practice quiz 3 deviations from mendel
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
A plant scientist finds a corn plant with red seeds instead of yellow. They cross the true-breeding red x yellow and find that the F2 has a 3:1 ratio. Interestingly, while storing the seeds in the lab the researcher realizes that mice prefer the yellow seeds to the red. This is most likely an example of which genetic phenomenon?
Pleiotropy
The same plant scientist finds another corn plant with purple seeds instead of yellow. They cross the true-breeding purple x yellow and find that the F2 has a 9:7 ratio. This is most likely an example of which genetic phenomenon?
Epistasis
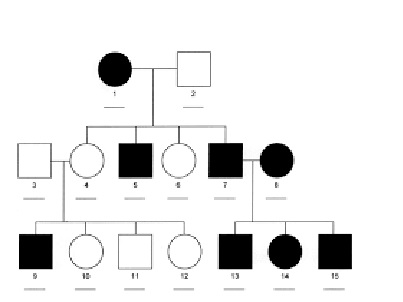
This pedigree is an example of what type of inheritance? Assume that in this case there is no, and I mean absolutely no, possibility of outside individuals being heterozygous.
X linked recessive
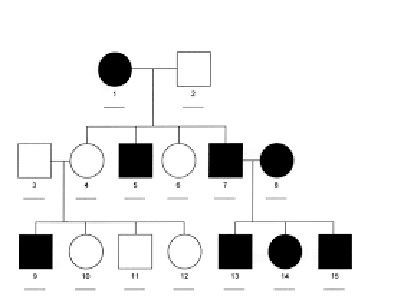
In this pedigree, which individual must be homozygous for the gene causing the trait (use the #s below the individuals to identify the individuals.) Again assume that in this case there is no, and I mean absolutely no, possibility of outside individuals being heterozygous.
Individual 1
A corn researcher takes a true-breeding plant that grows 6 feet tall and crosses it with a true breeding plant that grows 5 feet tall. The F1 progeny are all 5.5 feet tall and the researcher knows there is only one gene involved. What type of genetic phenomenon is this?
Incomplete dominance
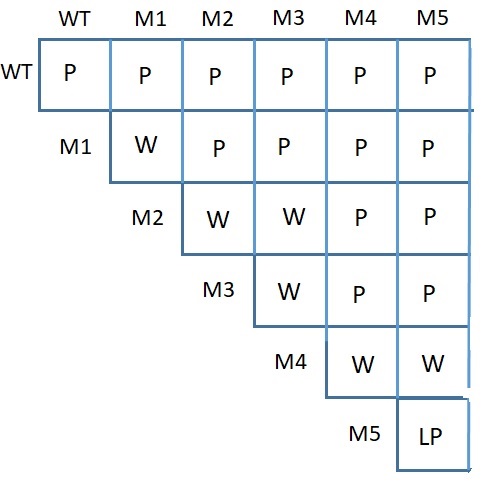
A plant scientist (Yes, all real scientists are plant scientists) found a set of white and light purple plants from a species where wildtype is Purple. Using the complementation cross table, how many genes have they found that influence this trait?
3
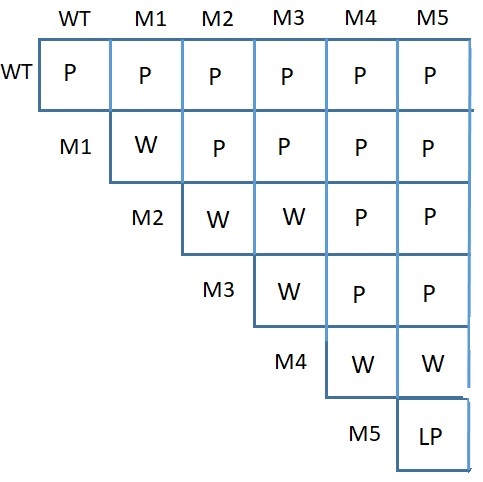
In the same complementation cross as previously shown. The researcher takes the F1 from the cross between M1 and M2 and selfs them. Which of the phenotypic ratios would you predict in the F2?
Variant of 9:3:3:1