ap microeconomics unit 2
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What are the 5 shifters of demand
Demand shifters
Taste and preferences
Market size
Price of Related Goods Substitutes + Complements
Changes in Income
Expectations
What are complementary goods?
A pair of goods where one is often needed to enjoy another; like cookies and milk.
If x and y are complements, an increase in the price of x will cause the demand for y to
decrease
If x and y are complements, a decrease in the price of x will cause the demand for y to
increase
The law of demand, ceteris paribus (Latin for "all other things being equal"),
as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity demanded will decrease, and vice versa, assuming all other factors that could influence demand remain constant
What is the law of supply
Ceteris Paribus Producers sell more at high prices and less at low prices.
What are substitute goods?
A pair of goods where one can be used in place of the other; like ice cream and frozen yogurt
If x and y are substitutes, an increase in the price of x will cause the demand for y to
increase
If x and y are substitutes, a decrease in the price of x will cause the demand for y to
decrease
What are normal goods in regards to changes in income?
These are goods that people buy more of when they have larger incomes; like shoes.
If consumers’ incomes increase, demand for normal goods will
increase
What are inferior goods?
These are goods that people buy less of when they have more income; like generic brands.
If consumers’ incomes increase, demand for inferior goods will
decrease
Income effect
As prices fall, your income has more purchasing power so you can afford to buy a larger quantity.
Substitution effect
As prices fall, substitute goods look less attractive so consumers buy a larger quantity.
What are the 6 non-price determinants of supply?
1. Prices of resources or inputs
2. Government tools (taxes decrease supply, subsidies increase supply, & regulations generally decrease supply).
3. Competition (number of sellers)
4. Technology
. Prices of other goods
6. Producer Expectations
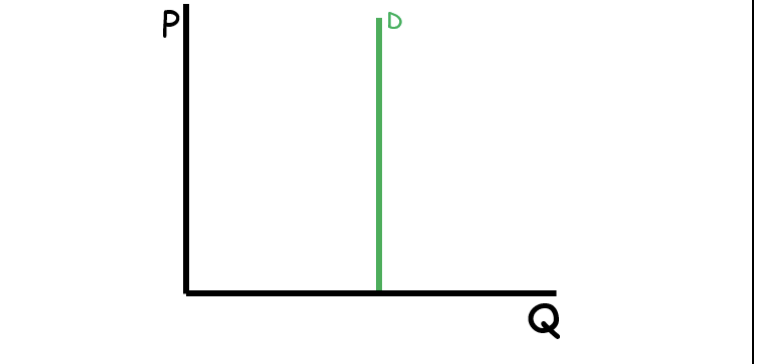
Perfectly Inelastic
0
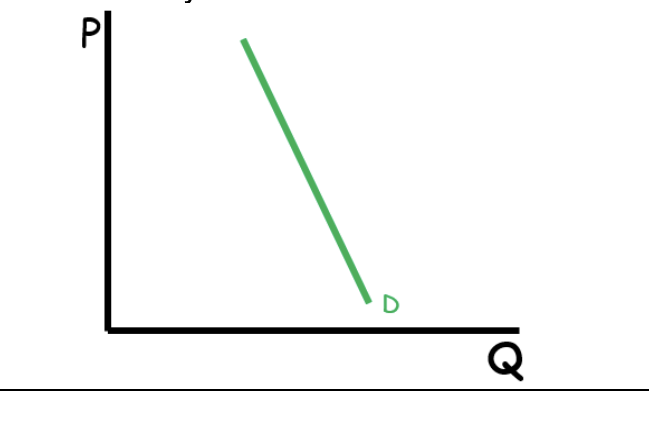
Relatively Inelastic
<1
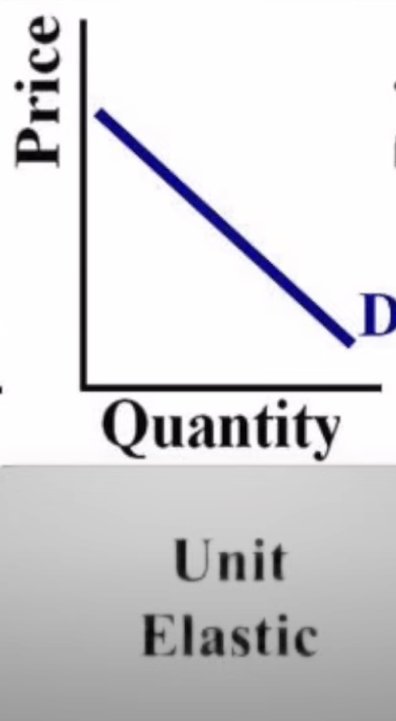
Unit Elastic
1
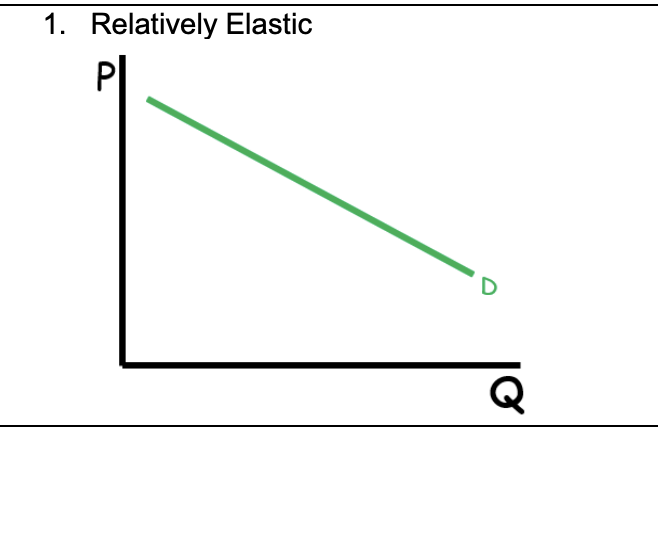
Relatively Elastic
>1
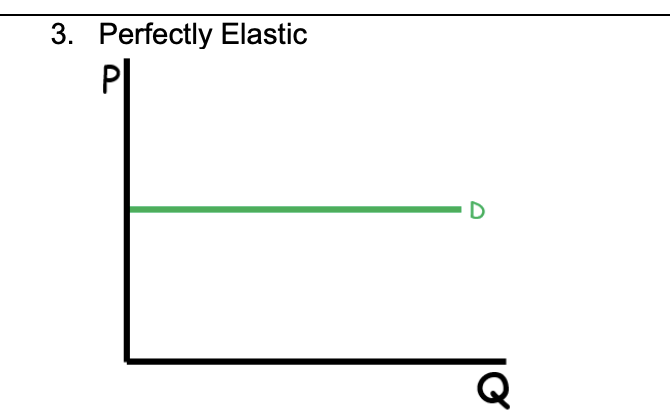
Perfectly Elastic
∞
Formula for Total Revenue
TR= Price * Quantity
If price decreases and TR increases, the demand curve is
Elastic
If price decreases and TR doesn’t change, the demand curve is
Unit Elastic
If price decreases and TR decreases, the demand curve is
Inelastic

formula for elasticity percentage change
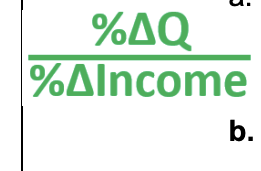
Income Elasticity Formula
negative coefficient means its inferior good
Price Elasticity Formula
%Quantity/%Price
Cross Price Elasticity
CP= %change in quantity of x/ %change price of y
positive coefficient= goods are substitutes
negative coefficient= goods are complements
Consumer surplus
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a product (the demand curve) and the price they actually pay.
Producer surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a product (the supply curve or marginal cost) and the price received.
Economic surplus
Consumer surplus, producer surplus, and any tax revenue added together.
Deadweight loss
AKA efficiency loss, is a reduction of economic surplus.
Allocative efficiency
When economic surplus is maximized. Marginal social benefit equals marginal social cost. (In a competitive market without externalities allocative efficiency is at equilibrium. A firm is allocatively efficient when P=MC)
An increase in the price of good X causes buyers to want to buy more of good Y. Which of the following explains the resulting change in the market?
A. The demand curve for good X will shift to the right because the goods are substitutes in consumption.
B. The demand curve for good Y will shift to the right because the goods are substitutes in consumption.
C. The demand curve for good X will shift to the left because the goods are complements in consumption.
D. The demand curve for good Y will shift to the left because the goods are complements in consumption.
E. There will be a downward movement along the demand curve for good X because the goods are complements in consumption.
Which of the following correctly describes the income effect associated with the law of demand?
If the price of a normal good decreases, the purchasing power of a consumer’s income increases and therefore consumers will be willing and able to purchase more of the good.
Which of the following will occur as a result of a decrease in the prices of the inputs used to produce a good?
The quantity supplied would increase at each possible price for the good.
Assume that the market for a good is characterized by a downward-sloping demand curve and an upward-sloping supply curve. Suppose that there is an improvement in technology for producing the good. Which of the following would occur?
The total economic surplus in the market would increase.