Unit 4 - Carbon, Atoms, Energy, and Climate
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
molecule
two or more atoms chemically joined together

biosphere
Parts of the land, sea, and atmosphere in which life can exist
permafrost
Ground that is permanently frozen (below 32 degrees F or 0 degrees C) for two or more years.
weather
The day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere, including temperature, precipitation, and other factors at a particular place and time. (compares to a person's mood)
carbon budget
The cumulative amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4) emissions permitted over a period of time to keep planetary warming within a certain temperature threshold.
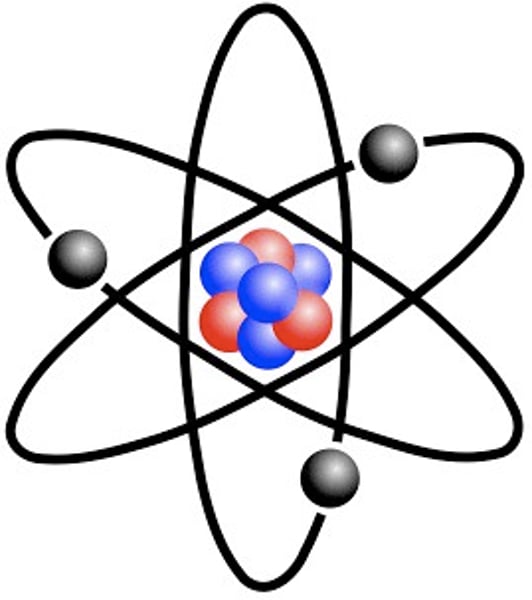
atom
Basic unit of matter
element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
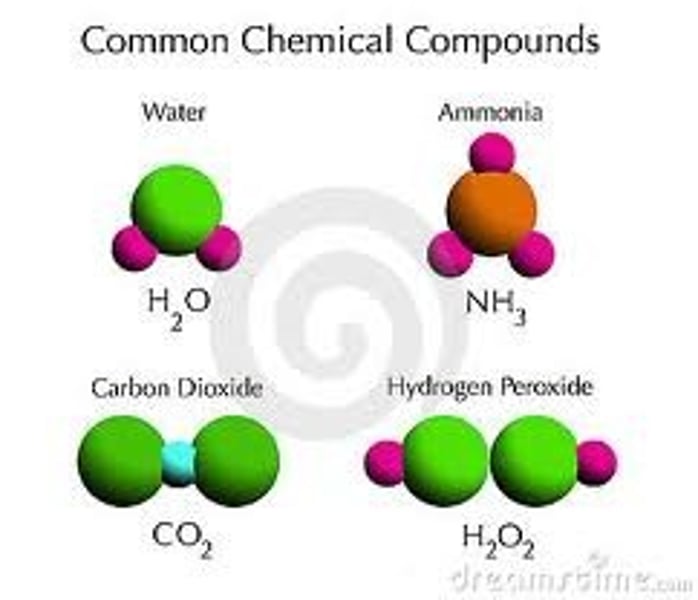
compound
two or more elements chemically joined together (i.e. elements aren't just mixed).
carbon
An element that can be found in all living things
carbon dioxide
a chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms bonded on either side by a carbon atom (CO2). Usually present as a gas.
hydrocarbon
a chemical compound containing hydrogen and carbon and often found in fossil fuels
calcium carbonate
a white, chalky substance found in the shells of many sea creatures (CaCO3).
hydrosphere
All of the water on Earth
atmosphere
the gases surrounding the Earth (or another planet)
lithosphere
The rocky, outer-layer of the Earth
proton
A positively charged particle found in the nucleus of an atom
neutron
A small particle in the nucleus of the atom, with no electrical charge
electron
A negatively charged subatomic particle
mixture
A material composed of two or more elements and/or compounds that are physically mixed together (i.e. not chemically combined).
energy
The ability to do work or cause change.
climate
The typical weather conditions in an area over a long period of time. (compares to a person's personality)
greenhouse gas
Gases in the atmosphere that trap energy, generally in the form of heat energy (infrared).
renewable resource
A resource that comes from natural sources or processes that are constantly replenished or replaced.
non-renewable resource
A resource of economic value that cannot be readily replaced or replenished by natural means on a level equal to its consumption.
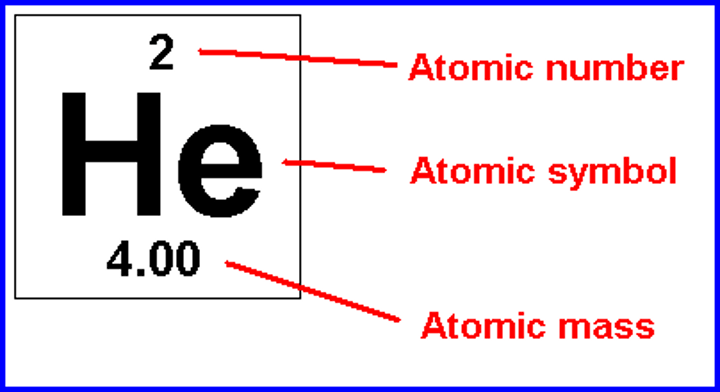
atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
atomic mass
The total number of protons and neutrons in a nucleus.
ocean acidification
Decreasing pH of ocean waters due to absorption of excess atmospheric CO2 from the burning of fossil fuels.
positive feedback
A mechanism that tends to magnify a process or increase its output.
negative feedback
A mechanism that dampens or weakens the response of a system to a particular event/process.
tipping point
The point at which a fundamental shift in the behavior of a system occurs.