10.3 Enzyme-coupled receptors
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
2 types of enzyme-coupled receptors
have their own enzyme activity
associate with another enzyme
4 types of extracellular signals that bind to enzyme-coupled receptors
growth factors
growth hormones
insulin
cytokines
5 types of growth factor extracellular signals
Insulin-like (IGF)
Epidermal (EGF)
Platelet-derived (PDGF)
Fibroblast (FGF)
Nerve (NGF)
Growth, proliferation, differentiation, survival of cells
extracellular signals are growth factors
slow cellular response to enzyme-linked receptors
changes in gene expression occurs
Changes in cytoskeleton
rapid cellular response to enzyme-linked receptors
extracellular signals are proteins attached to surfaces over which a cell is crawling
Receptor tyrosine kinases
largest class of enzyme-coupled receptors
has single transmembrane segment
Poorly suited to transmit a conformational change across the membrane
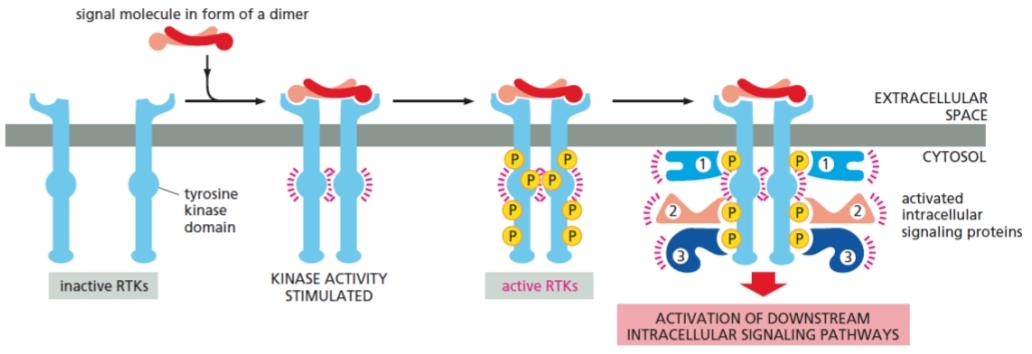
Dimerization
process caused by extracellular signal binding to RTK
results in two RTKs to link
activates kinase activity within receptor tails
Phosphorylation
process that dimer tails does upon one other
occurs on specific tyrosine residues
Docking sites
purpose of newly phosphorylated tyrosines for other intracellular signaling proteins
Ras
monomeric GTP-binding protein associated with the membrane
protein mostly indirectly activated by RTKs
directly activated by Ras-GEF
with a covalently attached lipid group for attachment to the inner plasma membrane
Mutant Ras
protein mutation involved in human cancers
exhibits no GTPase activity
cannot hydrolyze its bound GTP to be inactivated
promotes uncontrolled cell proliferation
Oncogene
type of mutated Ras gene
promotes uncontrolled cell proliferation and development of cancer
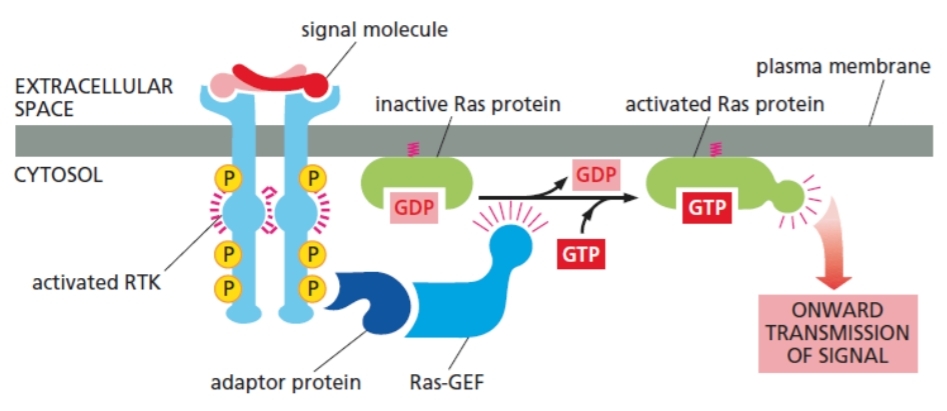
6 steps of activation of Ras by RTK
RTK activated
adaptor protein docks to specific phosphorylated tyrosine
Ras guanine nucleotide exchange factor (Ras-GEF) recruited by adaptor protein
Ras-GEF exchange GDP into GTP to activate Ras
GTP-activated Ras initiate multiple
downstream signaling pathways
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs)
promote exchange of bound GDP for GTP
switches on the GTP-binding protein like Ras
GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs)
stimulate hydrolysis of GTP to GDP
switches off the GTP-binding protein like Ras
MAP-kinase cascade
initiated phosphorylation cascade by GTP-activated Ras
Mitogens
extracellular signal molecules that stimulate cell proliferation
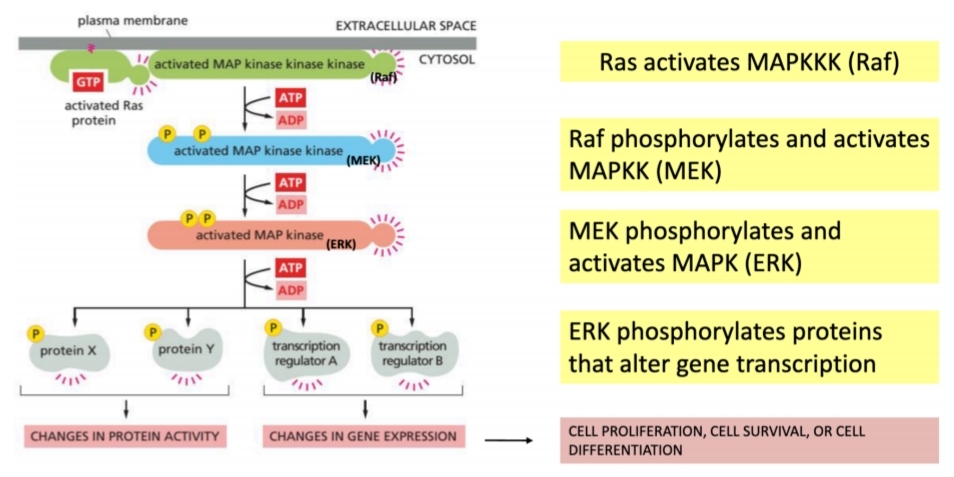
5 steps in the MAP-kinase cascade
Raf (MAPKKK) activated by GTP-activated Ras
MEK (MAPKK) phosphorylated by active Raf
ERK (MAPK) phosphorylated by active MEK
transcription regulators phosphorylated by active ERK
control over cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation
Protein tyrosine phosphatases
involved in termination of RTK response
protein that dephosphorylates added group to RTK dimer tails and other involved intracellular signaling proteins
Endocytosis
termination of RTK response
receptors are destroyed by digestion in lysosomes
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase)
enzyme activated by RTK to promote cell growth and survival
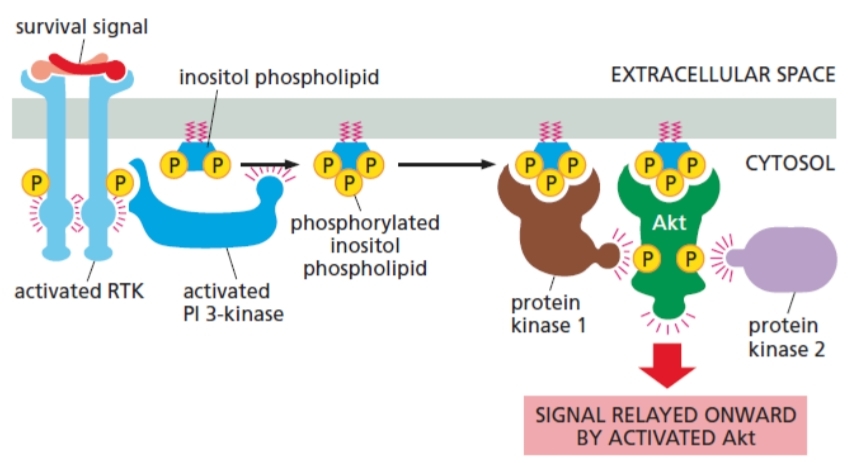
6 steps in activation of PI-3-kinase-Akt signaling pathway
extracellular survival signal (eg. IGF) activates RTK
PI 3-kinase recruited and activated by RTK
inositol phospholipid phosphorylated by PI 3-kinase to be docking sites
protein kinase B (Akt) docks
Akt is phosphorylated and activated by kinases
Activated Akt is released from plasma membrane and phosphorylates various intracellular signaling proteins
Protein kinase B (Akt)
serine/threonine protein kinase
promotes growth and survival of cell types
inactivates signaling proteins by phosphorylation
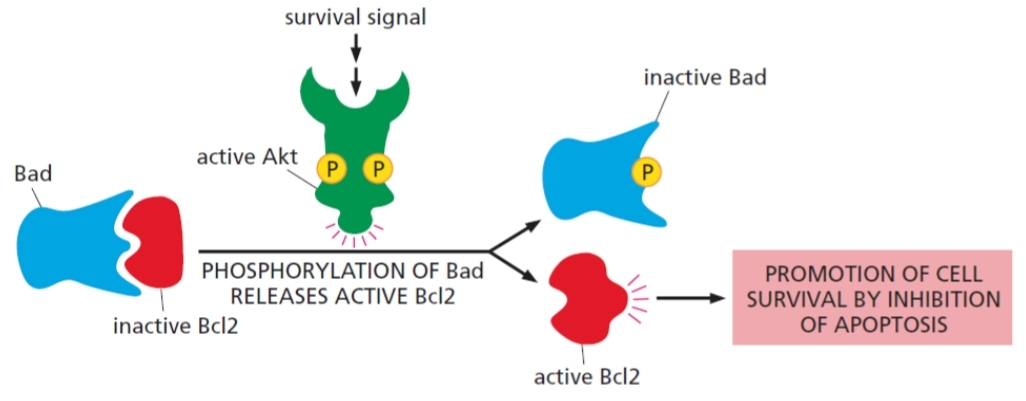
5 steps of Akt in cell survival
Bad phosphorylated by AKt
Bad rendered inactive
active Bcl2 released
cell survival promoted
Bcl2 VS Bad
Bcl2: suppresses apoptosis
Bad: unphosphorylated form inhibits the Bcl2; promoted apoptosis
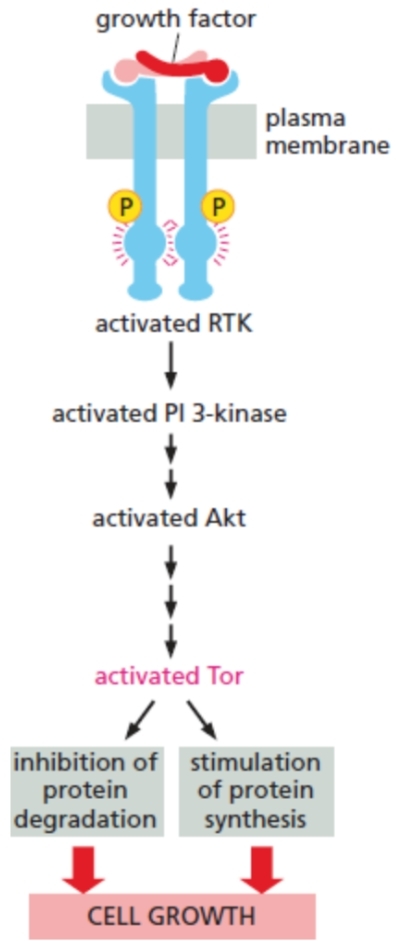
5 steps of Akt in cell growth
growth factor bind to RTK
PI-3-kinase-Akt signaling pathway activated
Tor shutdown protein is phosphorylated by Akt
Tor activated
Tor stimulates protein synthesis and inhibits protein degradation
Tor
large serine/threonine kinase
stimulates cell growth
enhances protein synthesis and inhibiting protein degradation
Rapamycin
anticancer drug
slows cell growth by inhibiting Tor