Light Dependent Reaction
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- uplean vids notes to repeat+ better undertsanding + do recall qus on uplearn or refresh ect
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Photosynthesis takes place in the… of leaves
chloroplasts
The first stage of photosynthesis is the…
The second stage of photosynthesis is the…
light dependent reaction
light independent reaction
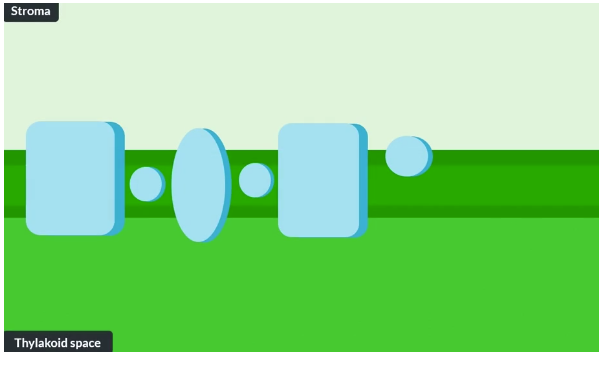
where does the Light Dependent Reaction occur
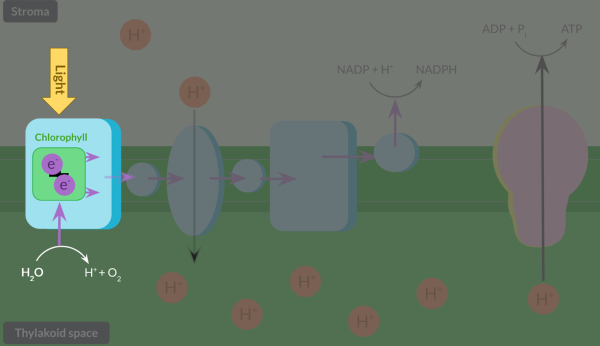
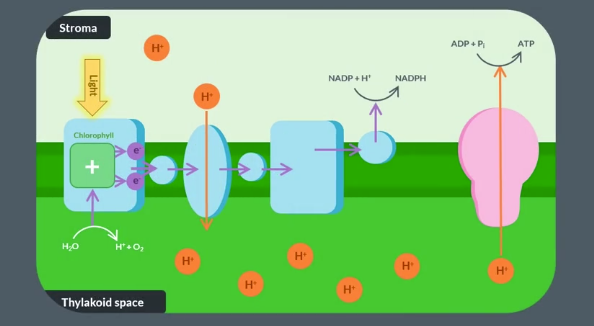
In the thylakoid MEMBRANE → sits between thylakoid space and stroma
Protons move down the proton gradient, from the …… to the …..
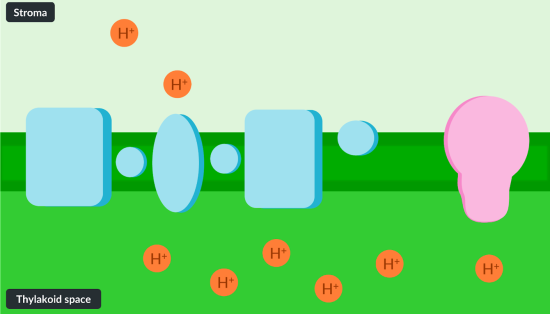
thylakoid space
stroma
enzyme embedded in the thylakoid memebrane is called …………. and synthesises……+ ……. to make……….. which reqires energy via ……… from the ……… of water which is called chemi…….
atpsynthase
ADP+Pi
ATP
H+/ protons
photolysis
chemisosmosis
Where is the prootn gradient estanblished. refernce to conc aswell as where protons go through
in the thylakoid to stroma
high concnetration of H+ in thylakoid therofre DIFFUSE down conc grad to stroma
Through ATP synthase
the movement of ions aross a partially permeable membranes from an area of high concnenrtation in the thylakoid space to the low concnentration in the stroma is called ….
chemisomosis
………………means ADP by reacting with PI to make ATP thru ATP synthae
photophosphorelation
What can the proton gradient be also called…. and why
Electrochemical Gradient:conc grad involving charged particel (H+) ions
The light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis takes place in the…… ……… . One important molecule produced in the light-dependent reaction is ATP, which is produced by an enzyme called …….. ………... To catalyse the production of ATP, energy is provided to the enzyme by the diffusion of protons down a…………………… gradient via a process called ……………. The protons move from the thylakoid space into the ………… . This method of producing ATP is known as ………..
thylakoid memebrane
atp synthase
proton concnetration
chemisomosis
stoma
photophosphoelation
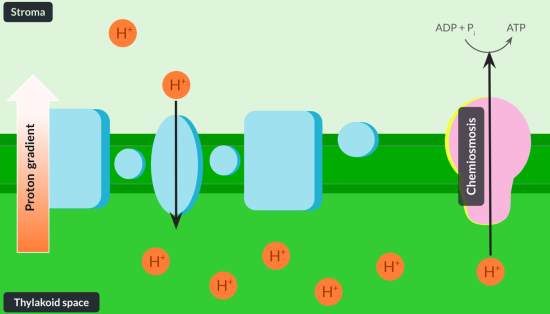
Name the process that prodcues molecule of ADP tp molecule ATP
photophophorealtion
To maintain the proton gradient, protons are …. …. fom the ….. to …… To ensure theres a … concnetraion of protns in thylakoid space cf w stroma. The active transportneeds energy and comes from the ….. and …… and electrons
ctively transported
stroma
thylakoid space
higher
oxidation
reduction
When a substance loses …./……, this is an ………reaction.
When a substance gains ……/……., this is a ………reaction.
hydrogens/eletrons
oxidation
hydrogens/electron
reduction
examples of oxidation using Na, Zn
Na → Na+ + e-
Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
examples of reduction reactions using Cl2, Cu
½Cl2 + e- → Cl-
Cu2+ + 2e- → Cu
Oxidation-Reduction reactions in terms of electrons
When one substance loses electrons, another substance gains them.. Eg) NaCl
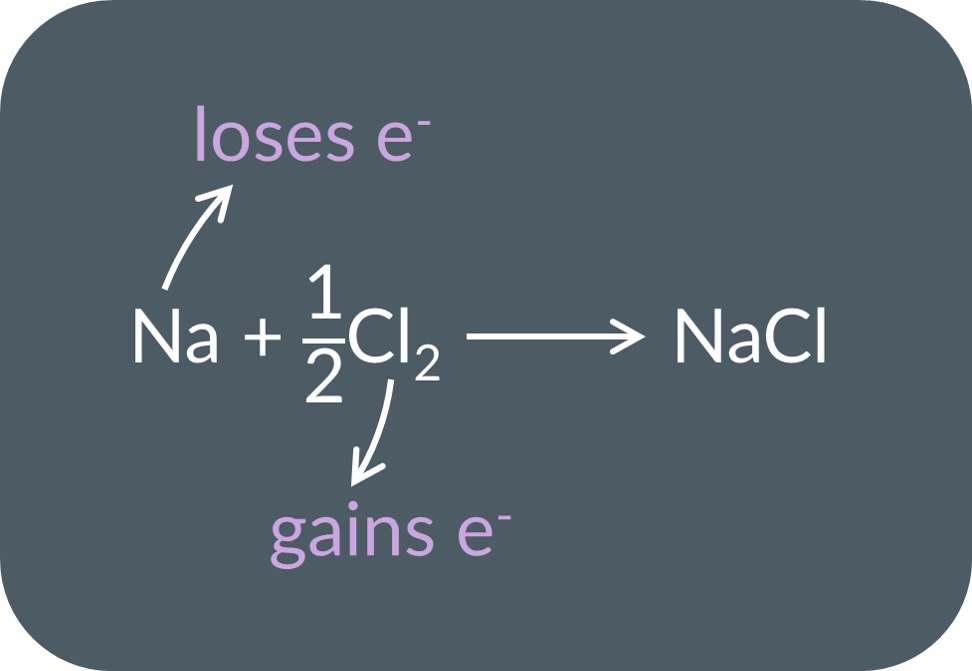
Energy for the actove transport of protons is supplied by …….. whcih are provided by …..
electrons
chlorophyll
Photoionstaion is when…..
light absorbed by chlorophyll and transpferred (energy) to the elctrons gain energy making them ‘exitatory’/excited state
When exited electrons move out of the chlorphyll, its ………. with a ……. charge
oxidised
positive
Electrons move through the electron transfer chain via a series of…
oxidation and reduction reactions
The series fo these reactions release….. enabling the …. …….. of protons from the stoma to the thylakoid psace to mainatain a proton gradient. The protons arent invlved in the ……-……. ……..
energy
active transport
oxidation-reduction
reactions
If the electron transfer chain grinds to a halt, this means that…
protons can’t be actively transported into the thylakoid space.
but the protons can still be diffues down a conc grad throughh atp synthase but as cocnentration is same across each side of membrane there will be no more proton gradient . If there isn’t a proton gradient, this means…
ATP can’t be produced: no diffusion means not atp synthesis as prprovideotons needed to rpovide energy
NADP is a C- enzyme what does this mean?
molecule helping an enzyme carry out its function
Once electrons reach the end of the transport chain, NADP is reduced by……….. an ….. and a ……… in the …….. (. which hasn’t been yet actively transported) at the same time. This form …….. alo known as ….. ………
gaining
electron
proton
stroma
NADPH
reduced NADP
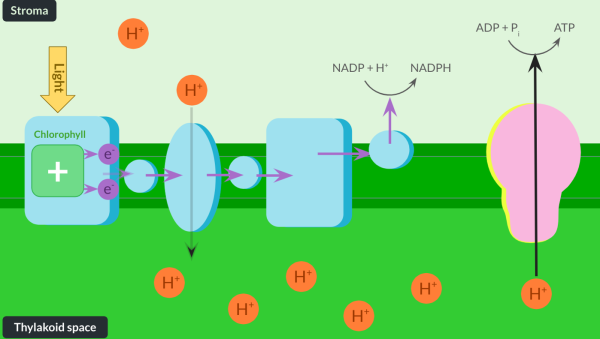
The two molecules needed for the LIR produced by the LDR are….
ATP
NADPH
The electons replaced during photoionisation of chlorophyll are replaced by the ……. of a …… molecule
photolysis
water
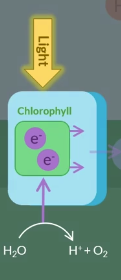
PHOTOLYSIS is when….. and occurs in the …. ….
water is split up via energy transferred from light into protons, oxygen atoms, electron. and occurs in the thylakoid space
Electrons produced by the photolysis of water replace those….
lost from chlorphyll
While the protonprodcued help maiantan the …. of …. in the ….. ……
concentration
protons
thylakoid
space
The oxygen produced is….
diffused out of the plant
used in respiration
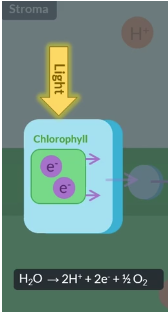
Once light hits the leaf, it’s absorbed by chlorophyll.
This light energy is…
the elctrons then
transferred to a pair of electrons
get excitatiry and propell out of the chlorophyll
To replace the electrons which have left the chlorophyll, light splits water into electrons and…
and this reaction is called ….
protons and oxygen
photolysis
next the electrons that left the chlorophyll move acrooss a set of protein complexes in teh thylakoid membrane through a series of ……
Biologists collectively refer to the complexes and molecules in the membrane as the…
asthe elctrons move through the ETC the OX+RED reactions result in release of energy, eabling a protein complex to actively transport …..
this ensures a …… is maintained across the thylakoid memebrane from the thylakoid space to the stroma
oxidation and reduction reactions
electron transfer chain
protons
proton/electrochemical gradient
the elcetrons at the end of the ETC react with …
This forms…
As a result of maintaing the proton gradient, protons in the thylakoid space diffuse down the proton gradient and back into the stroma via an enzyme.
This process is known as ,….
and supplies atpsynthase with energy to catalyse a reaction…..
NADP and a proton
reduced NADP or NADPH
ATP synthase
Chemiosmosis
ADP+Pi → ATP
Adaptation 1
The thylakoid membrane has a large surface area for molecules involved in the light-dependent reaction. This maximises the amount of ATP and NADPH that can be made at one time.v
Adaptation 2
Proteins in the grana hold the chlorophyll in such a way that the maximum amount of light can be absorbed at one time.
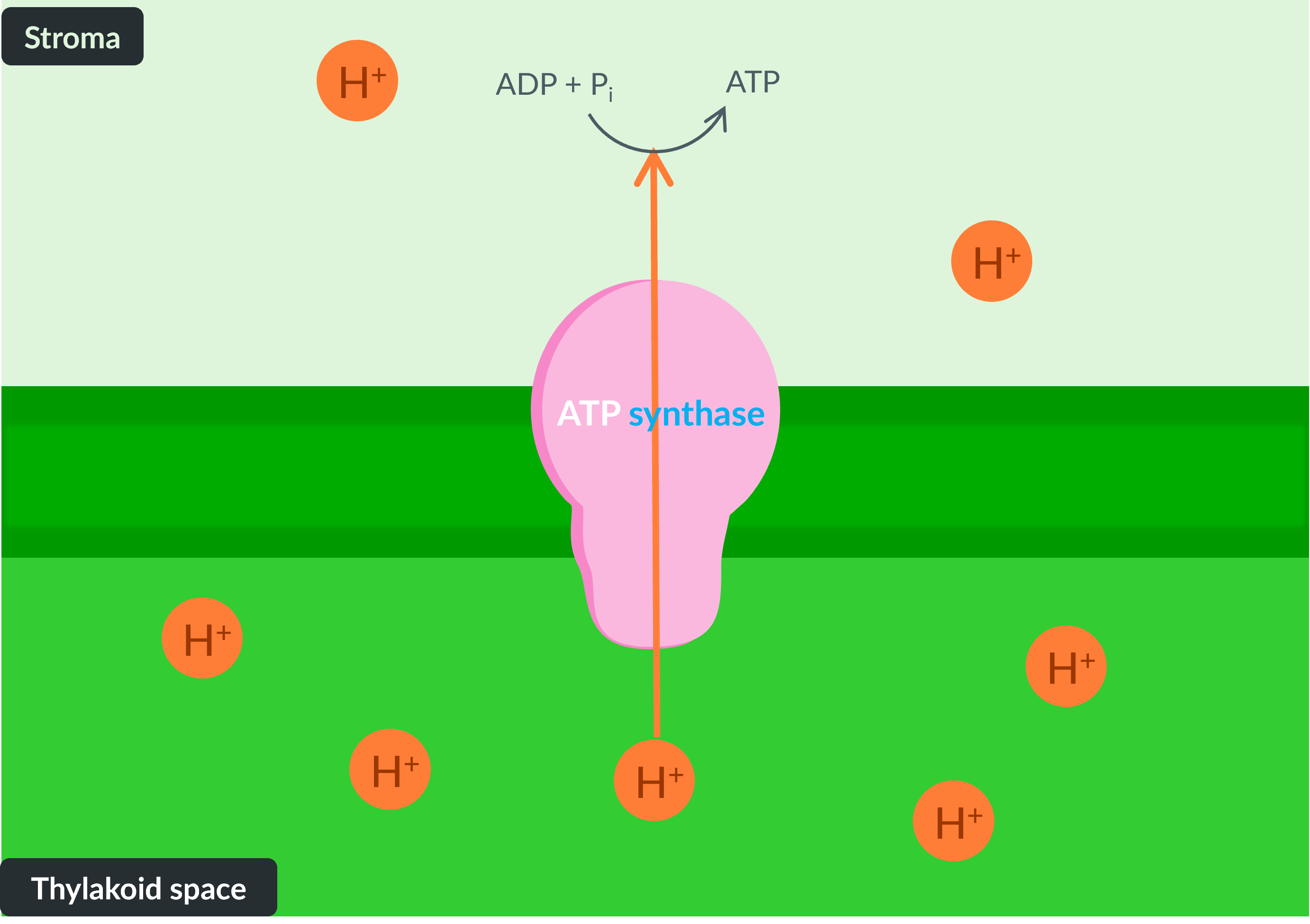
Adaptation 3
The thylakoid membranes contain ATP synthase for efficient ATP production. The membranes are also selectively permeable which allows them to establish and maintain a proton gradient.
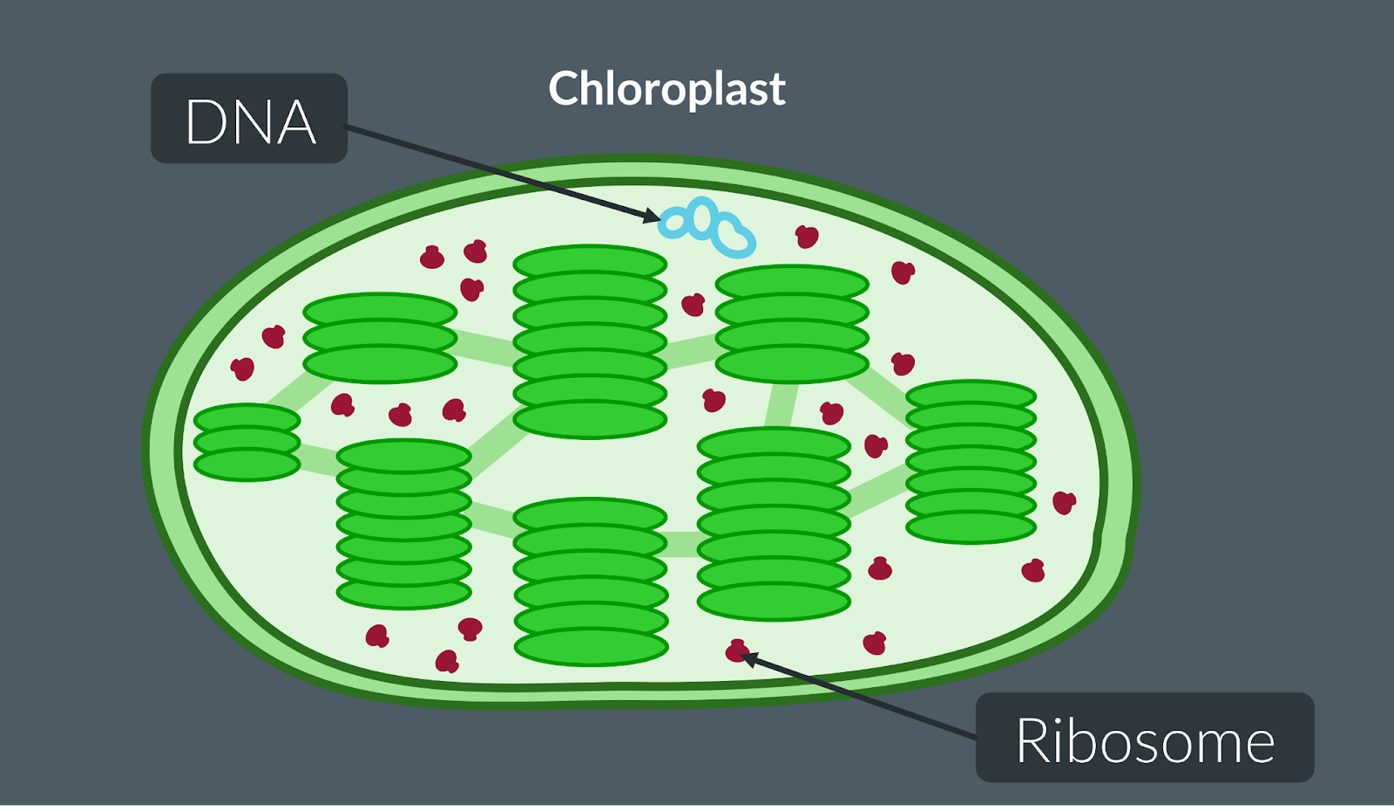
Adaptation 4
Chloroplasts contain both DNA and ribosomes. This means that proteins involved in the light-dependent reaction can be easily and quickly produced.
Explain the role of water in the light-dependent reaction.
Photolysis of water provides electrons to replace the electrons lost from chlorophyll during photoionisation.
In photolysis, light splits water into electrons, protons and oxygen.
Protons help maintain the high concentration of protons in the thylakoid space, and oxygen diffuses out of the plant or is used in respiration.
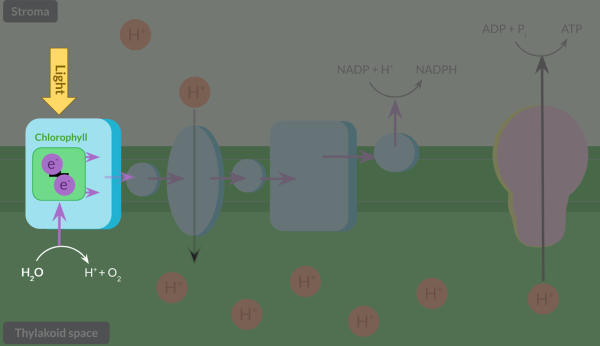
A student carried out an investigation of the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis in spinach leaves.
Explain fully how the student can use cell fractionation to isolate chloroplasts from a sample of spinach leaves.
….
The student used a redox indicator called methylene blue to investigate the light-dependent reaction. Methylene blue is blue when oxidised and colourless when reduced.
She set up three test tubes as follows:
Tube 1:1cm3 of the suspension without chloroplasts and 9cm3 of methylene blue, without tinfoil around the tube
Tube 2: 1 cm3 of chloroplast suspension and 9cm3 of methylene blue, with tinfoil around the tube
Tube 3: 1 cm3 of chloroplast suspension and 9cm3 of methylene blue, without tinfoil around the tube
All three test tubes were placed in a water bath at 25°C for 20minutes. The student recorded the colour of the solution in each test tube after 2020 minutes.
All three test tubes appeared blue initially. After 20 minutes, Tube 1 and Tube 2 remained blue while the solution in Tube 3 turned green.
Explain why Tube 2 remained blue but Tube 3 turned green.
……
What is the purpose of Tube 1?
Cell fractionation has three steps: homogenisation, filtration and ultracentrifugation. The sample of spinach leaves must be placed in an ice cold, isotonic buffer solution and homogenised using a homogeniser to break up the plasma membranes of cells. This produces a homogenate solution, which is filtered to remove large debris and unbroken cells. The resulting filtrate is placed into a tube and spun in a centrifuge at low speed. The resulting supernatant is pipetted into another tube and spun again at a faster speed. The resulting pellet, at the bottom of the tube, contains chloroplasts.
In Tube 3, methylene blue was reduced by electrons from the electron transfer chain in the light-dependent reaction. Methylene blue turns colourless when it is reduced but Tube 3 appears green because chlorophyll in chloroplasts has a green colour.
In Tube 2, there is no colour change because the tube is covered in tinfoil which prevents light entering the tube and reaching the chloroplasts. In the absence of light, the light-dependent reaction cannot take place so there are no electrons to reduce methylene blue. Therefore, methylene remains oxidised and remains blue.
Tube 1 contains methylene blue but no chloroplasts. This acts as a negative control to show that methylene blue does not change colour in the absence of chloroplasts. It shows that it is electrons from the light-dependent reaction that are responsible for reducing methylene blue and making it colourless.
Describe the process of photoionisation during the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis.
When light hits a leaf, chlorophyll absorbs the light. Light energy is transferred to electrons within chlorophyll, which are said to be in an excited state. After the electrons gain energy, they leave chlorophyll. Therefore, chlorophyll becomes positively charged as it is oxidised. This process is known as photoionisation.
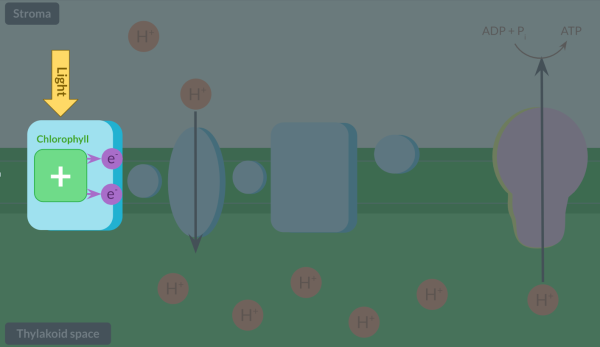
Describe the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis. Include details about what happens to electrons at the end of the chain in your answer.
After photoionisation, electrons move through a collection of protein complexes and molecules known as the electron transfer chain in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions. Electrons at the end of this chain react with NADP and a proton to form reduced NADP, another product of the light-dependent reaction.
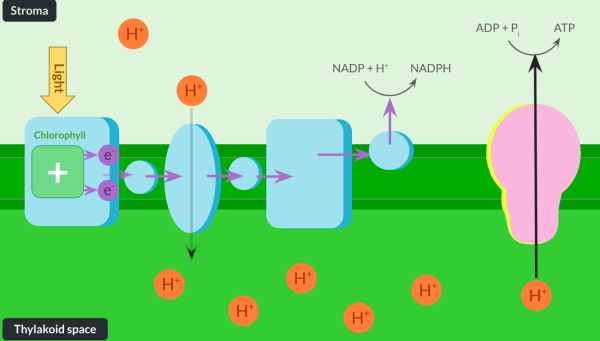
Describe how electrons lost from chlorophyll during photoionisation are replaced.
Once electrons in chlorophyll are lost during photoionisation, they are replaced by water in a reaction called photolysis. In this reaction, light splits water into electrons, protons and oxygen. Protons help maintain the high concentration of protons in the thylakoid space, and oxygen diffuses out of the plant or is used in respiration.
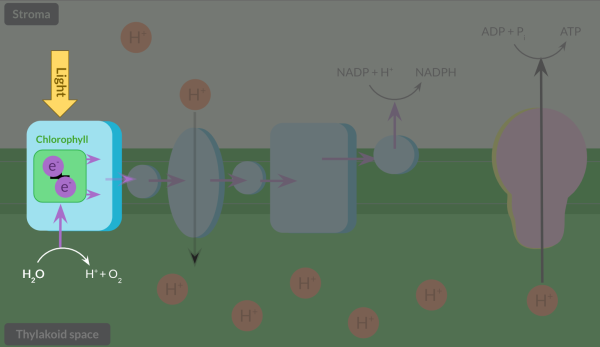
Outline fully the light-dependent reaction of photosynthesis, including details of the products of the reaction.
Once light hits the leaf, it is absorbed by chlorophyll, which is contained in a protein complex in the membrane. This light energy is transferred to a pair of electrons, leaving the electrons in an excited state. This is called photoionisation. These electrons leave chlorophyll and are replaced by electrons from the splitting of water in a photolysis reaction.
The electrons that left chlorophyll move along a set of protein complexes and molecules in the membrane, called the electron transfer chain, via a series of oxidation-reduction reactions. These reactions release energy, which is transferred to a protein complex in the thylakoid membrane, which actively transports protons from the stroma into the thylakoid space.
This maintains the proton gradient which allows chemiosmosis to occur, where protons diffuse back into the stroma via an enzyme called ATP synthase. Chemiosmosis supplies the enzyme with energy to catalyse the reaction of ADP and PiPi to form ATP.
Electrons at the end of the electron transfer chain react with NADP and a proton to produce reduced NADP, an important molecule that is required for the light-independent reaction.
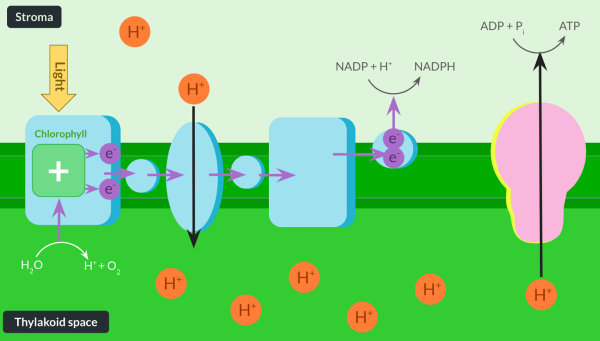
Explain the role of water in the light-dependent reaction.
Photolysis of water provides electrons to replace the electrons lost from chlorophyll during photoionisation. In photolysis, light splits water into electrons, protons and oxygen. Protons help maintain the high concentration of protons in the thylakoid space, and oxygen diffuses out of the plant or is used in respiration.