Case 9: Nancy Jones
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
GFR
Fluid filtration rate through kidneys (glomerulus → Bowman’s capsule
Normal: 120 mL/min/1.73m2
GFR: Measurement
Glomerular marker clearance
Markers
Inulin: Gold standard
Urine creatinine: Creatine (in muscles) metabolism byproduct
Small secretion in tubules = Over-estimate GFR = eGFR
BUN and Serum creatinine: Increased = Low GFR
GFR: Determinants
Control renal blood flow (RBF)
Myogenic response
Tubuloglomerular feedback
RAAS
GFR Determinants: Myogenic Response
Increase RBF = Afferent arteriole stretch = Reflexive vasoconstriction = Increase resistance = Constant RBF + GFR
GFR Determinants: Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Increased afferent arteriole pressure = High RBF + GFR = Increase Na+ and Cl- delivery to early DCT = Detected by macula densa cells
Macula densa cells release adenosine = Stimulate afferent arteriole constriction = Decrease RBF + GFR
GFR Determinants: RAAS
Decreased afferent arteriole pressure = Low RBF + GFR = Detected by JG cells
JG cells release renin = Activate RAAS = Stimulate efferent arteriole constriction + Increase Na+/water reabsorption = Increase RBF + GFR
Renal Clearance
2 mechanisms:
Glomerular Filtration: Passive clearance
Small and unbound molecules filtered
Tubular Secretion: Active clearance
In PCT
Large and protein-bound molecules eliminated by transporters (antibiotics, diuretics)
AKI: Description
Sudden renal function loss with increased creatinine and BUN
Prerenal: Low perfusion (most common)
Renal: Kidney damage
Postrenal: Inadequate urine drainage
AKI: Epidemiology
Risk factors:
Older age
Infections
Pneumonia
CKD
HTN
Meds
NSAIDs
Nephrotoxic antibiotics
AKI Etiology: Prerenal
Decreased renal perfusion
Hypovolemia
Hemorrhage
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Diuretics
Hypotension
Decreased circulation/arterial volume
CHF
Liver failure
Pancreatitis
Renal artery stenosis
Drugs
NSAIDs
ACE inhibitors
AKI Etiology: Renal
Direct kidney injury
Acute Tubular Necrosis: Tubule damage from ischemia or toxicities
Most common cause
Ischemia: Hypoxia, hypotension
Toxicity: Contrast
Acute Interstitial Nephritis: Renal interstitium inflammation
Drug hypersensitivity
Glomerulonephritis: Glomerular inflammation
Vascular diseases
AKI Etiology: Postrenal
Bilateral urine flow obstruction from renal pelvis to urethra
Acquired obstructions
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Tumours
Stones
Iatrogenic (catheter injuries)
Neurogenic bladder: Disrupted detrusor/sphincter innervation → Urinary retention
Congenital malformations
AKI Pathogenesis: Prerenal
Decreased blood to kidneys (perfusion) = Low GFR (kidney function loss)
JG cells secrete renin = RAAS activation = Aldosterone increase Na+/water reabsorption = Increase urine osmolality (high solutes)
***High Na+ in blood = ADH secretion = Increase urea and water reabsorption
High blood BUN:creatinine ratio
AKI Pathogenesis: Renal
Ischemia + toxin exposure = Tubular cell necrosis/apoptosis = Decreased reabsorption capacity (kidney function loss)
Increased Na+/water in urine = Decreased urine osmolality (low solutes)
AKI Pathogenesis: Postrenal
Bilateral urinary flow obstruction = Retrograde urine flow to kidneys = Increase hydrostatic pressure in tubules = Decrease GFR (kidney function loss)
AKI: Clinical Presentation
4 phases
Initiating event (kidney injury)
Maintenance (oliguric/anuric) phase
Polyuric/diuretic phase
Recovery phase
AKI Clinical Pres: Initiating Event
Asymptomatic
Symptoms of underlying cause
AKI Clinical Pres: Maintenance Phase
Oliguria
Anuria
Fluid retention (pulmonary edema)
Hyperkalemia
Met acidosis
Uremia
AKI Clinical Pres: Polyuric/Diuretic
Polyuria: Increased urine output (glomerular filtration returns to normal)
Abnormal tubular reabsorption
Electrolyte and water loss
Dehydration
Hyponatremia and hypokalemia
AKI Clinical Pres: Recovery Phase
Kidney function and urine production normalize
AKI: Investigations
Blood test
Urinalysis
Imaging
AKI: Blood Test
Prerenal:
High serum creatinine
High BUN:creatinine
Renal:
High serum creatinine
High BUN:creatinine
Postrenal:
High serum creatinine
Normal BUN:creatinine
AKI: Urinalysis
Prerenal:
Low Na+ and urea
High osmolality and specific gravity
Microscopy:
Hyaline casts (clear tube-shaped proteins)
Renal:
High Na+ and urea
Low osmolality
Microscopy:
Granular, brown, pigmented casts
Cellular debris and renal tubular epithelial cells → Tubular injury/necrosis
RBC cast
Glomerulonephritis
Postrenal:
Oliguria
Neurogenic Bladder: Normal
Stones, Malignancy: Hematuria, crystals
AKI: Imaging
Ultrasound and noncontrast CT
Mostly for postrenal AKI:
Confirm cause
Bladder distension
Stones
Bilateral hydronephrosis (collecting system distension)
AKI: Treatment/Management
Treat underlying cause
**Dialysis
**Supportive care
Discontinue nephrotoxic substances
Manage volume status
AKI: Complications
Oliguric/Anuric Phase:
Hypoxia
From pulmonary edema
Hyperkalemia
Low urine K+ excretion
Met acidosis
Low urine NH4+ excretion
Low bicarb reabsorption
Polyuric/Diuretic Phase:
Electrolyte and water loss
Normal filtration + impaired reabsorption
Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT)
Support or replace kidney function
Dialysis
Kidney transplantation
RRT: Indications
A: Acidosis (severe met)
E: Electrolyte abnormalities
I: Ingestion
Toxins
Meds
O: Overload of fluid (refractory)
U: Uremia
Pericarditis
Encephalopathy
Bleeding
RRT: Dialysis
Remove solutes and water from blood through diffusion (bypass kidneys)
Hemodialysis:
Diffusion across semipermeable membrane = Remove solutes
Ultrafiltration = Hydrostatic pressure gradient = Remove excess water
Peritoneal Dialysis:
Diffusion across peritoneum (semipermeable membrane)
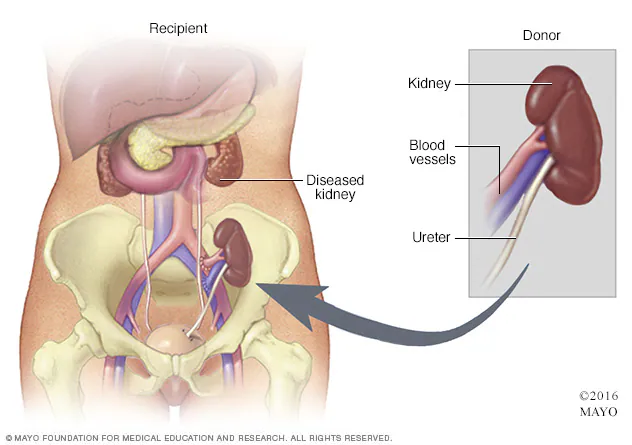
RRT: Kidney Transplantation
Kidney donation from living or deceased donor
Prefer left kidney from living (longer renal vein)
Placed in iliac fossa (mostly right)
Extraperitoneal position
Increase vascularization + decrease complications
Indication: Severe/end-stage renal disease
Indigenous Health Practice: Smudging
Traditional ceremony to purify/cleanse soul of negative thoughts
Process:
Plants ignited to create smoke
Waft smoke over person + inhale
Dispose ashes outside (soil)
Hospitals Can:
Modify policies to accommodate smudging
Create smudging areas
Other Indigenous Health Practices
Sweat Lodge Ceremonies:
Purification
Involve steam in room and prayer
Pipe Ceremonies:
Passing pipe with blessed tobacco in circle
For spiritual and physical cleansing