Economic and traditional use of algae and climate change
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What did kathleen drew baker discover?
in 1949 she found the Conchocelis phase of pyropia, revolutionizing the nori industry in Japan
What are the benefits to seaweed aquacultre?
Land may not be required
Fertilizers not required/environmentally friendly?
Often in developing countries, analternative to fishing
Provides nursery habitat for fish and other organisms
Filter undesired nutrients from system
Has provided jobs to women/alternative livelihoods
why are seaweeds good to eat?
high in:
minerals
fiber
vitamins
protein
What does it mean if you encounter a nereocystis with two heads?
one will come face to face with a powerful supernatural creature from the sea- marking the door to the underworld (Haida nation)
Uses of seaweeds by caostal first nations
herring spawn on kelp
bull kelp halibut fish hook
bull kelp fishing line
What is the most important seaweed globally?
pyropia
on the coast when stinging nettle grows, the pyropia will be ready
as well as with the salmon moon
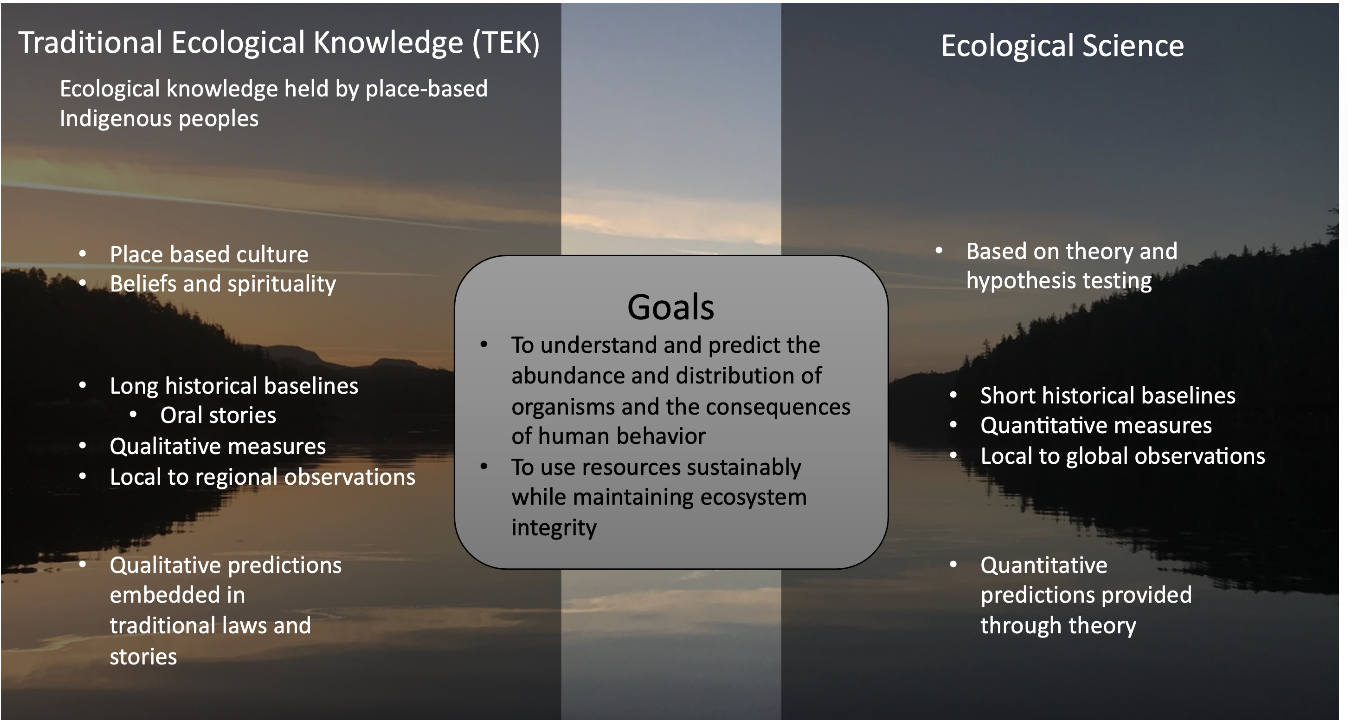
TEK and Ecological Science
How does increase in pCO2 affect seaweeds
increase water temp
decline of species
herbivore metabolism increases
reproduction
snow melt, decreases salinity
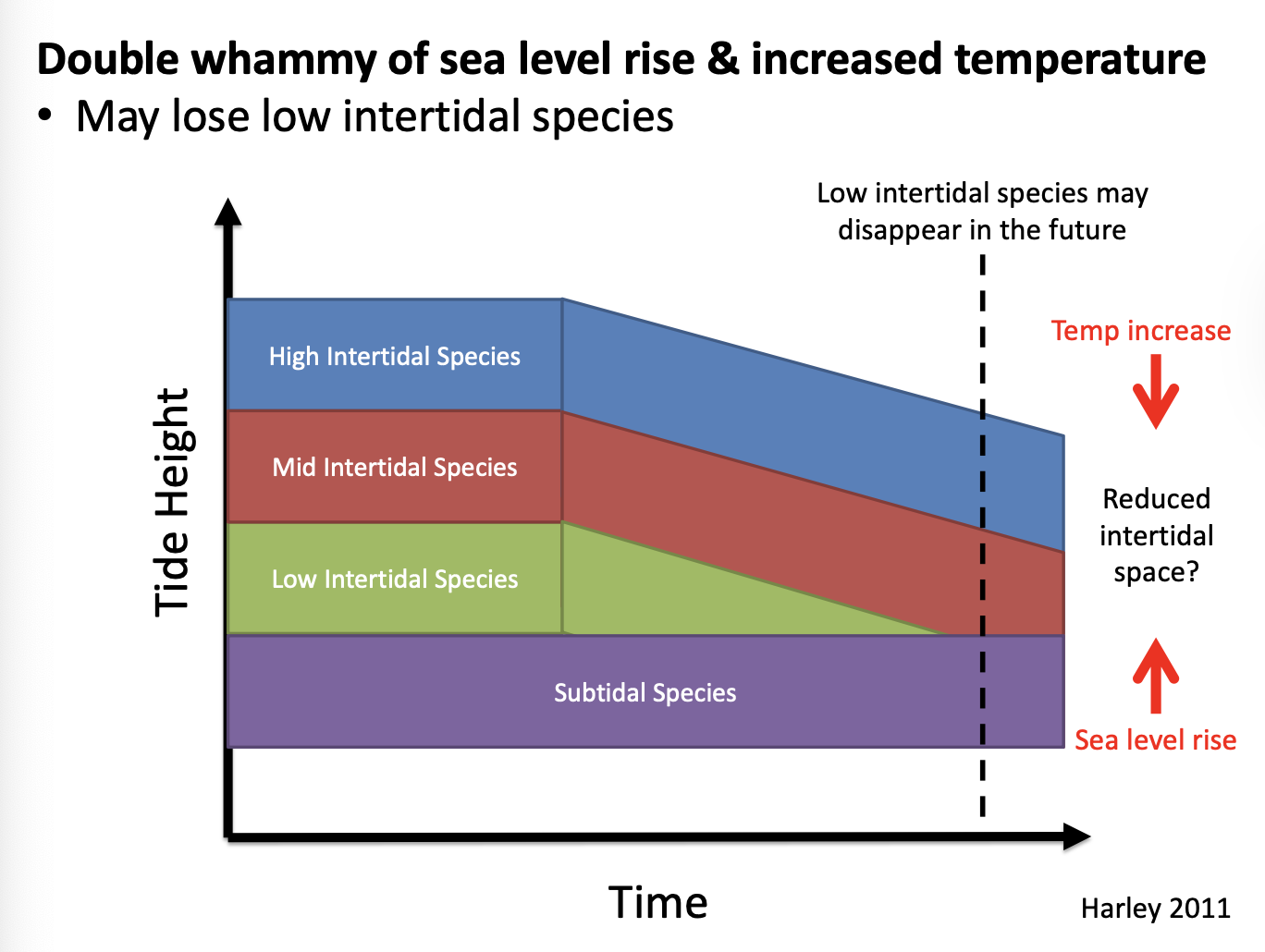
sea level rise
loose low intertidal species
reduce intertidal space
decreased pH
calcifiers negatively affected
increased co2 can fuel photosynthesis in some kelps and diatoms
increased co2 could mean higher C:N ratios and lower nitrogen which could decrease herbivory
reducded pH delays spore settlement and inital mucilage gel i reduced
What are two research question regarding pH?
will warming increase herbivory and lead to a decline in kelp forests?
will reduced pH remove herbivores and corallines, and lead to an increase in fleshy algae?
can algaes save us?
seaweed reduces methane produced by cow by 58% by eating asparagopsis
seaweed based packaging
carbon sequestration by kelp
What are the issues with kelp sequestration?
seaweed phostynthesis and takes up co2 which creates a deficite of co2 in the water in seconds, but then theres a delay in co2 to come in from the atmosphere:
the difference in partial pressure of CO2 between air and water is weak there for diffusion form atmosphere to ocean can take weeks to years
as these time scales are different, in the meantime grazers and fish are creating cos that the parcel of low co2 absorbs
also movement of this low co2 chunk of water
ultimate control is Air-sea equilibrium