STAT 164 - SAMPLING - CHAPTER 3
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CHECK INSTAT READING ROOM FOR EXAMPLES OF SYS AND CL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
SAMPLING
It is a process of selecting a subset of n units from the universe or population of N units to gather information or make inferences about the population as a whole.
sample
The selected subset is called the _________ which will represent every unit of the population.

Why do we use samples?
Non-Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
Samples are obtained haphazardly, selected purposively or are taken as volunteers
Non-Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
The probabilities of selection are unknown.
Non-Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
They should not be used for statistical inference.
Non-Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
They result from the use of judgment sampling, purposive sampling, etc.
Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
Samples are obtained using some objective chance mechanism called randomization and hence are called random samples.
randomization
Probability Samples
Samples are obtained using some objective chance mechanism called _____________ and hence are called random samples.
sampling frame
Probability Samples
They require the use of a complete listing of the elements of the universe called the _____________.
Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
The probabilities of selection are known
Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
They allow valid generalizations about the population.
Probability Samples
TYPES OF SAMPLES
They require the use of a complete listing of the elements of the universe called the sampling frame.
RANDOMIZATION
It is a mechanism to determine which random samples to select
RANDOMIZATION
It involves using a random mechanism such as random number generator or a randomization table to generate ID numbers of random samples to include in the final set of samples.
SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING (SRS)
Most basic method of drawing a probability sample.
SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING (SRS)
Assigns equal probabilities of selection to each possible sample.
Subtypes: SRS w/ replacement and SRS w/o replacement
What are the subtypes of SIMPLE RANDOM SAMPLING (SRS)?
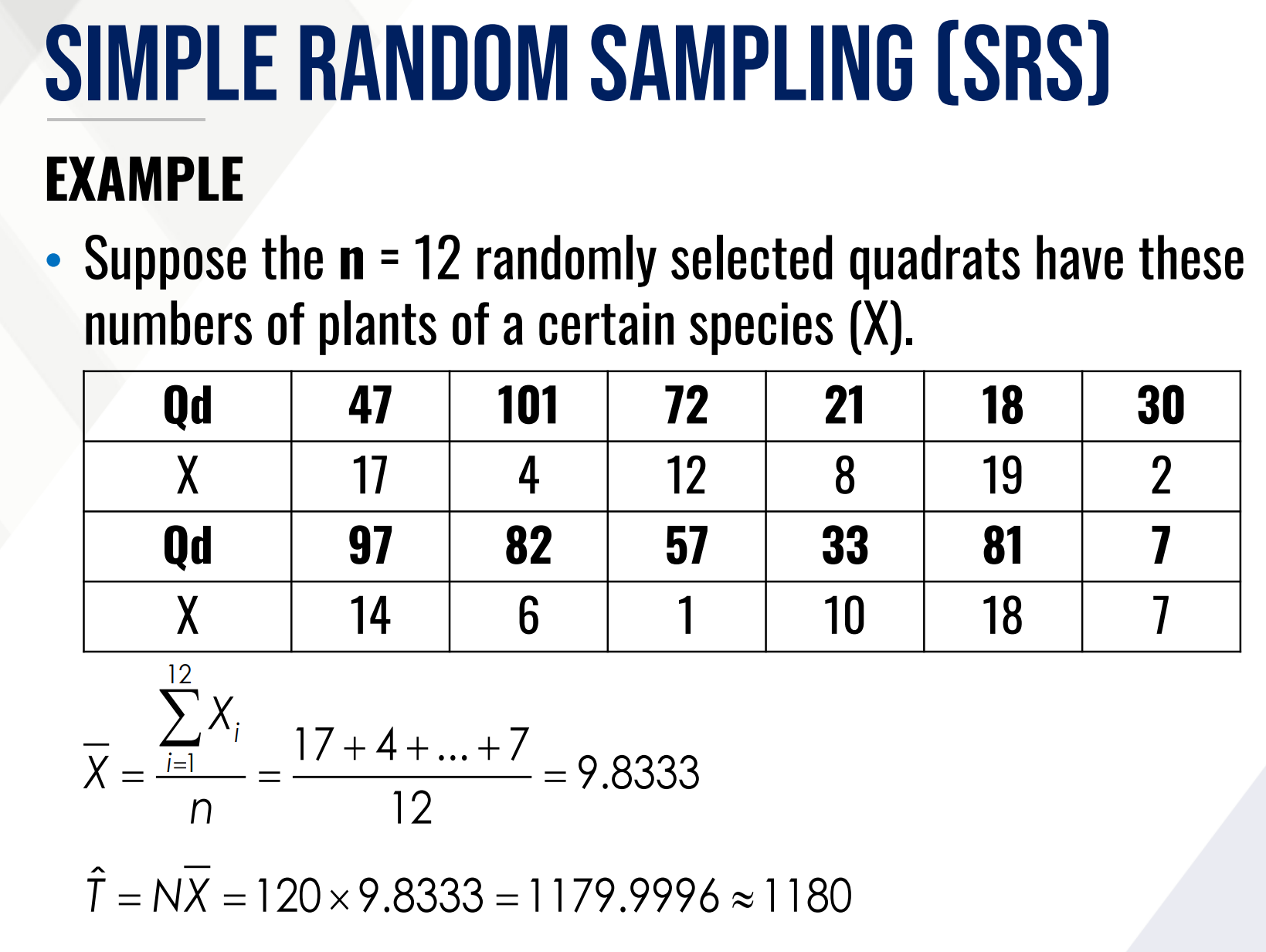
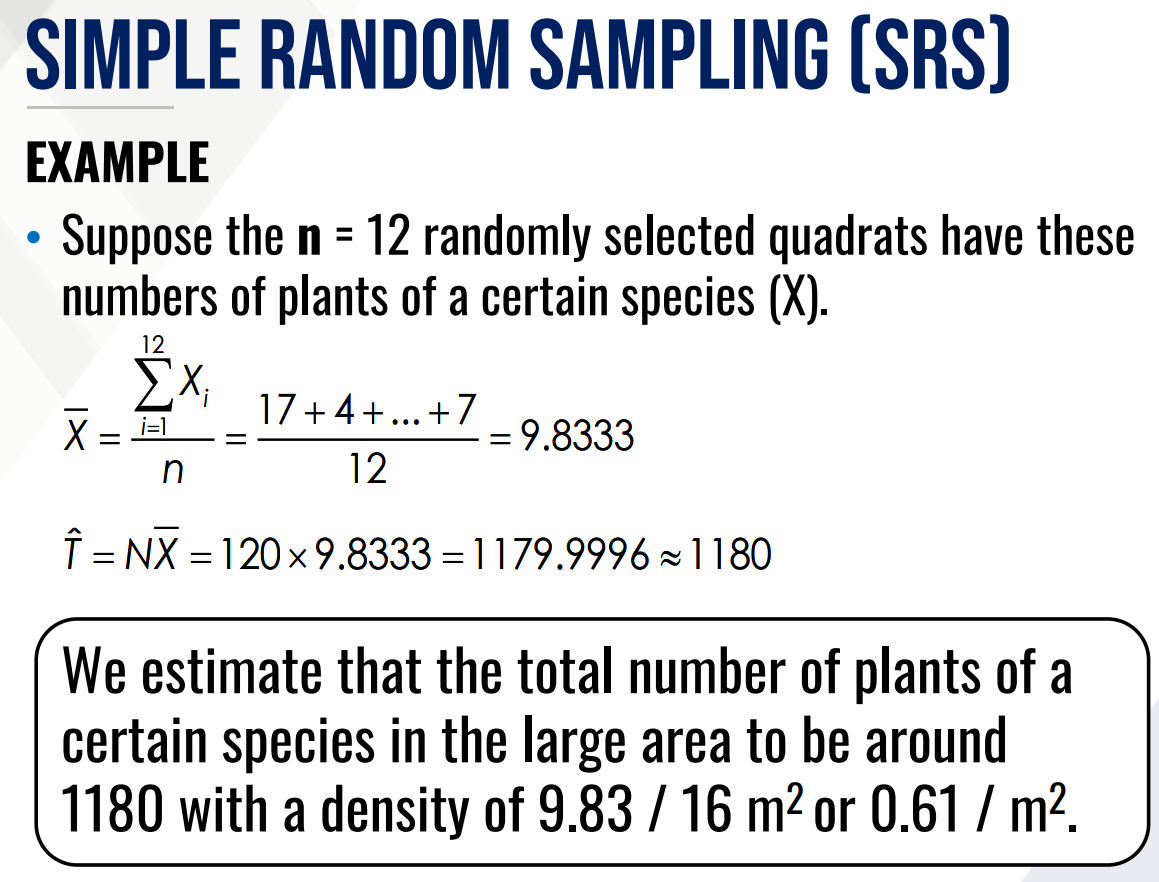
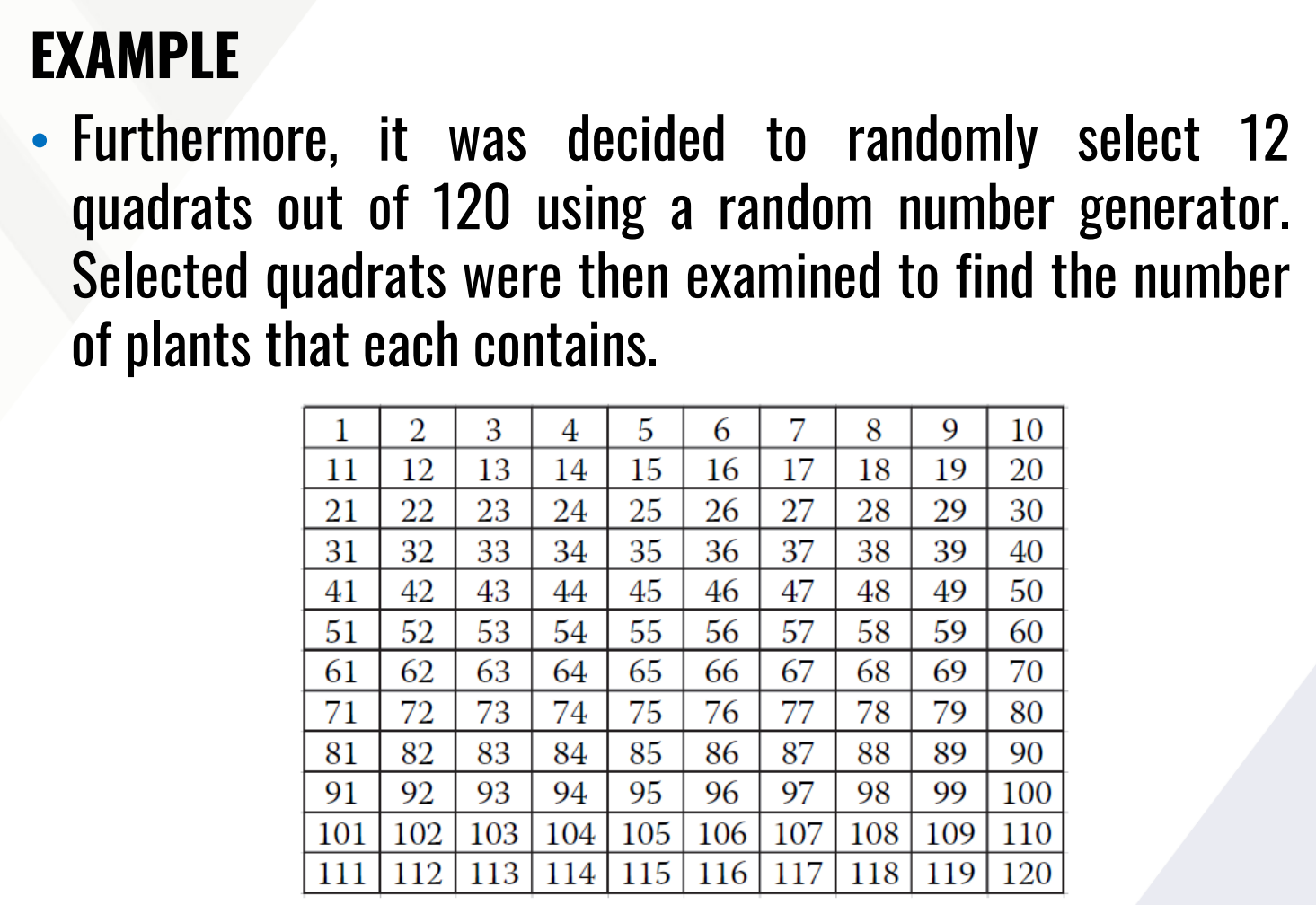
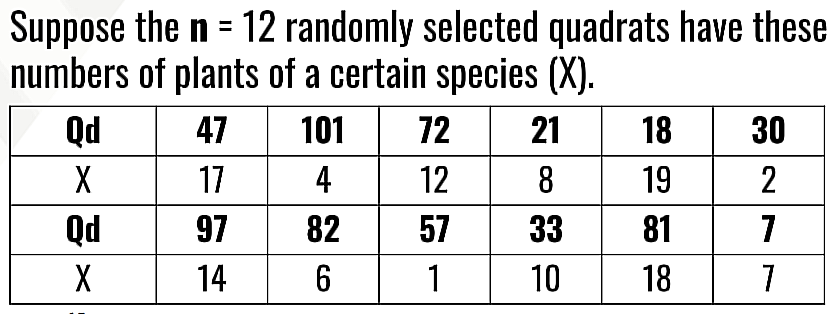
Solve for density and total number of plants within the area.

STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING (STRS)
The population is divided into L mutually exclusive sub-populations called strata.
strata
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING (STRS)
The population is divided into L mutually exclusive sub-populations called _____________.
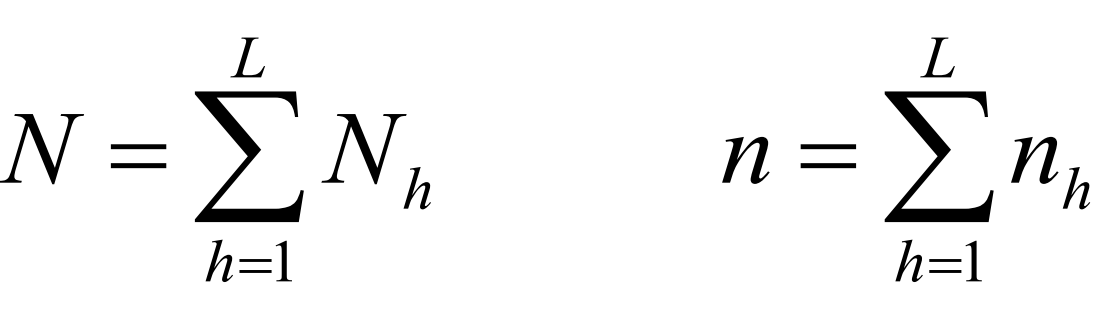
Independent SRS are obtained from each stratum.
What is the formula for N and n?
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING (STRS)
It gives better cross-section of the population and simplifies data gathering.
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING (STRS)
It allows inferences for each stratum and generally increases the precision of the estimates.
STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING (STRS)
Homogenous within, heterogeneous across: Types of stratification are those based on spatial location or based on some demographic profile within which the population is expected to be fairly uniform.

STRATIFIED RANDOM SAMPLING (STRS)
Sample size n will be divided equally or proportionally among L strata.
What is the formula for equal and proportional allocation?
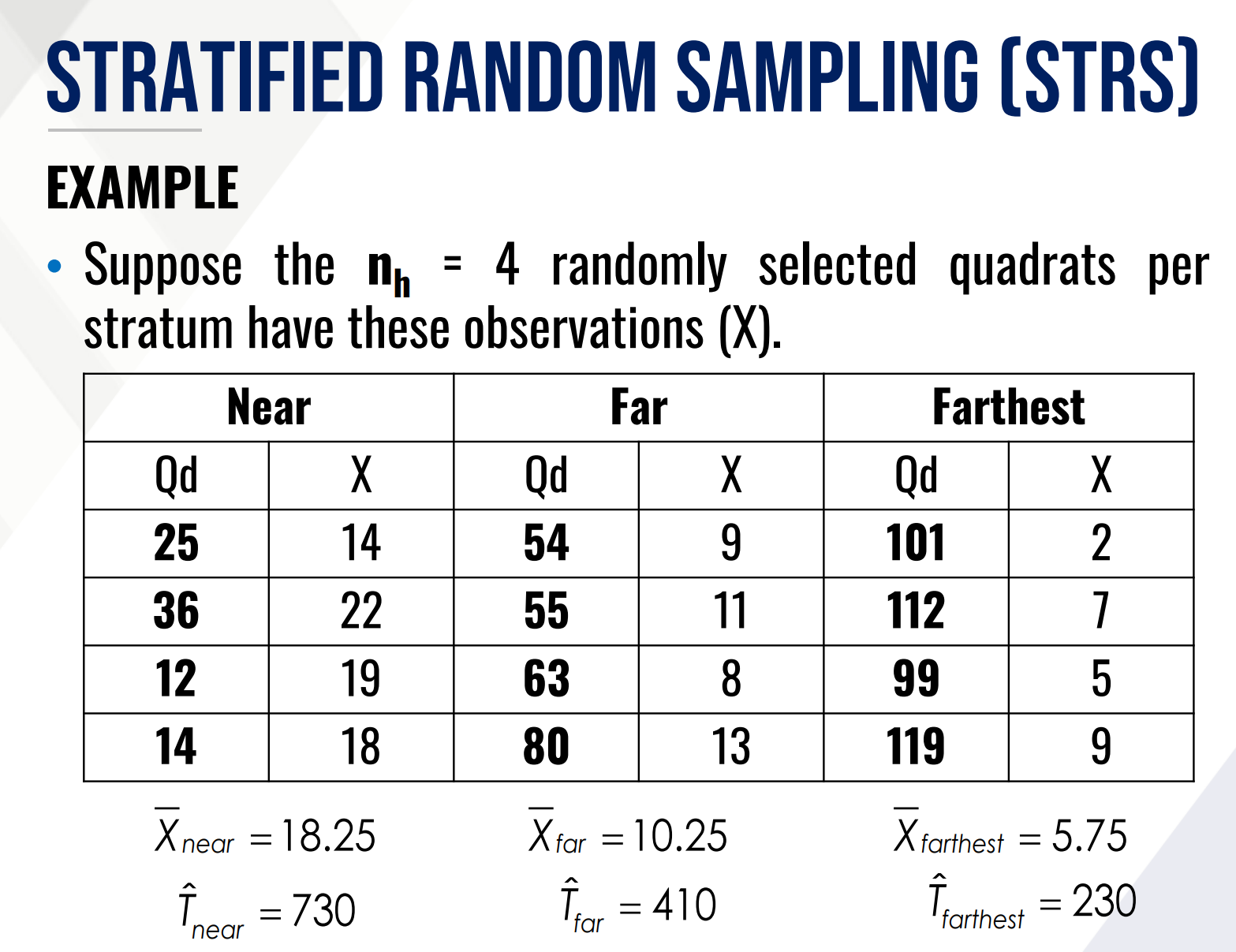
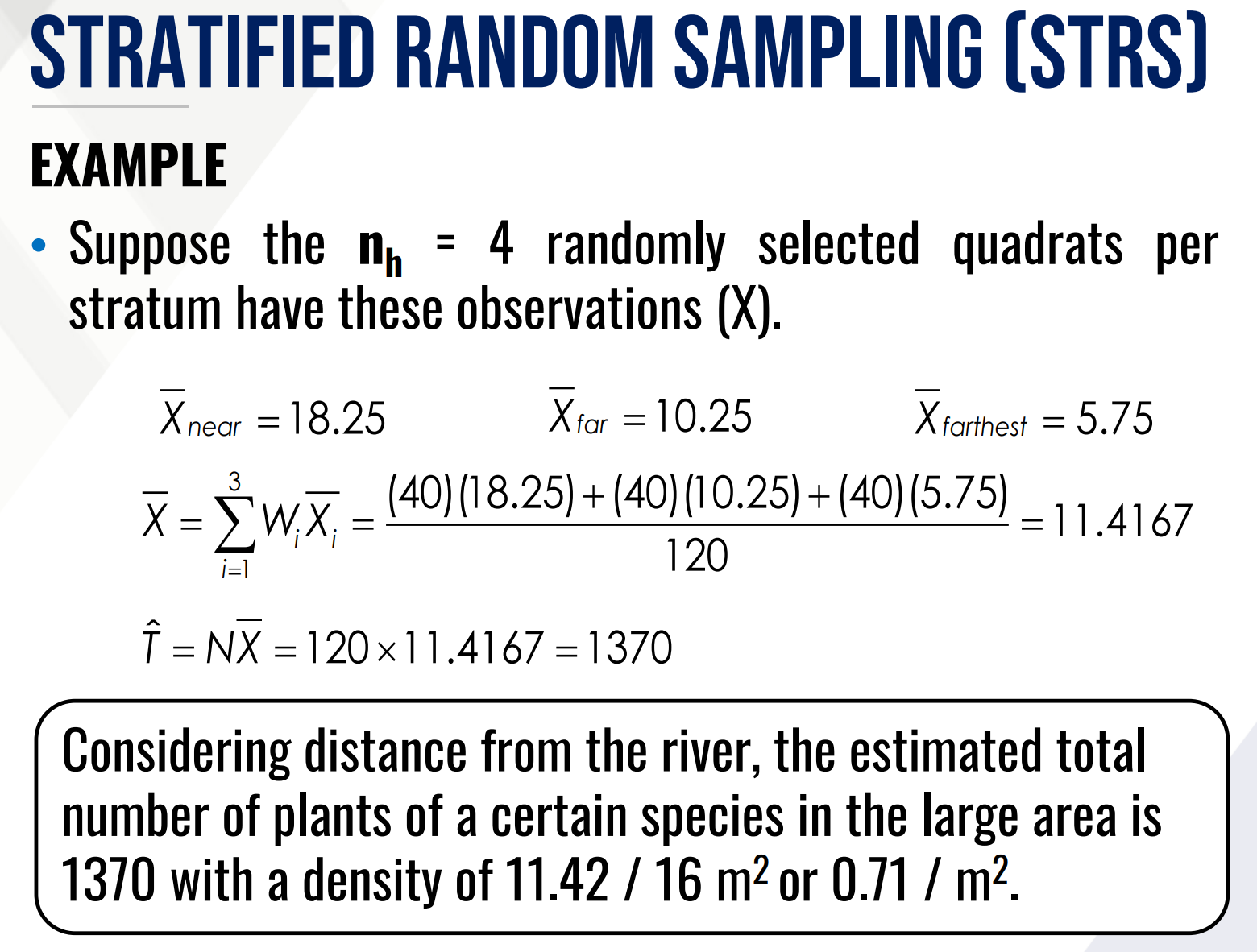
Solve for density and total number of plants within the area.
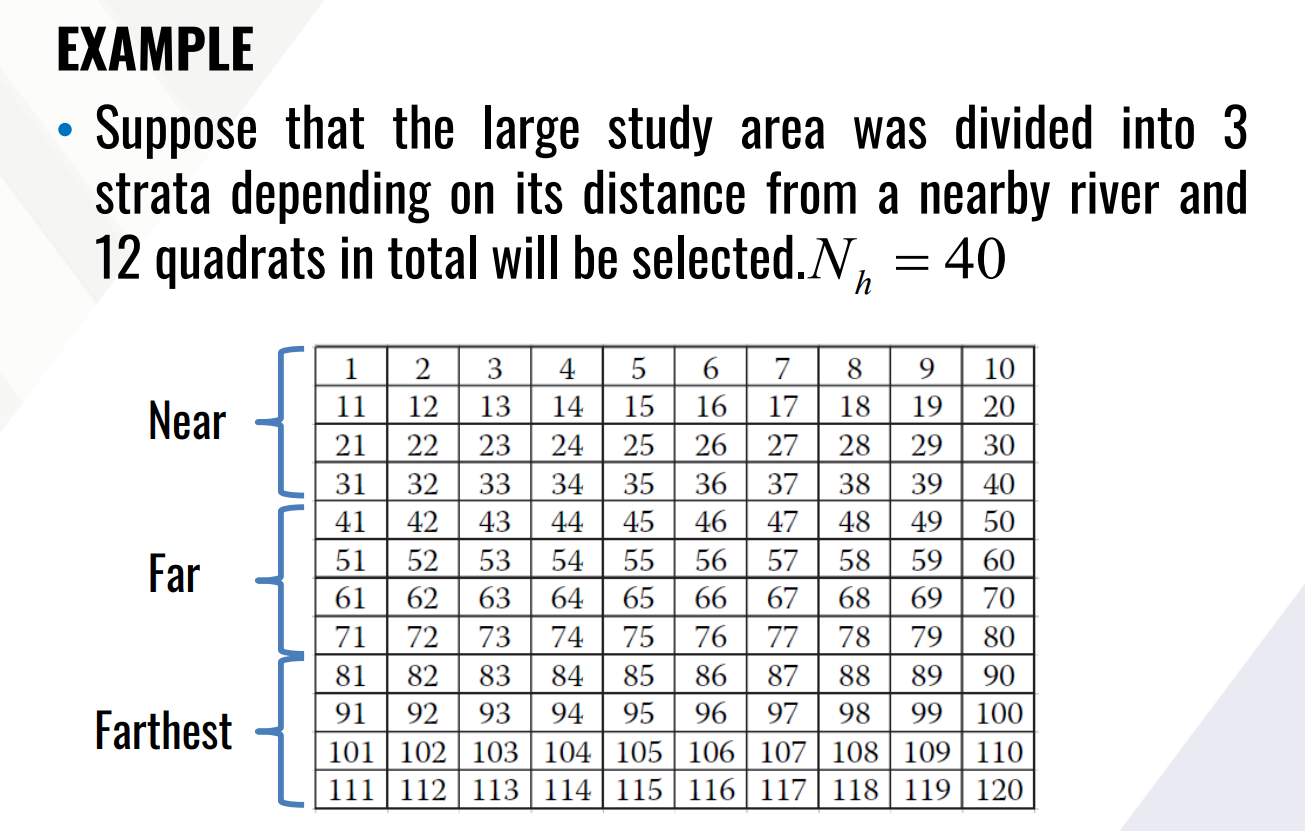
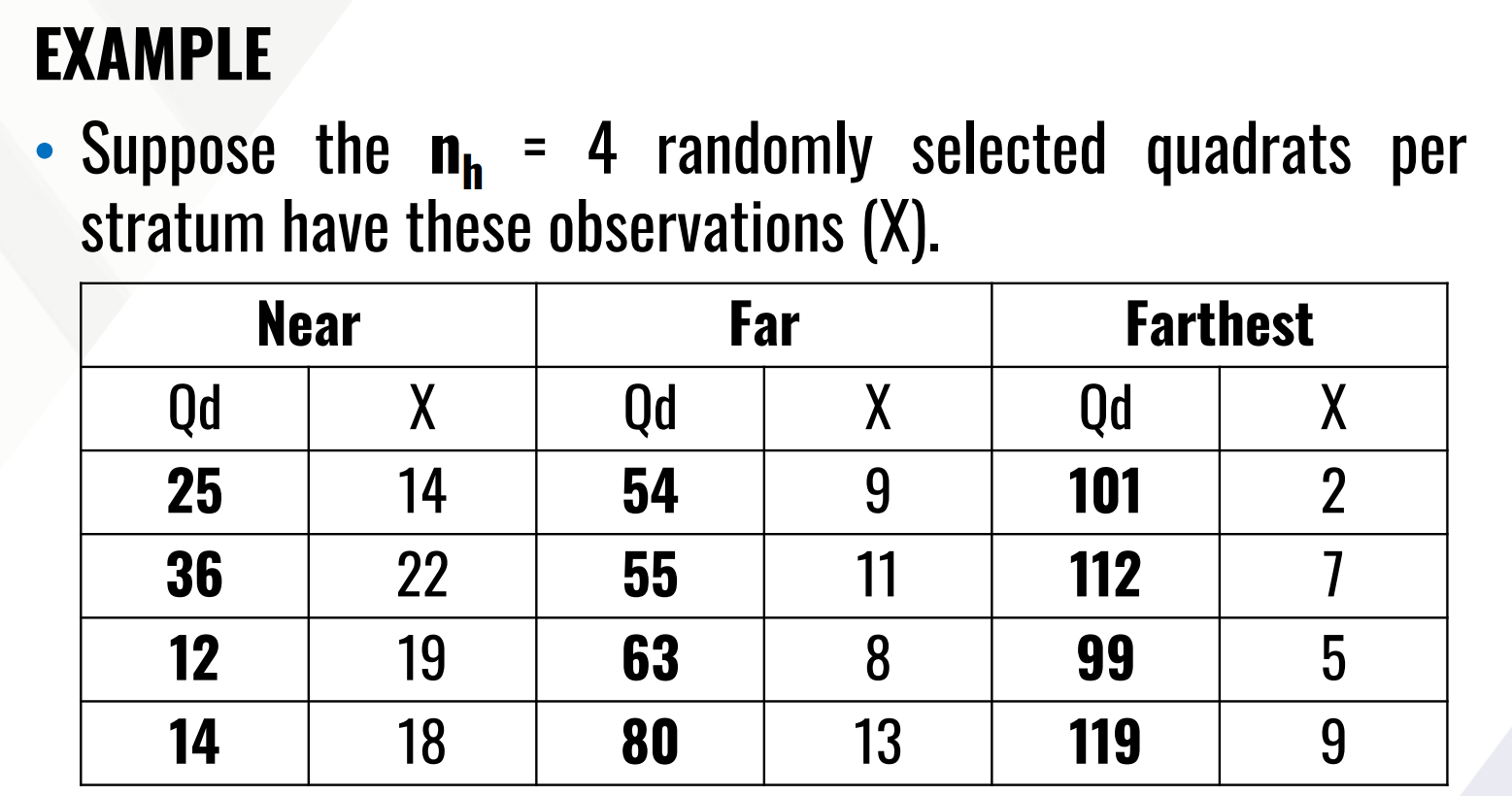
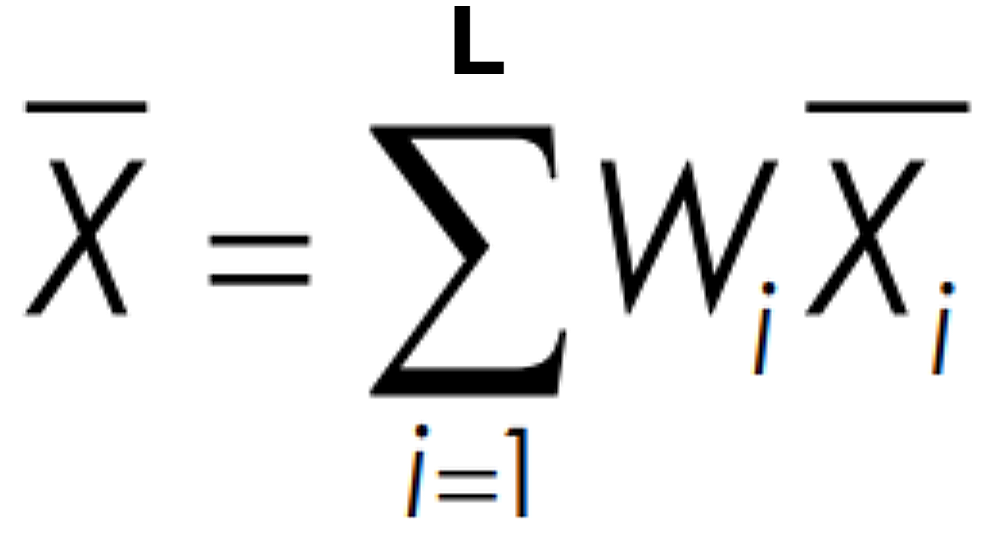
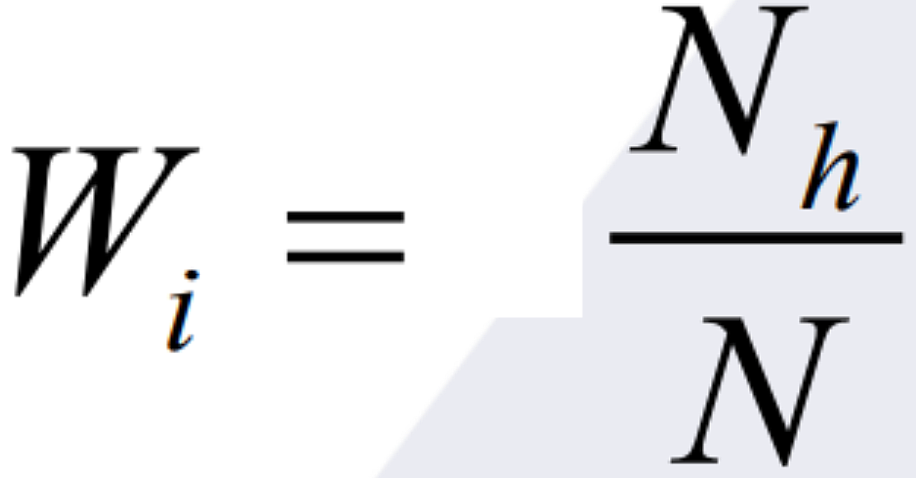
Nh is the population of a strata
N is the total population of all strata
What is the formula for the total mean of an SRS
SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING (SYS)
Adopts a skipping pattern in the selection of sample units.
SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING (SYS)
Gives a better cross-section if the listing is linear in trend but has high risk of bias if there is periodicity in the listing of units in the sampling frame.
SYSTEMATIC SAMPLING (SYS)
Allows simultaneous listing and selection of samples in one operation.
Gives better coverage than SRS.

What is the formula for skipping pattern of SYS?

If 1 to n, then:

If 1 to N, then
S = random number*population size
The random start S is selected from a range based on what factor?
What is the formula for it?

Adaptive sampling
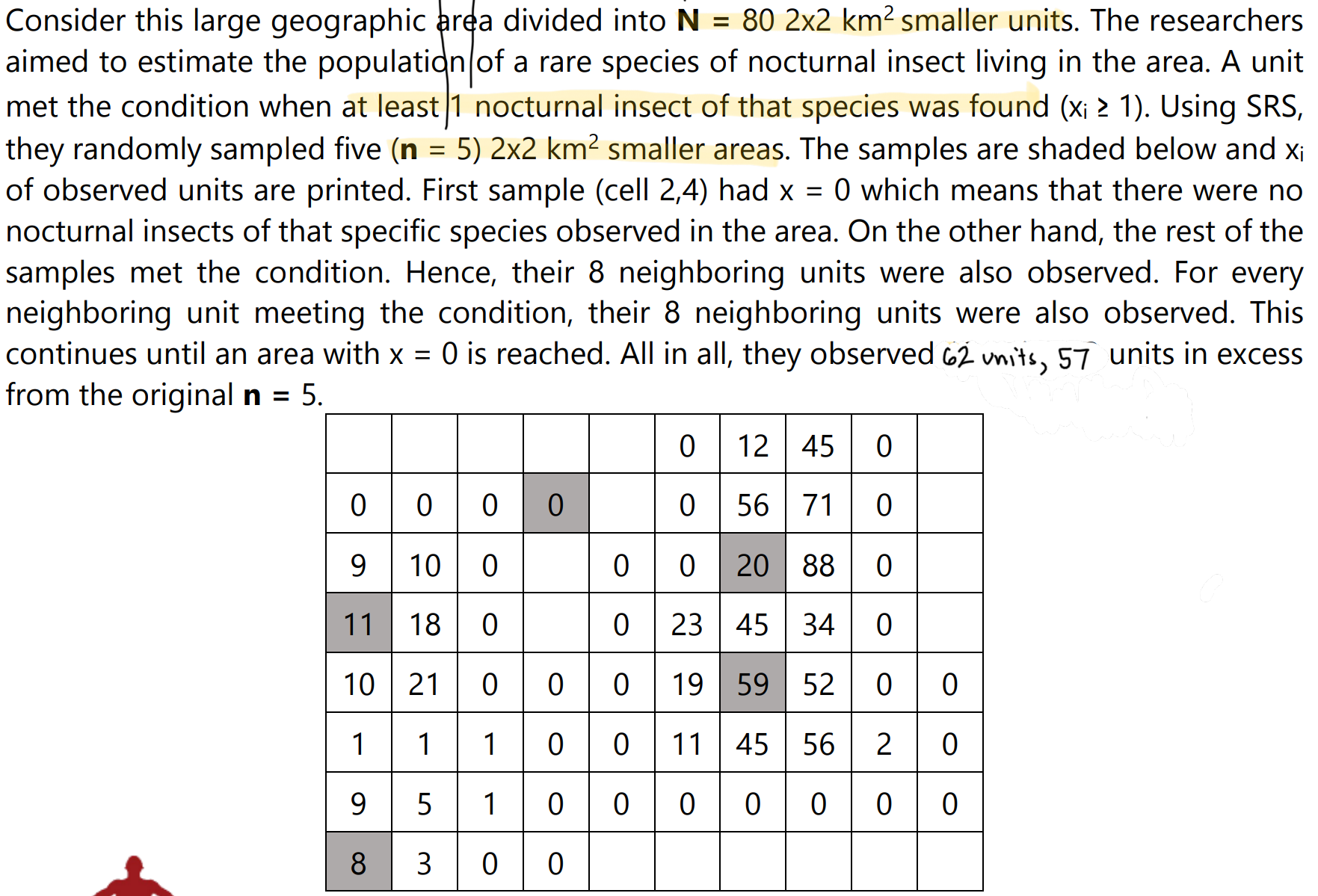
Used when ecologists study rare and clustered populations that exhibit extreme biological processes. Rare and clustered populations are those that are difficult to detect or are sparse in some sense.
Adaptive sampling
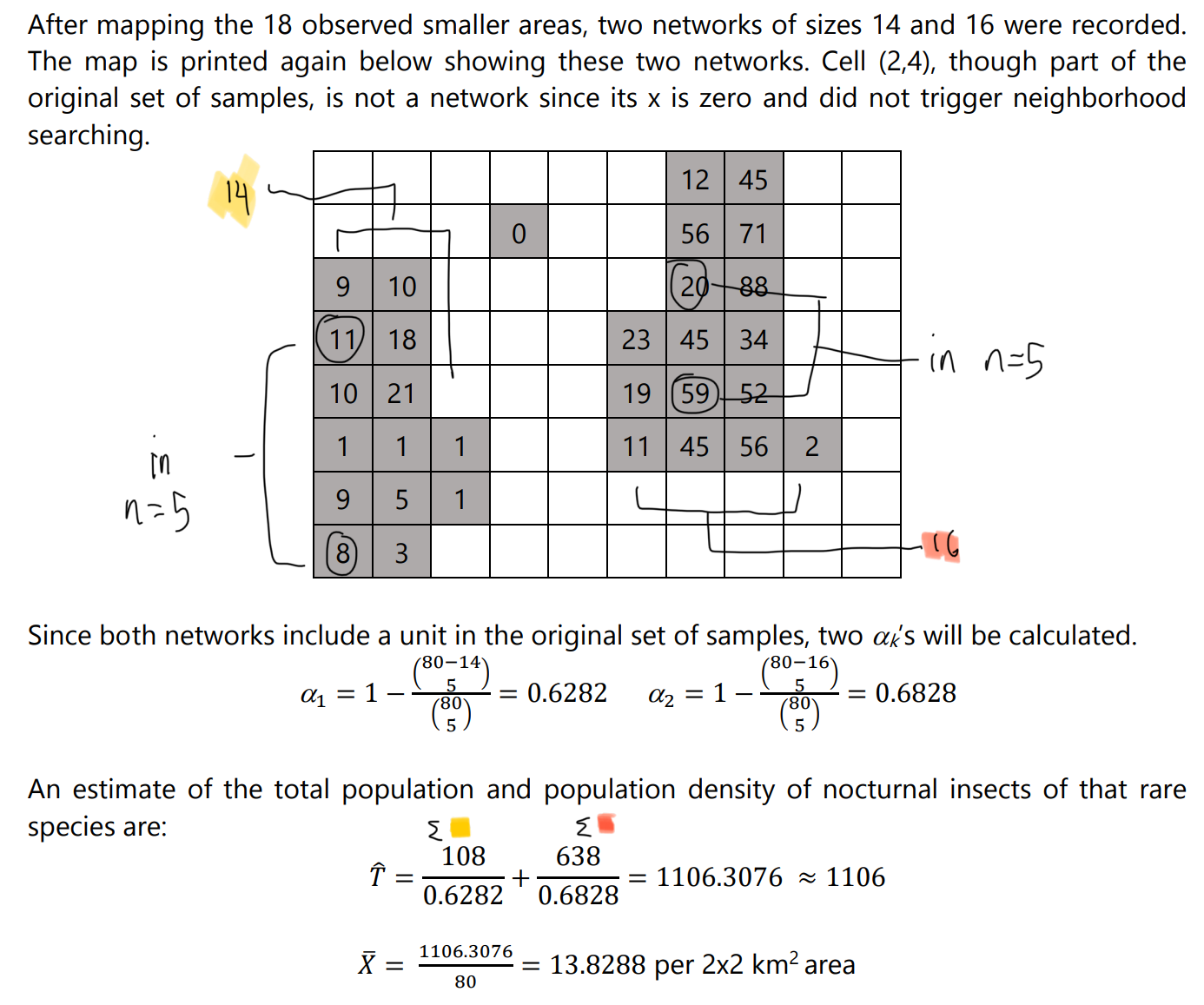
It is a probability sampling technique that involves selecting a set of original sample units, searching their neighborhood, and including the neighbors in the final set of samples for as long as certain conditions are met.
Adaptive sampling
The focus of this sampling method is on estimating the population density (mean number per area or per unit) and population abundance (total number in the population).
Here are the general steps of adaptive sampling.
Divide the population into N non-overlapping units. These units will serve as the population units.
Determine a threshold value C that identifies whether a sample satisfies the condition. This condition can be a threshold of the response (ex. observing at least one rare plant)
Randomly select the original sample units n from N. This step may use any of the four basic sampling methods discussed in Chapter 3A.
Observe and record the response (xi) from each sample unit.
If a sample meets or exceeds C (xi ≥ C), then adaptive selection is triggered, and their respective neighboring units are also sampled. This search of neighboring units continues as long as a neighboring unit satisfies C.
The final sample contains all units in the original set of samples n, plus the neighboring units which satisfied C.
Record the networks of sample units. These are clusters of units that surround the unit in the original set of n samples that triggered neighborhood searching.
Calculate the estimate of total population or population abundance using Horvitz-Thompson estimator:
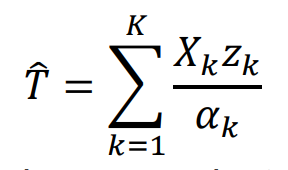
where Xk is the total of xi in the network, zk equals 1 if any unit in the kth network is in the original n sample units or equal 0 otherwise, and αk is the initial intersection probability or the probability that at least one unit in the network will be in the original set of n samples. It is equal to:
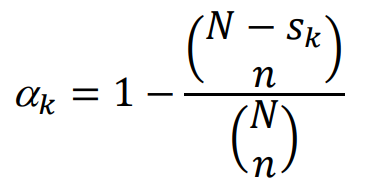
Where sk is the size of the network or the number of units in the network.
Calculate the population density by:
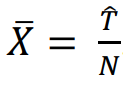
Here are the general steps of adaptive sampling.
Divide the population into _____________ non-overlapping units. These units will serve as the _____________ units.
Determine a _____________ that identifies whether a sample satisfies the condition. This condition can be a threshold of the response (ex. observing at least one rare plant)
Randomly select the _____________ from N. This step may use any of the four basic sampling methods discussed in Chapter 3A.
Observe and record the _____________ from each sample unit.
If a sample meets or exceeds _____________, then adaptive selection is triggered, and their respective neighboring units are also sampled. This search of neighboring units continues as long as a neighboring unit satisfies _____________.
The final sample contains all units in the original set of samples n, plus the neighboring units which satisfied _____________.
Record the _____________ of sample units. These are clusters of units that surround the unit in the original set of n samples that triggered neighborhood searching.
Calculate the estimate of total population or _____________ using Horvitz-Thompson estimator:
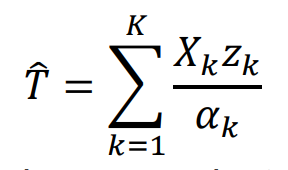
where Xk is the total of xi in the network, zk equals 1 if any unit in the kth network is in the original n sample units or equal 0 otherwise, and αk is the initial intersection probability or the probability that at least one unit in the network will be in the original set of n samples. It is equal to:
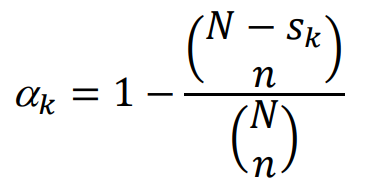
Where sk is the size of the network or the number of units in the network.
Calculate the population density by:
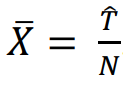
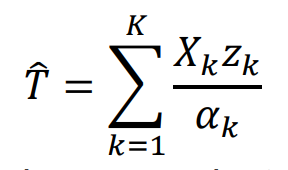
where Xk is the total of xi in the network, zk equals 1 if any unit in the kth network is in the original n sample units or equal 0 otherwise, and αk is the initial intersection probability or the probability that at least one unit in the network will be in the original set of n samples. It is equal to:
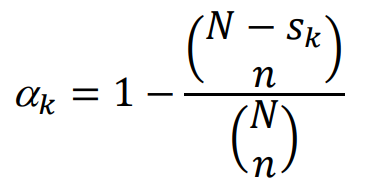
Where sk is the size of the network or the number of units in the network.
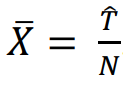
What is the Horvitz-Thompson estimator formula for Adaptive sampling?
Also the formula for pop. density.
Line Transect Sampling
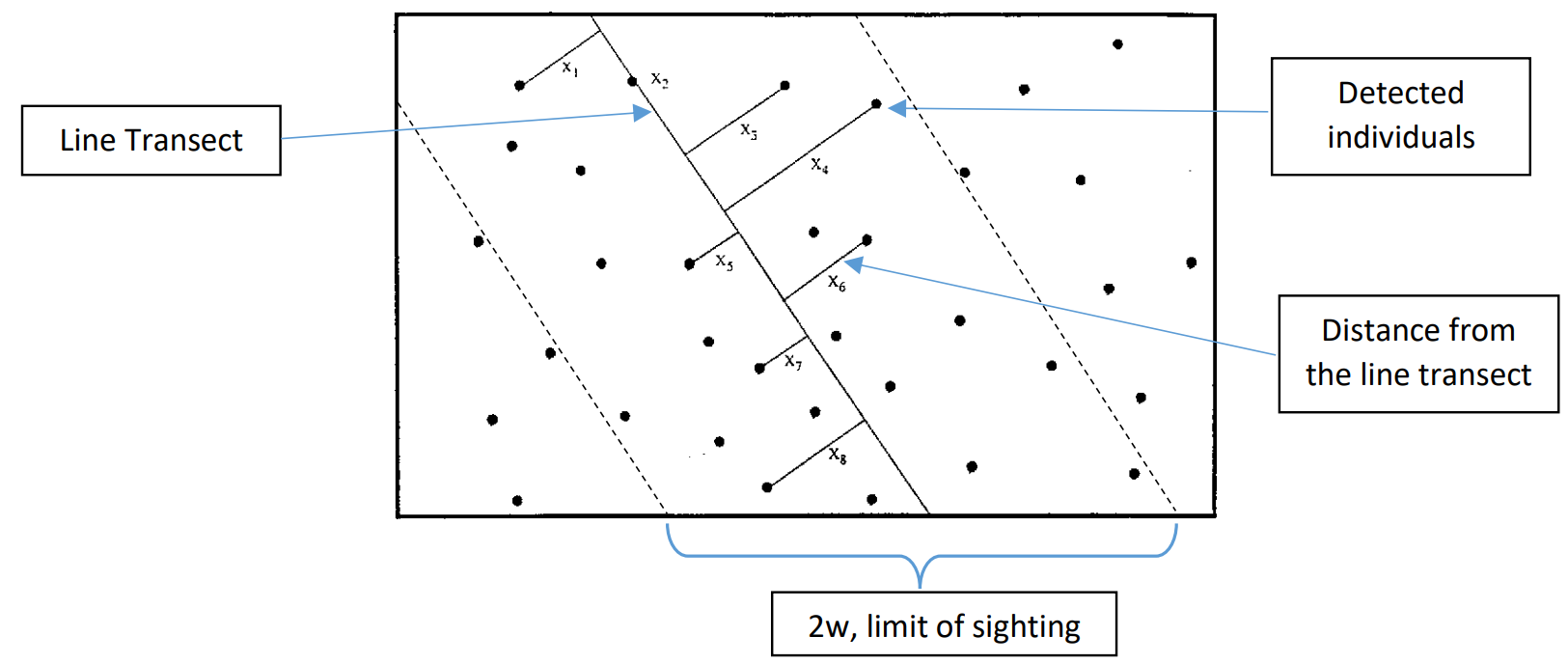
Also called Distance Sampling, is intended for the estimation of the population abundance of rare, mobile, difficult-to-detect animals, plants, or any other organisms.
Line Transect Sampling
The basic idea is that an observer moves along a line randomly positioned in the study area, looking to the left and right for the animal or plant of interest.
half-width (w)
For instance, if w = 8 ft, then the observer walks along the line transect looking to the left up to 8 ft, and to the right up to 8 ft, for a total width equal to 2w = 16 ft.
When an individual of the species of interest is detected, the sighting is recorded together with its perpendicular distance from the transect line.
Line Transect Sampling
The distance from the transect line up to the limit of sighting, called ____________, is set before the actual observation.
Line Transect Sampling
An estimate of the total population using line transect sampling is:
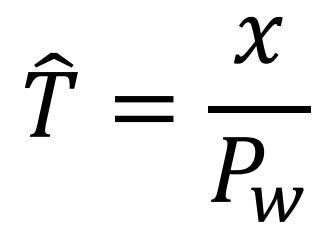
where x is the actual number of detected individuals and Pw is average probability of detection within the limit of sighting equal to:
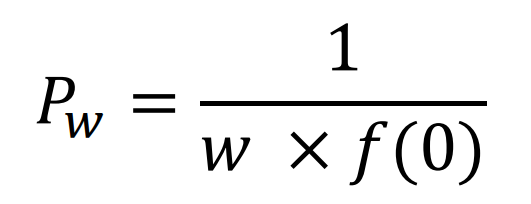
where f(0) is the probability density of detecting an individual exactly on the line transect. Estimating f(0) requires mathematical techniques that are beyond the scope of our course. For sake of convenience, its value will be provided during exercises or examinations.
Moreover, an estimate of the population density is:
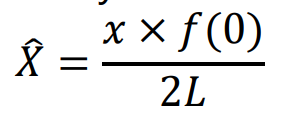
where L is the total length of all line transects.
Line Transect Sampling

An estimate of the total population using line transect sampling is:
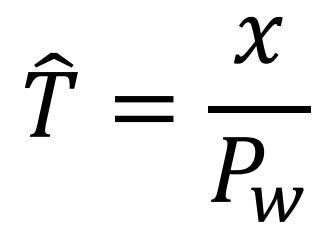
where x is the actual number of detected individuals and Pw is average probability of detection within the limit of sighting equal to:
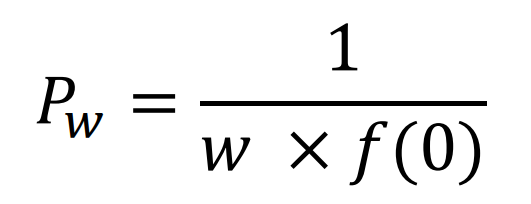
where f(0) is the probability density of detecting an individual exactly on the line transect. Estimating f(0) requires mathematical techniques that are beyond the scope of our course. For sake of convenience, its value will be provided during exercises or examinations.
Moreover, an estimate of the population density is:
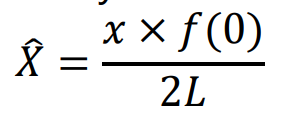
where L is the total length of all line transects.
An estimate of the total population using line transect sampling is:
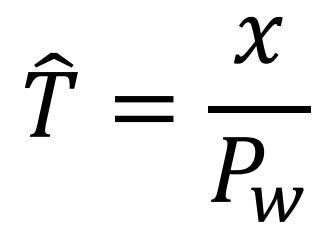
where x is the actual number of detected individuals and Pw is average probability of detection within the limit of sighting equal to:
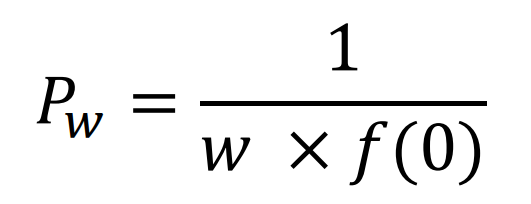
where f(0) is the probability density of detecting an individual exactly on the line transect. Estimating f(0) requires mathematical techniques that are beyond the scope of our course. For sake of convenience, its value will be provided during exercises or examinations.
What is the estimate of the total population formula for Line Transect Sampling?
Moreover, an estimate of the population density is:
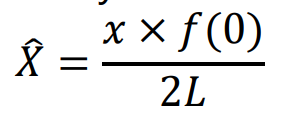
where L is the total length of all line transects.
What is the estimate of the population density formula for Line Transect Sampling?
Point Transect Sampling
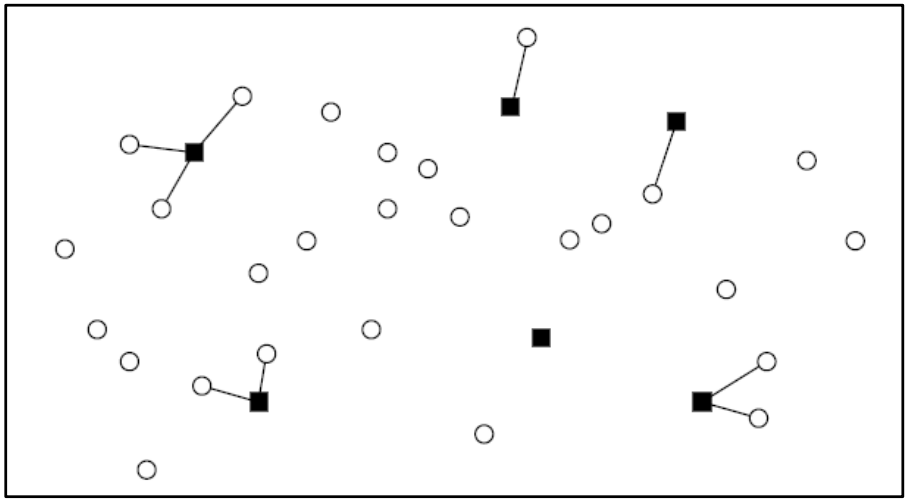
A variation of line transect sampling called _____________ uses several points, instead of a line, randomly chosen within the study area. The objects from each point are then recorded, with their distances from the points as shown in the illustration below with six sample points (squares) with detections (circles) ranging from none to three.

?
Moreover, an estimate of the population density is (Note: 1 km = 3280.84 ft):
?
Capture-Recapture Sampling
Also known as mark-recapture method, this sampling technique includes marking n1 individuals, releasing them back to their natural habitat, and recapturing n2 individuals from the same population where the n1 individuals were sampled.
Capture-Recapture Sampling
This allows us to estimate the size of a population. One aspect that should be kept in mind is the fact that the marking should not jeopardize the survival of an animal.
Capture-Recapture Sampling
Suppose that a sample of n1 animals is taken from a population consisting of N animals.
These animals are then marked and released back into the population.
On a second capture occasion, a random sample of n2 animals is taken from the same population.
These n2 animals are observed, and the number of marked animals m from n2 is recorded.
Therefore, it might be expected that the proportion of marked animals in the recapture phase will be approximately the same as the proportion in the population.
That is, m/n2 is approximately equal to n1/N so that an estimate of the population size is:
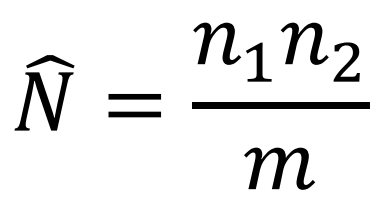

Capture-Recapture Sampling
Suppose that a sample of __________ animals is taken from a population consisting of __________ animals.
These animals are then __________ and __________ into the population.
On a second capture occasion, a random sample of __________ animals is taken from the same population.
These __________ animals are observed, and the number of marked animals m from n2 is recorded.
Therefore, it might be expected that the proportion of __________ animals in the recapture phase will be approximately the same as the proportion in the __________.
That is, m/n2 is approximately equal to n1/N so that an estimate of the population size is:
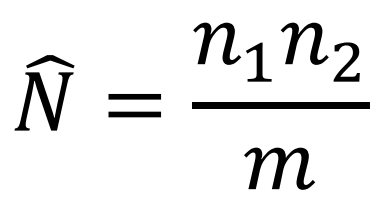

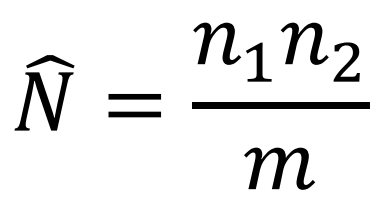
What is the estimate of the population size formula for Capture-Recapture Sampling?
Capture-Recapture Sampling
Though the procedure seems easy, the estimator assumes that:
1. The population is closed so that there are no losses and gains in the time between the capture and recapture phases.
2. n2 samples are randomly chosen from the population.
3. No marks are lost before the recapture phase, and all marked animals are recognized as such during the recapture phase.
To achieve the first assumption, the phases must generally be carried out over a relatively short period of time.
If not and if the population is open such that new animals enter through birth and immigration, and animals leave through deaths and emigration, then other developments of capture-recapture sampling must be performed.
Capture-Recapture Sampling
Though the procedure seems easy, the estimator assumes that:
1. The population is __________ so that there are no losses and gains in the time between the capture and recapture phases.
2. __________ samples are __________ chosen from the population.
3. No __________ are lost before the __________ phase, and all marked animals are recognized as such during the recapture phase.
To achieve the first assumption, the phases must generally be carried out over a relatively __________ period of time.
If not and if the population is open such that new animals enter through birth and immigration, and animals leave through deaths and emigration, then other developments of capture-recapture sampling must be performed.