SNC1W: Electricity Unit Test Review Package
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Energy
The ability to do work.
Chemical Potential Energy
Energy released when chemical reactions take place; sources include fuel, food, and batteries.
Elastic Potential Energy
Energy stored in a stretched or compressed object that wants to return to its original state.
Electrical Energy
Energy transferred by an electric current.
Sound Energy
Energy in the form of a sound wave.
Thermal Energy
Energy of an object due to its temperature; also known as heat energy.
Light Energy
Energy in the form of visible electromagnetic radiation.
Nuclear Energy
Energy released when nuclear reactions take place; this is the source of the Sun's energy.
Useful Energy
Energy transferred to the intended purpose of a device.
Wasted Energy
Energy transferred to an unintended purpose.
What are Protons, where are they found, and what’s their charge?
Subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom that have a positive charge.
What are Electrons, where are they found, and what’s their charge?
Subatomic particles that are found in the orbital of an atom and have a negative charge.
What are Neutrons, where are they found, and what is their charge?
Subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom that have no charge.
Conductivity
The ability of metals to conduct electricity and heat due to free electrons.
Malleability
The ability of metals to be hammered into sheets.
Ductility
The ability of metals to be drawn into wires.
Static Electricity
Stationary electrical charges that accumulate on the surface of objects.
Electrostatic Series
Arranges materials based on their ability to hold on to electrons.
Charging by Friction
Charging that occurs when different materials are rubbed together, causing electron transfer.
Charging by Conduction
Charging that occurs when a charged conductor touches a neutral conductor, transferring charge.
Charging by Induction
Charging that occurs when a charged object causes a temporary movement of electrons in a neutral object.
Laws of Electric Charge
Opposite charges attract, like charges repel, and negative/positive and neutral attract.
Current and what is a measured in?
The flow of electrons through a conductor measured in Amps.
Potential Difference
The amount of electrical potential energy per Coulomb, also known as voltage.
Volt
A unit that measures electrical potential energy per Coulomb.
How do batteries work in a circuit (what transformations take place)?
In a battery, a chemical reaction takes place that creates a build up of electrons on the negative side of the terminal. When connected to a circuit, a battery provides energy to push electrons uniformly since they are repelled to the negative side and attracted to the positive side.
What happens to potential difference in a Series Circuit?
the voltage is split among all the loads.
What happens to potential difference in a Parallel Circuit?
The voltage stays the same across each component.
Current in Series Circuits
The current stays the same because there’s only one pathway for all the electrons.
Current in Parallel Circuits
The current is divided by the number of paths available in the circuit.

What does this represent on a circuit diagram?
connecting wire
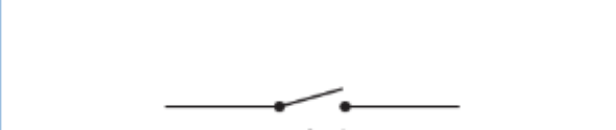
What does this represent on a circuit diagram?
switch
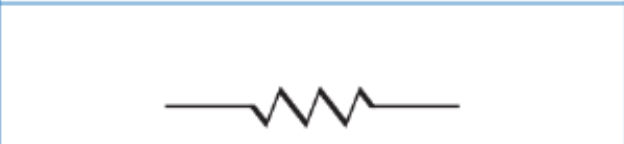
What does this represent on a circuit diagram?
Resistor/load

What does this represent on a circuit diagram?
Battery
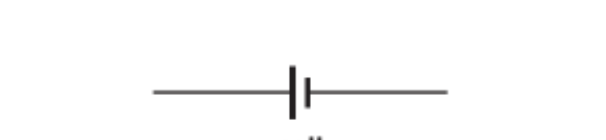
What does this represent on a circuit diagram?
Cell
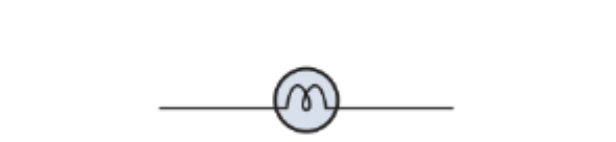
What does this represent on a circuit diagram?
Bulb
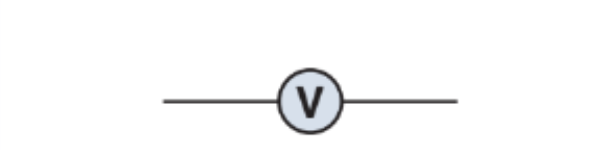
What does this represent on a circuit diagram, how is it wired and what does it do?
Voltmeter, wired in parallel, measures the potential difference (V)
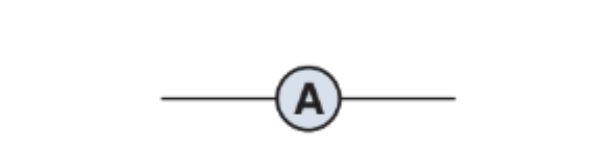
What does this represent on a circuit diagram, how is it wired and what does it do?
Ammeter, wired in series, measures the current flowing through the circuit (amps)
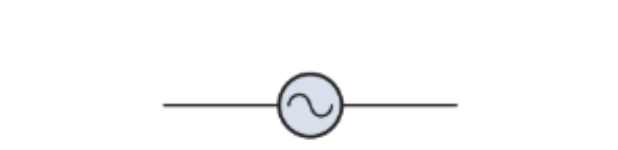
What does this represent on a circuit diagram?
AC source