Prehistoric Art - Terms & Art
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
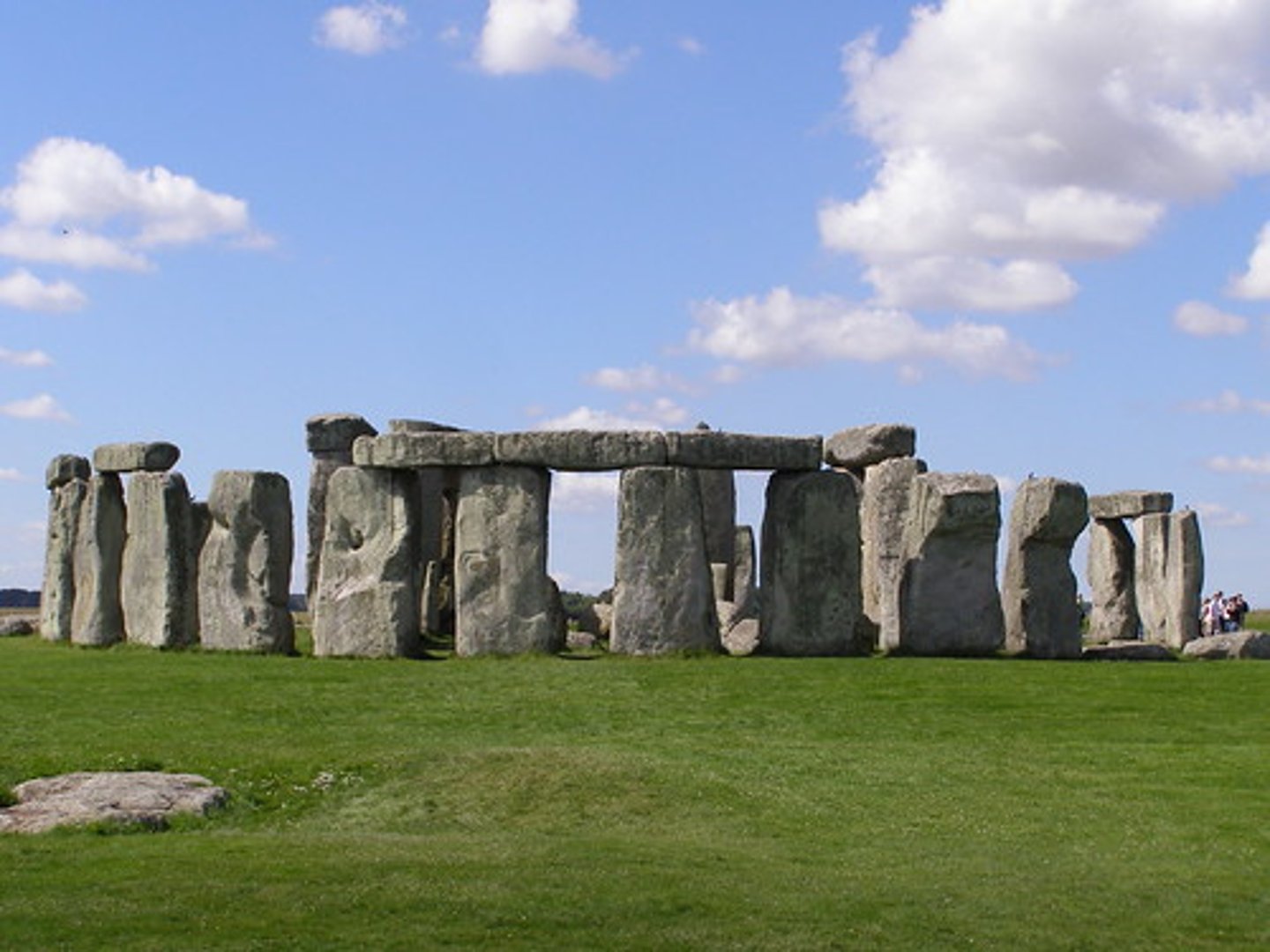
What: Stonehenge
Where: Salisbury Plain, England
Why made/what for: burial sight/to keep time of the seasons
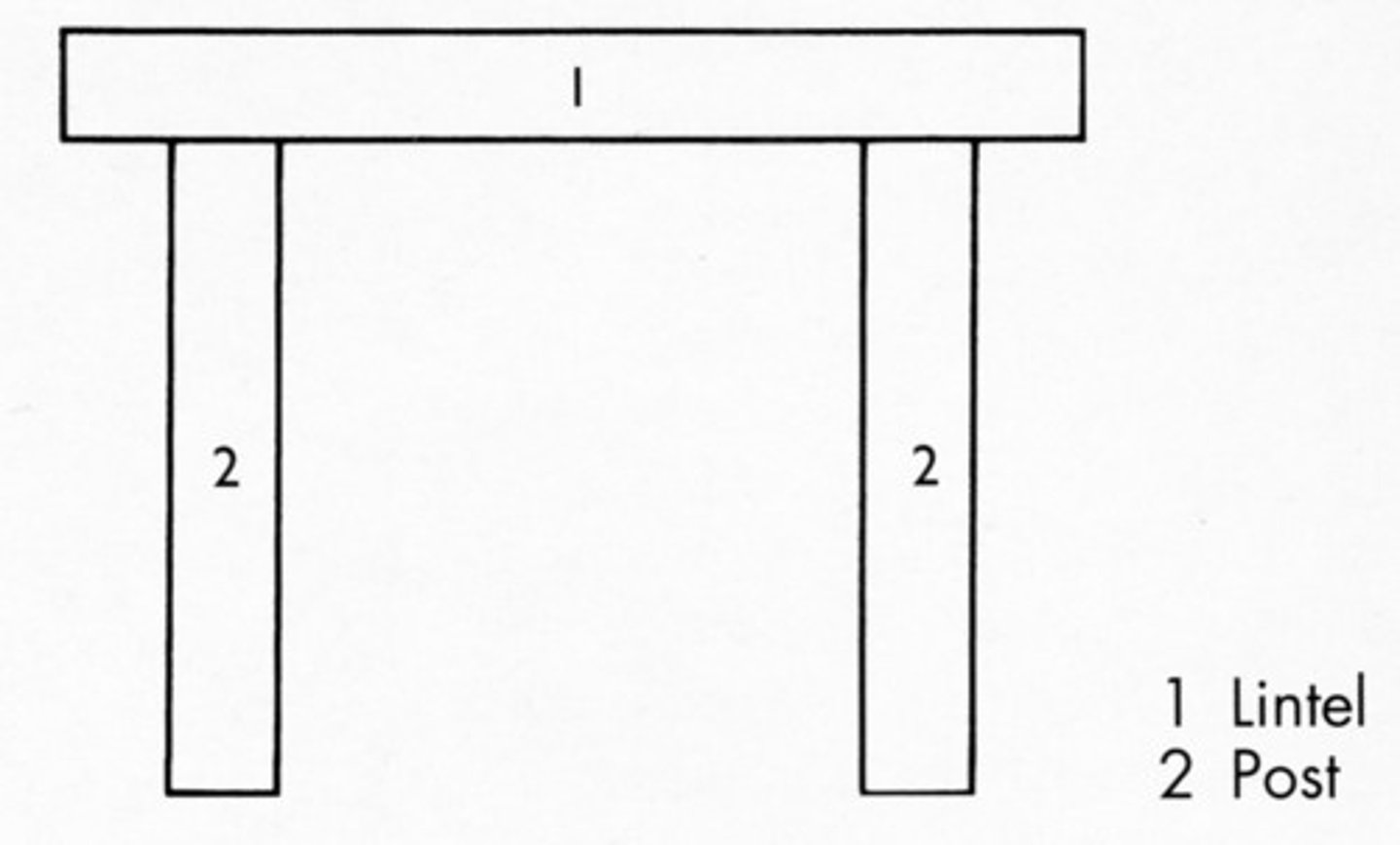
How made: Multi-step process over many years. Post and lintel construction used.
When made: 3,000-1,500 BCE

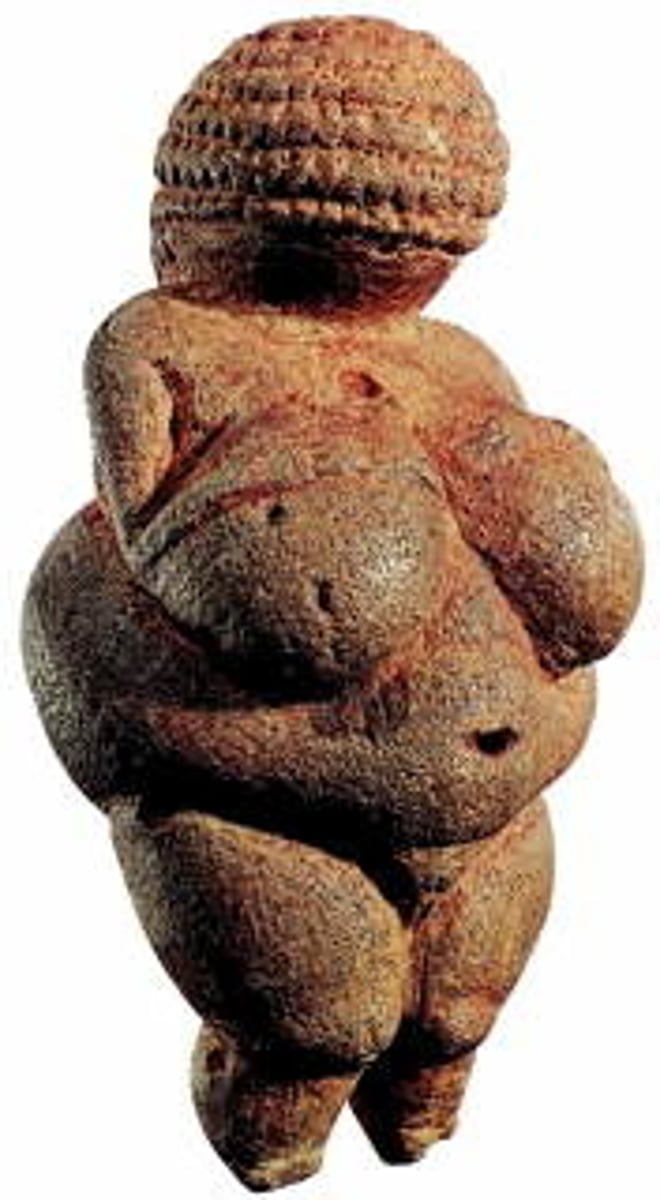
What: Venus of Willendorf.
Limestone, 11.1 cm High.
Where: Willendorf (original), Naturhistorisches Mueseum, Vienna (present)
Why made/What For: to emphasize the childbearing parts of a woman. Without written language it is difficult to know for sure, but it could be for appreciation of the female body and child bearing parts, or even a gift for a lover.
When made: 24,000-22,000 B.C.E, Paleolithic

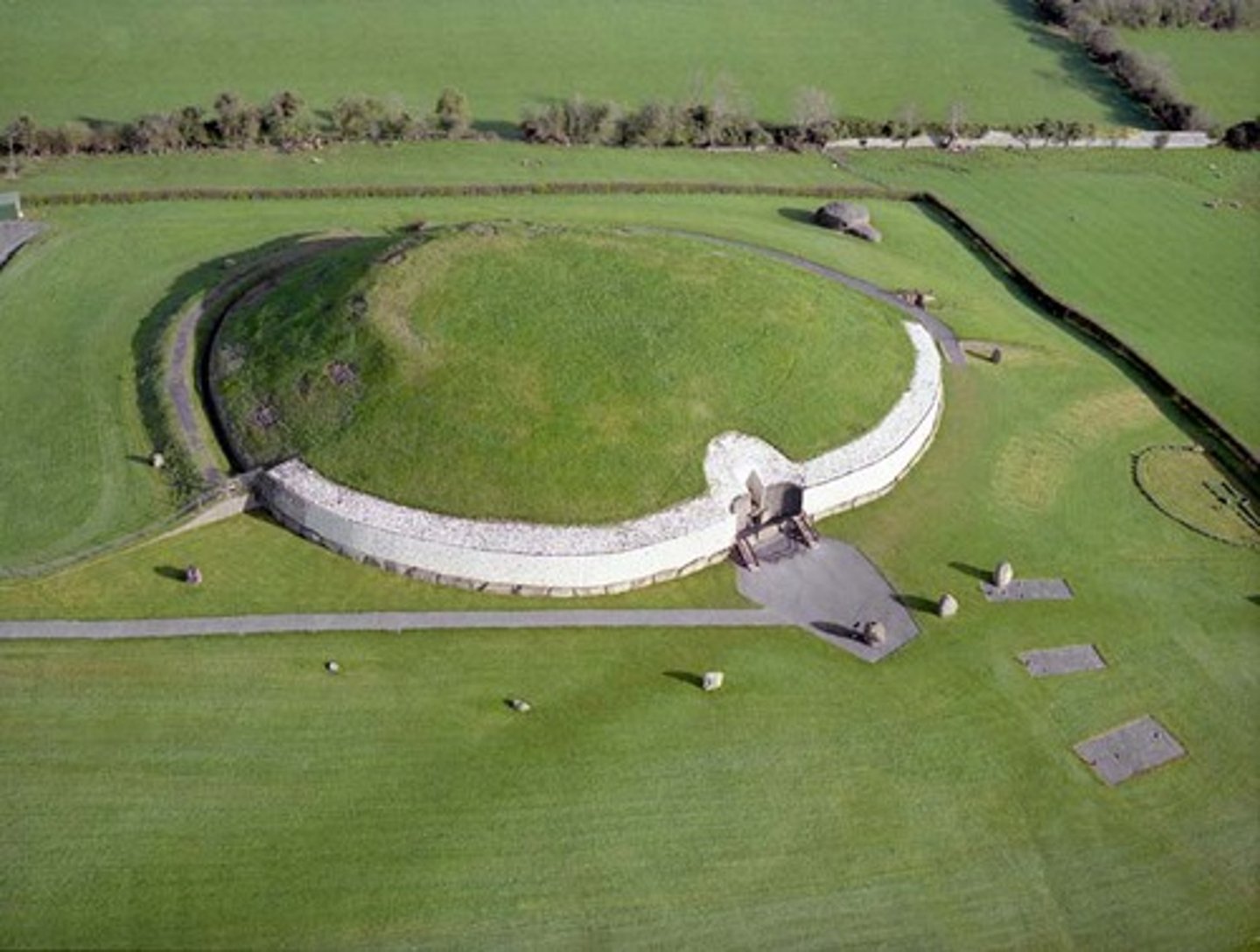
What: New Grange Tumulus
Where: Newgrange, Ireland
Why made/what for: Burial sight/tomb
How made: corbelling techniques.
When made: 3200-2500 BCE

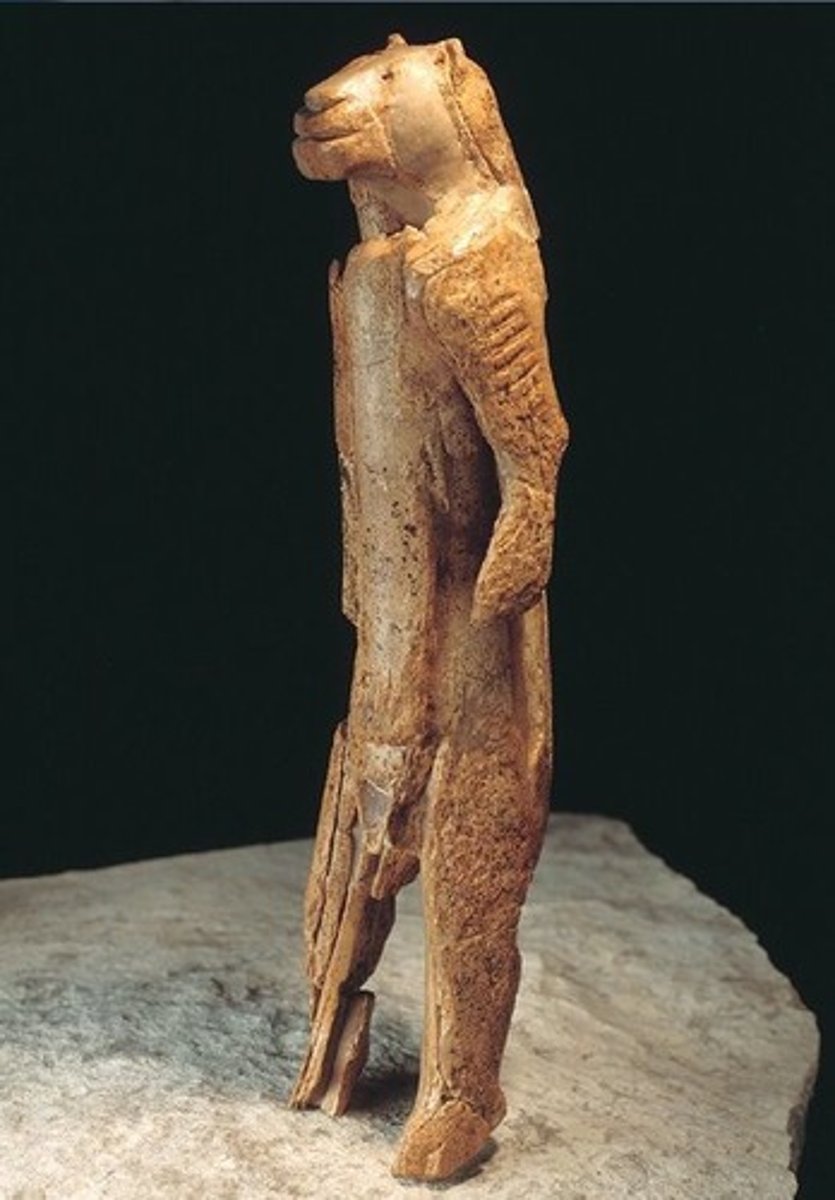
What: Lion Man
Where: Stadel Cave, Baden-Württemberg, Germany
Why made/What for: Wear of the statue in certain places suggests religious purposes.
How made: Carving from a mammoth tusk, sculpture in the round.
When made: 30,000-28,000 BCE.

Tumulus
a tomb in the form of a mound (i.e. New Grange)
Corbelling
a building technique technique in which each course of stone projects slightly beyond the one below (overlappng stones).
Relief Sculpture
Sculpture that projects from a flat background
Post and Lintel Construction
2 posts with a horizontal beam on top (i.e. Stonehenge)
Neolithic
New Stone Age; Early settlement, domestication of animals, less nomadic behavior and art.
Sculpture in the Round
Freestanding figures, carved or modeled in three dimensions.
Megalithic
Made of large stones
B.C.E
Before Common Era
Paleolithic
Old Stone Age; Nomadic Behaviors.
Mesolithic
Middle Stone Age
dolmen
stone monument utilizing post and lintel building used to bury the dead
Stele
A carved stone slab used to mark graves or to commemorate historical events.
Hieratic/Hierarchical Scale
Use of scale to indicate relative status difference in art
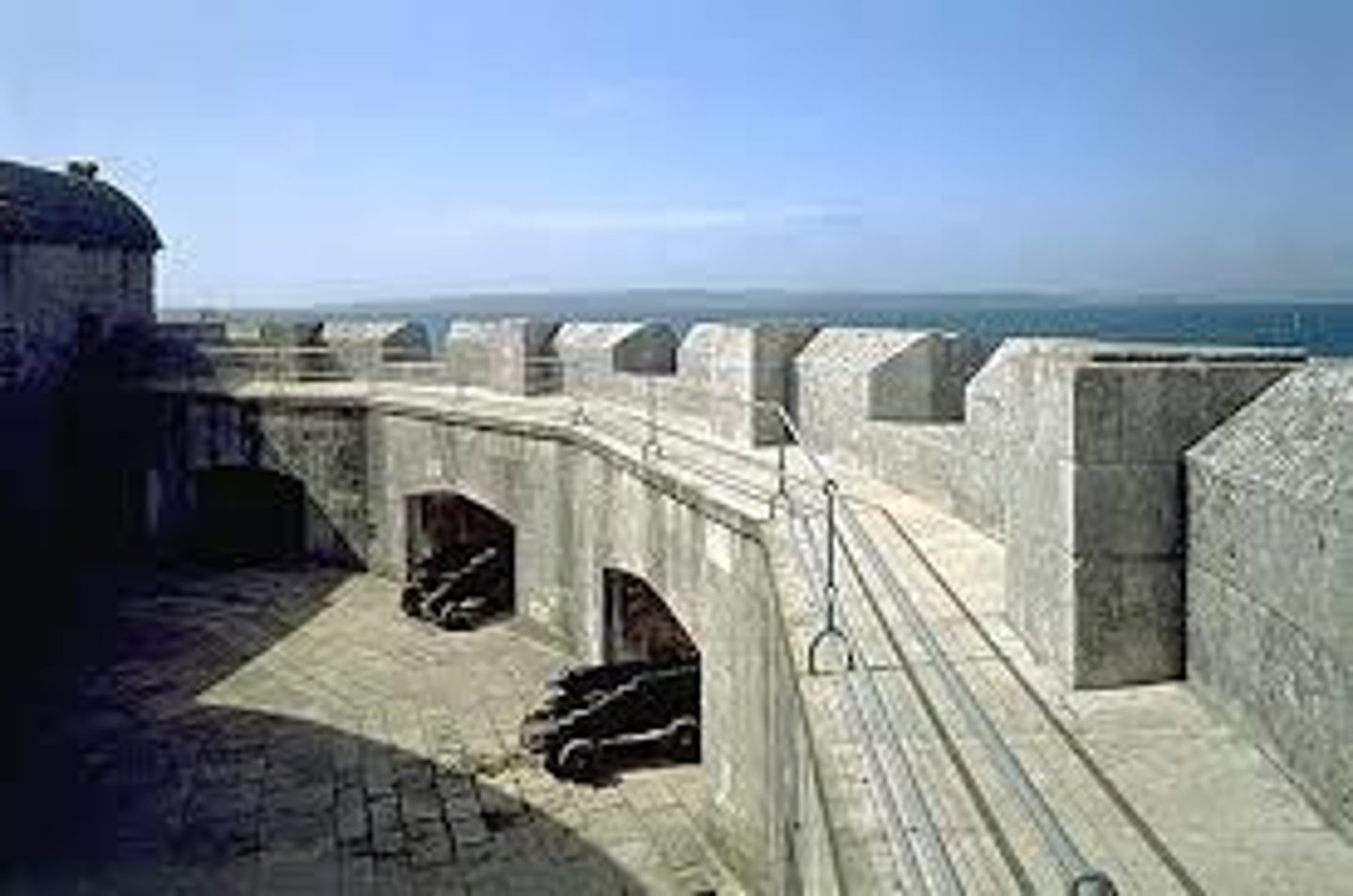
Crenellation
a rampart built around the top of a castle with regular gaps for firing arrows or guns

high relief
a carved panel where the figures project with a great deal of depth from the background
low relief
carving in which the design stands out only slightly from the background surface
cuneiform
first system of writing, developed by the Sumerians using a wedge shaped stylus and clay tablets.
ziggurat
A pyramid shaped temple tower
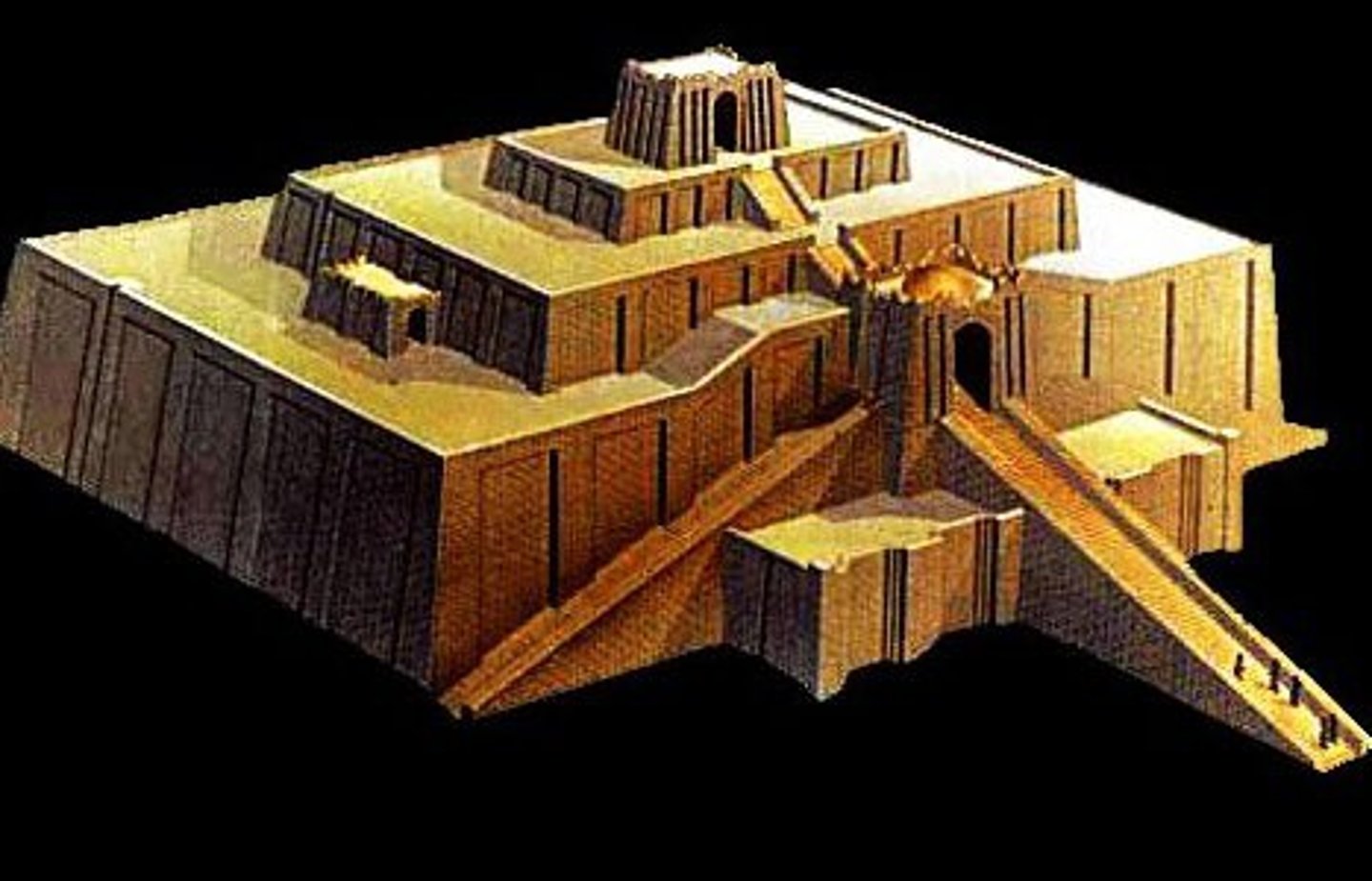

registers
layers of a story/marking a narrative

sumeria
Southern region of Mesopotamia where the earliest known cities arose.
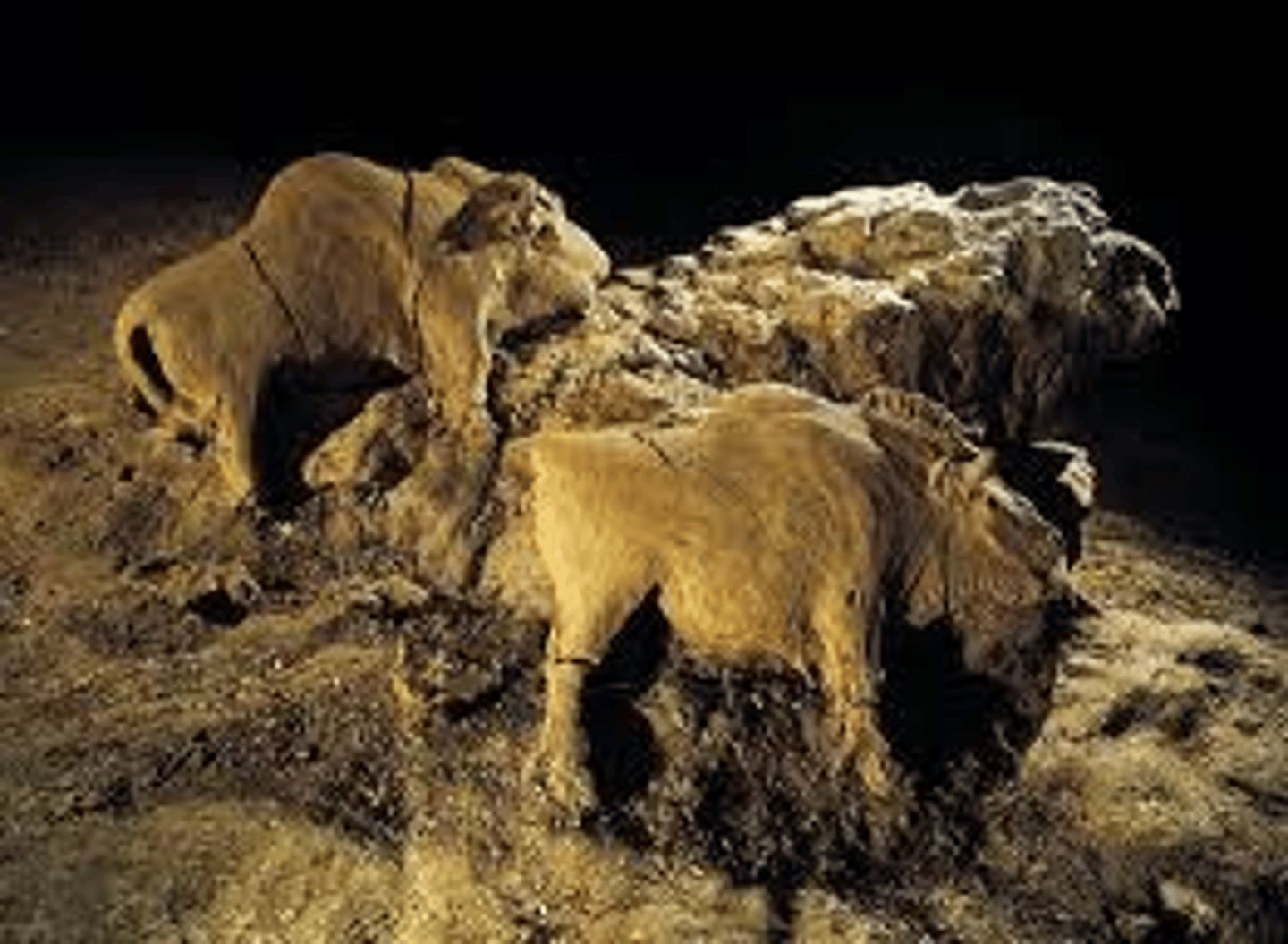
What: Two Bison Relief
Where: cave at Le Tuc d'Audoubert, France
Why made/what for:
How made: additive sculpture
When made: 15,000-10,000 BCE

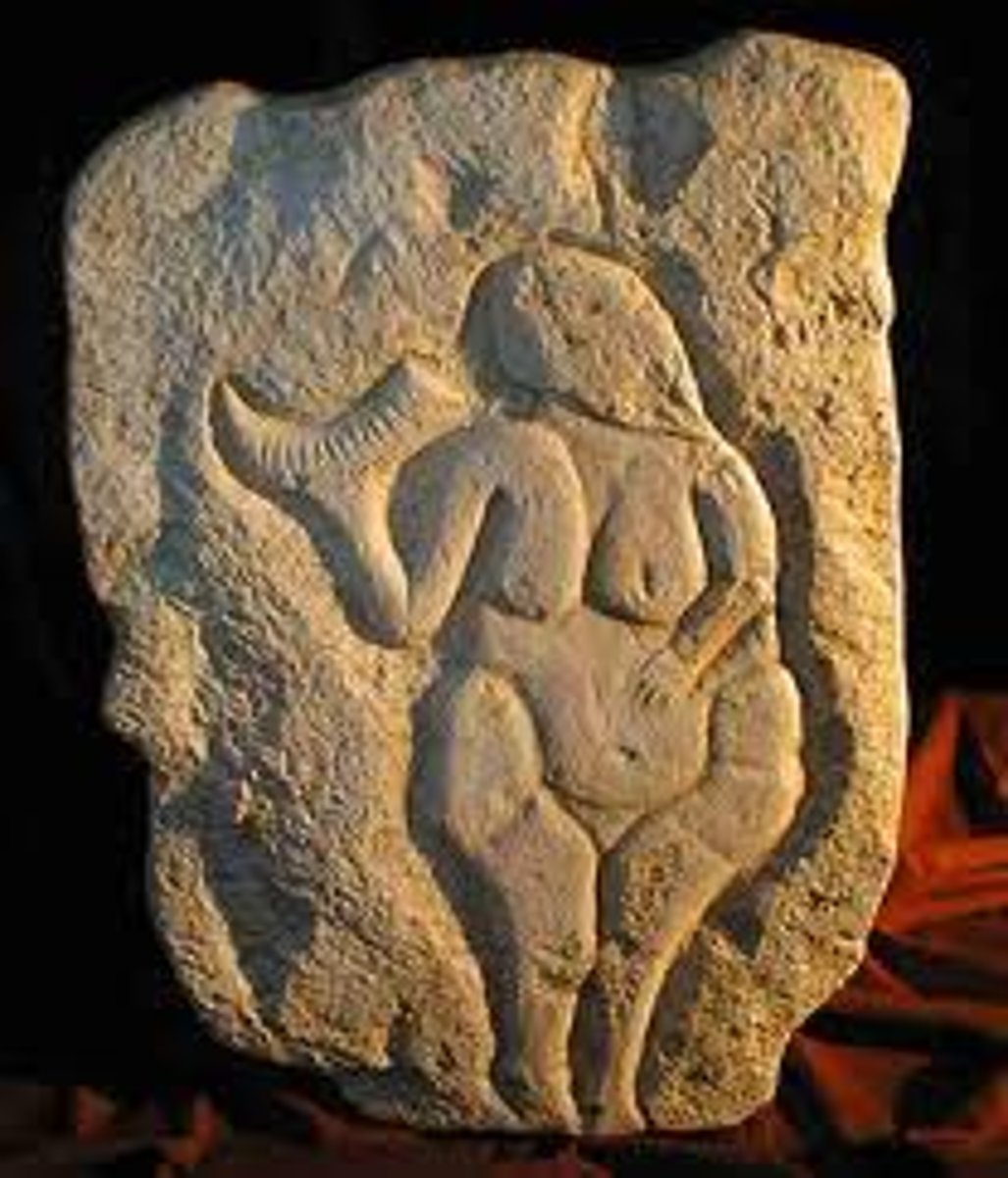
What: Woman holding bison horn relief
Where: Laussel, France
Why made/what for:
How made: relief carving
When made: 25,000-20,000 BCE

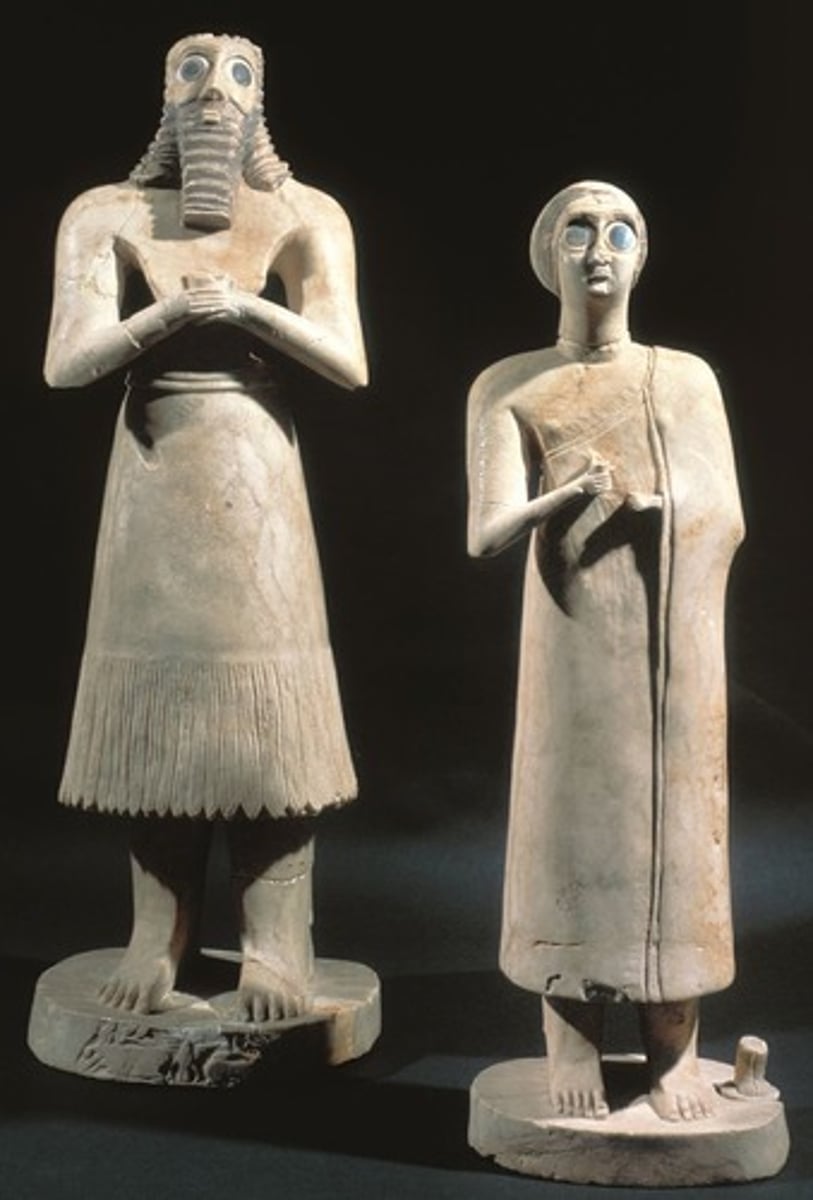
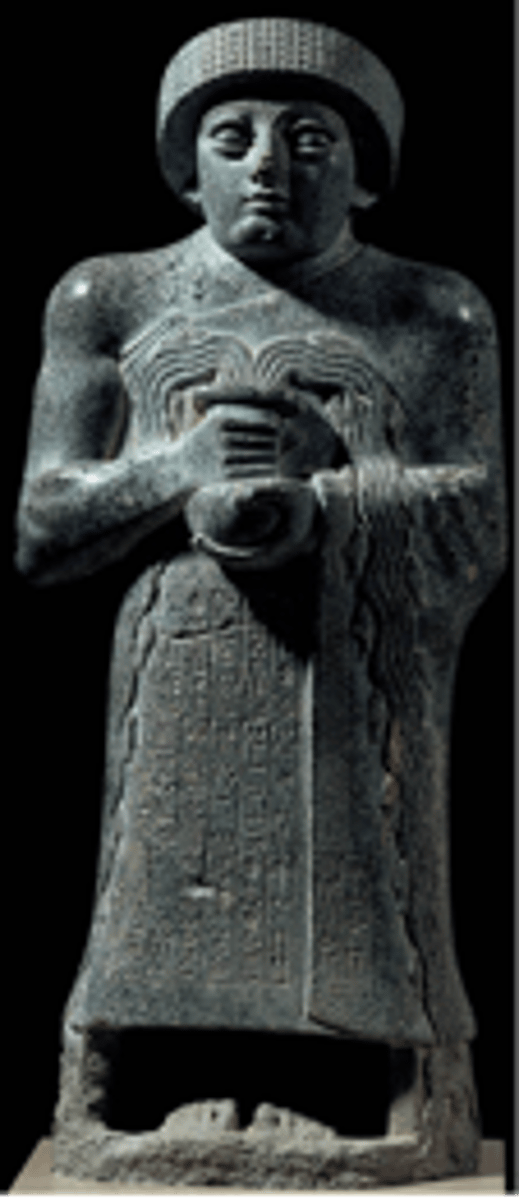
What: Votive Statues
Where: Iraq
Why made/what for:
How made: carving
When made: 2700 BCE

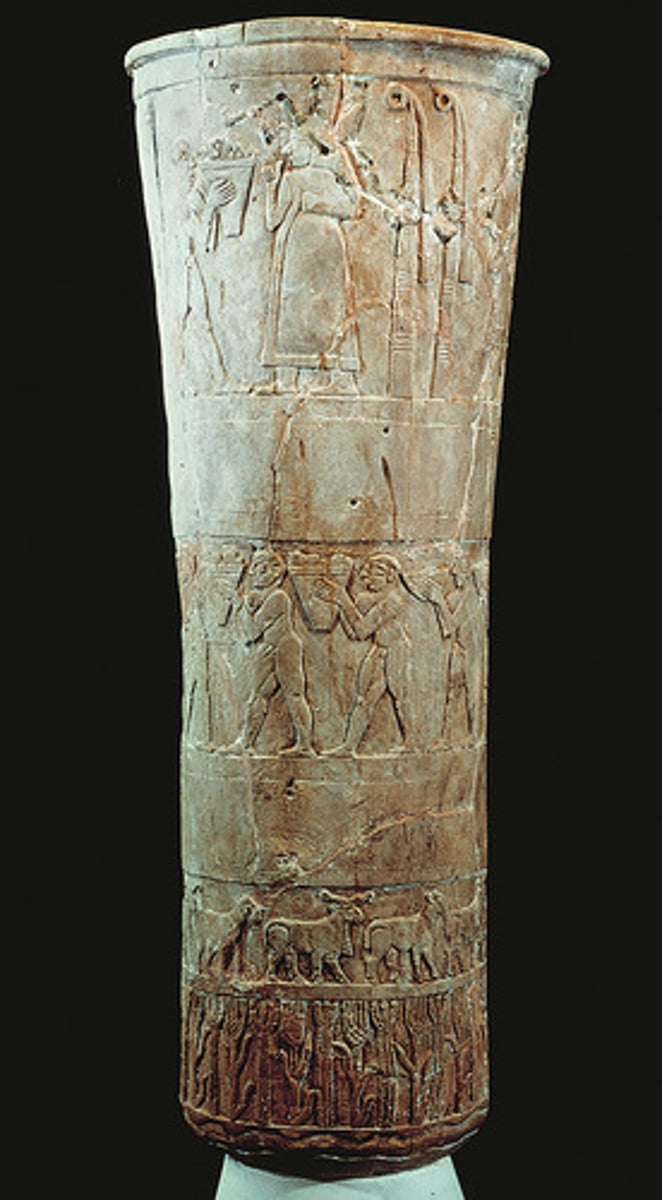
What: Presentation of offerings to Inanna (warka vase)
Where: Uruk/Iraq
Why made/what for:
How made: carving
When made: 3300-3000 BCE

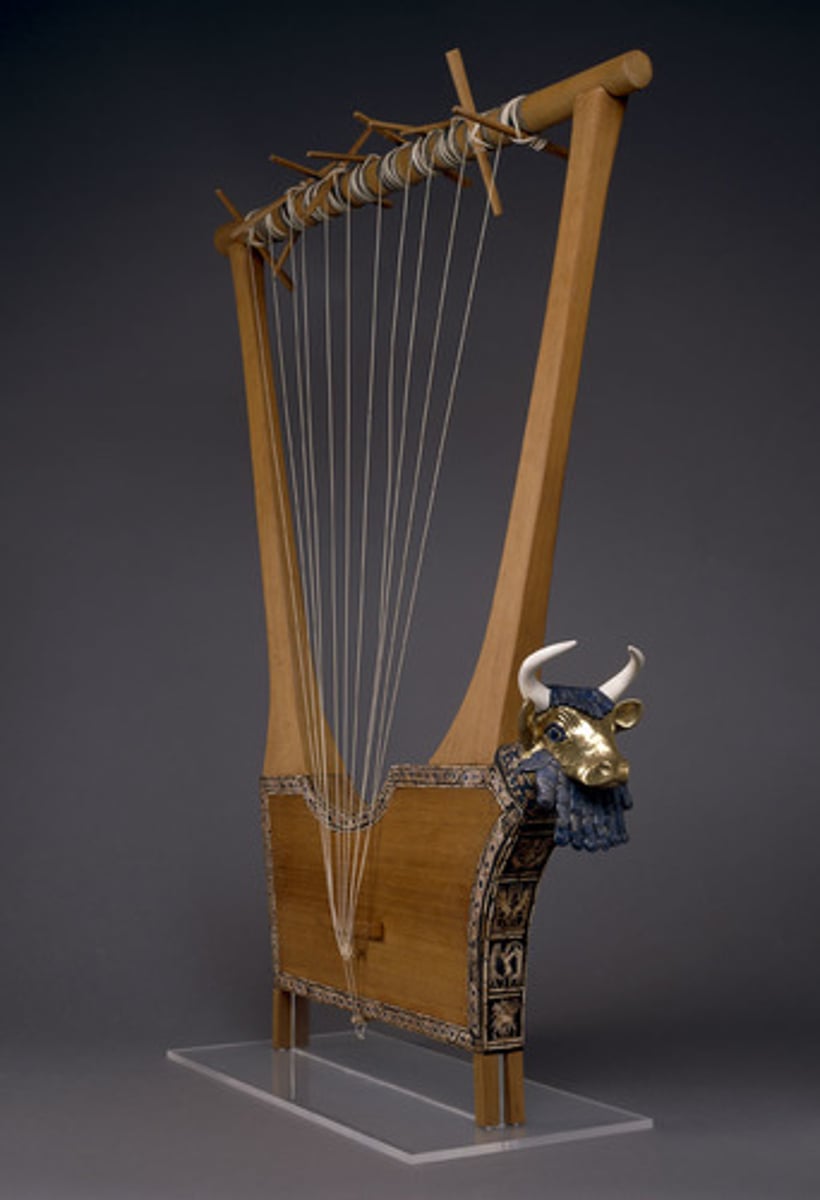
What: Bull headed harp
Where: Iraq
Why made:
How made: carving
What for:
When made: 2600-2500 BCE

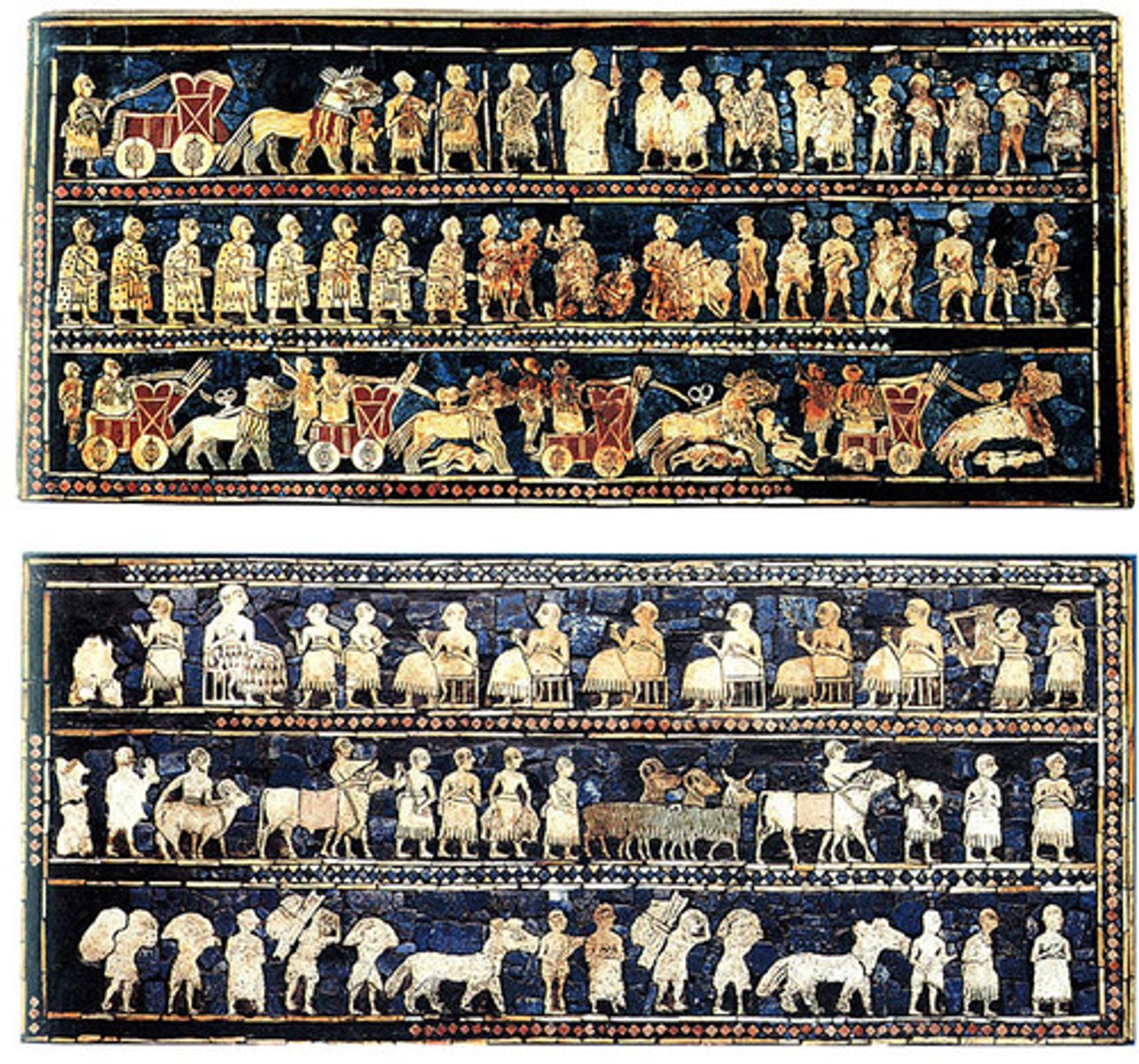
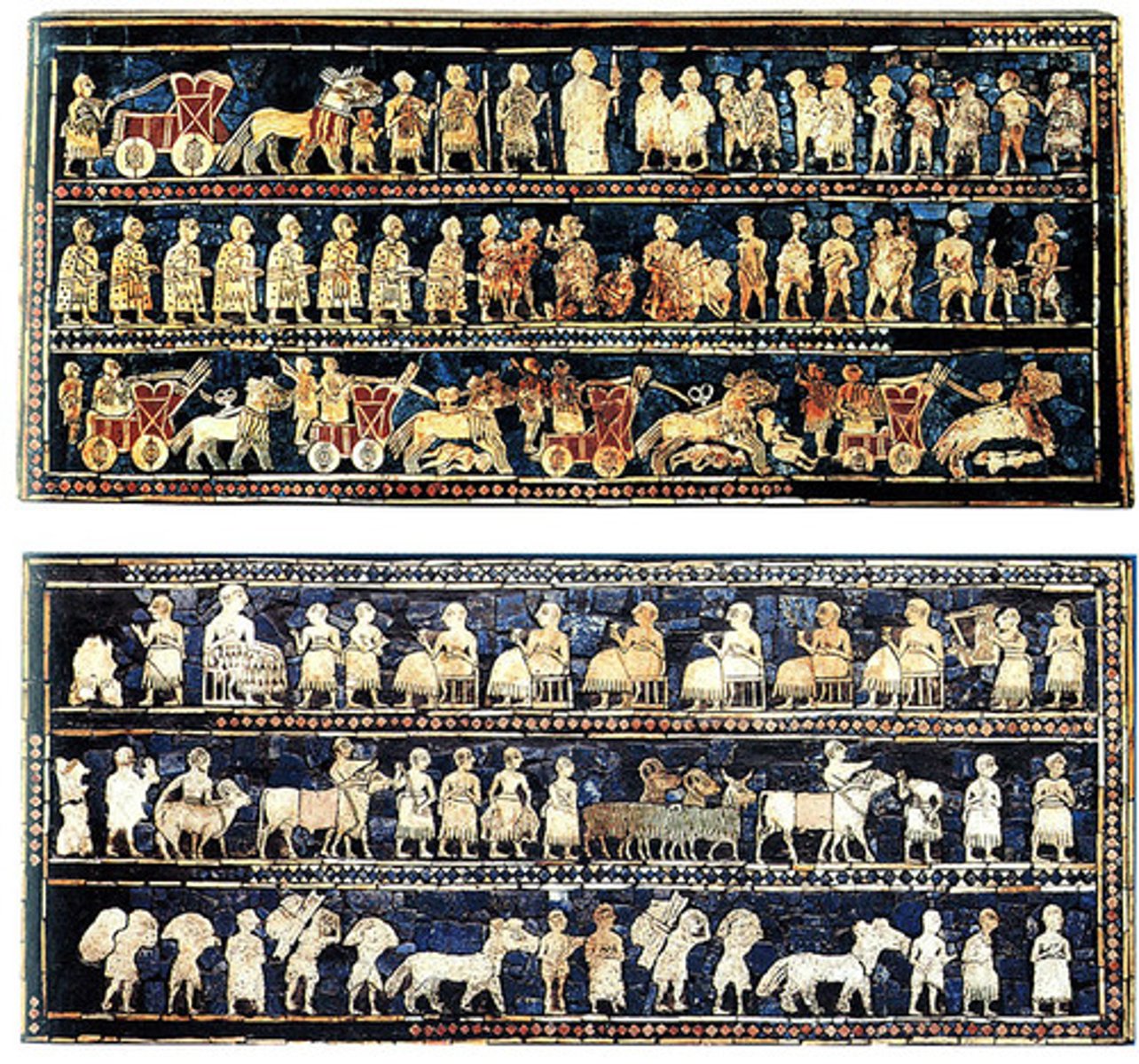
What: The standard of Ur
Where: Ur/Iraq
Why made:
How made:
What for:
When made: between 2600-2400 BCE

What: Stele of Naram-Sin
Where:
Why made:
How made: relief carving
What for:
When made: Roughly 2200 BCE

What: Gudea holding an overflowing water jar
Where: Iraq
Why made:
How made:
What for:
When made: 2090 BCE

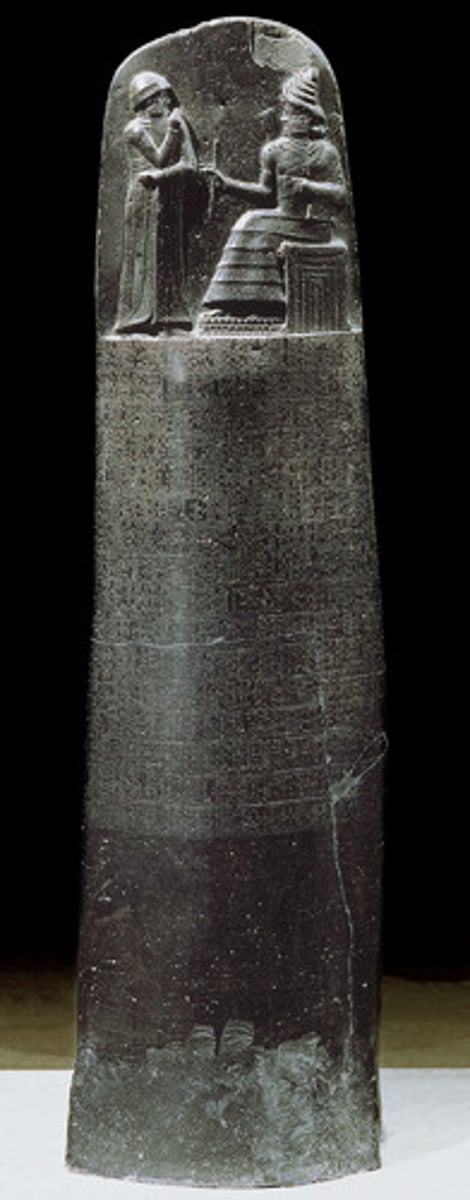
What: Stele with law code of Hammurabi
Where: Susa/Iran
Why made:
How made:
What for:
When made: 1792-1750 BCE

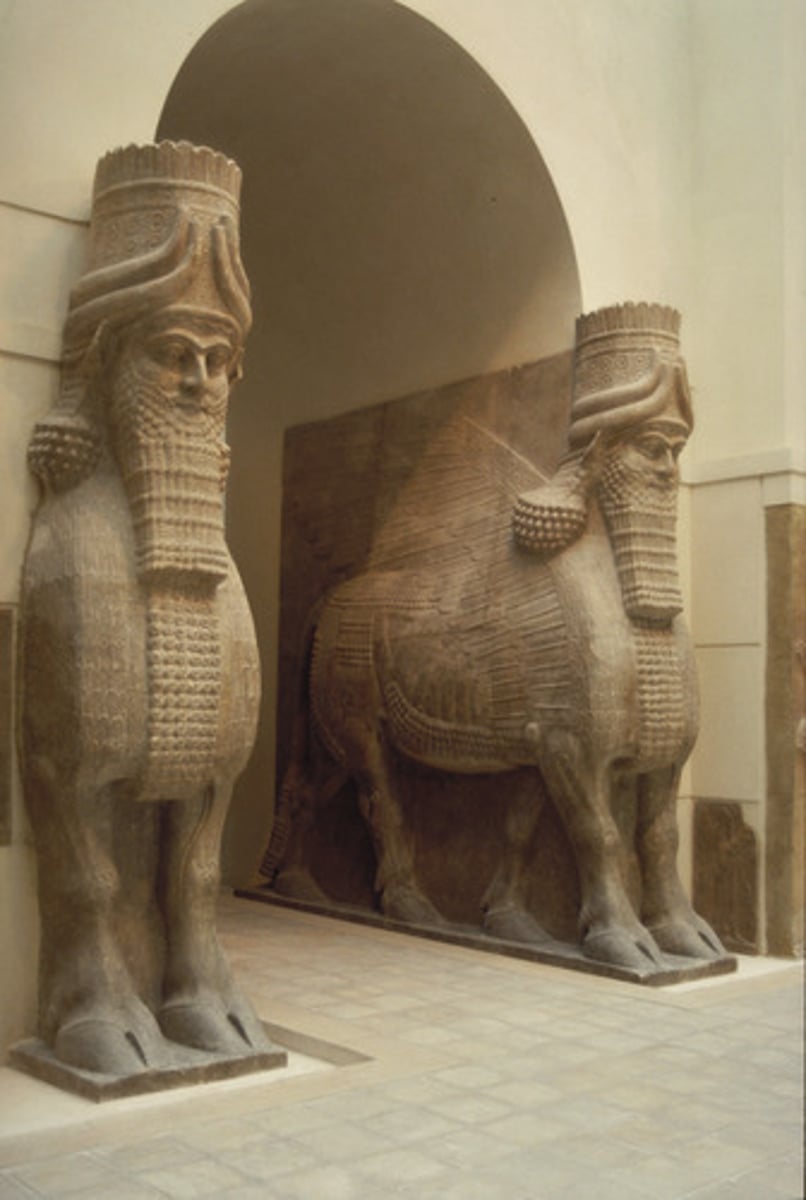
What: Lamassu
Where: Sargon/Iraq
Why made: Decoration and representation of Kings and their power
How made: Carving
When made: 720-705 BCE

Mastaba
an ancient egyptian mudbrick tomb, a smaller version of a pyramid
Necropolis
city of the dead (i.e. the great pyramids)
Colonnade
row of columns

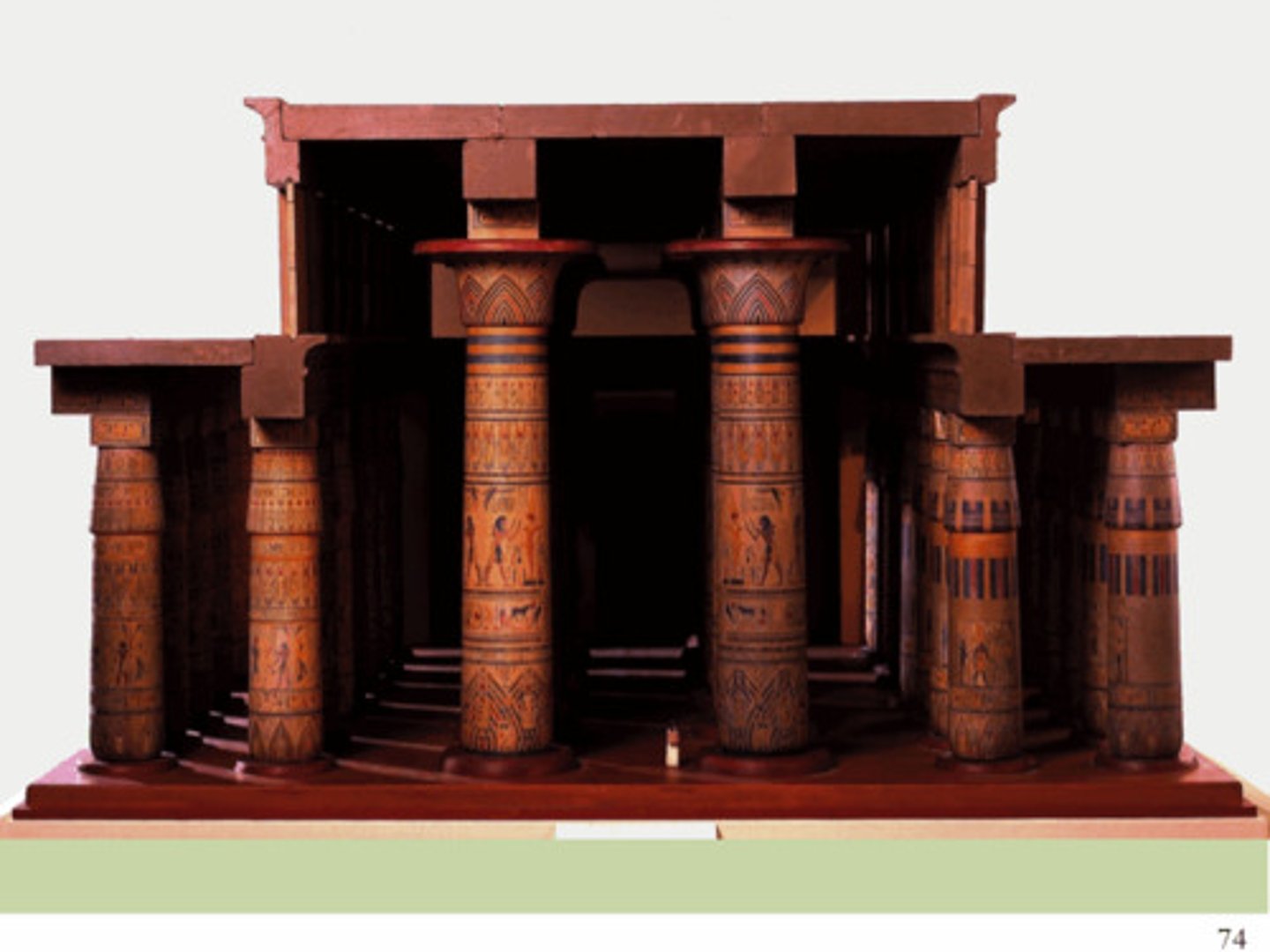
Hypostyle Hall
a hall with a roof supported by columns

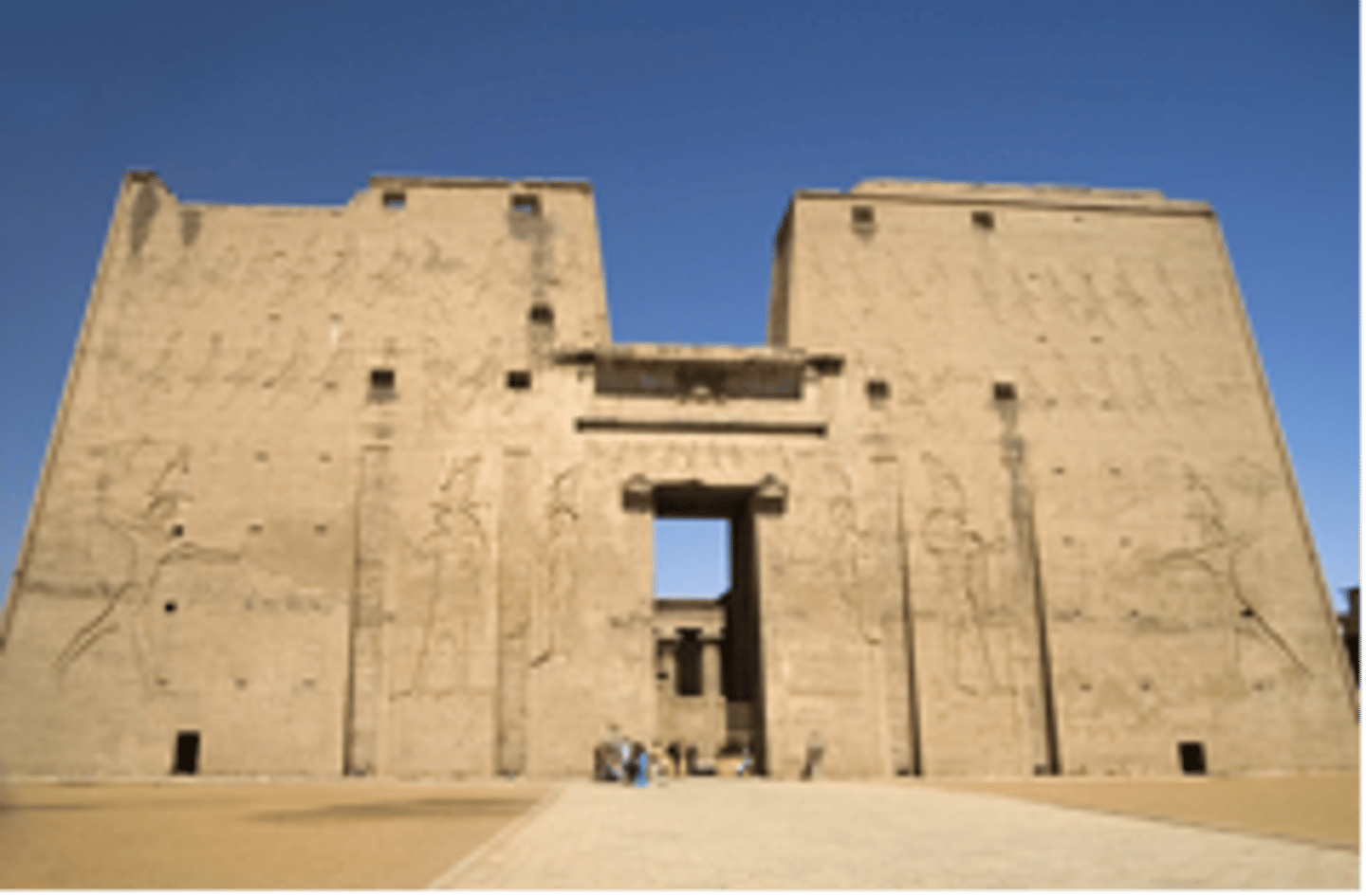
pylon
The wide entrance gateway of an Egyptian temple, characterized by its sloping walls

Capital
tops of columns
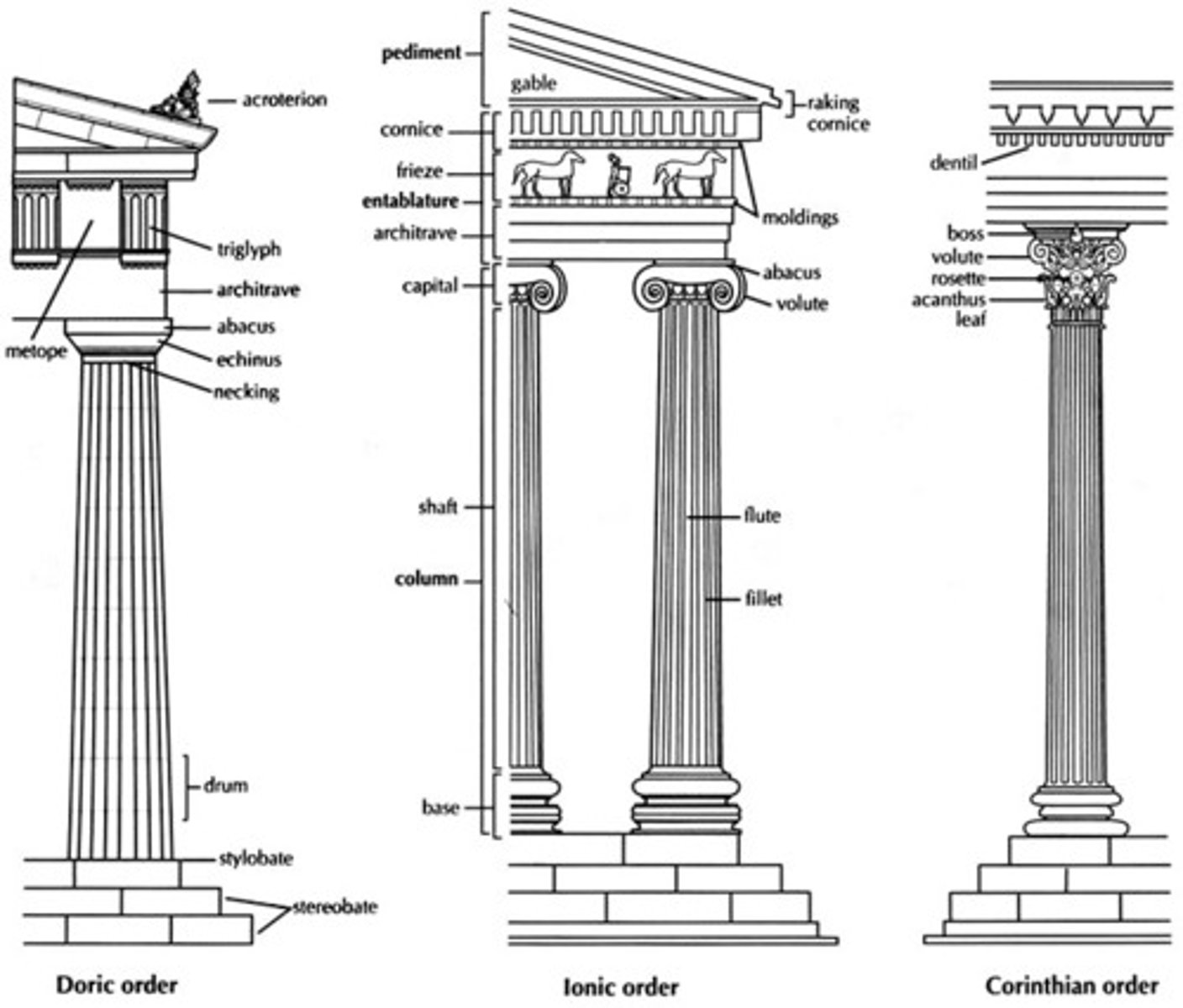
Clerestory
A row of windows in the upper part of a wall.
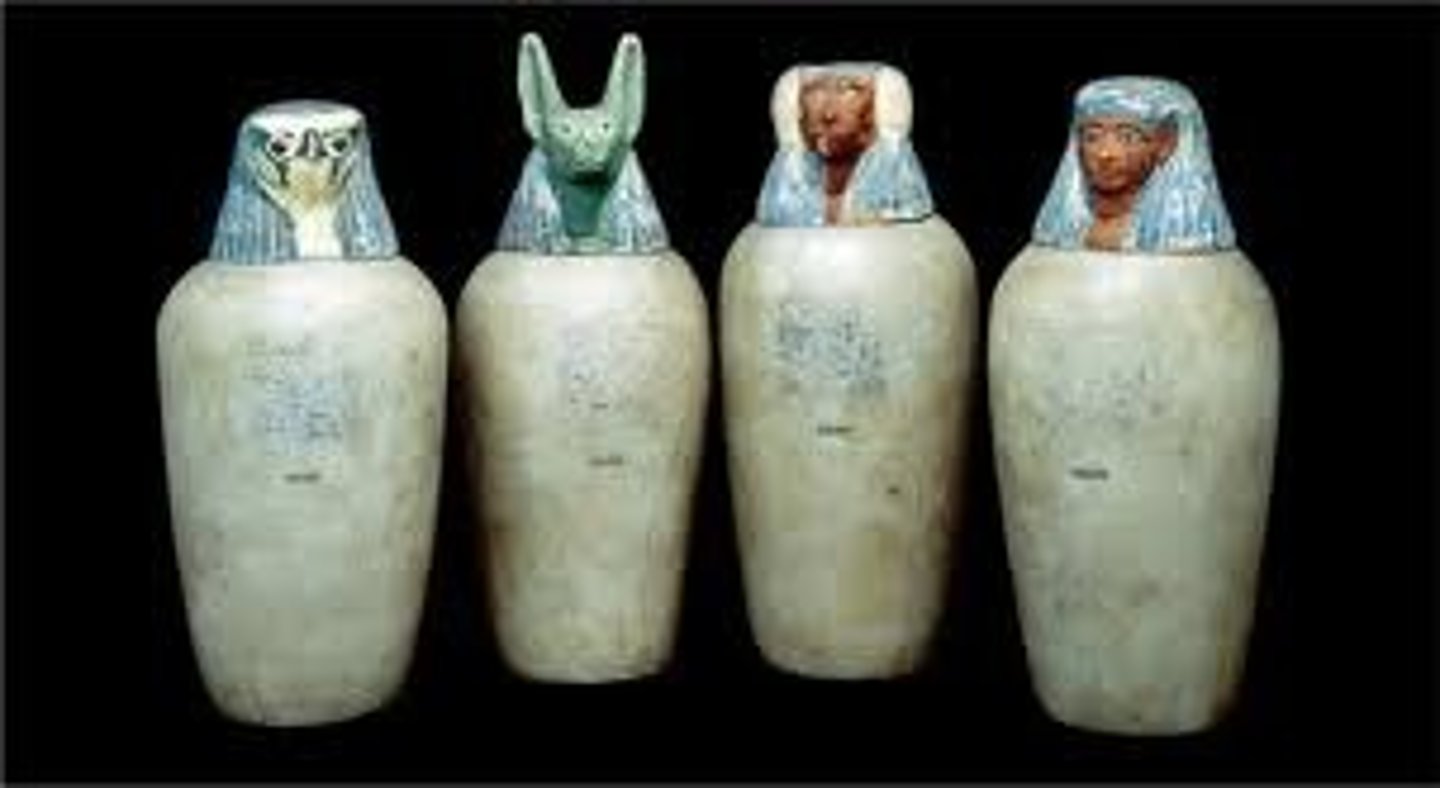
Canopic Jar
Where "innards" go after mummification

Ka
soul/spirit
ma'at
Order
Kemet
Egyptian name for Egypt, means "the Black Lands"
Papyrus
Egyptian paper
Obelisk
A tall, four-sided pillar that is pointed on top
Cartouche
a carved tablet or drawing representing a scroll with rolled-up ends, used ornamentally or bearing an inscription.
Polytheism or monotheism
Belief in one God
Ankh
an Egyptian symbol of life
Iconoclasm
Opposing or even destroying images, especially those set up for religious veneration in the belief that such images represent idol worship.
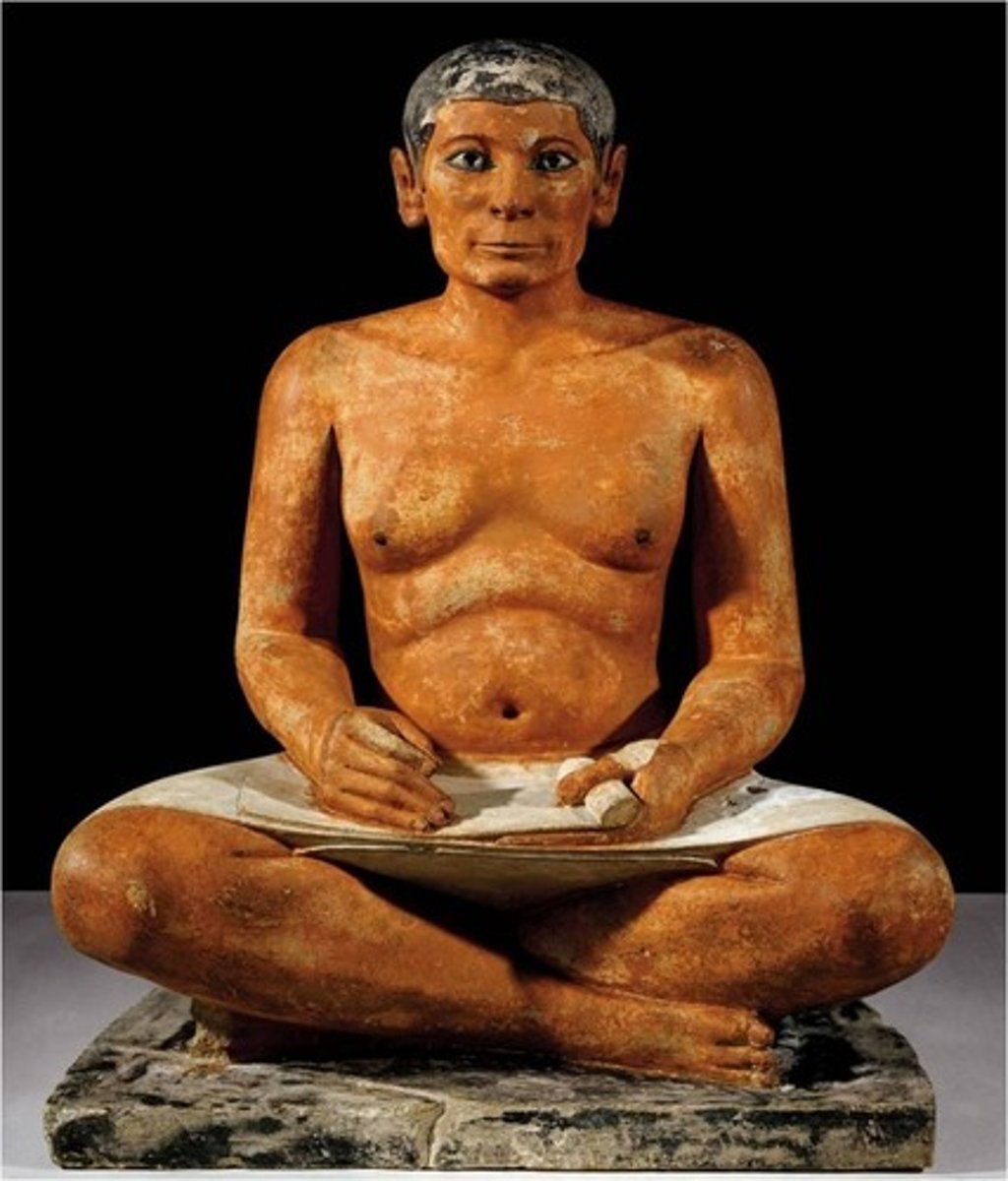
The Seated Scribe

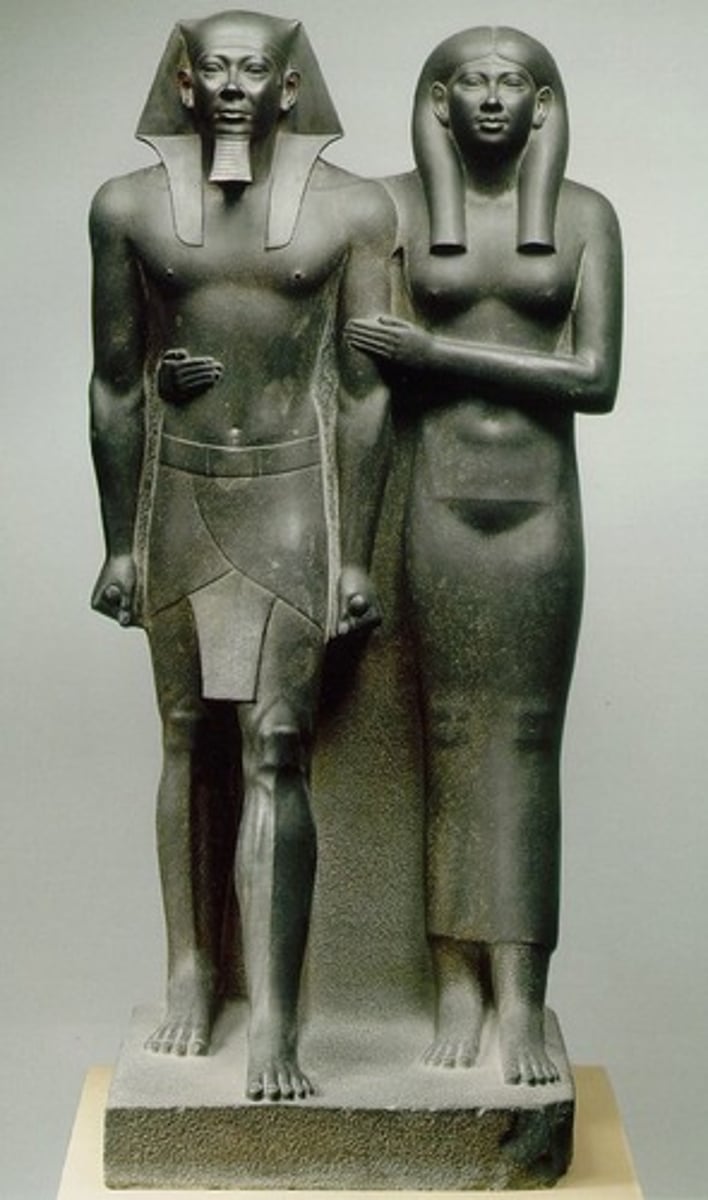
Menkaure & Khamerernebty
