ANFS 240 - Muscles & Joints
1/194
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
Muscle
soft tissue made up of specialized cells called myofibers, main purpose is contraction
Cardiac muscle
Specialized type of muscle that makes up the heart wall, striated and involuntary
Epicardium
What is cardiac muscle externally surrounded by?
Smooth Muscle
specialized type of muscle that lines blood vessels and viscera (internal organs), involuntary, not striated
Skeletal Muscle
striated & voluntary, makes up half of the weight of an animal, typically consumed as food
Epimysium
(1) dense connective tissue that surrounds the entire muscle belly
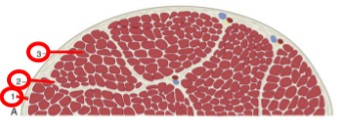
Perimysium
(2) loose layer of connective tissue that surrounds small bundles of myofibers
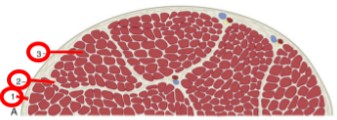
Endomysium
(3) thin connective tissue that surrounds each myofiber
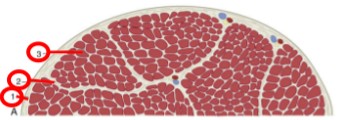
Tendons
epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium all meet at the end of each muscle belly, this is how most muscles attach to bone
contraction
shortening the length of the myofibers, & therefore the muscle as a whole
relaxation
passive process that allows the muscle to return to its original shape and position
locomotion
movement of the animal in a direction
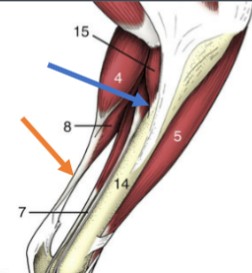
tendinous
(orange) muscles terminate in tendons that attach them to the periosteum of the bone, not the same as a ligament
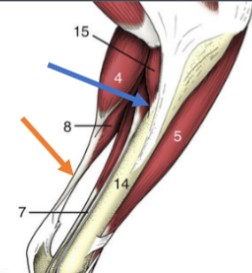
fleshy
(blue) apparent direct attachment of bone to muscle via very short tendons
aponeurotic
a flat sheet of tendinous connective tissue that attaches muscle to bone, common in trunk muscles
apneurosis
flat, broad tendon
agonist
responsible for primary motion of a joint
antagonist
muscles that opposes the motion of the agonist
synergist
aids the motion of the agonist
fixator
stabilizes the proximal end of the limb while the distal end moves
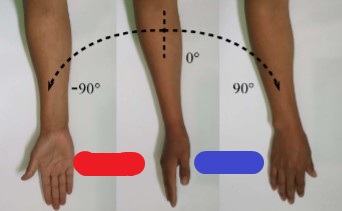
pronation
(blue) palmar/plantar side rotates medially toward the palmar/plantar direction
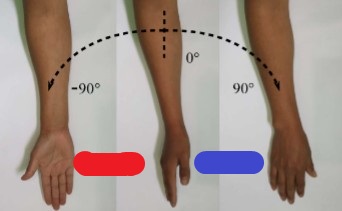
supination
(red) palmar/plantar side rotates laterally toward the dorsal direction
parallel
(1 & 2) all fascicles run the same direction, greatest amount of contraction → not efficient, less strong
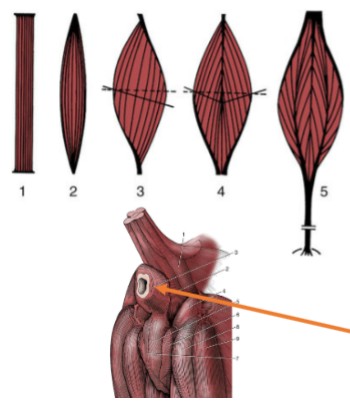
Pennate
(3, 4, & 5) fascicles run at an angle, less shortening → stronger contractions
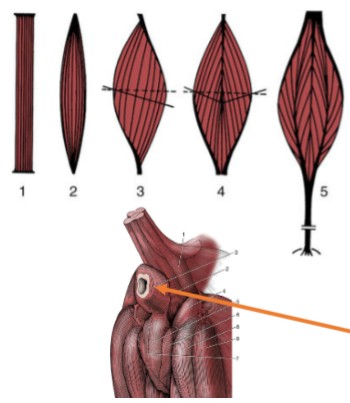
Unipennante
(3)
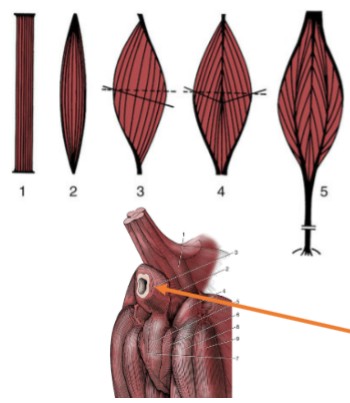
Bipennate
(4)
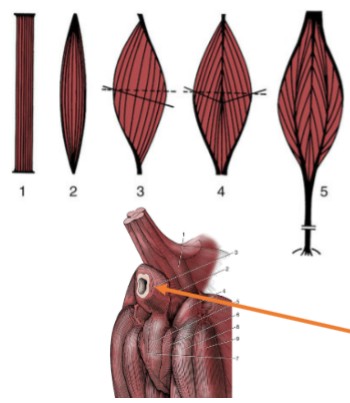
Multipennate
(5)
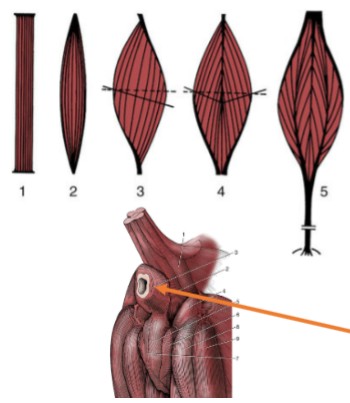
Sphincter
(orange) fibers encircle an opening and contract around it
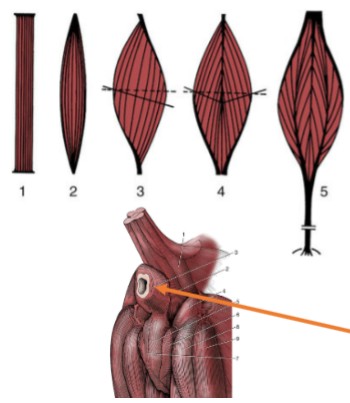
Origin
(red), more proximal or central muscle attachment to bone
Insertion
(blue), more distal or peripheral attachment, typically moves with extremity & will be drawn to the origin
Fascia
connective tissue that separates & surrounds larger structures
Superficial fascia
loose connective tissue that is underneath the skin
Intrinsic muscle
muscles whose origins and insertions are both within the limb
extrinsic muscle
girdle muscles whose origins are on the trunk and insertions are on a limb
Pectoral Muscles
forelimb girdle muscles, ventral, responsible for adduction of the forelimb, major flight muscles in birds
pectoantebrachialis
Origin: manubrium
Insertion: humerus (just proximal to the elbow)
Function: adduction of the forelimb
Pectoralis Major
Origin: body of the sternum
Insertion: diaphysis of the humerus
Function: adduction of forelimb
Pectoralis Minor
Origin: body of the sternum
Insertion: ventral humerus
Function: adduction of the forelimb
Xiphihumeralis
Origin: xiphoid of the sternum
Insertion: ventral humerus
Function: adduction of the forelimb
Sternomastoid
V-shaped paired muscles
Origin: cranial manubrium
Insertion: hyoid bone
Function: flex the head (pair) or turn the head (singly)
Sternohyoid
Ventral, paired strap-like muscles
origin: first costal cartilage and manubrium
Insertion: hyoid bone
Function: retracts the hyoid bone
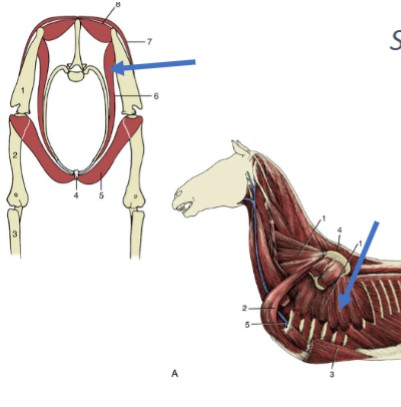
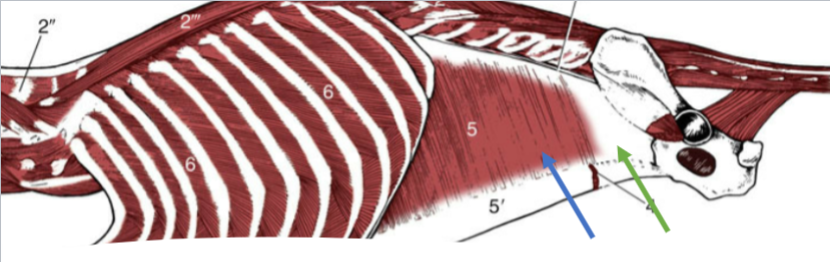
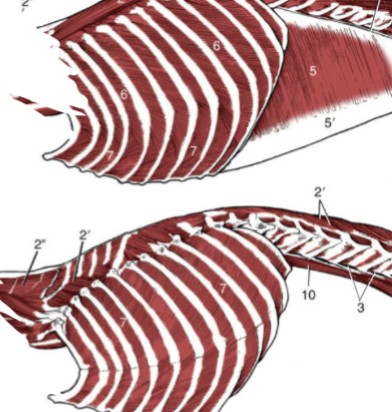
Latissimus Dorsi
dorsal and lateral muscle, large, broad, flat - caudal to the trapezius
Origin: spinous processes of 4th and/or 5th thoracic and 6th lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: the medial side of the proximal humerus shaft
Function: retracts the limb, drawing the forelimb dorsocaudally. If limb is fixed, it advances the trunk forward
Brachiocephalicus
cranial girdle muscle, consist of two distinct muscles: clavotrapezius & clavobrachialis,
Origin: occipital bone and transverse process of cervical vertebrae
Insertion: lateral side of proximal radius and ulna
Action: shoulder extension; neck lateral flexion, raise shoulder and pull forelimb forward
Clavotrapezius
blue
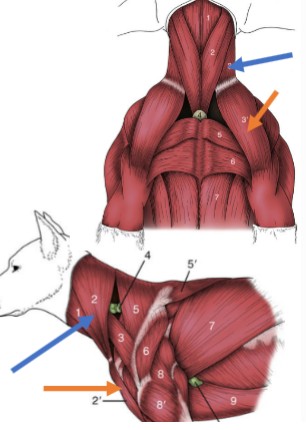
Clavobrachialis
orange
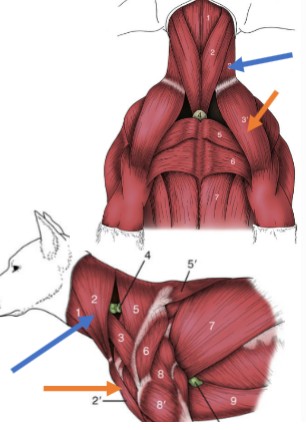
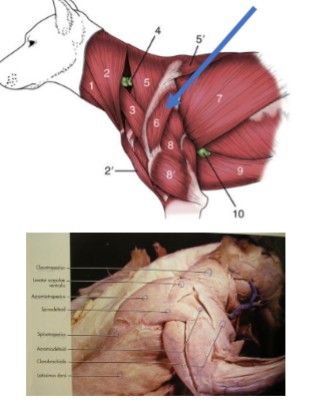
Trapezius muscles
cranial and dorsal, made up of two parts
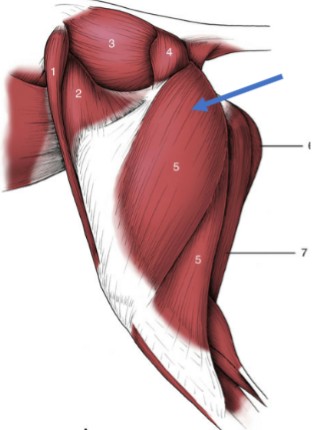
Acromiotrapezius
(5) cervical, thin, fan-shaped muscle, paired that both share an aponeurosis at their origin
Origin: dorsal spinous process of cervical vertebrae
Insertion: spine of the scapula
Function: elevate and abduct the forelimb
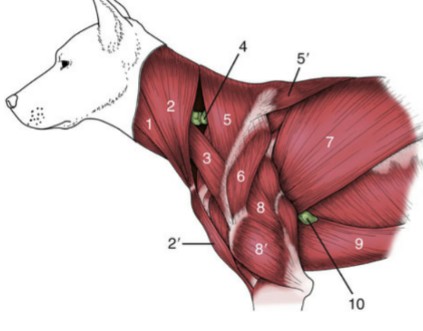
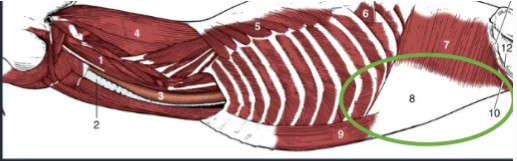
Spinotrapezius
(5’) thoracic, flat, dorsal, triangular muscle, caudal to acromiotrapezius
Origin: dorsal spinous process of the thoracic vertebrae
Insertion: spine of the scapula
Function: dorsal and slight caudal movement of the scapula - aids in advancing the forelimb
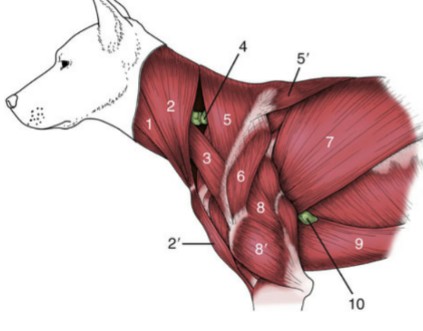
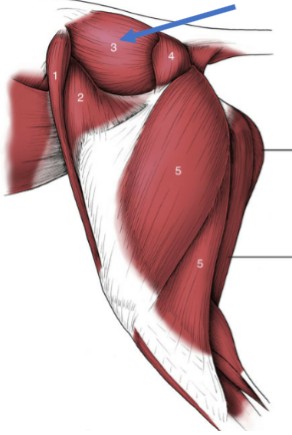
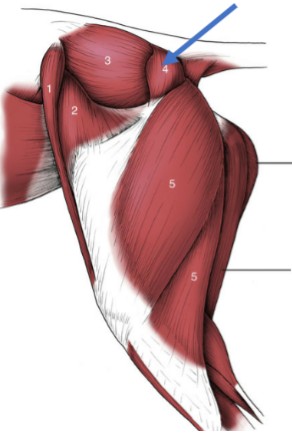
Deltoid muscles
two separate muscle bellies in the cat (spinodeltoid & acromiodeltoid)
Origin: scapular spine (at or near the acromion)
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
Action: flex the shoulder
Triceps brachii
3-headed muscle, on the caudolateral forearm, agonist to biceps brachii during flexion
Lateral & Medial heads:
Origin: (L&M) Humerus, (Long head) caudal edge of the scapula
Insertion: olecranon of the ulna
Action: extend the elbow joint and flex shoulder when the elbow is in extension
Serratus ventralis
large fan-shaped muscle deep to the scapula, one of the main muscles attaching the forelimb to the trunk
Origin: transverse processes of C3-C7 + first 7 ribs
Insertion: deep surface of the scapula
Function: support the trunk
Gluteus medius
large, cranial rump muscle
Origin: lateral crest of the wing of the ilium
Insertion: proximal femur
Action: extend the hip & abduct the limb
Gluteus maximus
smaller rump muscle, superficial, caudo-distal to the hip joint
Origin: lateral border of the sacrum
Insertion: proximal femur
Action: extend the hip, abduct the limb
Caudofemoralis
only in cats, just caudal to the gluteus maximus
Origin: transverse process of the first coccygeal vertebrae
Insertion: lateral patella
Action: abduct & extend the pelvic limb
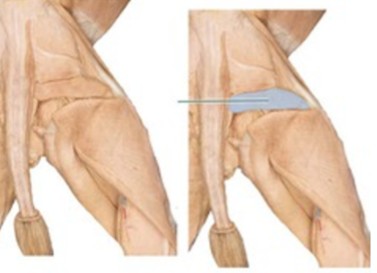
Hamstring muscles
What group does the biceps femoris, semimembranosus, and semitendinosus belong to?
Biceps femoris
very large muscle on the caudolateral side of the femur
Origin: ischiatic tuber of the os coxae
Insertion: proximal end of the tibia/fibula
Action: flexion of the stifle, extension of the hip
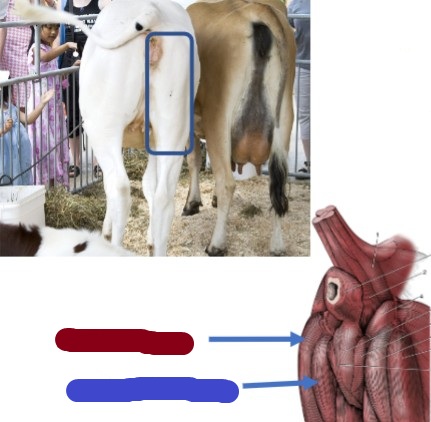
Semimembranosus
(blue) Clinical relevance, where to give vaccines, more medial
Origin: ischiatic tuber of os coxae
Insertion: proximal ends of tibia/fibula
Action: flex stifle, extend hip
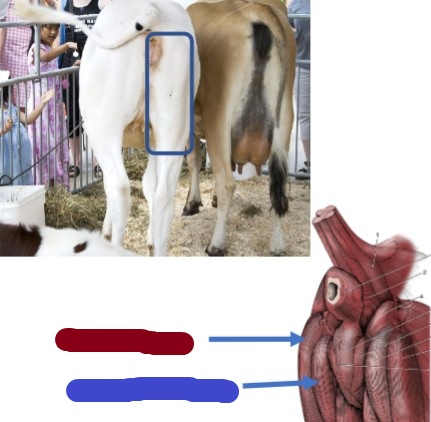
Semitendinosus
(red) Clinical relevance, where to give vaccines, more lateral
Origin: ischiatic tuber of os coxae
Insertion: proximal ends of tibia/fibula
Action: flex stifle, extend hip
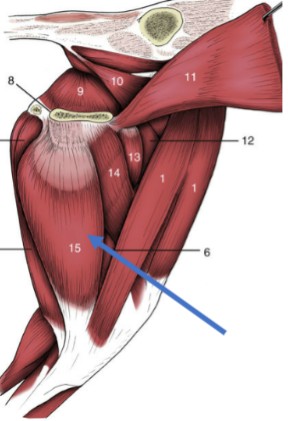
Gracilis
wide, thin muscle that covers the superficial aspect of medial thigh
Origin: ventral pelvic symphysis
Insertion: cranial border of the tibia
Function: flexion of the stifle, extension of the hip, adduction of the limb
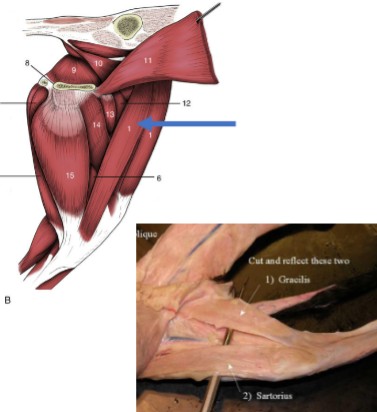
Sartorious
thinner strap-like muscle on the inner thigh, more cranial than the gracilis
Origin: crest of the ilium
Insertion: patella & proximal tibia
Action: hip flexion, stifle extension, limb adduction
Quadriceps complex
What is a 4-headed muscle that extends the stifle, made up of vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, and the rectus femoris?
Vastus medialis
(red) 1/3 of Quadriceps complex
Origin: diaphysis of the femur
Insertion: tibial tuberosity & patella
Action: extend the stifle
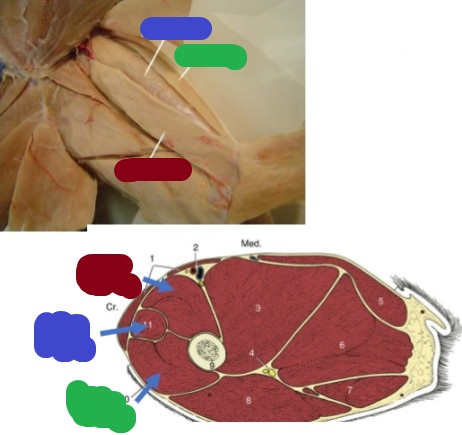
Vastus Lateralis
(green) 1/3 of Quadriceps complex
Origin: diaphysis of the femur
Insertion: tibial tuberosity & patella
Action: extend the stifle
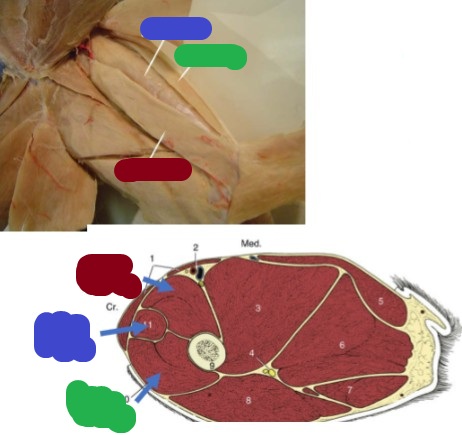
Rectus femoris
(blue) cranial to vastus medialis
Origin: ilium
Insertion: tibial tuberosity
Action: extension of the stifle/flexion of the hip
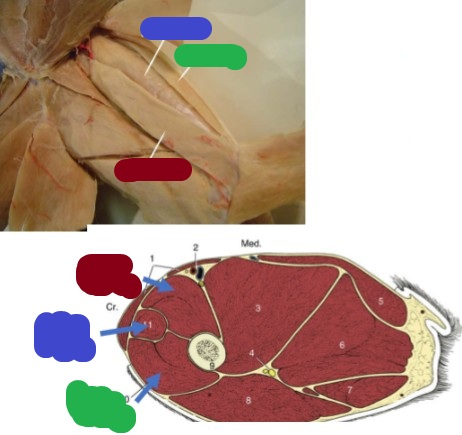
Vastus Intermedius
(red) 1/3 of Quadriceps complex
Origin: diaphysis of the femur
Insertion: tibial tuberosity & patella
Action: extend the stifle
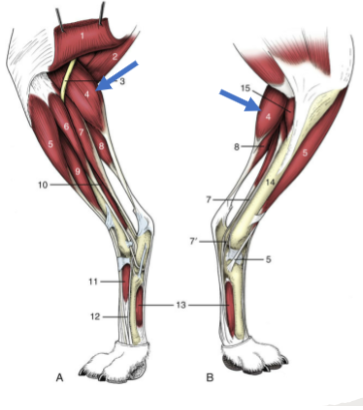
Gastrocnemius
caudal muscle along the tibia/fibula, calf muscle, with 2 head: medial and lateral
Origin: patella and caudal surface of the distal femur
Insertion: calcaneus via the Achilles tendon
Action: extend the hock
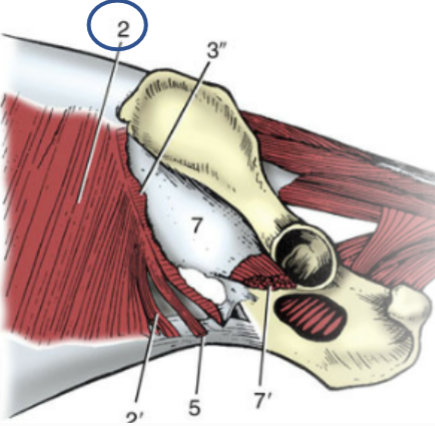
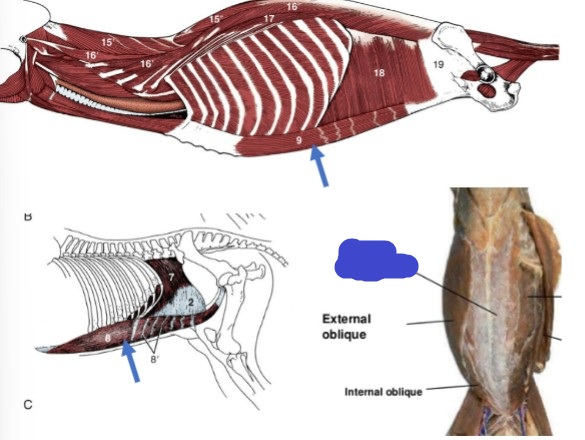
Abdominal muscles
what muscle group has 4 muscles in total, form the wall of a cavity, that functions are: flexion the spine, labored exhalation, expulsion of urine, feces, and/or a fetus, and vomiting, and contain all large, flat muscles with large aponeurotic insertions?
External abdominal oblique
fibers run caudoventrally, abdominal muscle
Origin: last 9-10 ribs and thoracolumbar fascia
Insertion: linea alba via aponeurosis
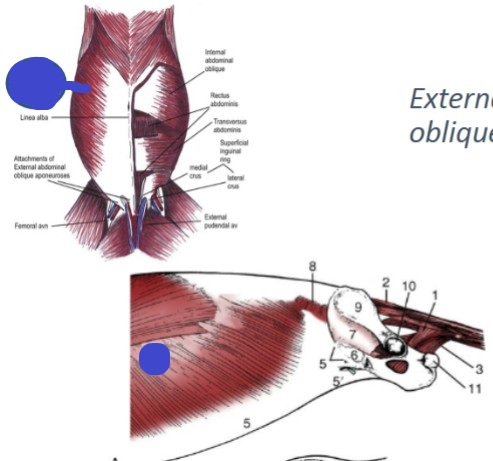
Internal abdominal oblique
fibers run cranioventrally, abdominal muscle
Origin: last 9-10 ribs and thoracolumbar fascia
Insertion: linea alba via an aponeurosis
Transversus
(blue) deepest abdominal muscle, fibers run transversely (ventrally)
Origin: costal arch, lumbar vertebra, and ileum
Insertion: linea alba
Significant caudal aponeurosis (green)
Rectus abdominis
most ventral abdominal muscle, long and narrow
Origin: pubis
Insertion: costal cartilage
Diaphragm
What is the main muscle of respiration that’s a wide, thin muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity, contains 3 openings for the esophagus, aorta, and caudal vena cava, and moves cranially (expiration) and caudally (inhalation) to decrease/increase the thoracic volume?
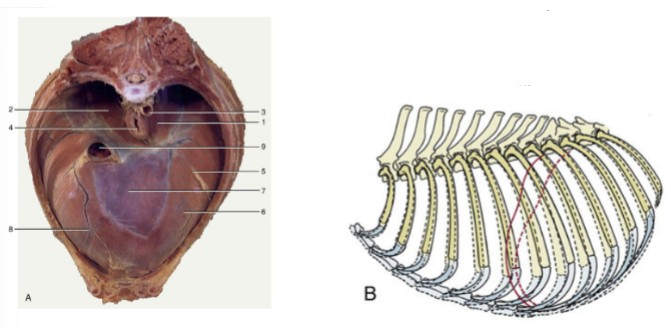
Intercostal muscles
muscles between each rib
External: superficial and runs caudoventrally
Internal: deep and runs cranialventrally
Engaged during inspiration and expiration
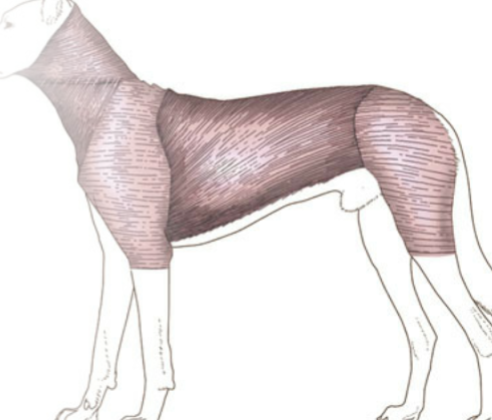
Cutaneous trunci
thin, very large superficial sheet of muscle that spans the trunk, particularly well-developed ventrally in many large animals, “twitches” or shakes the skin in response to flies and other irritants
biceps brachii
relatively thick muscle lying on the cranial surface of the humerus, only one head in the cat
Origin: scapula
Insertion: radius
Function: flexes the elbow
Circulatory System
Network of vessels that carry fluid throughout the body, specifically blood for cardiovascular system and lymph for lymphatic system (significant part of the immune system)
Cardiovascular System Functions
Carry oxygen throughout the body to tissues (collected in the lungs)
Carry nutrients throughout the body to tissues (collected in the GI tract)
Carry hormones throughout the body to tissues (collected from specialized endocrine glands)
Remove waste from cells & deliver to organs for processing and elimination
Development of cardiovascular system
Early and common origin in the developing embryo, all are related and have specialized tissues unique to this system
Peripheral blood vessels
those that carry blood from the heart to tissues and return blood to the heart
artery
takes blood away from the heart, have very thick, strong walls, made of 3 layers, can withstand and support high blood pressure
arteriole
smallest arteries
Vein
brings blood back to the heart, thinner-walled than arteries, similar construction to arteries, but much thinner tunica interna, and a tunica media that is thinner and with far less elastic tissue (often collapsed unless blood pressure is increased), and has valves to prevent backflow because pressure is lower
Venule
smallest veins
Capillary
the tiny connections between arterioles and venules where the transfer of materials (oxygen, nutrients, etc) happens
Tunica interna
innermost part of the artery, specialized layer of connective tissue with an inner elastic membrane surrounding it externally; very smooth
Tunica media
middle layer of artery, thickest layer made up of elastic tissue and smooth muscle
Tunica adventitia
external layer of artery that is mostly fibrous, limiting the expansion of the artery and keeping it from stretching out and slowing down blood flow
What can backflow cause?
clots and obstructions
Capillaries
very narrow endothelial tubes, supported by very delicate connective tissue, allows for transfer of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to and from the blood due to how thin-walled they are
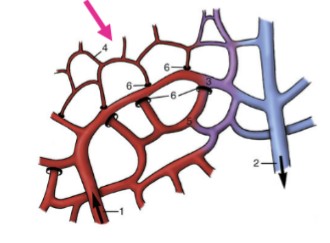
How does transfer of oxygen, nutrients, and waste occur?
fluid escapes into the tissue from the arteriole side due to higher pressure, then reabsorb fluid from venule end
capillary bed
network of capillaries that supplies blood and removes waste from organs
Where are capillary beds densest?
More “active” areas due to the increase in blood exchange
Sinusoids
specialized type of capillary found in organs like the liver, spleen, and bone marrow, wider than regular capillaries and often have fenestrations (small holes) in their wall which allow for larger compounds to flow in and out of the vessel
Flow of blood
Heart → Artery → Capillary → Vein → Heart
Heart
Central organ that pumps blood continuously that has rhythmic, self-sustaining contractions
Right atrium
3
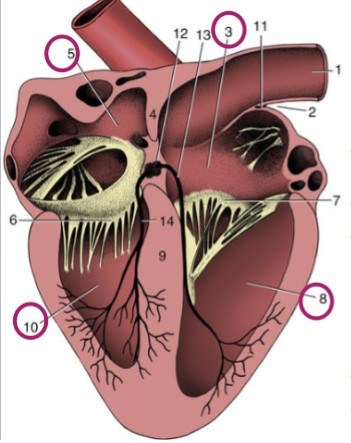
Left atrium
5
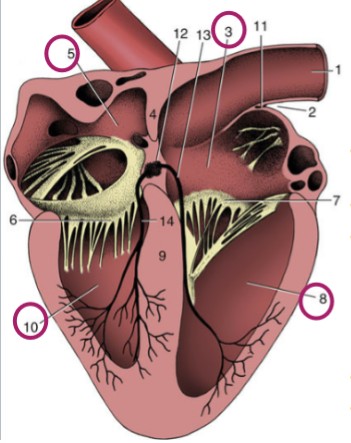
Right ventricle
8
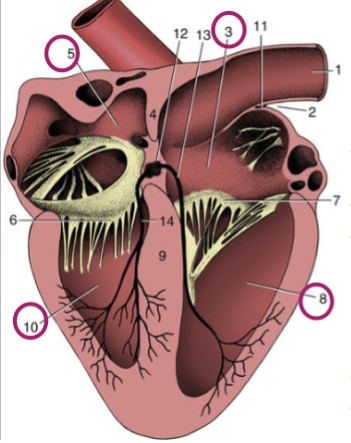
Left ventricle
10
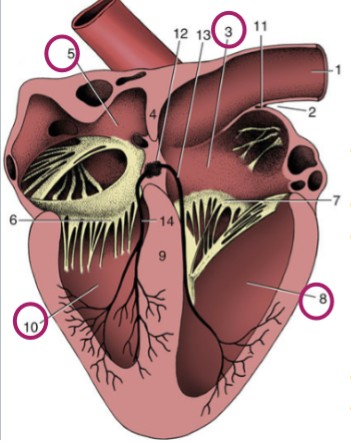
Atria
thinner-walled, cranial/dorsal part of heart, stretchy, accepts blood