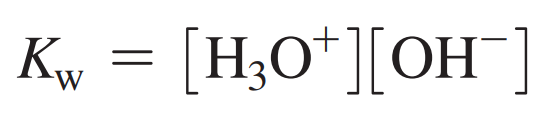Chapter 10: Acids and Bases and Equilibrium
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
Last updated 5:26 AM on 1/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Arrhenius Acids
Substances that produce hydrogen ions when they dissolve in water.
2
New cards
Svante Arrhenius
A Swedish chemist to first describe acids and bases.
3
New cards
*–ic acid*
The most common form of an oxygen-containing acid has a name that ends with *____*.
4
New cards
*–ate*
The name of oxygen-containing acid polyatomic anion ends in *____*.
5
New cards
*–ous acid*
An acid that contains one less oxygen atom than the common form is named as an *____*.
6
New cards
*–ite*
The name of less oxygen atom polyatomic anion ends with *___*.
7
New cards
Arrhenius Bases
These are ionic compounds that dissociate into metal ions and hydroxide ions when they dissolve in water.
8
New cards
Group 1A and Group 2A
Most Arrhhenius bases are formed from ____ metals.
9
New cards
hydroxides
Typical Arrhenius bases are named as ____
10
New cards
J. N. Brønsted and T. M. Lowry
They expanded the definition of acids and bases in 1923.
11
New cards
Brønsted–Lowry acid
It can donate a hydrogen ion to another substance.
12
New cards
Brønsted–Lowry base
It can accept hydrogen ion.
13
New cards
Conjugate Acid–Base Pair
It consists of molecules or ions related by the loss of one H+ by an acid, and the gain of one H+ by a base.
14
New cards
Amphoteric
Substances that can act as acids and bases.
15
New cards
acid
The strength of an ____ is determined by the moles of H3O+ that are produced for each mole of acid that dissolves.
16
New cards
base
The strength of a ____ is determined by the moles of OH- that are produced for each mole of base that dissolves.
17
New cards
Strong acids
These are examples of strong electrolytes because they donate H+ so easily that their ionization in water is virtually complete.
18
New cards
Weak Acids
These are weak electrolytes because they ionize slightly in water, which produces only a few ions.
19
New cards
Diprotic Acid
Carbonic acid that has two H+, which ionize one at a time
20
New cards
Strong Bases
These are ionic compounds that dissociate in water to give an aqueous solution of metal ions and hydroxide ions.
21
New cards
Weak Bases
These are weak electrolytes that are poor acceptors of hydrogen ions and produce very few ions in solution.
22
New cards
Equilibrium
* The rates of the forward and reverse reactions become equal.
* The reactants form products at the same rate that the products form reactants.
* It has been reached when no further change takes place in the concentrations of the reactants and products.
* The reactants form products at the same rate that the products form reactants.
* It has been reached when no further change takes place in the concentrations of the reactants and products.
23
New cards
Le Châtelier’s principle
It states that when equilibrium is disturbed, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions change to relieve that stress and reestablish equilibrium.
24
New cards
acidic solution
In this solution, the \[H3O+\] is greater than the \[OH-\].
25
New cards
basic solution
In this solution, the \[OH-\] is greater than the \[H3O+\].
26
New cards
pH Scale
A range of numbers typically from 0 to 14, which represents the \[H3O+\] of the solution.
27
New cards
7\.0
A neutral solution has a pH of ___.
28
New cards
acidic
In ____ solutions, the pH is below 7.0.
29
New cards
basic
In ____ solutions, the pH is above 7.0.
30
New cards
Salt
An ionic compound that does not have H+ as the cation or OH- as the anion.
31
New cards
Neutralization
A reaction between an acid and a base to produce water and salt.
32
New cards
Titration
A laboratory procedure n which we neutralize an acid sample with a known amount of base.
33
New cards
Antacids
These are substances used to neutralize excess stomach acid.
34
New cards
Buffer Solution
It maintains pH by neutralizing small amounts of added acid or base.
35
New cards
Acidosis
A condition that occurs when there’s an increase in the CO2 level that leads to a low blood pH concentration.
36
New cards
Alkalosis
A condition that occurs when there’s a decrease in the CO2 level that leads to a high blood pH concentration.
37
New cards
Ionization of Water Formula