2.6.1 - Possible Macroeconomics Objectives
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
econ
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What are the 5 main macroeconomic objectives?
1. economic growth 2. low unemployment 3. low and stable inflation 4. balance of payments equilibrium 5. balanced government budget
What are the 2 other macroeconomic objectives?
1. environmental protection 2. greater income equality
What is the annual target rate of economic growth for most developed countries?
2-3% is considered sustainanbe growth
Why is 2-3% a good rate?
less likely to cause excessive demand pull inflation
What does economic growth have positive impact?
1. confidence 2. consumption 3. investment 4. employment 5. incomes 6. living standards 7. government budgets
What was growth like from 1998-2007?
steady, fluctuating between 2-4%
What was growth like from 2008-2015?
global financial crisis, followed by bounce back due to government intervention and then steady growth
What was growth like from 2016-2019?
gradual disinflation possible due to future expectations regarding brexit
What was growth like from 2020+?
supply chain issues due to brexit
Define monetary policy
using the money supply and interest rates to manipulate consumptions and therefore AD
What is the target rate for unemployment?
4-5%
Is the target level of unemployment close to full employment?
yes, there will always be a level of frictional unemployment How are you doing?
What's Japans level of full employment?
2.5% unemployment, all countries are different
What is an example of an increased emphasis on the unemployment rate?
e.g racial unemployment, in 2021, black unemployment in uk was 11% and white was 4%
What can you say about the relationship between GDP and unemployment?
they're inversely proportional
What is the UK's target inflation rate?
2% using the CPI
Why is a low rate of inflation desirable?
it is a symptom of economic growth
What do demand side policies do to inflation?
ease demand pull inflation
What do supply side policies do to inflation?
ease supply side inflation
What was the inflation rate in 2023?
4-5%, eroding household purchasing power
What are 2 reasons low and stable inflation is important?
1. allows firms to plan for future investments 2. price stability for consumers
Why is it bad to have a high government debt?
lenders lose confidence in ability to repay and uk may have to increase interest rates
What tough choices can result from a deficit?
cutting public sector pay, raising taxes, reducing unemployment benefits
What was the most recent blow to the budget?
covid-19
In April 2021, what did the gov say their aim was environmentally?
to reduce emissions by 78% by 2035
What are 3 facts about the emissions aim?
1. based on emissions level of 1990 2. most ambitious climate change targets globally 3. includes international aviation and shipping emissions
What are 3 broader environmental aims?
1. focus on sustainability 2. reduction of negative externalities of production 3. 100% energy from renewable sources by 2035
What do high levels of income inequality cause?
social unrest
What is the gini target of most developed countries?
0.3-0.4
Why is perfect income inequality not desirable?
removes incentive to work and study
How does unchecked capitalism cause high income inequality?
1. wealthy can keep buying factors of production 2. concentration of ownership becomes more narrow
How can income inequality cause poverty?
a 1% increase in income inequality can push more households into absolute poverty
What is the acronym in remembering how to evaluate supply-side policies
TIPEE t - time log i - inequality p - popularity e - expense e - environment
What is the other acronym used to evaluate everything?
WEESTOP w - wider context e - equity e - effectiveness s - scale t - time o - opportunity cost p - prioritisation
What is the definition of inflation?
The general and persistent rise in the average price level of a country
What is the UK government target for inflation?
Low, stable inflation: 2% plus or minus 1%

What is the definition of unemployment?
The number of people out of work but actively seeking work

How is unemployment calculated?
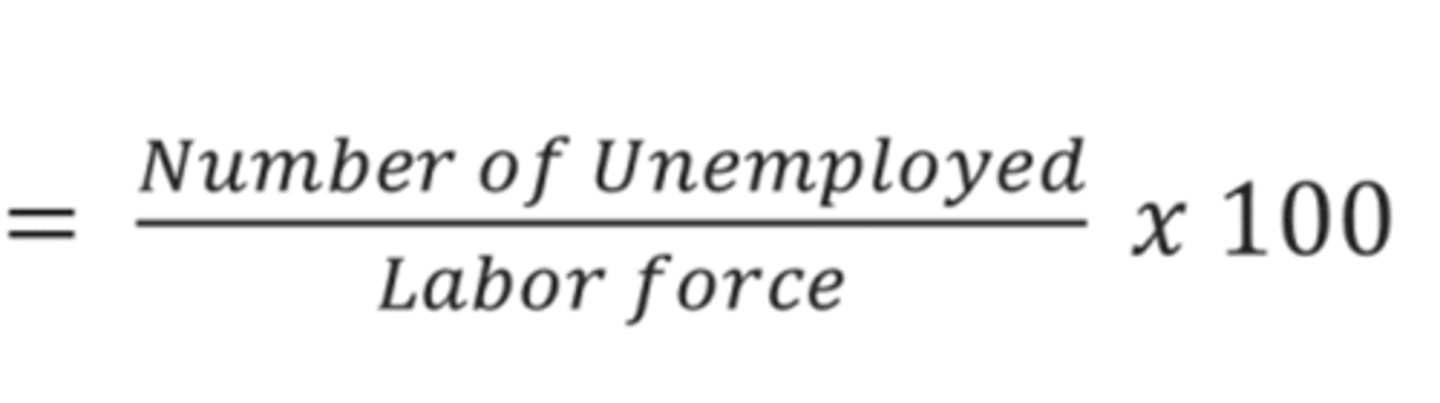
What percentage of the UK population are unemployed (2023)?
3.8%
What is meant by "Equilibrium in the Balance of Payments"?
Equilibrium in the flows of money in and out of the country (imports and exports), target for it to be equal
What are the pros and cons of having a Balance of Payment defecit
Pros: People in a country can enjoy a higher living standard as they are living beyond their capacity, people are more wealthy as they get consumer goods from abroad
Cons: Makes the economy seem weak and uncompetitive, can cause an increase in inflation levels
Why is Balance of Payments an indicator of a country's economy?
It shows how many goods and services a country is producing, and how much is being imported from abroad
What is the definition of GDP?
The Gross Domestic Product is the monetary value of all finished goods and services made in a country over a period of time
What is meant by "High, Positive, Sustainable Economic Growth"?
In the short run, an increase in the real percentage change in GDP. In the long run, it refers to increasing the productive capacity of the economy

What does it mean to "Balance the Government's Budget"?
When the government collects the same amount of money it spends
What can an increase in government debt do to an economy?
It can affect the currency and causes downgrades in the rating of a country and its ability to make future borrowings
What is the government target to protect the environment?
To reduce the UK carbon emissions to 5% by 2030 and to preserve the natural state of the environment

What is the meaning of 'relative poverty'?
Lack of income and resources precluding from having a standard of living considered acceptable by their society (e.g. 60% of median income in the EU)

What could a failure to reach some of these targets lead to?
A change in government
