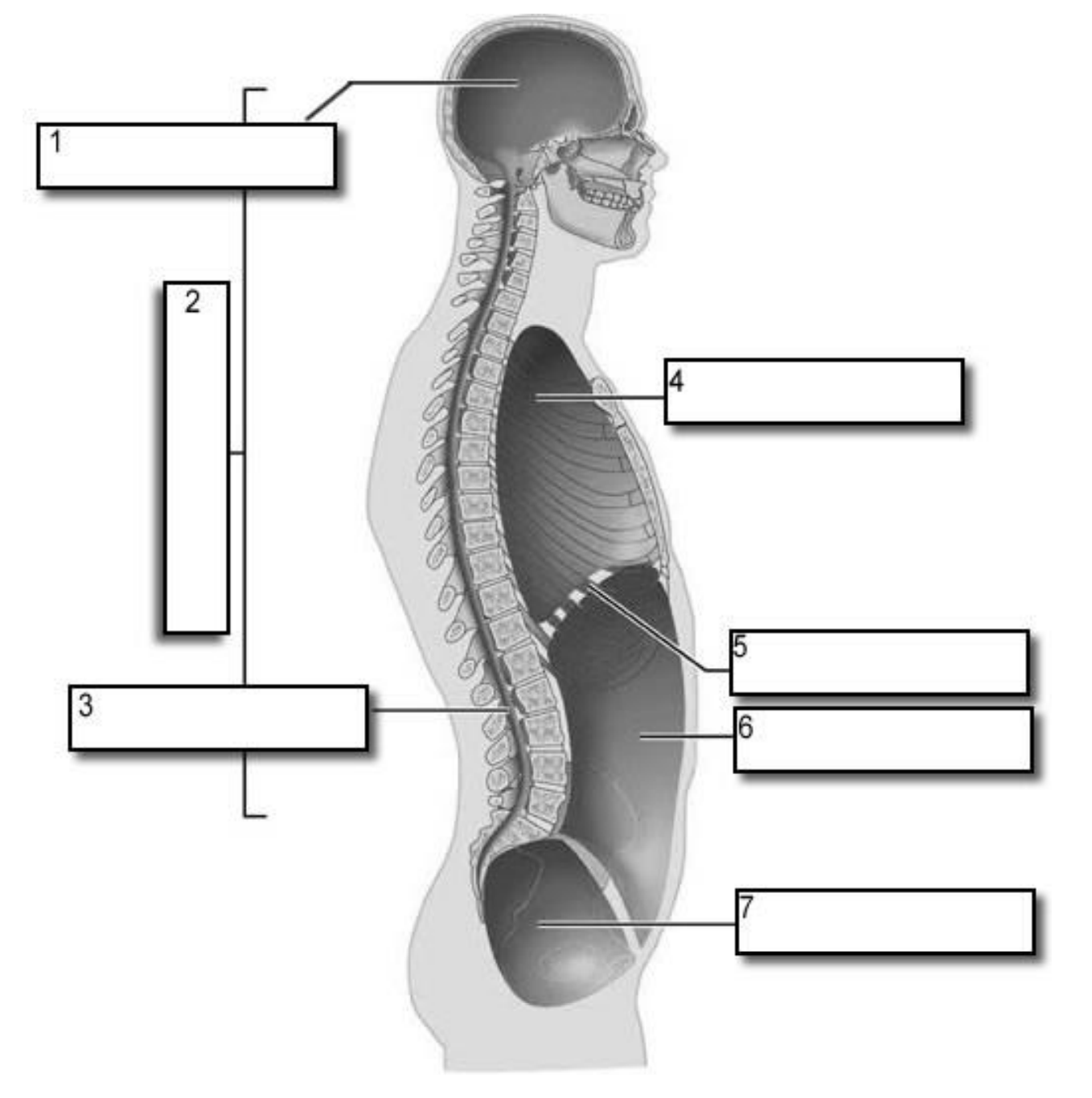
2?
Dorsal Cavity
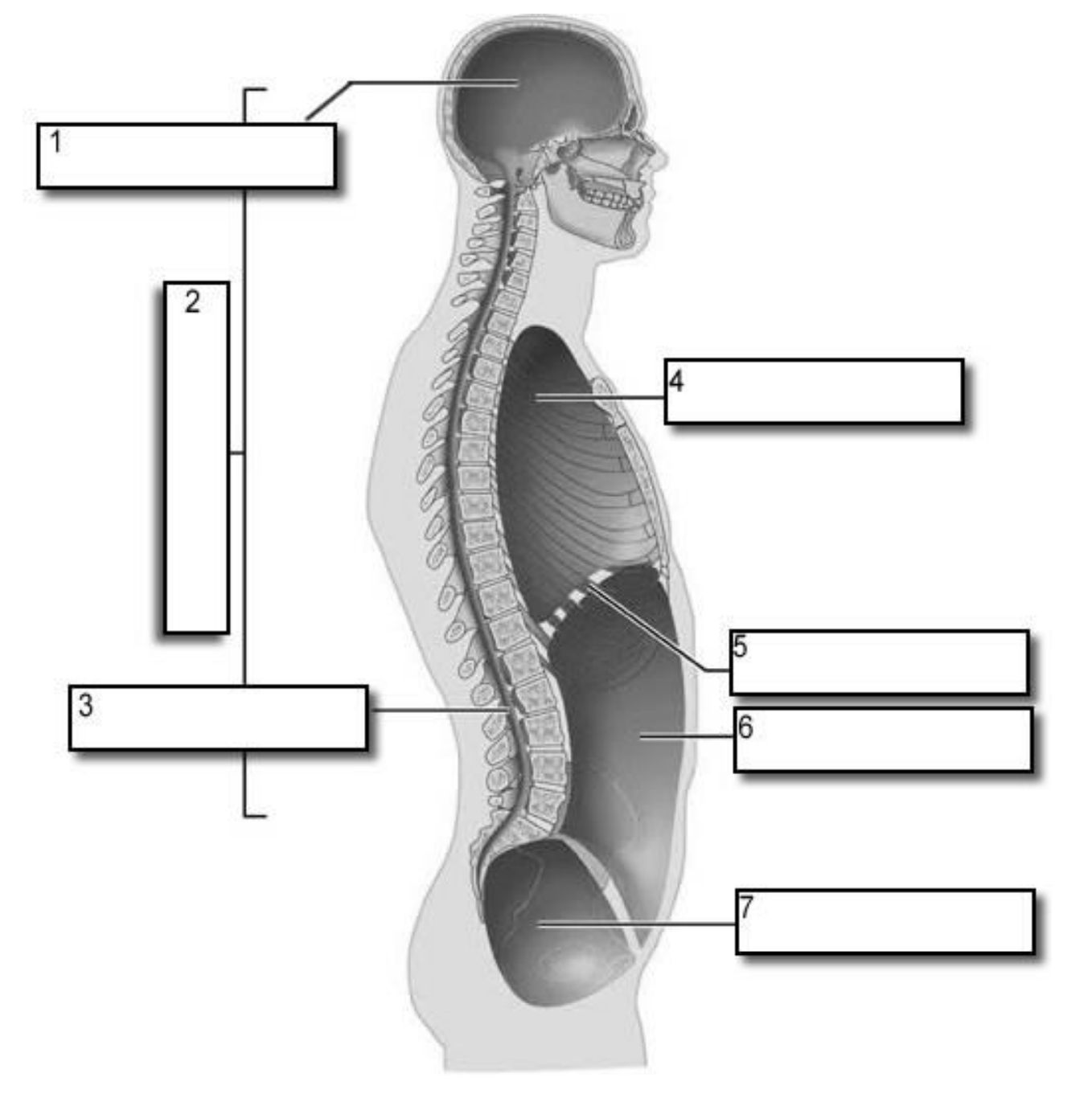
3?
Vertebral Canal
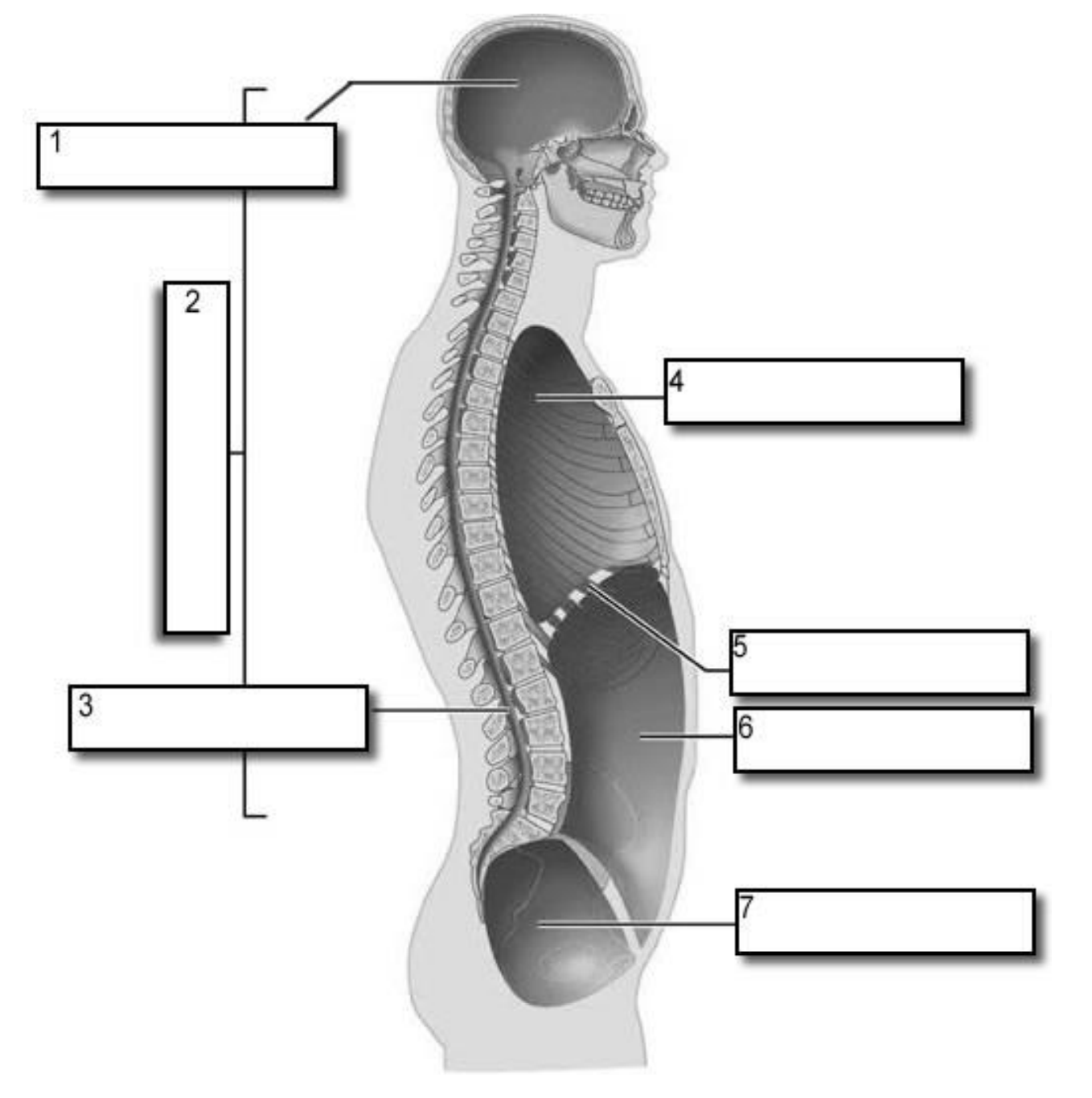
4?
Thoracic Cavity
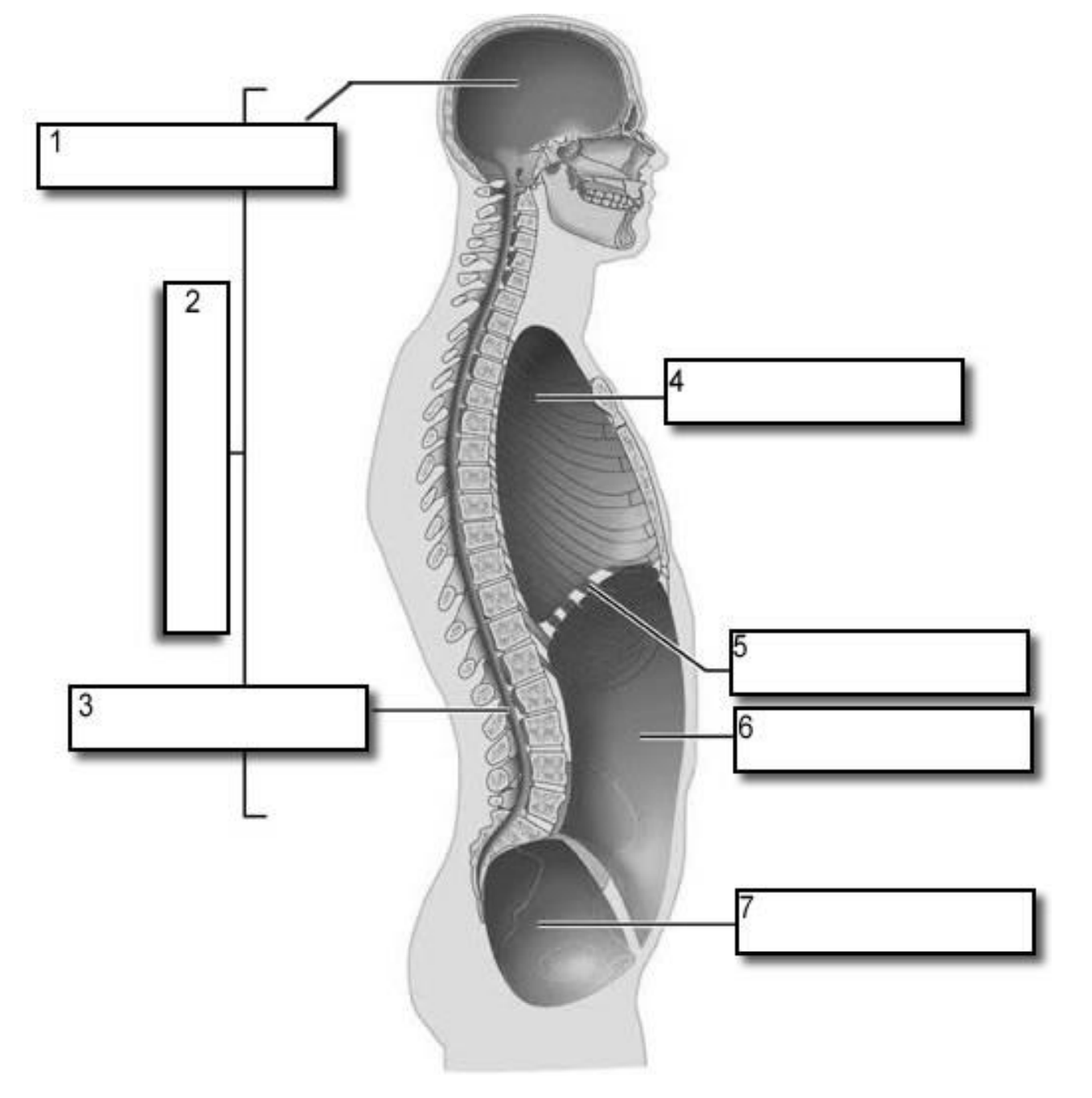
5?
Diaphragm
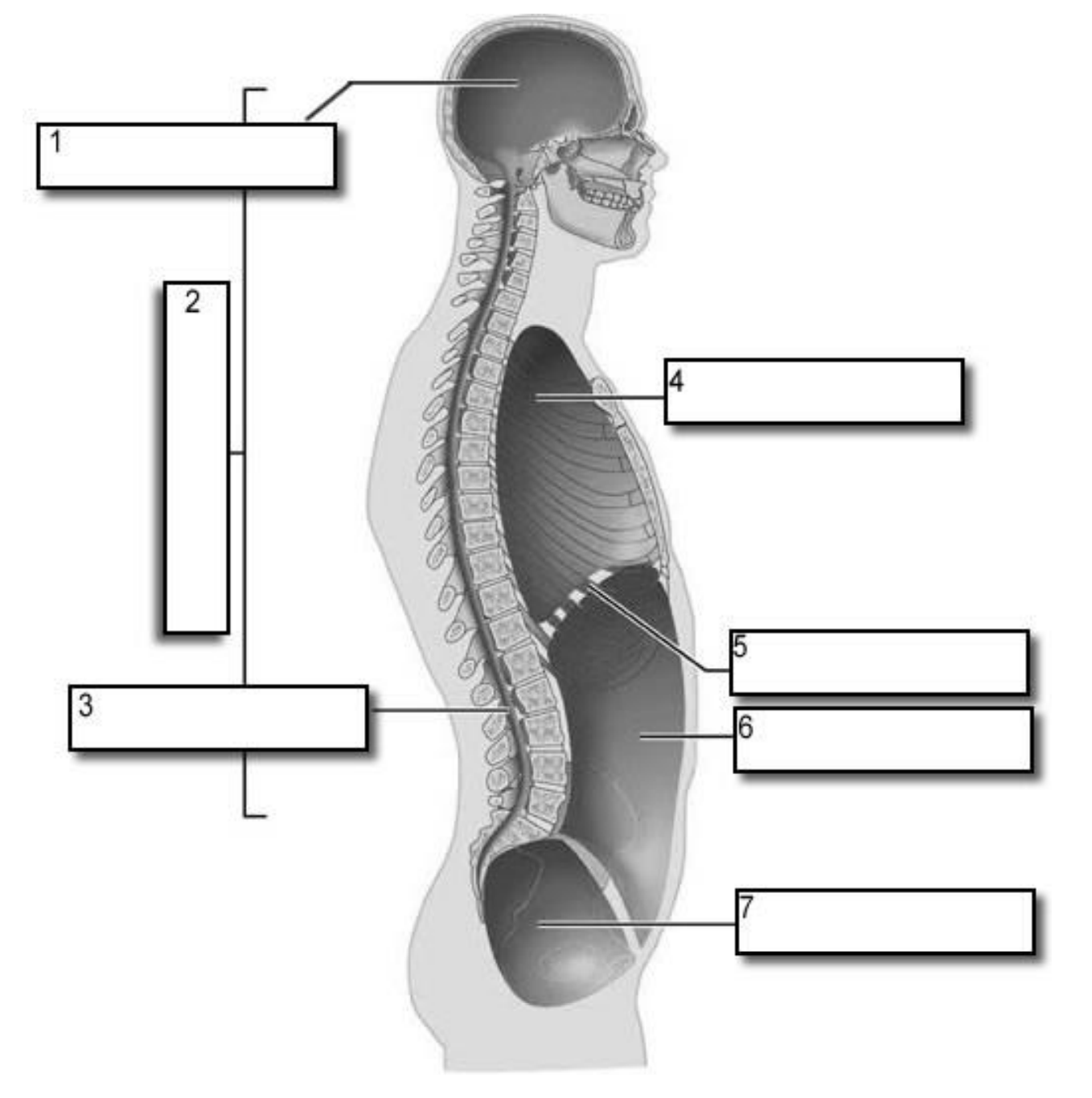
6?
Abdominal cavity
7?
Pelvic Cavity
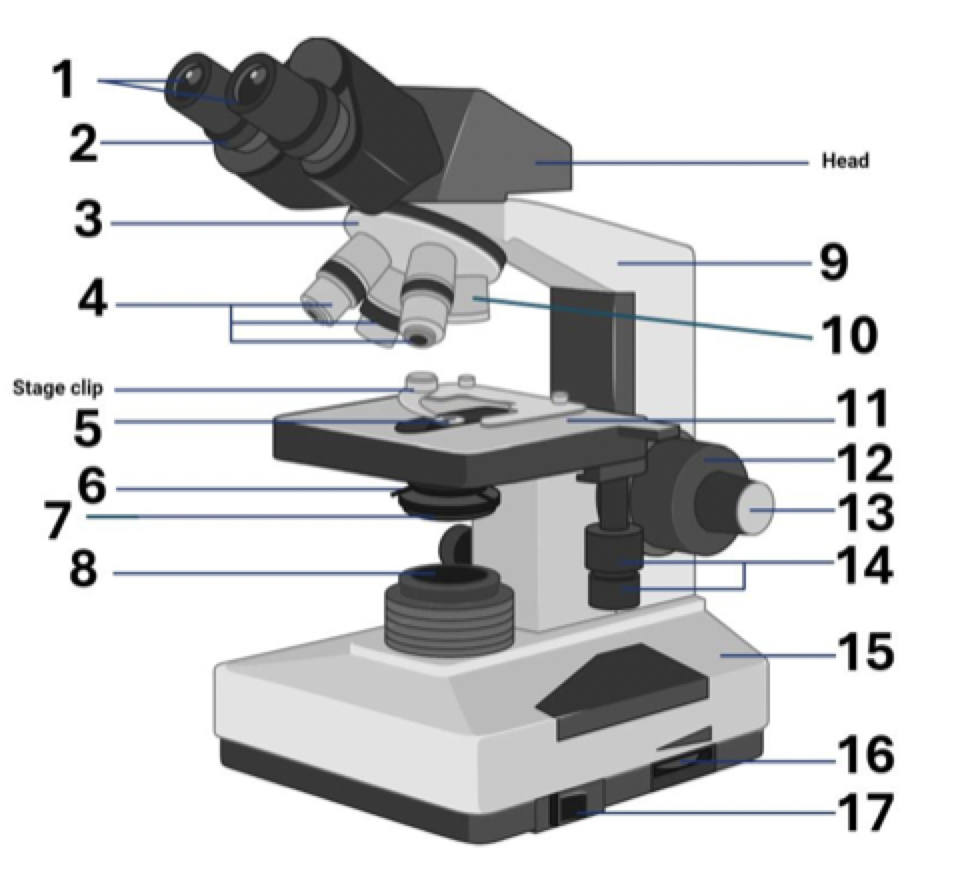
1?
Ocular lens (eye piece)
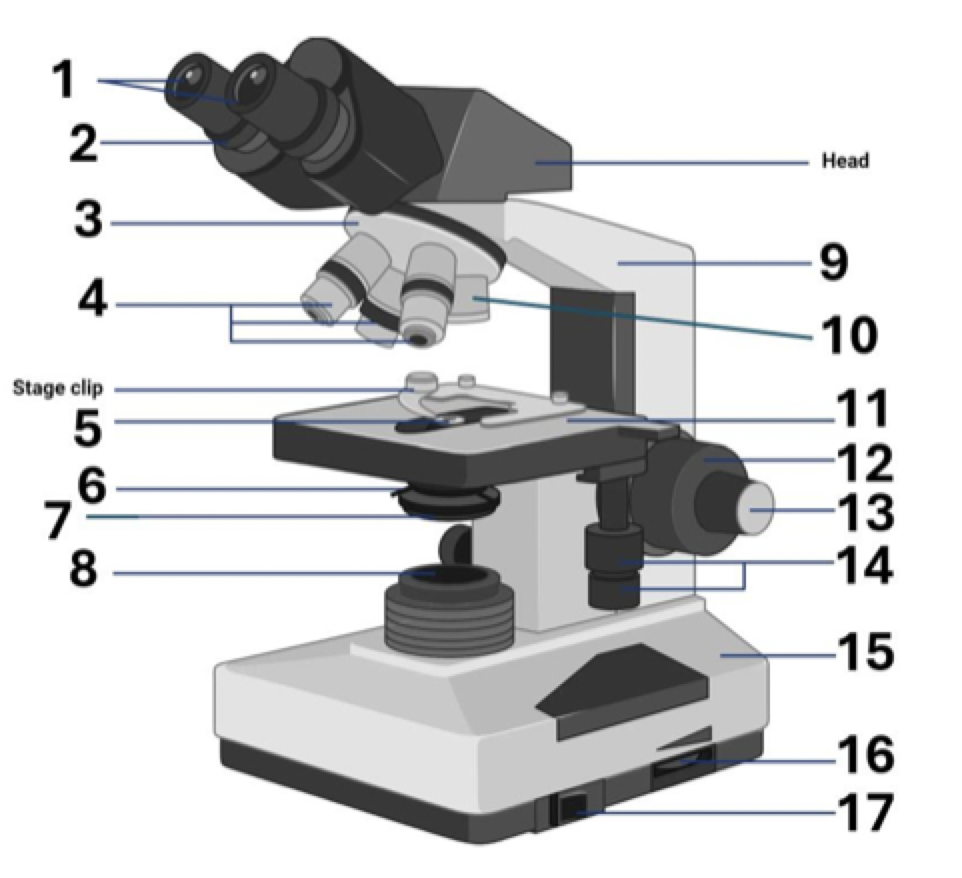
2?
Diopter Adjusment
3?
Nose piece
4?
Objective lens
5?
Aperture
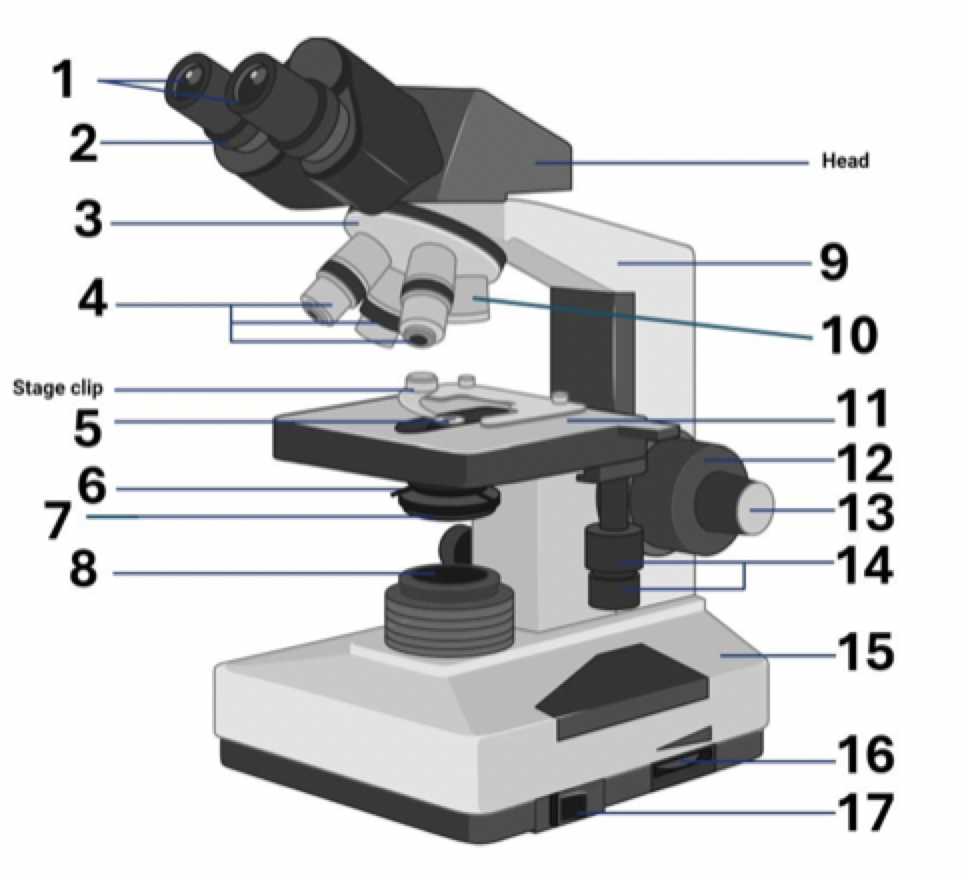
6?
Diaphragm
7?
Condenser
8?
Illuminator (light source)
9?
Arm (carrying handle)
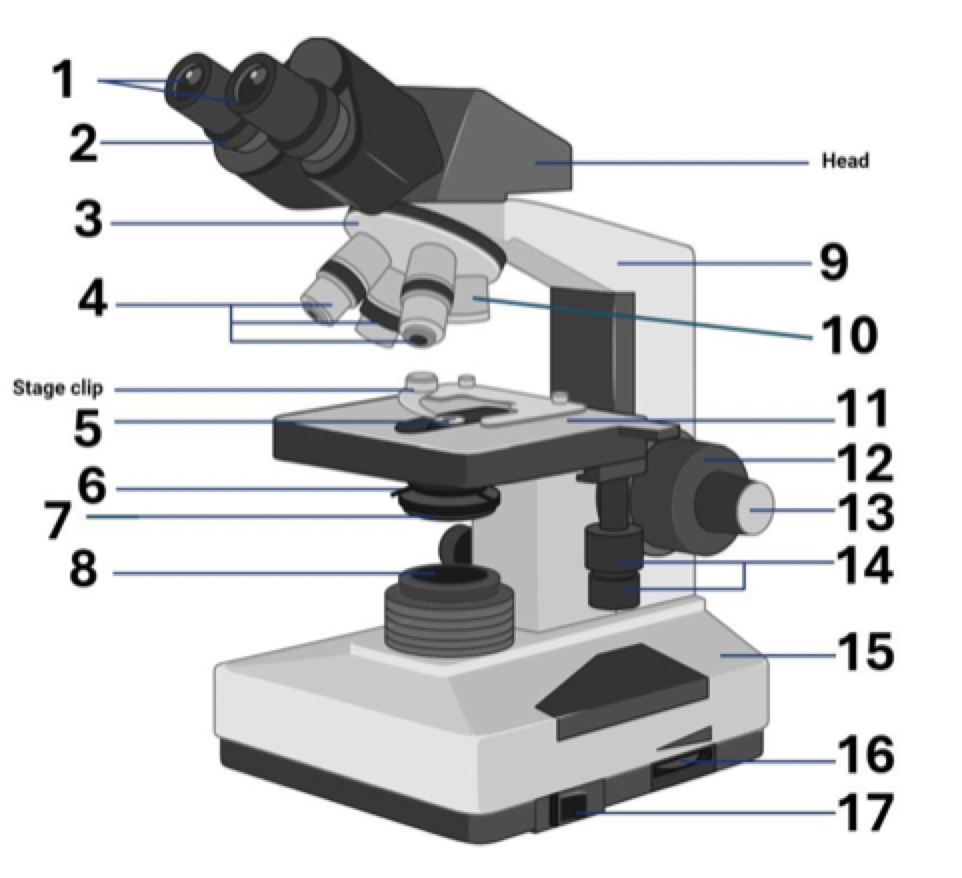
10?
40x Objective
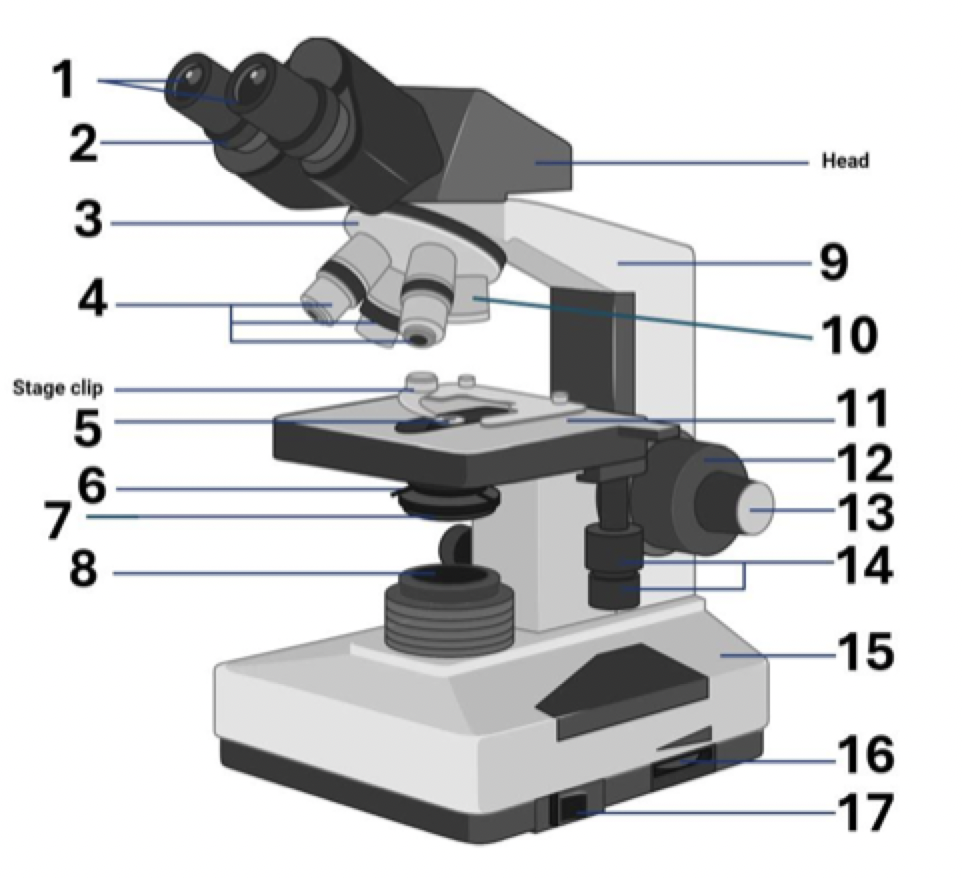
11?
Mechanical stage
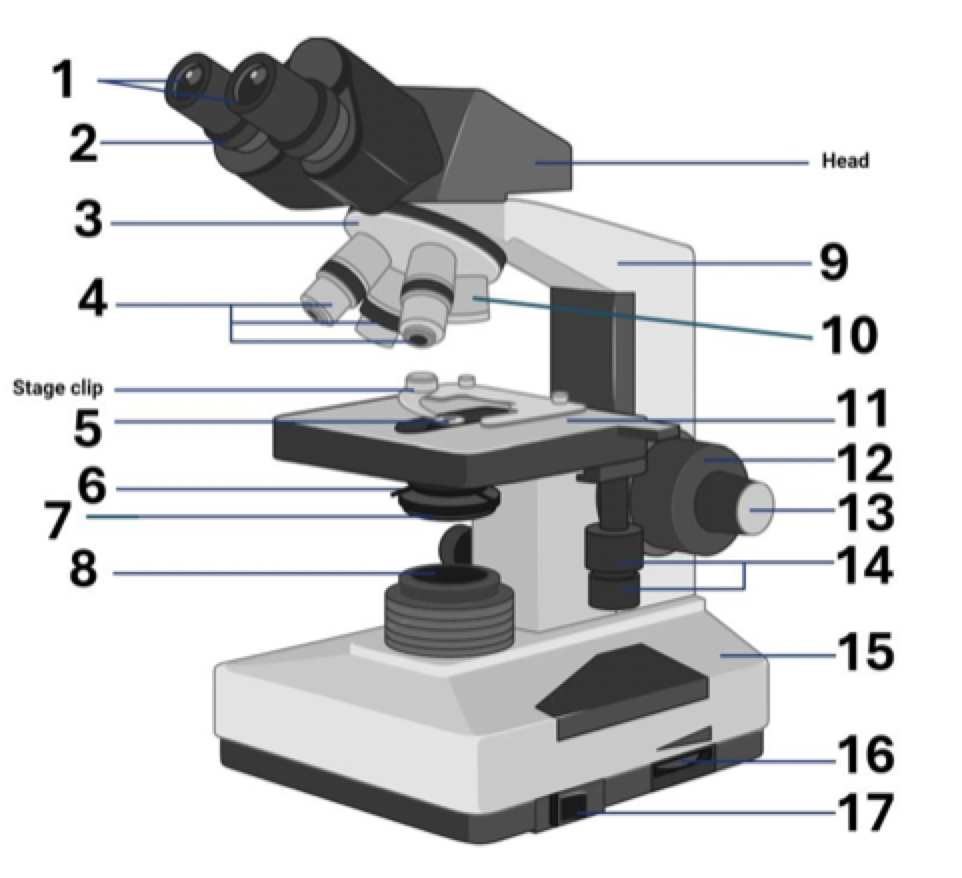
12?
Coarse adjustment
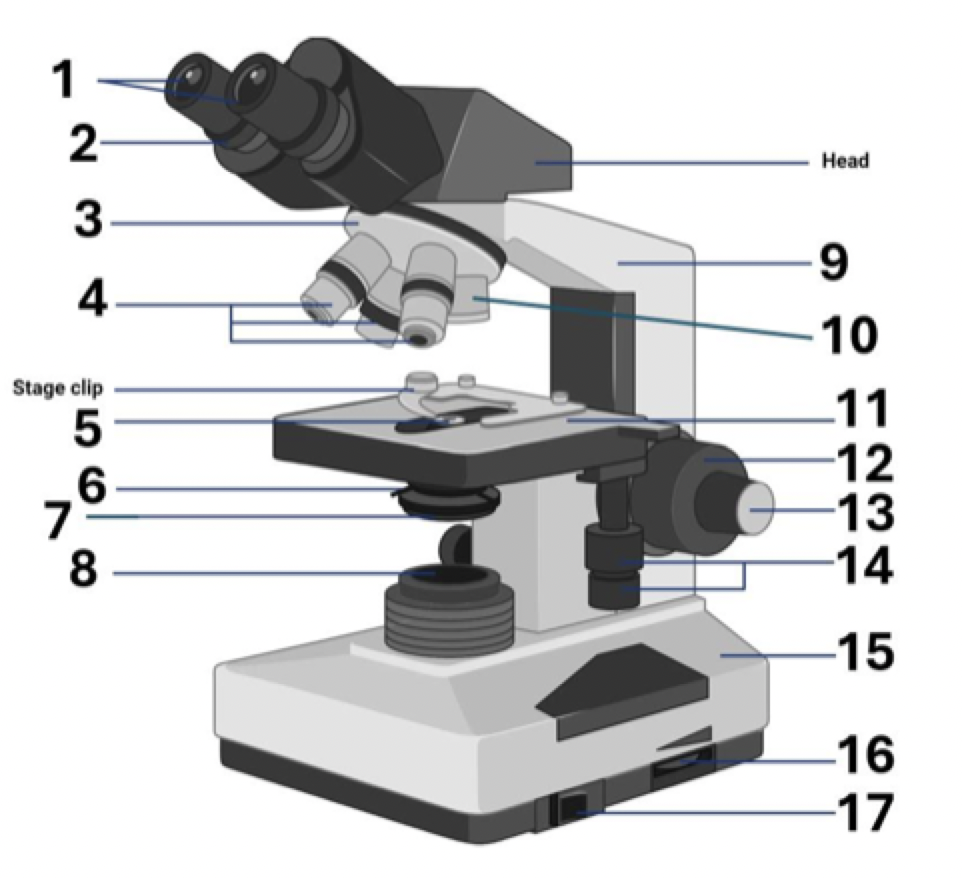
13?
Fine adjustment
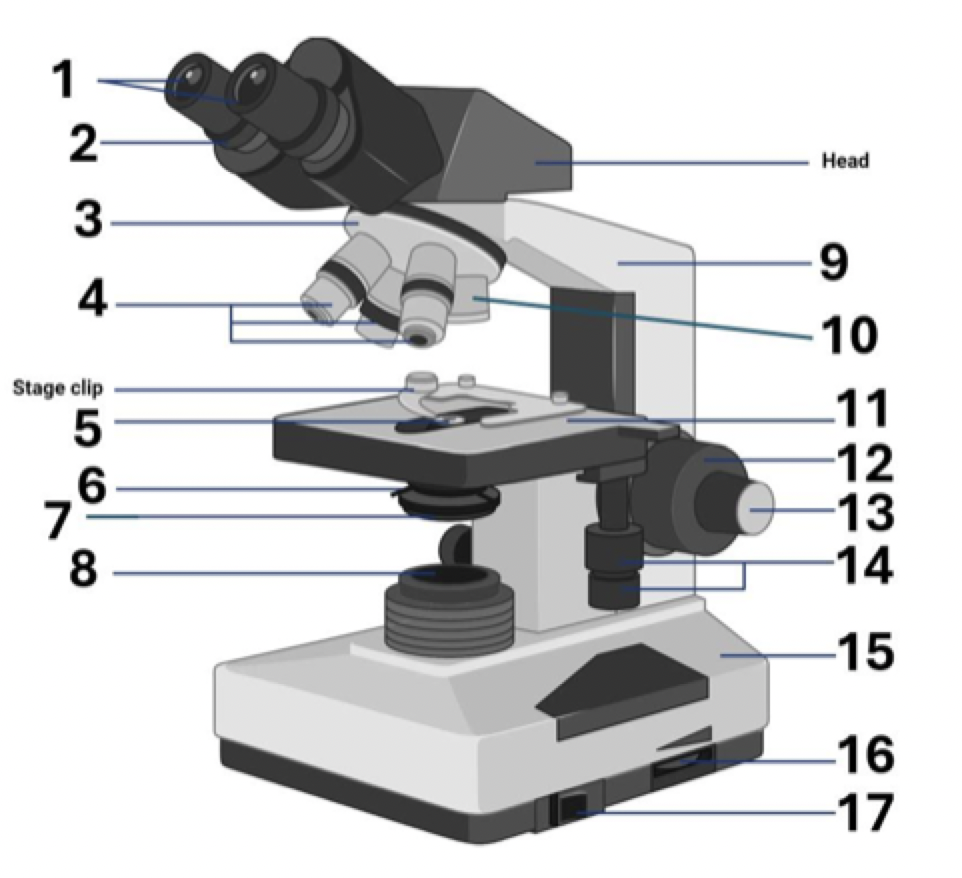
14?
Stage controls
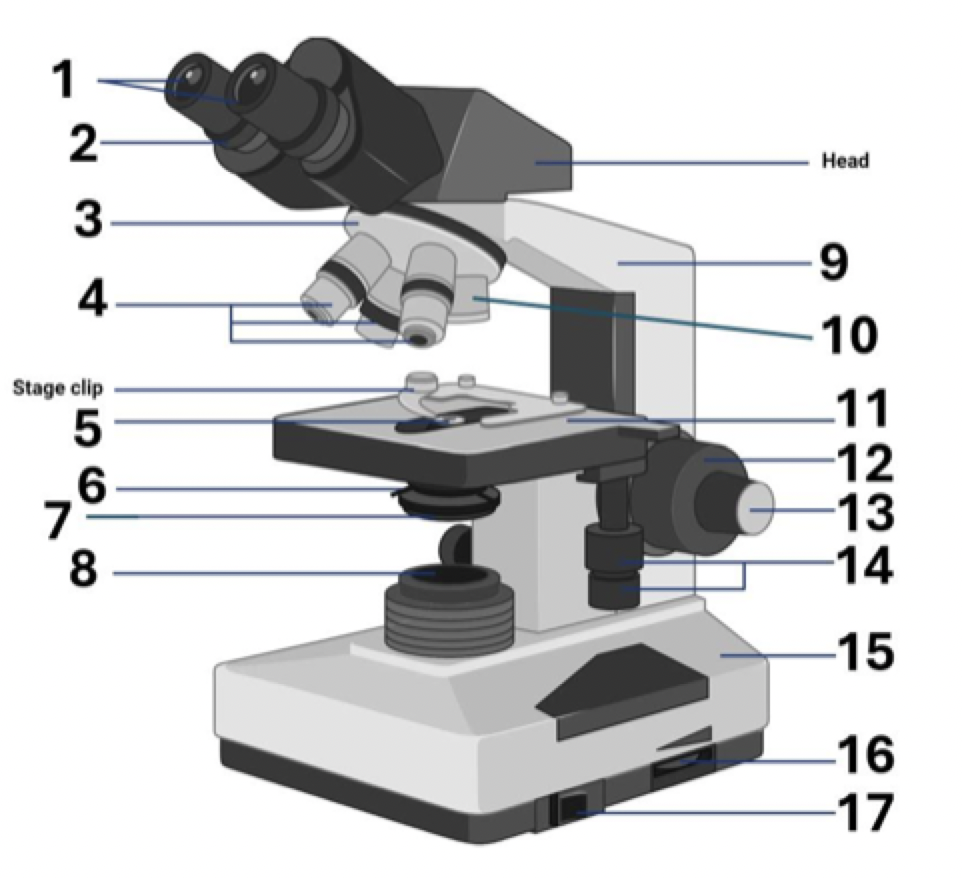
15?
Base
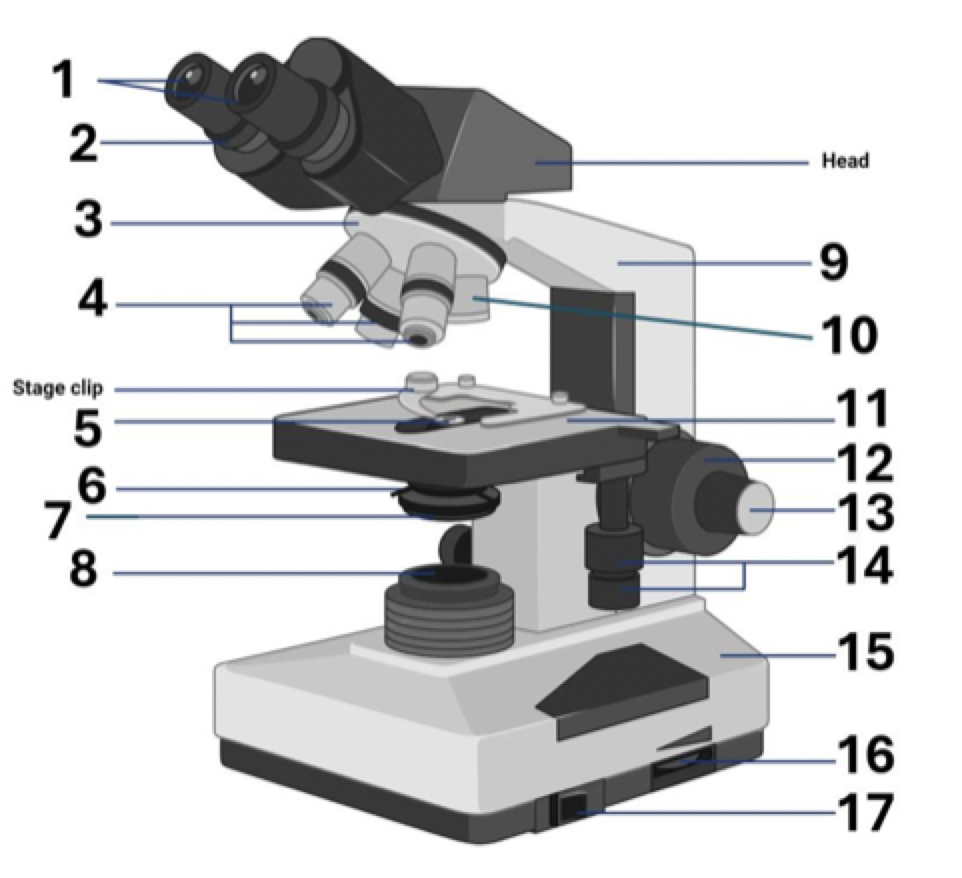
16?
Brightness adjustment
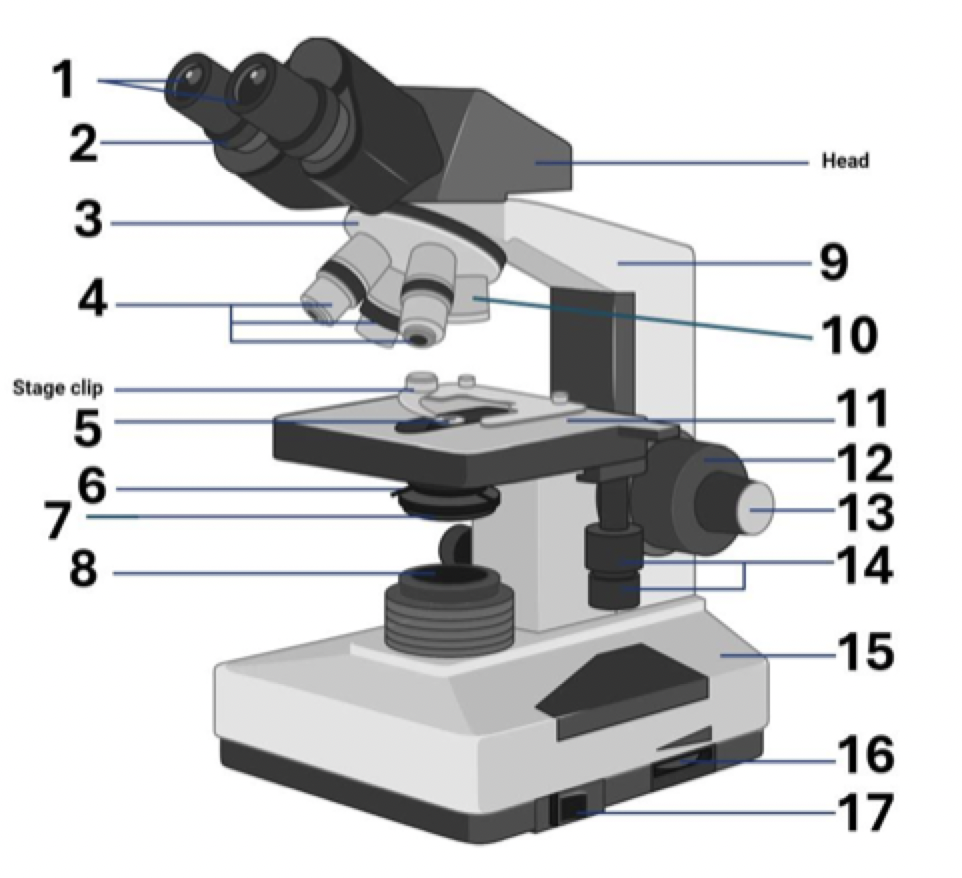
17?
Light switch
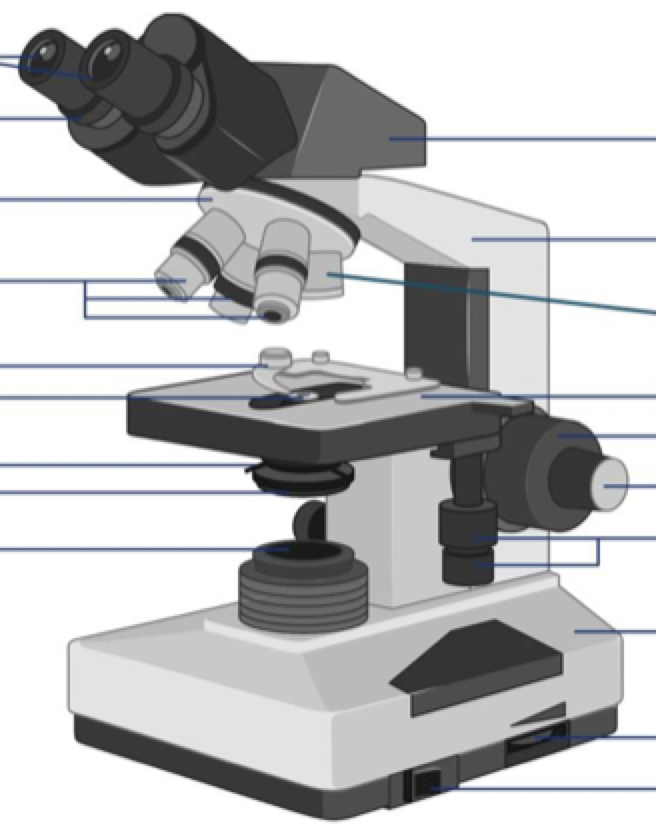
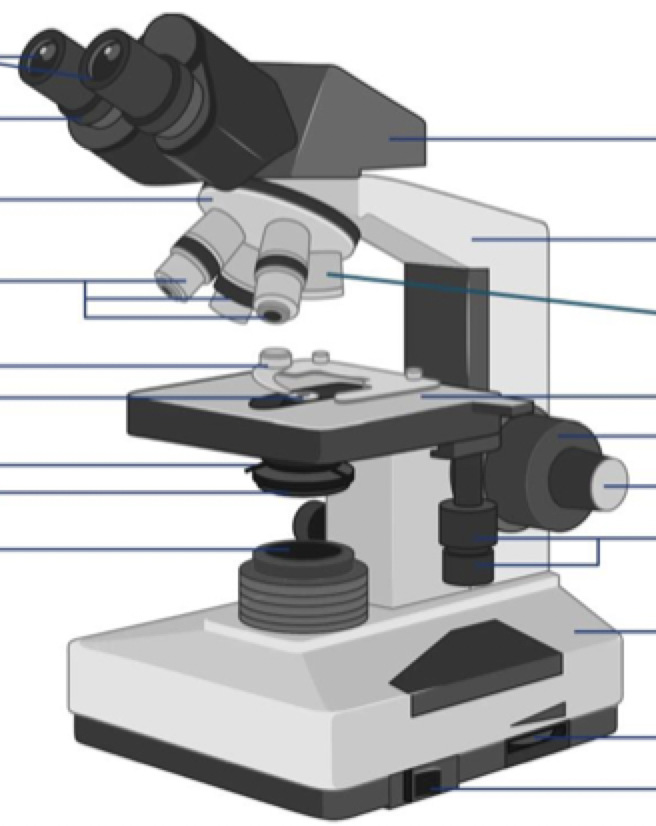
Where is the stage clip?
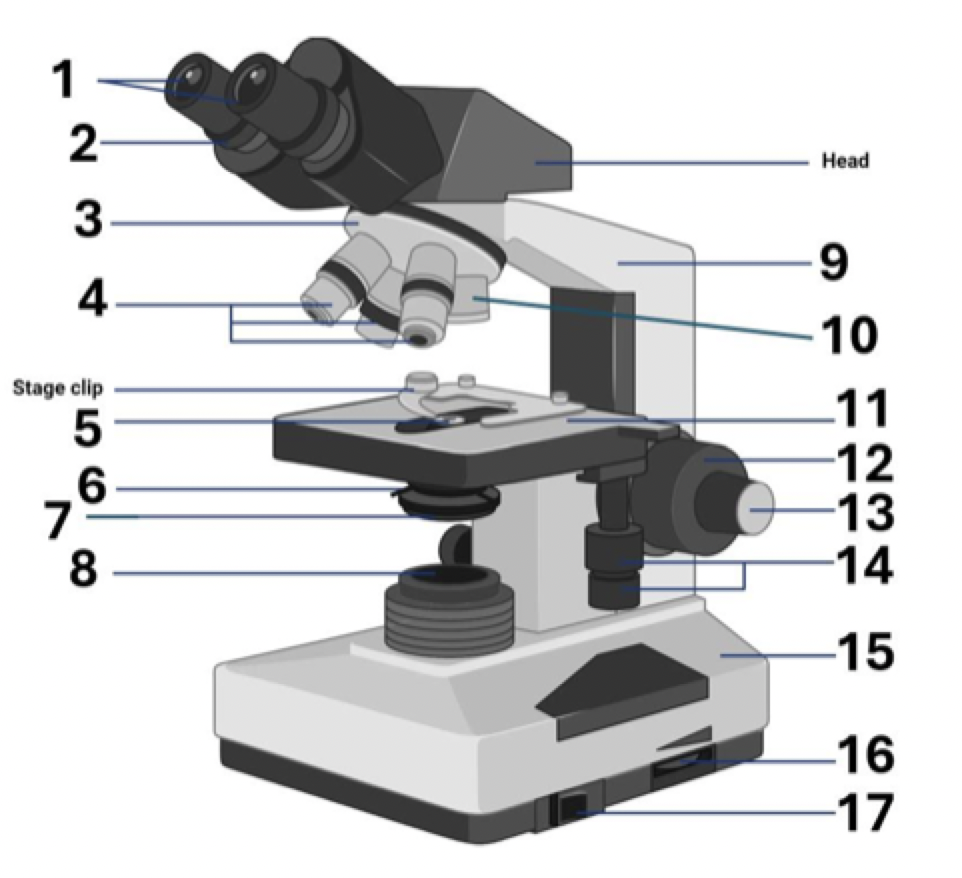
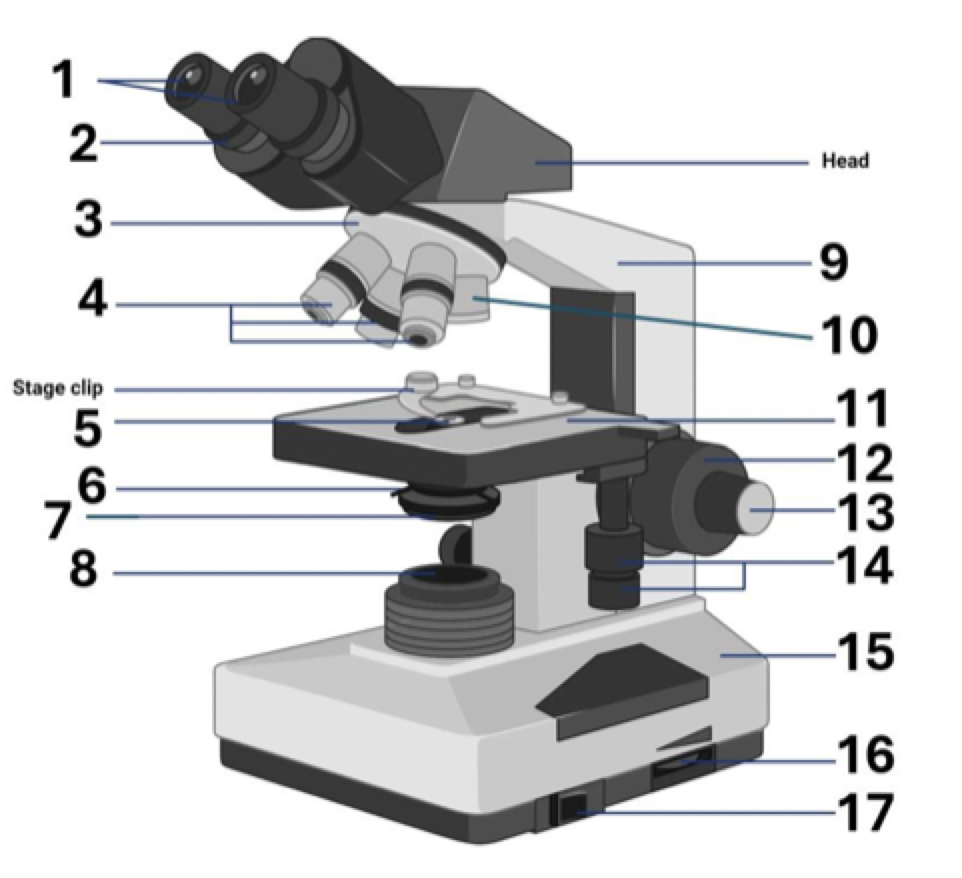
Where is the head?
Define resolution
The resolving power of an optical instrument, such as a microscope or camera
What is the smallest size a human eye can see?
Human egg
What limits an object’s ability to be seen with a microscope?
Scattering of light — we need objects big enough to scatter light as this allows us to view & observe them
What does the eyepiece do?
Used to look at the specimen
What does the diopter adjustment do?
Used to change focus on one eyepiece to compensate for differences in vision between viewer’s two different eyes
What does the nose piece do?
Houses all the objective lenses
What do the objective lens do?
Lens closest to the specimen; use light to magnify image of specimen
What does the aperture do?
Hole in stage where light comes through
What does the diaphragm do?
Controls the amount of light that reaches the specimen
What does the condenser do?
Lenses used to collect & focus light that reaches the specimen
What does the light source do?
Where light comes from
What does the arm do?
Structural component that connects the hand to the base
What does the 40x objective do?
A high powered lens
What does the mechanical stage do?
Where specimen is placed for viewing
What does the coarse focus do?
Used to focus image under low power magnification
What does the fine focus do?
Used to focus image under high power magnification
What do the stage controls do?
Used to move the stage mechanically
What does the base do?
Provides stability
What does the brightness adjustment do?
Controls intensity of the light bulb
What does the on/off switch do?
Turns light source on/off (duh)
How do you find total magnification with objective power?
Multiply by 10
How do you find objective power with total magnification?
Divide by 10
What is the total magnification of an eyepiece with objective power of 4x?
40x
What is the total magnification of an eyepiece with objective power of 10x?
100x
What is the total magnification of an eyepiece with objective power of 40x?
400x
What is the total magnification of an eyepiece with objective power of 100x?
1000x
How does a light microscope work?
Uses light to focus on a specimen
What is a light microscope used for?
Magnifying structures or specimen
Examples of light microscope use
Looking at living cells to determine of they are undergoing mitosis
How do fluorescent microscopes work?
Uses lasers to stimulate fluorescent molecules
What are fluorescent microscopes used for?
Seeing individual structure or organelles in a cell
Examples of fluorescent microscope use
Chloroplasts or cytoskeleton
How does a transmission electron microscope work?
Uses electron beams to visualize internal structures
What are transmission electron microscopes used for?
Seeing very detailed 2D images
Examples of transmission electron microscope use
Identifying a virus inside a cell
How do scanning electron microscopes work?
Uses electron beams to visualize a 3D surface
What are scanning electron microscopes used for?
Seeing and analyzing the surface of a cell