Identity and Personality
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
self-concept
: the sum of the ways in which we describe ourselves: in the present, who we used to be, and who we might be in the future
identities
individual components of our self-concept related to the groups to which we belong
self-esteem
our evaluation of ourselves
self-efficacy
the degree to which we see ourselves as being capable of a given skill in a given situation
locus of control
a self-evaluation that refers to the way we characterize the influences in our lives. Either internal (success or failure is a result of our own actions) or external (success or failure is a result of outside factors)
freud’s stages of psychosexual development
based on tensions caused by the libido, with failure at any given stage leading to fixation
Erikson’s stages of psychsocial development
Stem from conflicts that are the result of decisions we are forced to make about ourselves and the environment around us at each phase of our lives • Stages are trust vs. mistrust, autonomy vs. shame and doubt, initiative vs. guilt, industry vs. inferiority, identity vs. role confusion, intimacy vs. isolation, generativity vs. stagnation, integrity vs. despair
Kohlberg’s theory of moral reasoning development
Describes the approaches of individuals to resolving moral dilemmas • Six stages are divided into three main phases: preconventional (authority), conventional (social roles/expectations), and postconventional (universal ethical principles)
vygotsky’s theory of cultural and biosocial development
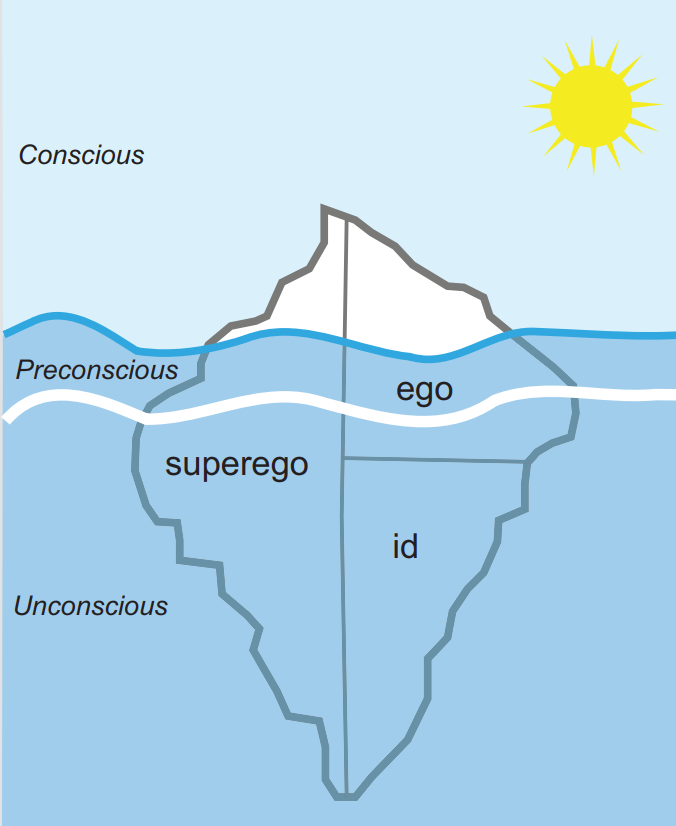
Psychoanalytic perspective
personality results from unconscious urges and desires • Freud: id, superego, ego • Jung: collective unconscious, archetypes
humanistic perspective
emphasizes internal feelings of healthy individuals as they strive toward happiness and self-realization • Maslow: hierarchy of needs • Rogers: unconditional positive regard
type and trait theory
personality can be described as a number of identifiable traits that carry characteristic behaviors
Type theories of personality
ancient Greek humors, Sheldon’s somatotypes, division into types A and B, and the Myers–Briggs type Inventory
Eysenck’s three major traits
psychoticism, extraversion, neuroticism
Trait theorists’ Big Five
openness, conscientiousness, extraversion, agreeableness, and neuroticism (OCEAN)
cardinal, Self-Concept and Identity central, and secondary