Sources of Finance- Lecture 5
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What should be the source of most of a companies long term finance?
Ordinary share capital (equity)
Who bears the greatest risk?
Ordinary Shareholders
Why do ordinary shareholders bear the greatest risk?
Receive dividends last (they aren’t guaranteed)
In liquidation they are paid last
What are the disadvantages of ordinary shares?
Dividends are not guaranteed
Dilution of control if new shares issued
Share price may fluctuate, affecting perceived company value
What are preference shares?
A type of equity security that gives shareholders priority over ordinary shareholders in dividends and in liquidation.
However no voting rights
Explain convertible preference shares.
Can be converted into ordinary shares at some future date
Explain cumulative preference shares.
If a dividend is not paid it will be carried forward for payment at some future date.
Explain redeemable preference shares.
Company can buy back the shares at a fixed future date or under specific conditions.
Explain participating preference shares.
Shareholders receive fixed dividend plus a share of additional profits
Why are preference shares called hybrids?
They have characteristics of both equity and debt
fixed dividends and priority (debt like) plus ownership and residual rights (equity like)
What is ex dividend?
Shares sold without the right to receive the next dividend
The dividend goes to the previous shareholder
What is cum dividend?
Shares sold with the right to receive the next dividend
What are the 3 methods of raising equity?
Issue of ordinary shares (rights issue) and (new issue)
Issue of preference shares
Retained earnings
Explain how retained earnings acts as a method of raising equity?
Retained earnings are profits from previous years are retained in the business instead of paid as dividends
Does not require issuing new shares
increases shareholders equity naturally
Cost effective, no external financing needed
What is a rights issue?
When a company offers existing shareholders the right to buy additional shares at a discounted price in proportion to their current holdings.
With a rights issue why are shares usually offered at a significantly discounted price from the market value?
To make the offer attractive and encourage shareholders to take up or sell the rights so that the issues are fully subscribed
Also safeguard should the market price of shares fall before the rights issue is completed
What are the advantages of rights issue?
Raises capital quickly without going to the public
Protects ownership of existing shareholders
Lower issue costs
What is the theoretical ex rights price?
The expected market price of a share immediately after a rights issue

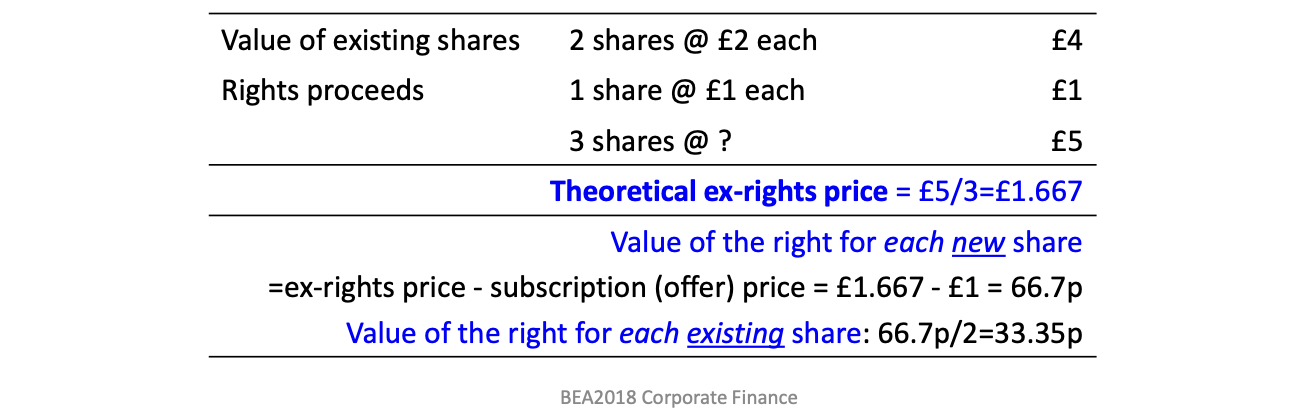
When would a rights issue impact shareholders wealth?
If the shareholder does nothing at all
The shareholder’s proportion of ownership decreases because the total number of shares increases
Why are rights issues cheaper then public issues?
Because they avoid extensive marketing, underwriting and regulatory costs.
How is control maintained with rights issues?
Existing shareholders are offered shares in proportion to their current holdings, so ownership and control are largely unchanged
How are rights issues fair to existing shareholders?
Shareholders are given the first opportunity to invest further at a discounted price
Why is it that limited funds can be raised with rights issue?
Existing shareholders may have limited personal funds, so rights issues may be unsuitable for raising very large amounts of capital
What are the disadvantages of a rights issue?
Limited funds can be raised
Less suitable for unlisted companies
Negative shareholder reactions
Market price uncertainty
How may shareholders react negatively to a rights issue?
They may feel pressured to either invest more money or sell their rights
Some may sell their shares, which can drive the share price down
What is a new issue?
When a company raises equity by issuing shares to new investors rather than offering them first to existing shareholders.
What is placing?
When a company issues new shares directly to a small number of institutional investors at an agreed price.
What are the advantages of placing?
Quick and cheap compared to a public offer
Lower issue costs (less marketing and documentation)
Certainty of funds
What is a public offer?
Shares are offered to the public usually through a stock exchange
What are the advantages of a public offer?
Can raise large amounts of capital
Wider ownership base
Increases company profile and visibility
What are the disadvantages of a public offer?
High issue costs (legal, underwriting,marketing)
Time consuming and heavily regulated
Share price risk if the offer is not well received
What are the advantages of being listed on the stock market?
Raising finance on flotation (IPO)
Improved access to future finance
Shares can be used as an acquisition currency
Enhanced corporate profile
Explain the advantage of raising finance on flotation? (stock market)
When a private company becomes listed existing owners can sell part of their shareholding to the public
This allows founders and venture capitalists to realise (exit) their investment while the company continues operating
How does being listed on the stock exchange improve a companies access to finance?
A listed company has easier and cheaper access to equity capital through:
Rights issues
News issues to the public
Listing increases investor confidence due to greater transparency and regulation
Can shares be used as acquisition currency? (stock market)
YES
Listed shares are more liquid and target company shareholders are more willing to accept listed shares than private company shares
How does being listed help a company’s profile?
It increases the company’s public visibility, credibility and reputation which can help with customers, suppliers and lenders
Provide a summary of the advantages of being listed on a stock exchange.
Listing on a stock exchange provides an exit route for existing shareholders, provides access to equity finance, enhances corporate profile and allows shares to be used a liquid currency in acquisitions.
What are the disadvantages of being listed on the stock exchange?
High costs of listing and compliance
Increased public scrutiny and loss of privacy
Pressure from shareholders
Greater risk of takeover
Increased vulnerability due to transparency
Explain how being listed on the stock exchange has high costs?
Obtaining and maintaining a listing is expensive involving:
Legal and advisory and listing fees
Ongoing compliance costs
Do listed companies have strict disclosure requirements?
Yes, listed companies on the stock exchange have stricter disclosure requirements than private companies increasing costs
How does being listed on the stock market lead to a greater risk of takeover?
If shareholder expectations are not met investors may sell their shares, reducing the share price
This increases the risk of a hostile takeover as the stock market acts as a market for corporate control
What occurs if being listed on the stock exchange leads to greater financial transparency?
Regular reports means that bidders are more easily able to select likely acquisition targets, whose shares they can then seek to acquire on the open market.
What are the ways a company can increase the number of shares in issue without raising any additional finance?
Scrip issues
Share splits
What is a scrip issue?
A conversion of existing capital reserves or retained earnings into additional shares
What is a share split?
A share split divides existing shares into a larger number of shares by reducing the nominal (par) value per share.
E.g. a company with 1 million shares with a par value of 50p each could, as a result of a share split have 2 million ordinary shares with par value of 25p each.
What are the two ways of raising long term finance?
Equity (long term finance without repayment)
Debt (long term finance with repayment)
What are the two main ways firms can raise long term debt?
Through banks - by taking a term load that is helf until it is fully repaid
Through financial markets- by issuing bonds
Explain what the term bond means?
A bond is a general label for long term loans made to companies where investors require regular interest payments and repayment of the principal at a fixed future date.
What actually is a bond?
A written promise to repay borrowed money usually with interest.
What does it mean when interest payments on bonds are treated as a business expense?
They are tax deductible
This creates a tax shield, because interest is paid before tax is calculated
What is a debenture?
A written acknowledgement of debt. It may be secured or unsecured.
What is the priority of payment for debentures?
Debentures are paid in order of issue
Earlier debentures have higher priority than later ones
What are debentures lower in the repayment hierarchy called?
Junior debentures
Subordinated debt
These carry higher risk and usually higher interest rates
What is a junk bond?
Unsecured loan stock
Issued by a borrower with sub investment grade credit quality
How can we judge how safe a bond is?
Through credit rating agencies (like Standard & Poor’s)
Those with a BBB or higher are safe
Low risk of default
Lower interest
What is the credit rating of a junk bond?
Below BBB so unsafe
High risk of default
High interest
What sort of companies issue junk bonds?
By financially weaker companies as they have low credit ratings and offer high interest because investors face a higher risk of not getting their money back
What is interest?
The money a borrower pays to the investor for using their money
It is the cost of borrowing
What are restrictive covenants?
They are rules or conditions in a loan agreement that the borrowing company must follow so that it stays financially safe and can repay its debts
What are some examples of restrictive covenants?
Dividend restrictions - limited profit it can pay to shareholders
Financial ratios- certain ratios must be kept above a minimum
Financial reports- must regularly send reports to the lender to monitor progress
Issue of further debt- limits how much new borrowing the company can take
Asset backing- must maintain a minimum level of tangible assets
What is asset backing?
A company’s tangible assets act as security for a loan, giving the lender confidence they can recover money if the company defaults.
What are deep discount bonds?
Bonds sold for much less than their face value (par value)
They pay a low or no interest during their life
When the bond matures the company repays the full face value
Why do investors like deep discount bonds?
Capital gains focus- most of their return is profits at the end instead of regular interest payments
Tax benefits- capital gains and interest income may be taxed differently so some investors prefer capital gains
Lower cash outflow during the life of the bond- they pay little or no interest which helps if cash flow is tight
What are zero coupon bonds?
Bonds that pay no interest at all
Investors make money only from the increase in value (capital gain) when the bond matures
What are asset backed securities?
Financial securities backed by future income, not physical assets like buildings or equipment.
e.g. patents,copyrights or mortgages
What are convertible bonds?
Bonds that pay interest but can be turned into shares, giving investors a chance to benefit from company growth while companies can borrow more cheaply
They are a hybrid: part debt and part equity
Why do companies issue convertible bonds?
They can pay lower interest than regular bonds because the conversion feature is attractive to investors
Useful for risky companies with high growth potential
Why do convertible bonds pay a lower interest?
Investor gets interest + the chance to become a shareholder if the company grows.
The conversion option is valuable so the investor is willing to accept lower interest in exchange
What are the downsides of issuing convertible bonds?
Dilution for existing shareholders
if conversion terms are too generous bondholders could gain a lot while current shareholders lose value
Must balance debt and equity carefully
What is a warrant?
A right to buy company shares in the future at a fixed price.
Usually issued with bonds as a “bonus” to make the investment more attractive
What are the benefits for investors of issuing warrants?
Low initial outlay compared to buying shares directly
Lower risk of loss than ordinary shares
High profit potential if the share price increases
What are the different instruments of debt?
Debentures
Junk bonds
Deep discount bonds
Zero coupon bonds
Convertible bonds
Warrants
Asset backed securities
Restrictive covenants
What is debt financing?
When a company borrows money from lenders (banks,bondholders or other investors) rather than issuing equity. The company must pay interest to lenders
Bank loans
Bonds/debentures
loan stock
Does debt dilute ownership?
No, unlike equity
How is debt financing cheaper than equity?
Interest payments on debentures are tax deductible, reducing taxable income and lowering the effective cost of debt. This makes debt financing cheaper than equity due to this tax shield.
What are some disadvantages of debentures?
Increased leverage
Cash flow obligations- fixed interest payments must be made regardless of project performance so uncertain cash flows create pressure
Explain the differences between warrants and convertible debt
Warrants are securities that gives holders the right (not the obligation) to purchase shares at a fixed price in the future whereas Convertible debt is a bond or loan that can be converted into a fixed number of companys shares at a fixed price
Warrants are issued by companies as a way to raise capital and convertible debt is issued as a way to hedge their investment
If the stock price goes up the holder of a warrant can make profit by exercising the right of the warrant and buying shares at the fixed price and if the stock price goes down the holder of convertible debt can make a profit by converting the debt into shares at the set price
warrants are attached to debt and convertible bonds are attached to equity so if bankrupt the warrants will still be valid but the convertible debt will be converted into shares of stock