Frame and Facial Measurements
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
In this session and the ones to follow you will gain more knowledge about facial and frame measurements as well as frame fitting and considerations for the dispense of one pair of spectacle lenses.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Why Meausre Facial Features?
To achieve best and most comfortable frame fit possible
To ensure the lenses are positioned appropriately
Poorly fitted frames can cause discomfort, permanent visual harm or even disfigurement. True or False?
True
The Measurements
Facial measurements can be used to specify frame measurements:
Frame Front
Pupillary distance
Head width
Frame Side
Front to bend
Downward angle of drop
Fit at the Nose
Apical radius
Splay angle
Frontal angle
Bridge height
Bridge Projection
DBR at 10 below crest
DBR at 15 below crest
Angle of crest
The frame side includes the front to bend and the downward angle of drop. True or False?
True
Top Tips
Be aware of patient sensibilities when measuring:
Personal Space! Gain consent before you start measuring
Avoid commenting on measurements
Observe how the patient uses their body
Communicate while taking measurements (e.g., what you are measuring; instructions)
Be aware of other considerations:
Hairpiece
Lack of mobility
Shyness
Be aware of certain considerations like _________, lack of mobility and shyness.
Hairpieces
Summary
Facial measurements are a set of coordinates which when taken accurately ensure a well fitted frame
Understanding facial features will allow you to advise your patient on the style of frame that would be most appropriate
Measurements are taken according to the type of frame the patient wishes to have
Care needs to be taken when moving around the patient – they will be very aware of sudden movements and more sensitive to being prodded with equipment near their face
Facial measurements are a _________ which when taken accurately ensure a well fitted frame.
Set of Coordinates
The Rees Fairbanks Guide
Contents
Guage Guide
Interpupillary Distance
Front Angle
Distance Between Rims
Head Width
Temple Width
Crest Height
Distance Between Rims (DBR) at 10 or 15mm Below Crest
Apical Radius
Front to Bend and Angle of Side
Downward Angle of Drop
Splay Angle
Segment Height
Segment Top Position
The Rees Fairbanks Facial Measurement Gauge has been designed to facilitate the _________, specification and final fitting of spectacle frames and mountings
Selection
Pupillary Distance
Required so that the optical centres are placed in front of the pupil centres – if the patient is looking through any other point of the lens, unwanted prismatic effects occur causing:
Visual discomfort
Diplopia
Measurement device: any accurate ruler is acceptable, pupillometer
Before trying to take PDs, Dispensing Opticians perform a Cover Test to check for any unusual eye movements.
Why do you think this is?
The Cover Test is taught in year two, but please take note, if the patient does have any strabismus or unusual eye movements, monocular PD’s should be taken with the other eye occluded
Take the measurement at arms length from patient
Secure the ruler against the Px forehead
Close your RE and instruct patient to look into your LE (i.e. Patient looking at infinity)
Place the ruler so that the zero mark is at the desired measuring point (i.e. edge of pupil or iris)
Do not move the ruler!
Close your LE and instruct patient to look into your RE (i.e. Patient looking at infinity)
Read off where the edge or the pupil or iris on the patient’s LE lines up on the ruler (same side of the iris used in other eye)
PDs are taken so that the optical centres are placed in front of the ________ to prevent an unwanted prismatic effect.
Pupil Centres
Near Centration Distance
This is the PD measured at near (i.e. not infinity) – this measurement should be less than the distance PD as the eyes naturally converge to look at near objects
Procedure:
Place an object (e.g. pen) at the patients near working distance and ask the patient to view it
Close your RE and place the frame ruler against the patients frame (or rest against patients nose in the frame plain) and line up with the patients pupil or iris, this is the zero point for the measurement.
Close your LE and making sure you are fully aligned to the patient take the measurement to the centre of the patients left pupil
Record the measurement?
What do you expect?
NB
A intermediate PD might be required based on working distances of tasks being performed
This is the PD measured at ______.
Near
Head Width / Temple Width
Use Callipers or use rulers: align the metal gauge of the ruler with temple (right) and place a second ruler perpendicular to the one you have aligned with right temple. Reading of the scale of the measurement ruler to the nearest 5 mm.
Be aware of the shape of the head
Measuring from the front is the preferred option as measuring from above will often give too big a measurement
Be conscious of the shape of the _______.
Head
Apical Radius
This is the size of radius across the nose at the point at which the frame will sit.
If you have any doubts choose a size up to avoid “pinching” the top of the nose
The ________is the size of radius across the nose at the point at which the frame will sit.
Apical Radius

Splay Angle
This is the ‘flare’ of the top part of the nose
Line up centre line with centre part of nose in the plane of spectacle frame – ruler is horizontal
Rotate the scale and measure splay angle
Equivalent frame measurement is the splay angle of pad
The splay angle is the ________ of the top part of the nose.
Flare

Frontal Angle
The ruler is held in the spectacle plane so that the short side of the metal rod is resting along the line of the nose where the bridge of the spectacles will sit. Ensure:
The correct position at the top of the nose
The ruler is level
The correct line along the side of the nose
When measuring the frontal angle use the ______ of the metal rod to take the measurement.
Short Side
Bridge Projection
This is how far the bridge of the nose project compared to the eyes
Adjust the ruler until set as the photo
Rest the curved lower portion of the curser on the nose at the point you wish the frame to fit
Slide the cursor in until it is just shy of the eyelashes
Bridge projection “0”-position: Eye lashes do not touch the cursor.
Eye lashes touch the cursor … take the reading (Positive)
_______ is how far the bridge of the nose project compared to the eyes if the eyelashes touch the ruler
Bridge Projection
Crest Height
Crest height = distance from lower lid top to bearing surface of the nose
Remove the cursor and use the 15mm step side of the ruler
Rest the bottom edge of the projection of the ruler horizontally on the bridge at the point you would like the bridge to fit.
Measure on the vertical scale at the top of the bottom eyelid (left eye in picture)
________ is the distance from the lower lid to the bearing surface of the nose.
Crest Height
DBR @ 10 and 15 Below
The ruler is held in the spectacle plane
Measured between the cursor and the vertical scale but read along the central scale.
As the name suggests:
The 10 below is on the 10mm step side. (reading=14mm)
The 15 below on the 15mm step side. (reading=15mm)
For________measurement the is held in the spectacle plane.
DBR
Angle of Crest
While holding the plastic part of the ruler vertical
Rest the metal bar running down the centre line of the nose
Ensure it is fully in contact with the area the bridge will sit and not being pushed up or down by other parts of the nose
For the _______ rest the metal bar running down the centre line of the nose.
Angle of Crest
Front to Bend
Specifies the length of the temple until it bends behind the ear
Too short: risk of pushing frame off the nose
Too long: frame slips down the nose
Measurement: place the metal rod of the gauge at the plane of the frame and align the gauge just above the patients ear; the reading is taken just above the ear
________ specifies the length of the temple until it bends behind the ear.
Front to Bend
Downward Angle of Drop
Is the angle the temple end needs to be bend down behind the ear
The reading on the scale needs to be deducted from 90 degrees
An angle too small might cause the frame to move (slip) and an to tight (angle too large) fitting causes pressure behind the ear (painful for the patients due to blood vessels and nerves running very superficially in this area)
Typical complaints if too tightly fitted: “My whole head hurts. I cannot locate the pain.”
The ___________ is the angle the temple end needs to be bend down behind the ear.
Downward Angle of Drop
Predicting Facial Characteristics
Facial measurements will vary according to ethnicity and age
Large bridge sizes – children, African or East Asian descent, injury?
Head width – physiological characteristic
Nose shape – sinus shape? Sensitivities of the soft tissue to consider
Bridge projections – small in children. Consider long eyelashes. Thyroid eye disease
Bridge projections are small in children. True or False?
True
Need to Know
Facial measurements are a set of coordinates which when taken accurately ensure a well fitted frame
Understanding facial features will allow you to advise your patient on the style of frame that would be most appropriate
Measurements are taken according to the type of frame the patient wishes to have
Care needs to be taken when moving around the patient – they will be very aware of sudden movements and more sensitive to being prodded with equipment near their face
Understanding facial features will allow you to advise your patient on the style of frame that would be most appropriate. True or False?
True
Tools for Measurement
Both the City rule and the ABDO rule can be used to take measurements
Unless you intend purchasing your own it is worth trying both
Both the City rule and the ABDO rule can be used to take _________.
Measurements
List of Frame Measurements
Box Lens Size
Distance Between Lenses (DBL)
Bridge Height/ Bridge Width
Bridge projection
Angle of side
Frame Temple Width; Frame head width
Length to Bend/ Angle of Let Back/ Total Length/Length to Tangent
Downward angle of drop/ Length of drop
Apical Radius
Crest height
Distance Between Rims
Splay Angle of Pads
Distance between pad centres and tops
Frontal Angle of pad
Height of pad top
Bridge Width, Splay Angle of Pads, Distance between pad centres and tops, frontal Angle of pad and Height of pad top are for the ________.
Metal Frames
Boxed Lens Size / Boxed Centre Distance
This is comprised of a horizontal and vertical component, commonly known as ‘A’ and ‘B’ measurements. They are used on all frame types.
Together with the Distance Between Lenses (DBL) measurement, Boxed Lens Size is the most used frame measurement
BCD
distance between the most nasal point on the left lens to the most temporal point on the right lens.
Mathematically: BCD=DBL+A-measurement
Commonly used with modern remote lens ordering systems
Its importance is particularly pertinent when patients choose a very small frame
Boxed Lens Size is comprised of a horizontal and vertical component, commonly known as ‘A’ and ‘B’ measurements. True or False?
True
All adult stock frames have a positive bridge projection. True or False?
True
Crest Height
Aim: This is measured to ensure smooth, even contact with the nose (particularly in plastic frames)
Limitation: Because most frames are made symmetrical, fitting to a patient with an uneven nose can be problematic
Fitting to a patient with an uneven nose can be problematic as the crest height of most frames are made evenly. True or False?
True
The aim of the distance between the rims measurements is that it is important for ensuring that the weight of the frame and lenses is correctly spread out across the nasal fitting area. True or False?
True
Bridge Width
Measured on the bridge width line (5mm below the HCL)
Be careful not to measure the pad position or pad arm.
Aim: ensuring that the rims do not rest on the nose
Bridge width ensure the rims do not rest on the nose. True or False?
True
Bridge Height
Place the frame so that the HCL is at the centre of the Bmeasurement
The bridge height is the distance between “BW” and crest apex
Aim: The bridge height controls how much of the lens aperture is available for looking ahead
The ______ controls how much of the lens aperture is available for looking ahead.
Bridge Height
Apical Radius
This is the radius of the bridge section of the frame
It is measured using the circles along the edge of the ruler
Aim: This measurement should correlate with the facial measurement
The apical radius should correlate with facial measurements. True or False?
True
Pad Measurements
The position of the pad on the nose maintains the position of the lenses relative to the eye (horizontally and vertically)
Pads do not stop the frame sliding off the nose - that is the purpose of the sides (I.e. temples) and tips of a frame
Pads do spread the weight of the spectacles to maintain comfort of wear
It is good practice to specify the type of pad to be used (nylon, silicon etc)
Splay Angle of Pad
The splay angle of the pad ensures the pads sits in contact with the nose from both the front edge to back edge of the pad
With loose pads try to measure at the mid point of the movement
The angle can be adjusted using nose pad adjustment pliers
Frontal Angle of Pad
This measurement is one of the most often adjusted in practice
Too small a reading and the bottom ends will dig in, too high and the top will pinch
This is adjusted using nose pad adjustment pliers
Facial measurement associated with it: Front angle
Pads do not stop the frame sliding off the nose. True or False?
True
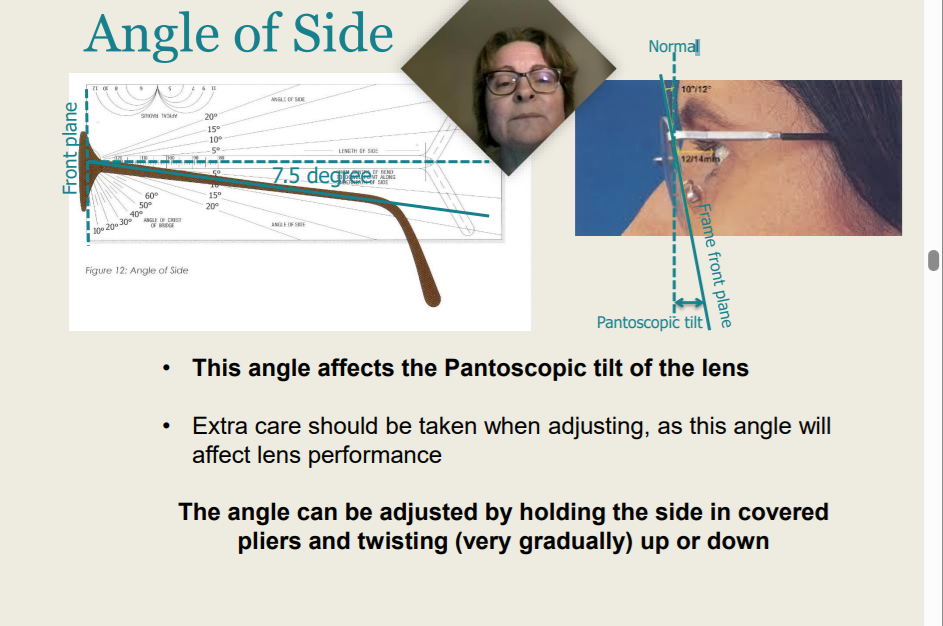
Angle of Side
This angle affects the Pantoscopic tilt of the lens
Extra care should be taken when adjusting, as this angle will affect lens performance
The angle can be adjusted by holding the side in covered pliers and twisting (very gradually) up or down
Extra care should be taken when adjusting, as this angle will affect lens performance. True or False?
True
Frame Temple Width
Measured at a line 25mm behind the back plane of the front
The front of the frame is lined up on the central scale on the rule, sides fully opened up.
The distance between the side as they cross the red line is measured Adjustments can be made at the hinge
The frame temple width is measured at 25mm behind the back plane of the front. True or False?
True
Downward angle of drop is also known as angle behind the ear. True or False?
True
The total length is the distance from the dowel point to the end of the side when a curl side is fully extended. True or False?
True
Need to Know
Frame measurements are a universal language designed to communicate about frame parameters
These measurements (in conjunction with the facial measurements from last week) demonstrates how a frame relates to the face
Although all the measurements are not often required, it is important you are comfortable in how they are obtained
Understanding frame measurements helps when performing adjustments and frame selection
Frame measurements are a universal language designed to communicate about frame parameters. True or False?
True
Systemic Fitting Approach
General: Nose to Ears (Front to Back)
Check the general alignment of the frame without being worn (Pre-adjustment)
Lens planes in alignment, show sides the same angle of let-back and touch both ends of the table?
Check the front (1)
Height appropriate and symmetric >adjust nose pads
Check width (2)
Does side cause indentation > widen (angle of led back) with pliers both sides equally
Check behind the ear (2)
Does it curve gently down behind the ear?
Start at top of ear and ‘curves’ along mastoid bone > check front to bend and re-align with fingers
Front → Width → Behind the Ear. True or False?
True
Frame Fit Metal
Measure facial features
PD, Splay angle, Frontal angle, Head width, Front to bend (both eyes)
Fit metal frame
General alignment, front to back (fitting triangle)
Measure frame features
Frontal angle of pads, splay angle of pads, Bridge width, Frame temple width, Frame head width, Angle of let back, length to bend, pantoscopic tilt
Fitting a metal frame need to adjust front to back. True or False?
True
Various Materials Frame
Frames
Plastic
Cellulose acetate (zyl; thermoplastic polymer) – mostly hypoallergenic (lacquer coating not), light and cheap, dye in mould
Cellulose acetate (zyl) - Heating Yes (58-62 degrees)
Cellulose acetate-propionate (nylon-based thermoplastic) – hypoallergenic, light and soft material, dyeing to only a few microns, ‘CP’ print to identify, hard to adjust
Cellulose acetate-propionate (nylon-based) - Yes, shrinks when heated above 67 degrees
Nylon (thermoplastic; polyamides, gliamides) – hypoallergenic, very light, for difficult shapes, in pure form little shine, temperature resistant – no heating, gets brittle with age, Safety-Specs and sun-glasses mainly, 3D printing frames
Nylon (brittle) - shrinks excessively when heated
Optyl (epoxy resin, thermoelastic) – hypoallergenic, memory shape, resistant to body acids, dyeing only a few microns, no cleaning with spirit-based materials/liquids
Optyl (epoxy resin) - Yes heat (80-120 degree)
SPX (co-polyamide nylon derivative)– hypoallergenic, very light, exclusive to Silhouette, limited adjustment range temperature 100-110ºC, high impact resistance, sides from zyl or cellulose propionate
TR90 (thermoplastic) – hypoallergenic, extreme light, rubber-like texture, flexible, high heat resistance, sportswear, withstands high temperatures (up to 350/400 degrees)
No heating
All of these plastics can be heated besides _________.
TR90
Various Materials Frame
Frames
Metal
Nickel Silver (60% copper, 20% nickel) – 5% magnesium for corrosion resistance, tough and good elasticity (‘spring back’) bridges and sides of combination frames
Monel (70% nickel, 15% copper, iron, magnesium) – mostly hypoallergenic, sturdy, robust and easy to adjust, corrosion resistance with electroplating,
Titanium – hypoallergenic, light, corrosion and perspiration acid resistance, durable, naturally grey > ion-plating to achieve various colours
Flexon (titanium-based alloy) – ‘memory metal’
Beryllium – hypoallergenic, cheaper than titanium, resistant to corrosion and tarnish, light, strong and bendable
Stainless steel (alloy of steel and chromium)– hypoallergenic, light, low toxicity, corrosion and perspiration acid resistance, flexible due to wire drawing (manufacturing) technique > unsuitable for high myopic or hypermetropic prescriptions and E-line bifocals
Aluminium – pricy, light, highly corrosion resistant, small amounts of silicon and iron make it hard and strong
Gold (18k or 24k) or silver – hypoallergenic, heavy, flexible/soft, corrosion-resistant
The nickel and Berrylium and aluminium is the easiest to adjust. True or False?
True
Nose Pieces
Nose Pieces
Silicone (sometimes hypoallergenic)
acetate
Rubber (rarely)
Polyvinyl chloride (hypoallergenic)
Titanium (hypoallergenic)
Side ends (plastics like frames)
acetate
PVC (hypoallergenic)
The silicone, rubber, polyvinyl chloride, titanium and PVC is _______.
Hypoallergenic
Dispensing and Allergies
Main Materials Causing Allergies vs Hypoallergenic
Nickel → Titanium (most plastics)
Cellulose acetate (zylonite) → Optyl, Nylon, Polycarbonate
Silicone → Vinyl, Titanium (less comfortable)
Rubber (less likely) → N/A
Solvents / dyes (coatings) → Make sure lens / frame does touch fave minimally
Titanium is less comfortable. True or False?
True