Chapter 1 - Introduction
1/51
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Genetics
The study of heredity and variation. It is a unifying discipline in biology that is centered on the study of genes. It provides explanations for inheritance and connects the most basic unit of biological information, genes, with inheritance across generations.
Gene
A unit of heredity. In modern times, it is defined as a segment of DNA that produces a functional product such as a polypeptide. It provides the blueprint that determines the traits of an organism.
Traits
Observable characteristics of an organism.
1) Nucleic Acids
2) Proteins
3) Carbohydrates
4) Lipids
What are the four main types of biochemicals contained in cells?
Organic / chemical bonds
Fill in the blank…
All cells are constructed from small ( ) molecules. These are linked together by ( ) to form larger molecules.
Macromolecules
Polymers constructed from smaller molecules called monomers. Nucleic acids, proteins, and carbohydrates are examples of these. Cellular structures form as a result of the interaction of these with molecules.
Chromosomes
DNA molecules and proteins assemble into these structures. Each contains many genes.
Genome
The entire collection of chromosomes in each cell of an organism. In humans, this contains 24 kinds of chromosomes, 3,000,000,000 base pairs, and around 27,000 genes.
Polypeptide
A linear sequence of amino acids. One or more of these structures are contained in proteins.
Structure / function
Fill in the blank…
Each cell contains many different proteins that determine cellular ( ) and ( ). The characteristics of a cell largely depend on the proteins it produces.
Proteosome
The collection of all the proteins that a cell makes at a given time. These proteins have diverse biological functions.
DNA / three-dimensional structure
Fill in the blank…
There are 20 different amino acids. Information in ( ) dictates the sequence of amino acids in a protein. The order of amino acids determines the type of protein and its ( ). Diversity of these structures generates large diversity of protein function.
1) Amino group
2) Carboxyl group
3) Side chain
What are the three main groups of an amino acid?
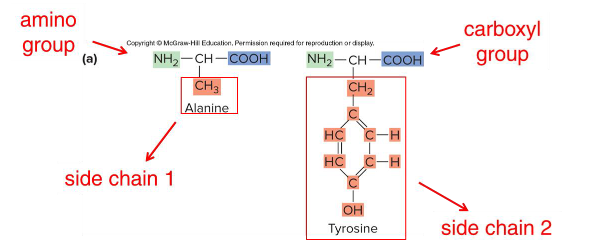
Side chain
Fill in the blank…
The structure of the ( ) determines the amino acid’s chemical properties.
Three-dimensional structure / function
Fill in the blank…
A different amino acid sequence results in a different ( ) which causes a different protein ( ).
1) Develops cell structure and influences cell shape and movement
2) Transportation of ions and small molecules across membrane and throughout organism
3) Cell membrane insertion
What are some of the functions of proteins?
Enzymes
Biological catalysts that accelerate chemical reactions.
Catabolic Enzymes
Enzymes that are involved in the breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones. They provide energy for the activities of cells.
Anabolic Enzymes
Enzymes that are involved in the synthesis of large molecules from smaller ones. They provide components for the construction of the cell.
RNA
A nucleic acid that may have been the first information-processing molecule. It can store, replicate, mutate, and express information. It can fold in three-dimensions and catalyze chemical processes. However, it is unstable and led to the evolution of other macromolecules.
DNA / RNA / proteins
Fill in the blank…
All organisms alive now use the same molecular specialization. ( ) is used to store and replicate biological information, ( ) is an intermediate in the production of proteins, and ( ) catalyze biological processes.
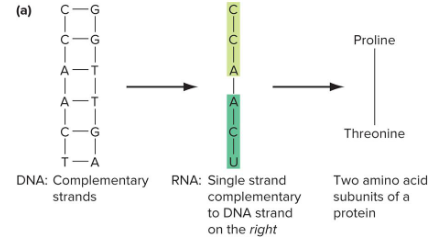
Transcription
A process that copies genetic information in DNA into a nucleotide sequence of ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Translation
A process that uses the nucleotide sequence in RNA to make the amino acid sequence of a protein.
Expression
Fill in the blank…
The information within DNA is accessed during the process of gene ( ), which is accomplished in two ways.
Genetic Code
A system in which bases are read as triplets to encode amino acid subunits of proteins.
Functions / similar
Fill in the blank…
Genes with similar ( ) in different organisms often have ( ) gene products.
Replace
Fill in the blank…
A gene from one organism can often functionally ( ) a gene from another organism.
Ex) The Pax6 gene is required for eye development in insects, mice, and humans. Expression of the human gene in fruit flies can induce eye development.
Trait
Any characteristic that an organism displays. The molecular expression of genes within cells leads to these characteristics. As such, these are controlled by genes.
Morphological Traits
Traits that affect the appearance of an organism.
Ex) The color of a flower.
Physiological Traits
Traits that affect the function of an organism.
Ex) Ability to metabolize sugar.
Behavioral Traits
Traits that affect the ways an organism responds to the environment.
Ex) Mating calls of bird species.
1) Genes are expressed at the molecular level (lead to expression of different proteins)
2) Proteins function at the cellular level (lead to differentiation of cells)
3) Traits are often observed at the organism level ( ex) dark vs. light moths )
4) Traits within a species are studied at the population level ( ex) dark moths in forested areas and light moths in unforested areas )
The relationship between genes and traits spans four levels of biological organization, which are…
Genetic Variation
Differences in inherited traits among individuals within a population. Some differences can be so striking that members of the same species are mistaken as different species.
Ex) In petunias, there are white vs. purple flowers

Morphs
Contrasting morphs within a single species.
Ex) Poison dart frogs
1) Gene mutations
2) Changes in chromosome structure
3) Changes in chromosome number
Genetic variation is a result of various types of changes to DNA at the molecular level, such as….
Alleles
Two or more expression forms of the same gene, usually caused by differences in gene sequences resulting from gene mutations.
Lost / duplicated / added
Fill in the blank…
Large segments of a chromosome may be ( ), ( ), or ( ) to another chromosome.
Single / set
Fill in the blank…
( ) chromosomes or a whole extra ( ) of chromosomes may inherited or lost.
Ex) People with Down’s syndrome have an extra chromosome
Environment
Fill in the blank…
The traits an individual expresses do not result from its genes along. Rather, traits are a result of the interaction between genes and the ( ).
Ex) An individual’s diet dictates his height and weight.
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
A human genetic disease in which two copies of a rare inactive allele responsible for metabolizing phenylalanine can’t do so. It results in the accumulation of phenylketones and results in mental impairment, among other symptoms.
Normally, humans have one or two functional copies of the gene that encodes phenylalanine hydroxylase and converts phenylalanine to tyrosine.
Infants are screened earlier and the treatment involves a diet low in phenylalanine.
Gregor Mendel
Proposed that during reproduction, genes are passed from parent to offspring. The principles of inheritance he proposed can be explained by chromosomes and their behavior during cell division.
Diploid
Sexually-reproducing organisms that have two copies of each chromosomes, one from each parent.
Homologs
Two copies of the same chromosome that contain the same genes, but not necessarily the same alleles.
Haploid
Cells that contain one copy of each chromosomes. Gametes fall under this classification (sperm and egg). Unification of these gametes during fertilization restores the diploid number in cells.
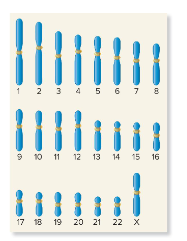
Genetic variation
Fill in the blank…
Sexual reproduction enhances ( ), resulting in combinations of traits not found in either parent.
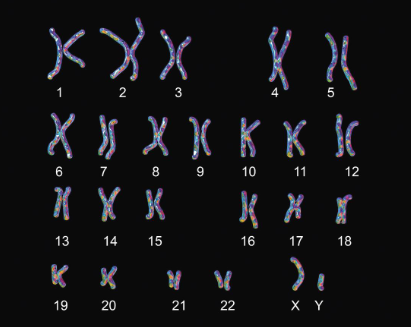
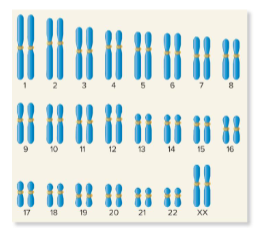
46 / homologous
Fill in the blank…
In humans, most cells have ( ) chromosomes, or 23 ( ) pairs. In males, the X and Y chromosomes are not homologous.
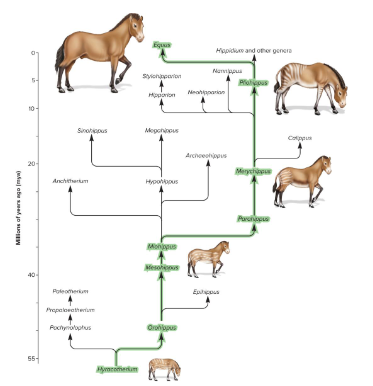
Biological Evolution
The genetic composition of a species evolves over the course of many generations. The genetic makeup of a population can change over many generations due to this process.
Natural Selection
The process in which individuals with greater reproductive success are more likely to pass their genes to future generations. In some individuals, random mutations lead to beneficial alleles, increasing reproductive success and leading to these alleles being passed down to future generations. Genetic changes accumulate as a result and lead to remarkable modification in the characteristics of a species.
Ex) Horses developed larger sizes, fewer toes, and modified jaws.
1) E.coli
2) S.cerevisiae
3) D.melanogaster (fruit fly)
4) C.elegans (sea worms)
5) M.musculus (mouse)
6) A.thallana (weeds)
What are some examples of model organisms?
Transmission Genetics
One of three fields in genetics that explores the inheritance patterns of traits as they are passed from parent to offspring. It is the oldest field in genetics and it examines how traits are passed from one generation to the next.
The conceptual framework for this field was developed by Gregor Mendel. A basic experimental approach in this field in the genetic cross (two individuals bred to each other over multiple generations to observe traits)
Molecular Genetics
One of three fields of genetics that focuses on the biochemical understanding of hereditary material. It deals with how the molecular features of DNA, RNA, and proteins underlie gene expression, organization, and function.
This is often done by studying mutant genes that have abnormal function.
Population Genetics
One of three main fields of genetics that is concerned with genetic variation and its role in evolution. It deals with the genetic variation of populations and how that variation is related to the environment.
Mathematical theories are often employed to explain the prevalence of certain alleles within populations.