PHR912: Block 2: Carbohydrate Metabolism 4
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Structure of Glycogen:
Branched polysaccharide, consisting of glucose units
Storage form of glucose
What kind of linkages are present in glycogen
alpha(1→4)
alpha (1→6) linkages at the branches
Every 8-14 residues
Anomeric carbon of glycogen:
Only one free anomeric carbon at the reducing end of glycogen
Due to the highly branched structure of glycogen:
Allowing for quick (parallel) access for biosynthesis or degradation
Where do glycogen molecules cluster together:
Tissues: Glycogen molecules
How does glycogen differ from amylopectin?
Glycogen is much more branched.
Where are the branch points in glycogen?
every 8-12 glucose units
Most cells only have how much of glycogen stored?
Small amounts
Where are the primary location of glycogen storage?
Liver and muscle
Glycogen storage can be compromised through:
Glycogen storage disease
What does liver glycogen do?
Used to maintain blood glucose levels (glucose buffering system)
Important fuel during anaerobic glycolysis where large amounts of glucose are consumed
Glycogen breakdown:
Glycogenolysis
How many enzymes are in glycogen breakdown?
Glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen debranching enzyme
Phosphoglucomutase
What is the end product of glycogen breakdown?
Glucose-6-phosphate
Why is phosphoglumutase reversible?
To allow the levels of glucose-1-phosphate and glucose 6-phosphate to easily altered in the cell.
Glycogen Phosphorylase:
Catalyzes glycogen phosphoryolysis to yield glucose-1-phosphate
Glycogen phosphorolysis definition:
Bond cleavage by subsitiution of a phosphate group
What is glycogen phosphorylase end product?
Glucose-1-phosphate
Glycogen phosphorylase removes:
glycosyl units one at a time from the non-reducing end of chain
Why can glycogen phosphorylase not function on short chains:
Cannot function on short chains of 4 residues of an alpha (1→6) branch point due to steric hindrance
How many forms does glycogen phosphorylase have:
2
Phosphorylase a
Phosphorylase b
Phosphorylase a:
Active glycogen phosphorylase
Phosphorylated at Ser 14; dimer of 2 identical 842-residue subunits
Phosphorylase b:
Inactive glycogen phosphorylase
“Blocked” dephosphorylated at Ser-14
What is the rate limiting step of glycogen breakdown?
Glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen phosphorylase phosphorylation/dephosphorylation is controlled by what?
Glucagon/Insulin
Activators of glycogen phosphorylase: Alloseric
AMP
Allosteric inhibitors of glycogen phosphorylase:
ATP
G6P
glucose
Because you have enough glucose, you dont need to break down more.
Glycogen degradation by glycogen phosphorylase:
Only non reducing end residues are cleaved off, one by one
What bonds do glycogen phosphorylase only act on?
Alpha-glycosidic bonds
What type of reaction is glycogen phosphorylase?
SN-1
What assists glycogen phosphorylase?
Pryidoxalphosphate
Glycogen Debreanching Enzyme:
Removes glycogen’s branches through trisaccharide transfer and hydrolysis of the remaining residue to yeild glucose
What does glycogen debranching enzyme also take care of?
Last 4 residues at branch points
2 catalytic activities of glycogen debrancing enzyme:
alpha (1→4) transglycosylase
alpha (1→6) glucosidase
Alpha (1→4) transglycosylase activity:
Transfers an alpha-(1→4) linked triasccharide units to a 4-position nonreducing end of another branch
Alpha- (1→6) glucosidase activity:
Hydrolyses the remaining alpha (1→6) linked glucose, releasing one free glucose unit per branch
Phosphoglucomutase:
Converts glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate
What reaction does phosphoglucomutase catalyze:
Glucose-1-phosphate → Glucose-6-phosphate
What is the intermediate for phosphoglucomutase?
Glucose-1,6-bisphoshate
First step of phosphoglucomutase:
A phosphoryl group is transferred from the active phosphoenzyme to G1P, forming glucose-1,6-bisphosphate (G1,6P)
Second step of phosphoglucomutase:
G1,6P rephosphorylates the enzyme by sactificing its phosphate at the 1-position, yeilding G6P
Where is glucose-6-phosphatase?
Only in the liver
What does glucose-6-phosphatase do?
Converts glucose-6-phosphate to glucose
Glucose-6-phosphatase equation:
G6P + H2O → Glucose + pi
Liver acts as the what:
Glucose buffering system
Glucose-6-Phosphatase allows the liver to do what?
Release glucose into the blood
Glycogen Phosphorylase (GP) is all below EXCEPT
GP’s b form is phosphorylated at Ser-14
Which of the following statements about the debranching enzyme is WRONG?
It moves 6-8 glucose residues from one glycogen branch to another
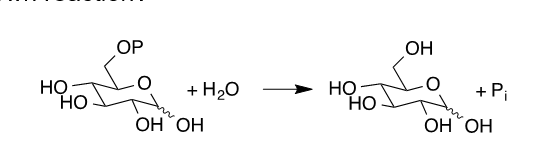
Where can you expect to find the enzyme catalyzing this shown reaction?
Liver
Glycogen biosynthesis (synthesis) is NOT the what?
Reverse of the breakdown pathway
Enzymes of Glycogen Biosynthesis:
UDP-Glucose pyrophosphorylase
Glycogen synthase
Glycogen branching enzyme
UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase:
Activates glucose
G1P + UTP → UDP-Glucose + PPi
Glycogen synthase:
Elongates glycogen chains at nonreducing ends
UDP-glucose + glycogen (n residues) → Glycogen (n+1 residues) + UDP
Glycogen branching enzyme:
Makes branches by transferring 6-8 residue sgments form the end of one chain to the 6-OH group of a glucose residue on the same or another glycogen chain
UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase covercomes the irreverisble step of?
Glycogen phosphorylase
UDP-glucose formation is: UDP glucose pyrophosphorylase
A phosphoanhydride exchange reaction
What is yielded during UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase?
A pyrophosphate for extra energy
What does UDP-glucose pryophosphorylase produce?
UDP-glucose
UDP-glucose may leave the pathway for:
Glycogen synthesis and be used for the addition of carbohydrates to other compounds (ex: glycopeptides)
Glycogen Synthease:
The glycosyl unit of UDP-glucose is transferred to the 4-OH group of a nonreducing end of glycogen
First step of Glycogen Synthase:
The UDP activator is removed leaving an electron-poor oxonium ion intermediate (UDP is a good leaving group)
Second step of glycogen synthase:
Oxonium ion intermediate is attacked by the 4-OH group of a glucose (at the end of nonreducing glycogen chain) under release of one H+ ion
Formation of glycogen is what kind of reaction?
Sn1
Glycogen Branching Enzyme
Provides the branches at 6-positions of glucose residues because glycogen synthase can only generate alpha(1 →4) linkages.
Other names for glycogen branching enzyme:
Amylo-1,4 → 1,6)- transglycosylase
Amylo-4:6-transferase
What does the glycogen branching enzyme cleave?
The 6-8 residues from a growing chain once it has reached 11-13 residues and attaches them alpha(1→6) to a glucose of the same or another chain to form a branch
How far must branch points be apart from one another?
At least 4 residues
Purpose of glycogen branching enzyme:
To maintain the highly branched structure of glycogen and allow branching for rapid growth.
Most of the synthesis consists of addition of glucose units to what?
Existing chain (glycogen primer)
The reducing end of glycogen is attached to what?
The protein glycogenin
Synthesis of glycogen primer 1st step:
Glycogenenin is glycosylated by a tyrosine glycosyltransferase at Tyr-194
Second step of synthesis of glycogen primer:
Glycogenin autocatalytically attaches up to 7 additional glucose units using UDP-glucose building blocks, making the chain long enough to serve as substrate for glycogen synthease
The glycogen branching enzyme is/does all below except?
Remove branches from glycogen
Glycogenin is/does all below except?
Is a unique enzyme of gluconeogenesis
The following reactions are/do all listed EXCEPT?
G1P + UTP → UDP-Glucose + 2Pi
The reactions are necessary in context with the glycogen breakdown
Allosteric: If ATP and G6P are high:
Glycogen biosnthesis is on: activation of glycogen synthase
Glycogen breakdown is off: Inhibition of glycogen phosphorylase
Allosteric: If AMP is high (ATP and G6P is low)
Glycogen degradation is on: Stimulation of glycogen phosphorylase
Glycogen synthesis is off: Inhibition of glycogen synthase
Hormonal: Insulin always cuases what?
Dephoshorylation
Hormonal: Glucagon always causes what?
Phosphorylation
Hormonal: Epinephrine stimulates what?
Muscles and liver
Glucagon only affects what?
Liver
Ca+2 also can stimulate what:
Muscles (not liver) to undergo glycogen breakdown
Which of the following statements concerning the regulation of the glycogen metabolism is WRONG?
AMP activates glycogen synthase
How could hereditary glycogen storage diseases be handled or treated in the future?
Not at all
Avoiding certain activties
Changing eating habits
Biologics → Enzyme replacement
Surgically
How is Anderson’s treated?
Not at all
How is McArdles treated?
Avoid certain activities
How is Hers’ and Cori’s treated?
Changing eating habits
How is Pompe’s treated?
Biologics → Enzyme replacement
How is von Gierke’s treated?
Surgically and drugs that inhibit glucose-uptake by the liver over surgical transposition of the portal vein to liver transplantation
Von Gierke’s Disease
Deficiency of liver glucose-6-phosphatase
Effects the ability to maintain blood glucose because glucose cannot be dephosphorylated
Effects of Von Gierke’s
Enlarged liver, hypoglycemia, failure to thrive
Pompe’s Disease:
Deficiency of alpha-1,4-glucosidase
Most devastating of the glycogen storage diseases
Large accumulation of glycogen in the lysocsomes of all cells
Expectancies of Pompe’s Disease:
Death by cardiorespiratory failure usually before reaching 1.
Cori’s Disease:
Incomplete glycogen degradation due to absence of debranching enzyme
Glycogen with abnormal structure accumulates in muscle and liver
Symptoms often disappear at puberty
Cori’s disease treatment and symptoms
Non-severe hypoglycemia
Can be treated with a high protein diet/frequent eating
Andersen’s Disease
Branching enzyme of glycogen biosynthetic pathway is missing
One of most severe
Liver glycogen exists in abnormal, long, unbranched amylose-type chains
Expenctancy of Andersen’s Disease
Victims seldom survive past 4 due to liver dysfunction
Liver dysfunction may be caused by an immune reaction to the abnormal glycogen
McArdle’s Disease
Deficiency of muscle glycogen phosphorylase
Painful muscle cramps and unusual fatigue during exercise
Symptoms do not usually appear before early adulthood
Liver glycogen phosphorylase exists in normal amounts
How to prevent McArdle’s disease?
Prevented by avoiding strenuous exercise
Hers’ Disease:
Deficiency of liver glycogen phosphorylase
Hypoglycemia, Hepatomegaly from inability of liver glycogen phosphorylase to respond to need for glucose
Not too severe