1-Sedimentary Rocks and Fossils
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What percentage of sedimentary rocks cover the earth’s surface?
75%
Why study sedimentary rocks?
contains all fossils and entire record of earth’s geological history
evidence for environmental change
source of economic minerals and materials
What are the kinds of sedimentary rocks?
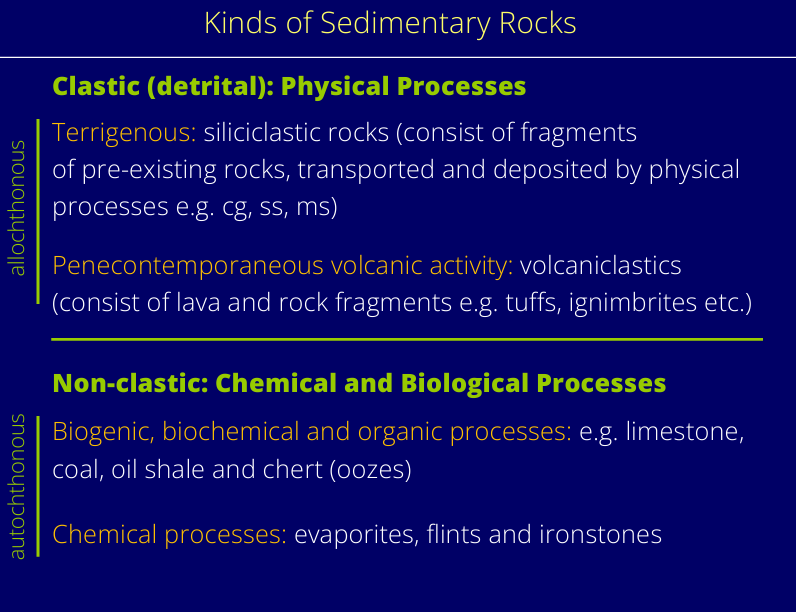
How do you describe a clastic sediment?
size
shape
composition
bulk properties
grain size distribution
texture
sedimentary structure
porosity
permeability
How do we measure particle/clast/grain size?
Sieving - standard for coarser grained sediment
Settling - standard for finer grained sediment, larger particles fall through water faster than smaller particles
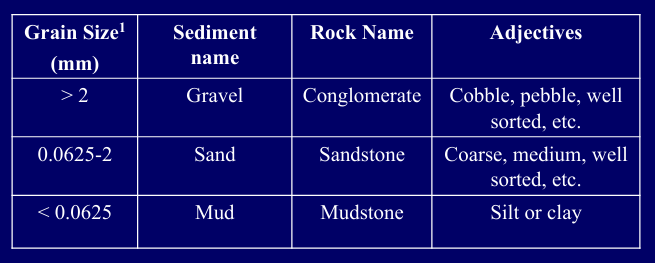
What is the Udden-Wentworth grade scale?
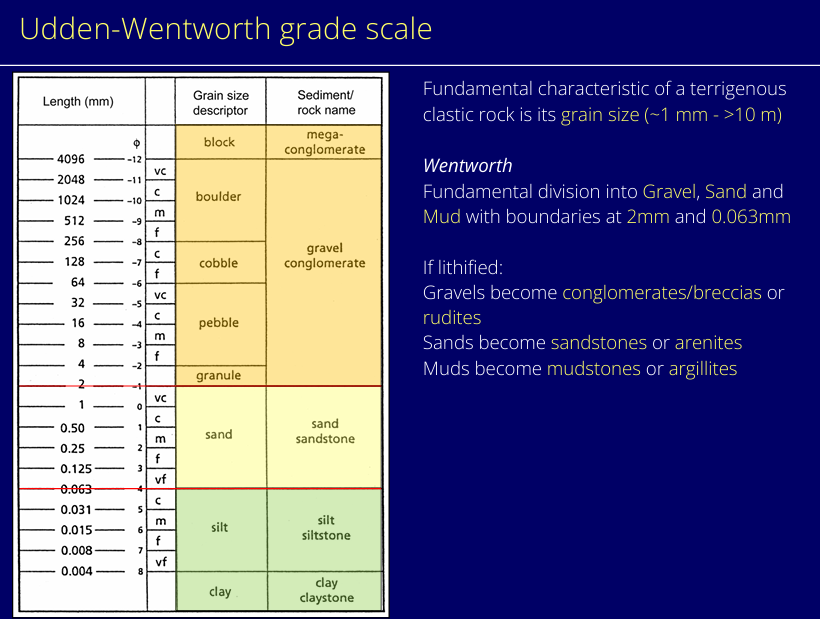
How do you calculate phi?

Overview of classification of terrigenous clastic rocks?
How do you describe particle shape?
Roundness (angularity) - sharpness of edges and corners
Sphericity - spherical circular
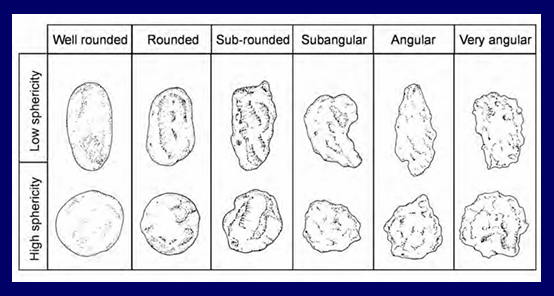
What determines size of particles, and shape and roundness?

What is packing or fabric?
The mutual arrangement of grains in the deposit
What is porosity and permeability?
Porosity: amount of void space, expressed as volume%
primary - formed at time of deposition
secondary - appeared in rock post depositional process
Permeability: describes the ease with which fluids can be forced through the porous sediment
What components are there to look at the geometry of the rock?
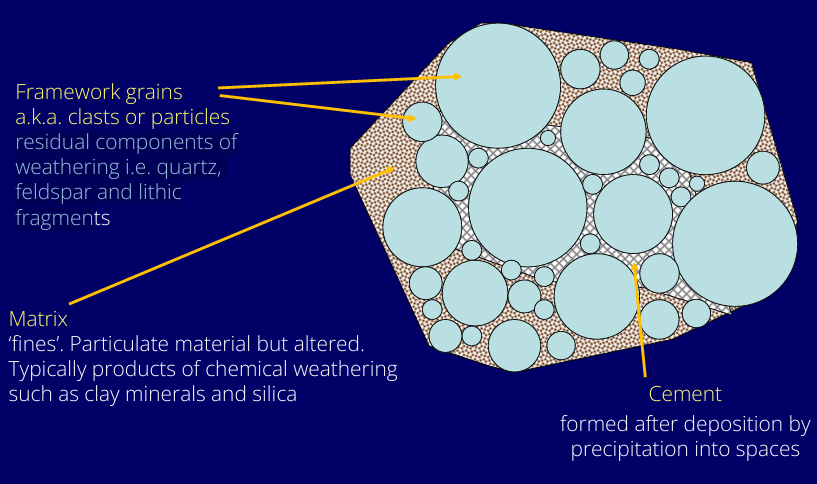
ppt slide of compositional components of sedimentary rocks

What is the origin of the clastic sediment?
Weathering of continental crust is primary source of terrigenous clastic material.

What are the major weathering processes?
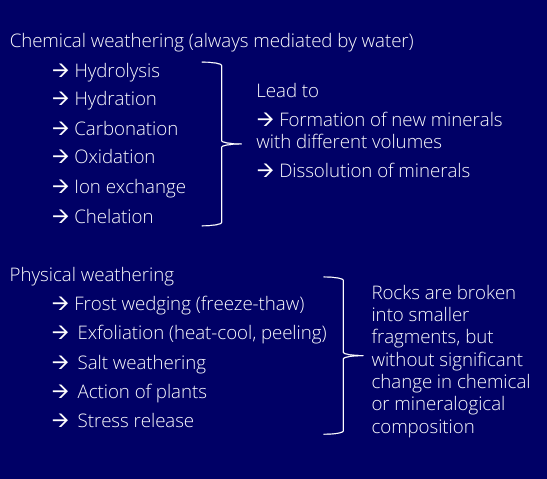
How does weathering control erosion rates?
chemical reactions quicker at high temps
high rainfall provide water needed for chemical weathering
humid tropics where chemical weathering is most rapid
arid and temperate climates where weathering rates are lower
Relief controls time available for weathering.
High relief = rapid erosion and short time for weathering
Low relief = low erosion and long time for weathering
In the Goldich Weathering Series, of susceptability of minerals to weathering, what mineral is most resistant to weathering?
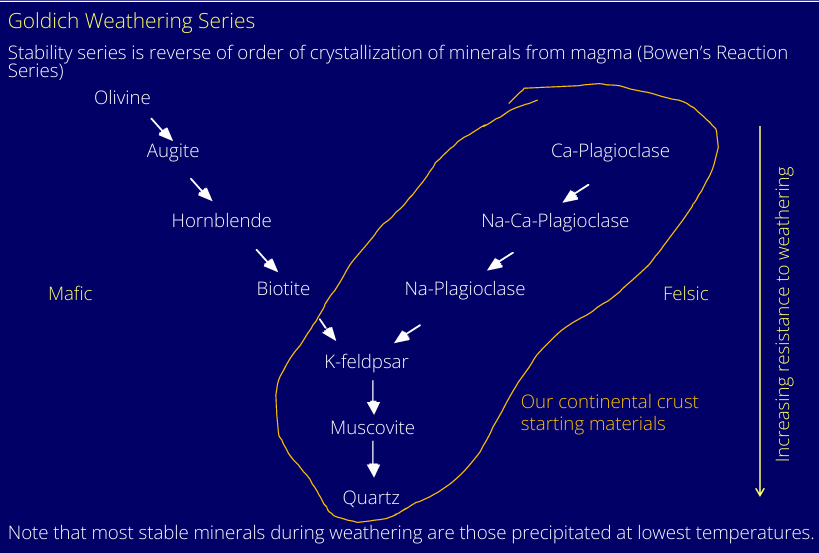
Tell me about quartz
most common mineral in sediments
effectively inert, stable at surface T and P
low solubility in water
resistant to chemical weathering
hard, and lack of cleavage
Gravel size quartz comes from vein quartz. Milky white
Sand size comes from crystalline source rocks e.g. granite, recycled quartz rich sandstone, or chert. Clear, glassy, slightly milky, NEVER DULL WHITE
Silt size quartz comes from fine grained metamorphic rocks, fine grained sediments, spalling of larger grains
What is meant by extinction?
Under crossed polars, extinction is where the mineral goes black every 90° rotation.
Tell me about feldspars
Subordinate to quartz in abundance.
feldspar content much more variable than quartz
mechanically weaker than quartz
cleavage
softer
chemically weaker, easily hydrolysed
unstable during weathering in soils
chemical weathers, reacts readily with water and weak acids to form clay minerals
white, cream, or pink but NEVER GLASSY, sometimes powdery if strongly weathered
Identifying feldspar and quarts

What are the different types of feldspars?

What are micas?
Silvery shiny catching light on bedding surface

What other constituents occur in sedimentary rocks?

What is responsible for the red/yellow/brown/purple colours?
Most sedimentary rocks contain some iron oxides.
Red = Hematite Fe2O3
Yellow, browns = Limonite/Goethite FeO.OH
What is the matrix often made from?
Clay minerals produced from chemical weathering of feldspars.
Often grey
What is cements?
Form during diagenesis
precipitated into pore spaces after de
position
lithifying agent that turns sediment in sedimentary rock
What are two common cements in sandstones?
1) quartz
2) Calcite
Difference between diagenesis and lithification.
Diagenesis = All post-depositional changes before metamorphism (includes lithification)
Lithification = Sediment → Rock
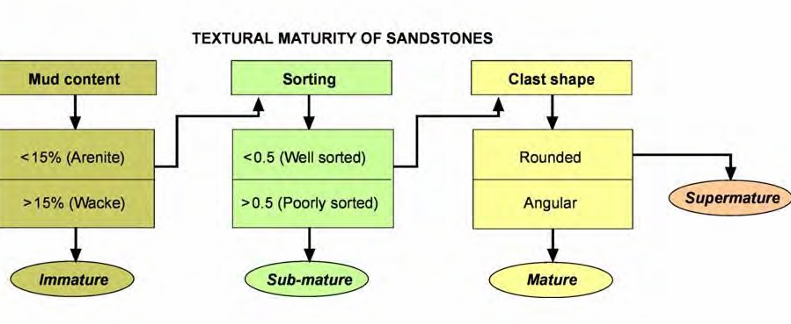
How do you classify sandstones?
Proportion of matrix, and then consider proportion of quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments.
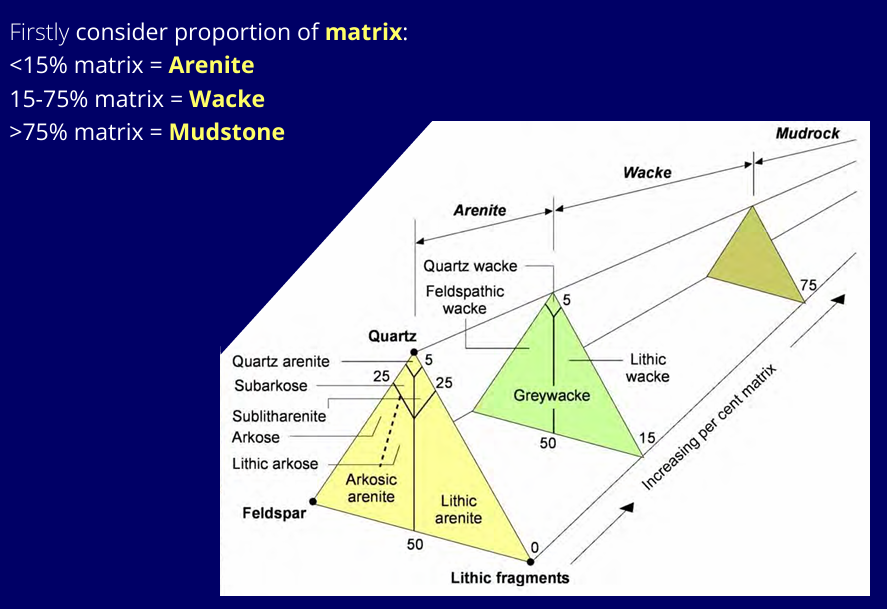
Classification of arenite from quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments
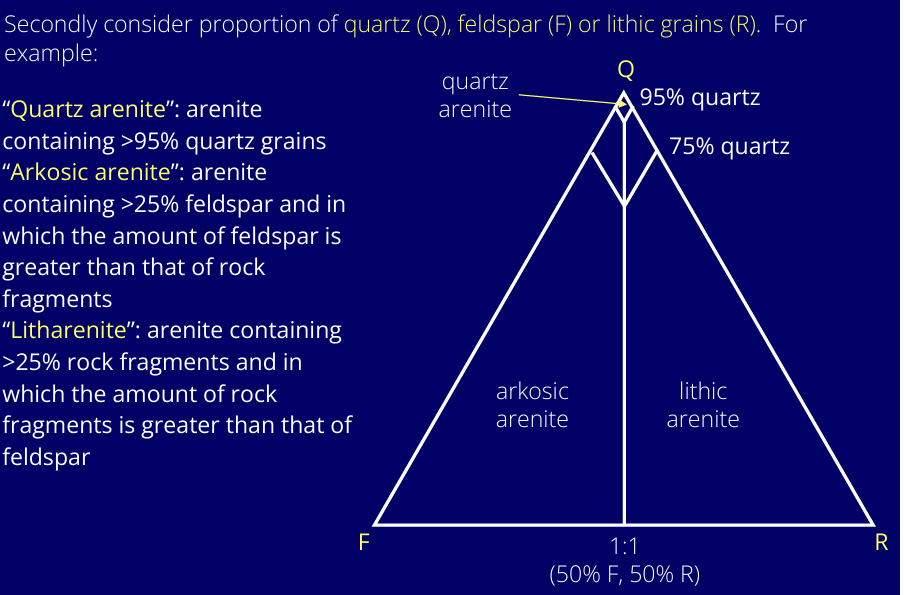
With increasing distance and time of transportation ….
grain size decreases
grain size sorting increases
angularity decreases/roundness increases rapidly
sphericity increases slowly
there is loss of feldspar, mica and other clasts in favour of clay matrix and quartz
The more matrix a rock has, tells us what about its transport?
The more matrix a rock has, the lower the energy, and the shorter the transport distance.
High energy & long transport → fine particles removed → well-sorted, little matrix.
Low energy & short transport → fine particles retained → poorly sorted, lots of matrix.
How does the name of the sandstone tell you about its maturity?