IB, Business and Management, Unit 1
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
1.1 What is a business?
an entity that combines resources to create a good or service in exchange for money/capital to satisfy customers.
Resource input - Process to add value - Product outputs
Resource input
- Human
- Physical
- Financial
- Enterprise
The process to add value
- Production
Product outputs
- Goods
- Services
Input
- Human: People required for a process
- Physical: Quality and quantity of materials (even machines)
- Financial: money required for product
- Enterprise: least tangible but important. the IDEA and functionality of a business.
production processes
- capital intensive: ss that use a large proportion of land or machinery inputs. (a lot of money) e.g. car factory
- labor-intensive: a large proportion of labor both low skilled and high skilled
outputs
- goods: tangible products. physical. primary/secondary sector
- services: intangible. not physical
business functions
large might need special managers for each
- HR: Employing people, rewards, recruits, train, fire
- Marketing: promote product, price, package, distribute
- Finance/Account: Funds available for service. Forecast, record, finance
- Production: Appropriate processes. Desired quality. Control stock, methods of production, efficiency
the success of a business depends on these departments.
business tactics
business tactics
- plan to achieve TACTICAL OBJ
- short term requiring middle manager
sectors of a business
goods
- primary: raw materials form the primary sector. extraction. Eg. fishing, mining. Ma harm environment
- secondary: processed raw materials into other good. usually manufacturing. durable/non-durable and capital goods. Eg. iPad
Services
- tertiary: services provided with secondary goods. growth in this sector. Eg. healthcare, education
- quaternary: services focused on knowledge. E-services, IT.

chain of production
step through sectors to create a good or product.
business growth
see diagram
horizontal
- intend to increase market share and power
- take advantage of economies of scale
vertical
- lower transaction costs. market power
- reliability of supply increases
sectoral change
- constantly changes in size due to development
- measured by no. of people working on each sector
- business adapts to changing the environment. developing countries move away from primary sector
entrepreneur and intrapreneurship
- vital as innovates products and new business opportunities
ENTRE/INTRA
- entre: self-employed or central in the start-up of the business
- intra: employed by organizations to innovate
- balance risk of failure vs. success
INNOVATION BY:
- marker reading: observe customers and competitors. Change?
- need seeking: communicate to find new needs and satisfy
- technology driving: research and development to improve
reasons for starting a business
- Rewards: not possible to get all rewards if working for someone
- independence: own boss and can make own decisions
- necessity: if you can't find work
- challenge: personal. overcome yourself
- interest: enjoy what you do
- finding a gap: USP. something worthy/profitable
- sharing an idea: share something you like
process: idea. and planning
1. organizing the basics: Where? How? What?
2. Researching the market: Gap? Will it work? Satisfy need?
3. planning the business: narrow down. business plan detailed elements
4. legal requirements: meet al law requirements for business
5. raise finance: get the money needed to start the business
6. test market: what will occur? pilot. test consumers. will it succeed?
problems in starting own business:
- organization: location, name, structure, supplies
- market search: poor, target not appropriate, too optimistic
- plan: not convincing, goals vague or contradicting
- legal: labor laws, registration, taxes
- finance: cash flow, raising capital
*start-ups high probability of failure
business plan purpose
purpose:
- support the launch of the idea
-attract funds and investors
- support strategic planning
- identify resources needed
- focus for development
business plan elements:
- ideas, aims and objectives
- organization
- HR
- finance
- marketing
- operations
executive summary:
summary of business plan
1.2 types of business organization
1.2
sole trader
FOR PROFIT (COMMERCIAL) ORGANIZATION
the simplest form of business one person fulfills reasons to start a business
- sole trader owns and runs the business: may employ others but decisions and managing rely on him.
- no legal distinction between a sole trader and business. the sole trader is the business. unlimited liability
-limited finance: usually comes from personal savings, etc.
- closed customer: small business allows interaction between business and customer
- privacy: and limited accauntability. usually don't need to declare finance exept to TAX authorities
- registring: relatively easy and not expensive. less legal paperwork
sole trader advantages
- all profits belong to sole trader
- control over decisions (complete)
- flexibility (own boss)
sole trader disadvantages
-competition (hard because small business)
- high stress from al decisions
- lack of continuity if accident to sole trader
-limited expansion and financing
- unlimited liability
partnership
FOR PROFIT (COMMERCIAL) ORGANIZATION
2 or more people. often friends or family (2-20 generally)
-decisions made by partners: own and run together
- no legal distinction: between business and partners
- unlimited liability
- finance: more capital than sole traders. considered more stable
- "sleepy partners" provide finance. but not active in roles of business
- more variation of services that sole traders. bigger business
- greater accountability: often declare finance (not legally everywhere)
- deed of partnership: done because it provides the rights and duties of partners like responsibilities, financing, profit division, liabilities, etc.
- not necessarily share profits equally. depends on agreement
partnership advantages
- more production and efficiency
- under range of experience
- greater stability and continuity
partnership disadvantages
- each has unlimited liability
-still few access to finance vs. LTD (private) & PLC (public)
- not complete control
- profit shared between partners
- disagreement in decisions
corporations
FOR PROFIT (COMMERCIAL) ORGANIZATION
companies:
OTHER ORGANIZATIONS AND PARTNERSHIPS
organization stabilized for specific purpose. restricted by regulation
Private Limited company
(LTD)
- ownership and transparency sell shares to friends and family. not public. has accountability so it needs to publish books and finances in some cases. only sell shares privately
- finance: capital from shareholders. new partners may require to pay a fee. easier access to bank loans and financing as it is more stable
- limited liability
- control/decisionmaking: according to the agreement signed. authority handed down usually to family connections.
public limited company
(PLC) very similar, but stocks are public and are sold in the stock market. difficult decisions as many partners and decisions made by voting in the annual meeting of shareholders.
for profit social enterprises
form of business that has a social and beneficial purpose. improve well being.
- want profit without minimalizing social benefit
corperatives
OTHER ORGANIZATIONS AND PARTNERSHIPS
- form of the partnership but more than 20
- each participates actively in the running of the business
- financial coorporatives (casas de empeños)
sells for low prices, however still gain profit
- housing
- workers
- producer
- consumer
microfinances
- low. income economies.
- small finance to those who can't get and charge interest forprofit
- public private partnerships
- between public and private sector to generate profit and benefit eg. supervia
- profit = important but not the priority
- collaboration between business and local community
- greater democracy
- operate same functions than other businesses
public private partnerships advantages
- favorable legal status
- strong community deal
- a benefit to all stakeholders
public private partnerships disadvantages
decision making is complex because of transparency
- may be insufficient capital for growth and financial strength
non-profit enterprise
supports beneficial to social
don't want to make profit
non governmental
eg. greenpeace, cruz roja
surplus
surplus
similar to profit
but not distributed
it is reinvested for purpose
surplus = total revenue - total costs
non-governmental organizzazione (NGO's)
NON-PROFIT SOCIAL ENTERPRISE
pay taxes
charities
NON-PROFIT SOCIAL ENTERPRISE
aim to provide as much relief as possible for others (philanthropy)
don't pay tax
- profit not generated
- donations are important as it can't rely on government funding
- unclear ownership and control
charities advantages
- help people
- spirit of community
- foster discussions about the allocation of resources
- can innovate
charities disadvantages
- lack control
- employees may serve as all force. Eg. Greenpeace pirates
- funding is irregular
1.3 organizational objectives
1.3
mission statement:
what company currently does
why?
Who we are?
what needs to be done?
targeted to stakeholders
may be affected by external environment
vision statement
what do we want
- desired position
- future
- stakeholders and motivate employees
- vision should not change
objectives
- strategic: medium-long term to guide company in rigth direction
tactical: short medium terl. to obtain strategic objectives
- operational: day 2 day set by floor managers to achieve tactical
aim
long term goals to reach vision
heriarchy:
vition statement
aims
mision statement + objectives
strategical
tactical
operational
also:
- corporate obj
-department obj
- team obj
- individual obj
business strategy
- plan to achieve strategic obj in order to work towards aim
- medium & long term
- require senior managers for decisions and aprove by CEO
- careful analysis of:
- where business is
- development of plan to get aims
- consideration of strategy implementations
- periodic evaluation process. determine if plan is working or not
business tactics
- plan to achieve TACTICAL OBJ
- short term requiring middle manager
SMART objectives
Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Time specific
business tactics
- plan to achieve TACTICAL OBJ
- short term requiring middle manager
need for organizations to change objectives
- change in:
- internal environment
- external environment
internal environment
changes in:
- leadership: change aim & obj or style
- HR : alter heriarchy
_ organization: merge or adquisition change
- product
- operation
external environment
- STEEPLE
Social
Technological
Economical
Ethical
Political
Legal
Ecological
ethical objectives
social or environmental benefit
good image for company
custometr loyalty
positive work environment
reduces risk of legal issues
satisfy expectations for ethical behabviour
increase profit
IMPACTS: business itself, competition has to respond, suppliers have to become ethical as well, customer loyalty, local community, government
corporate social responsibility
: business has obligation to operate in a way that will have a positive impact on society
importance of CSR
provides benefits of ethical obj
closely relatedº
SWOT analysis
first stages in planning process
based on perception
positive negative
internal Strength Weakness
external Opportunities Threats
more sources is more reliable
if done poorly can mislead business
only useful if properly done
SWOT and market position
can be strengthened by pairing key factors from each quadrant
Strength Weakness
Opportunity growth re-orientation
Threat defusing defensive
ansoff matrix
helps plan and set obj
groth strategies
considers existing markets and products
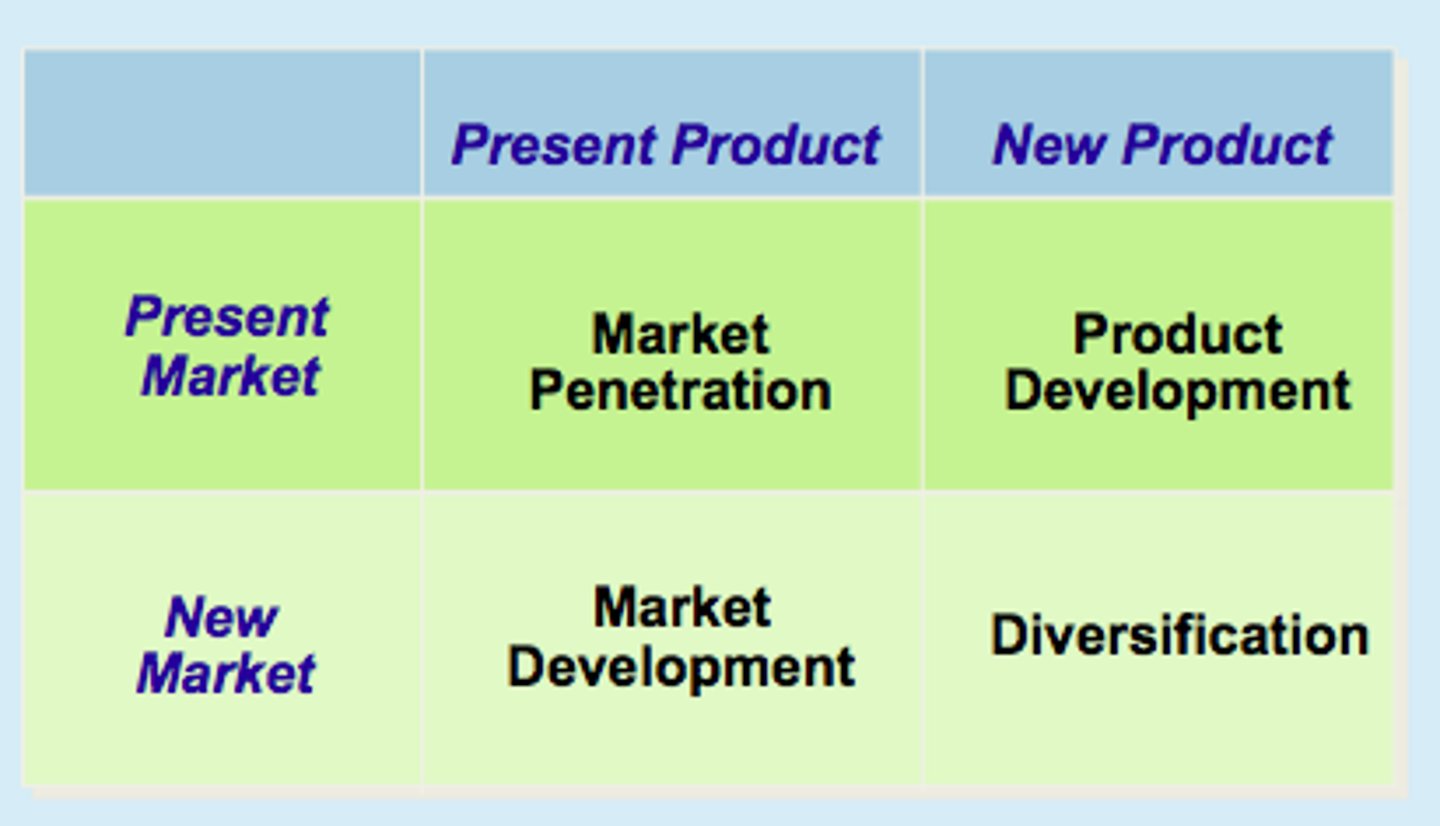
market penetration
sell more existing products in existing market
market development
new markets for existing products
opening walmart in australia failure
product development
new product in existing market
b¡diversification
new market new product
riskier
to reduce risk use effective market research
1.4 stakeholders
1.4
stakeholders
individuals or groups that have direct interest in business because actions will affect them
INTERNAL: work within business
EXTERNAL:outside business
GREY AREAS: may come together . Eg. worker of business afected as it lives where business is located
interest of internal stakeholders:
- shareholders return of investment
- CEO/manager to satisfy shareholder
- managers (senior and middle) supervisors focused on obj
workers protecting rights and working conditions
interest of external shareholders
gov: how business operates in the environment
suppliers: mantain relationship
community: products meet their needs. local impact
finances: return investments
pressure groups: impact on the area concern
Media: news & stories
stakeholder analysis
prioritizes ranks and interests of stakeholders
inside circle
- owners
-managers
middle circle:
- employees
-consumers
-finances
-suppliers
out circle
-community
-media
-gov
-pressure groups
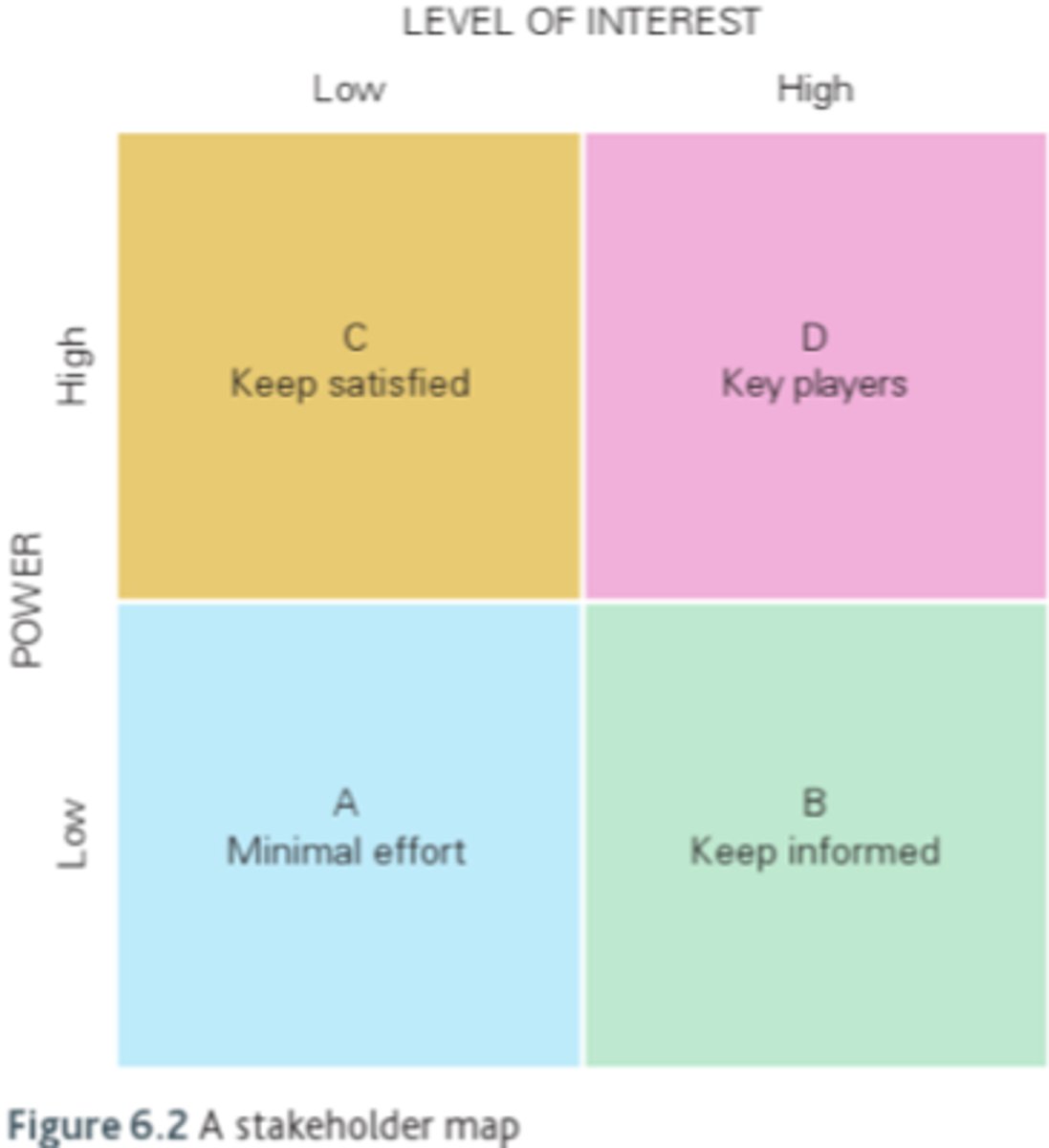
stakeholder mapping
A. rarely problem for business
B. make feel important
C. satisfied as they have power
D. most important. consult for decissions
importance:
least A B C D most
1.5 the external environment
high impact on business
steeple
Social
- lifestyle, education, social mobility, fashion / taste
Technological
- improvements, ICT, new tech, research, development cost, infrastructure
Economic
- eco cycle, growth rate, inflation, unemployment, exchange rate
Ethical
- corruption, codes of conduct, transparency, fair trade
Political
- stability,regional policies, trade policies
Legal
- regulations, health and safety laws, employment laws, competitor laws
Ecological
1.6 Growth and evolution
1.6
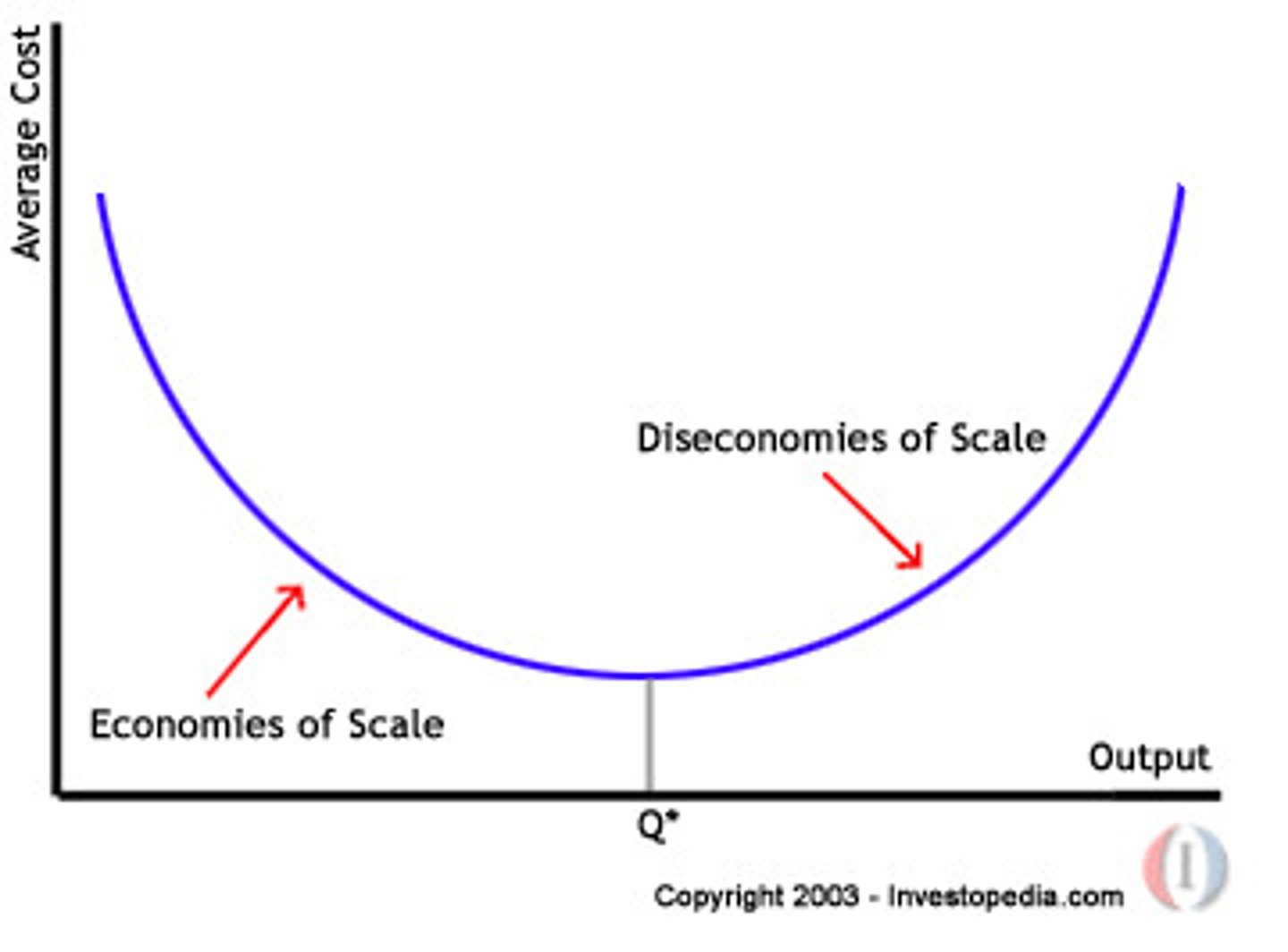
economies and diseconomies of scale
increase sale of operations become more efficient.
size and volume of output
economies of scale
reduction of average unit cost as increases size
sometimes becomes inefficient when growing. this is diseconomie of scale. increase in price per unit. if they grow past 100% capacity utilization, need to expand to continue production
efficiency: measured in terms of cost of production per unit
Total cost = fixed + variable cost
average cost = total cost / quantity produced
when growing, VC increases but FC spreaded in greater quantity
grow too much will need to expand rising costs and a bit of sales but not enough. this leads to diseconomies.
internal economies of scale
technical: law variable proportions. increase in VC but spread of FC
managerial: specialized
less risky than smaller business: financial
marketing: direct more effective campaigns
purchasing: bulk buying. - less costs
risk bearing: bigger product portfolio. less chance of failure
external economies of scale
consumers: more costumers if wider range. of products
employees: labour concentration. cheaper recruitment / training
internal diseconomies of scale + external
opposite advantages shown in economies of scale
-tech:
- managers too specialized inefficient
- financialy poor investments
. big marketing mistakes
- buy too much stock
- too high risks
- storage of skilled workers
Small vs. Big
Small
-greater focus on client
-exclusiv
-more motivation
-competitive advantage
-less competition
-more managable debts
-friend work environment
big
- greater chance of survival
-economies of scale
-higher status
-market leader
- increased market share
-loosing staff less worry
internal growth
organic growth
slow and steady
less risk
selling more products
develop product range
finance from banks, loans and retained profit
external growth
quick and risky
enter arrangement to work with another business
Joint ventures
external growth
agree to combine resources for goal.
strategic alliances c
collaborate for specific goal between business
more tha. 2 business may be part
franchise
external growth
expand
franchisor: original
franchisees: buy product to sell. have to be consistent with. franchisor. (% of sales)
franchisor provides:
stock
fitting
uniforms
staff training
legal financial aid
advertising and promotions
franchisee will
employ
set prices
wages
pay royalty (%)
local promotions
sell only franchisor products
advertise locally
globalization
world's regional economies becoming one
due to factors like technology
Impact of Globalization
increased competition: force business to become more efficient
greater brand awareness
known worldwide
skill transfer
and knowledge from all the world
closer collaboration
and new business opportunities
reasons for growth of multinational companies
- operating or registered in more than 1 country
- sometimes generate more reserve than actual countries
factors that allow MNC
improved communication - networks
dismanteling of trade barriers
disregulation of worlds financial market
increasing economic and political powe of mnc
IMPACT of MNC
economic growth
new. ideas
skill transfer
profits going elsewhere
brain drain
loss of market share
short term plans
environmental impact
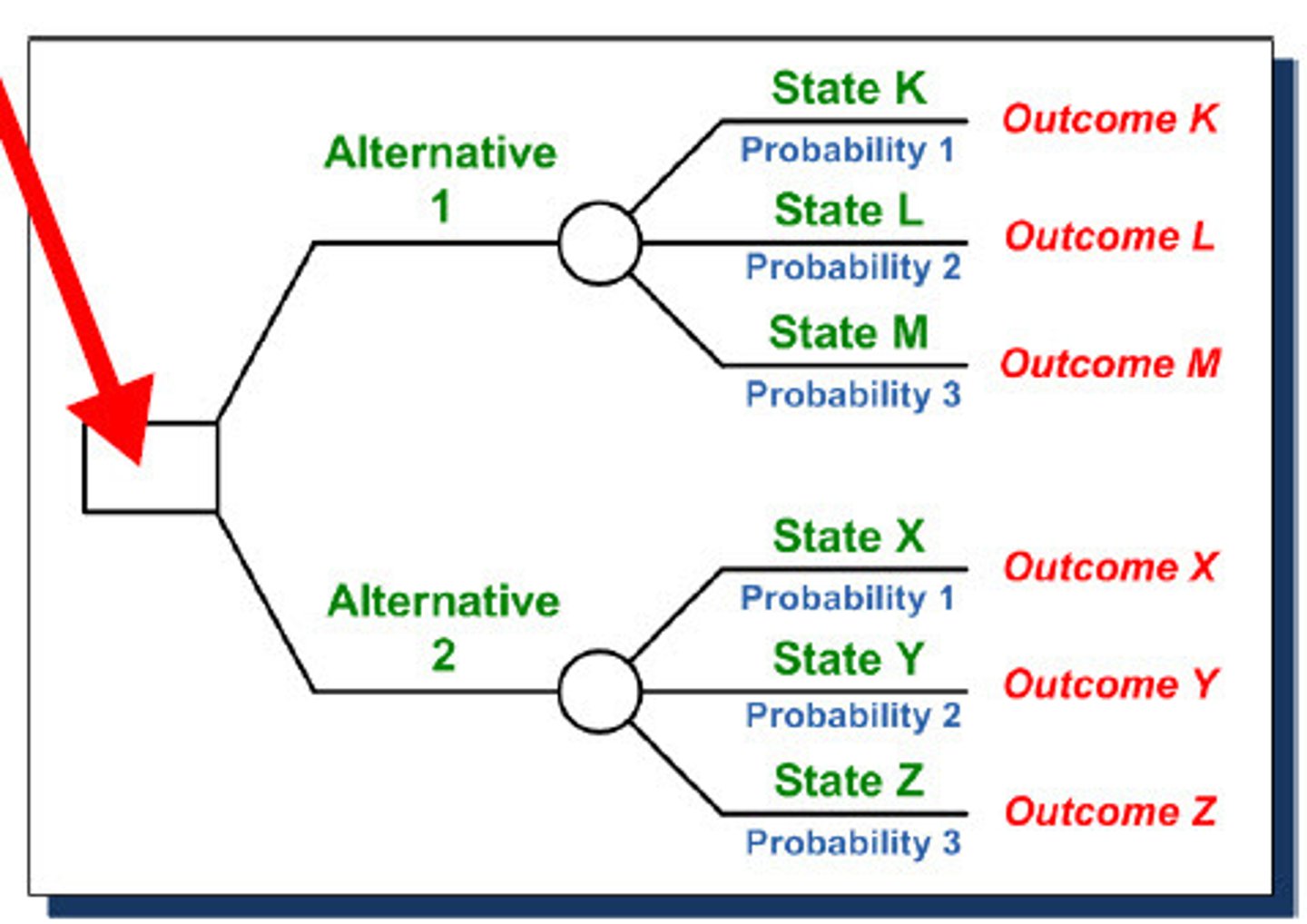
Decision trees
decision making problems
squares - business decision
circles - options
lines to circle - the cost of the option
lines from the circle - success/failure prob
over circle - expected outcome (prob of success x outcome of success) + (prob of failure x outcome of failure)
over/under square - final outcome calculated by (value over circle - the cost of the option)
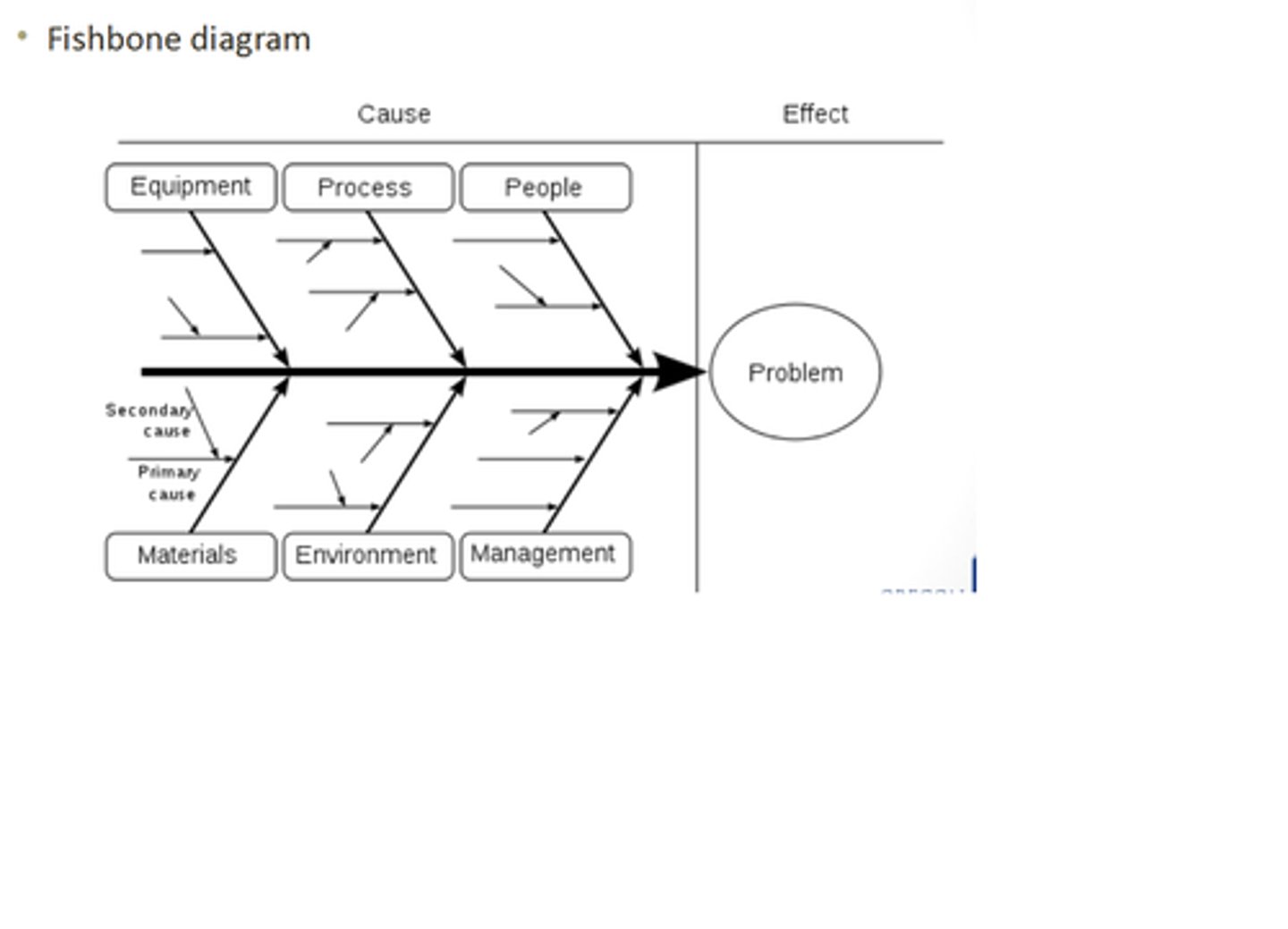
fishbone analysis
cause and effect diagram
identifies causes for effect or problem
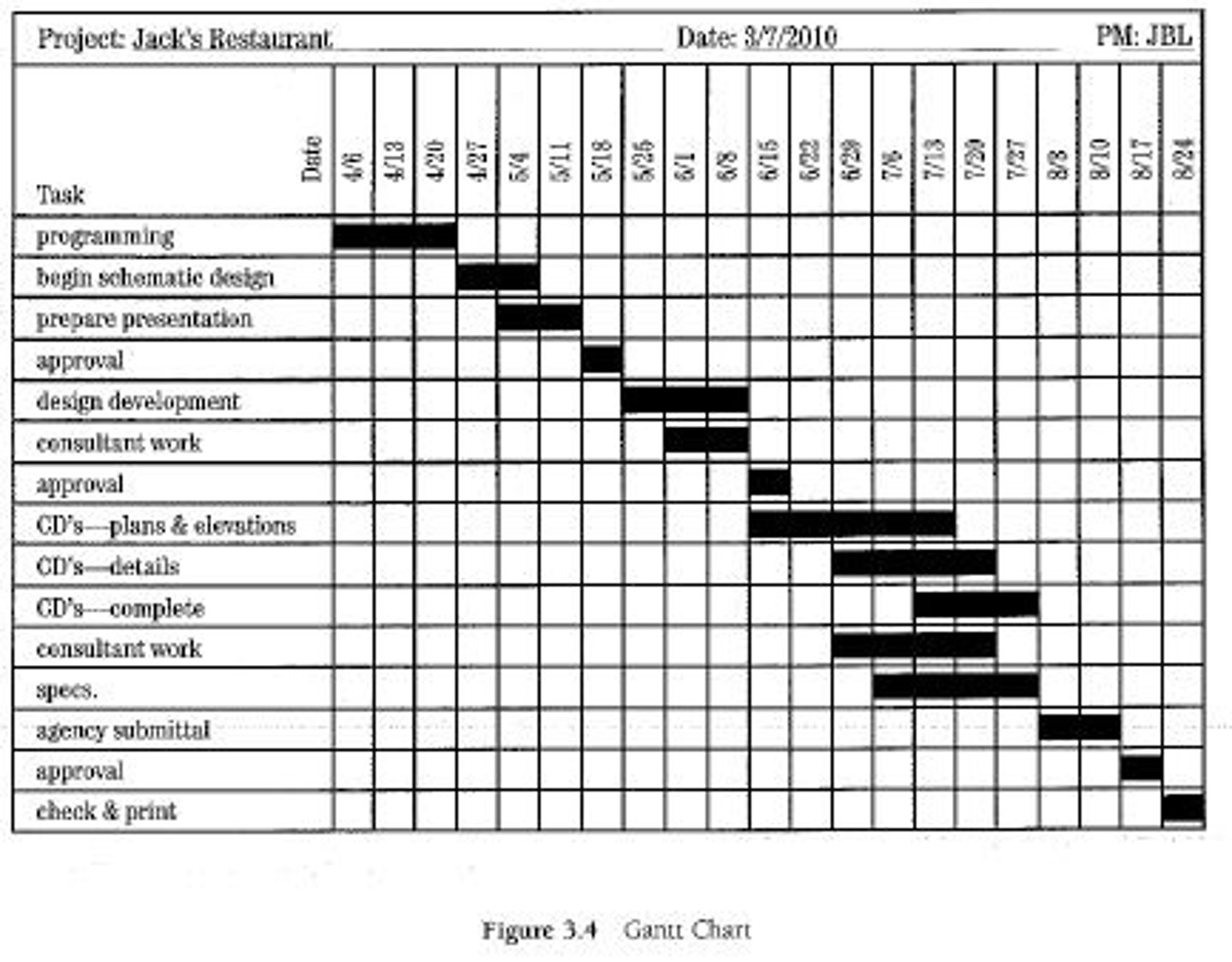
Gantt chart
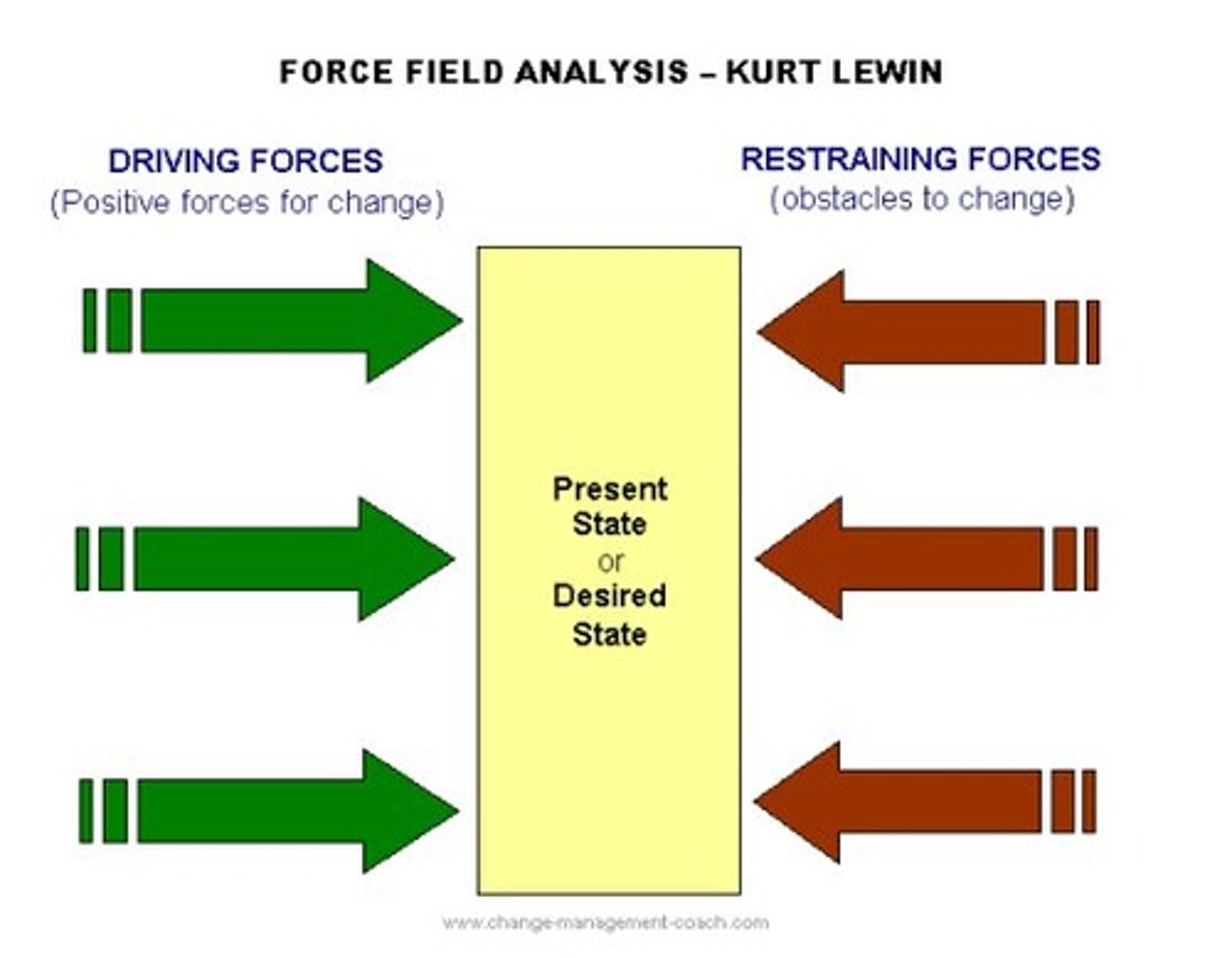
force field analysis
driving forces . initiate change and keep it going
restraining forces. decrease driving forces
0-5