Dental Lab Final
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Which type of charting is recommended?
4 handed charting
GR
Gingival recession
M
Mobility
O
Missing tooth
P
Periodontal Pocket
FE
Furcation exposure
GH
Gingival Hyperplasia
RE
Root exposure
RL
Resorptive lesion
FORL
Feline Odontoclastic Resorptive Lesion
RL
Root Lesion
Extractions are noted with a(n)?
X or //
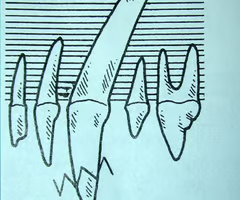
What is this representing?
Crown fracture

What is this representing?
Retained Deciduous
What instrument is used to detect plaque and calculus?
Explorers
What instrument is hooked to the rigt on one end and to the left on the other end?
Pigtail explorer
The primary use of this instrument is to measure pocket/sulcus depths around a tooth in order to check the health of the periodontium?
Periodontal probes
What instrument allows quick removal of large pieces of calculus?
calculus removal forceps
Scalers have ____ sharp sides and a sharp tip
3
Scalers can be used ____ only
Supragingivally
Curettes have ____ sharp sides and can be used subgingivally and supragingivally
2
Converts energy from a power source into a soundwave
Ultrasonic
_____ is not recommended because it easily damages the tooth
Rotary
Operates at lower speeds with higher torque
Can’t use water to cool teeth
Electric dental units
Compressed air from a cylinder or air compressor
Some compressors require oil for lubrication
Air must be drained daily to prevent condensation
Air-powered systems
What are low speed hand pieces used for?
Polishing teeth
What are high speed hand pieces used for?
Used for cutting teeth, root canal entries, and other procedures
The care of high speed hand pieces includes spraying lubricant into the ___ or the 2 large holes?
Smaller
What burs is used for cavity prep?
Pear shape and inverted cone
What bur is used for cutting teeth, root canal access
Cross fissure bur
What bur is used on alveolar bone?
Round bur
What bur is used in restoration?
finishing bur
T or F: burs should not go in sharps?
False
In dentistry, ______ is used for the rinsing of the root canal during root canal therapy?
Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl)
This removes scratches in enamel
Polisher
Removes plaque and calculus
ultrasonic scalers
Most popular and effective solution used in cases of gingivitis and periodontal disease it is effective against bacteria, fungus, yeast, and viruses
Chlorhexidine (concentration of 0.12%)
Normal gingival sulcus depth for dogs is _____ and for cats ____
1-3mm; ½ to 1mm
The puppy has _____ teeth and the adult dog has ____ teeth
28 and 42
What is the hardest substance in the bady? it is also fairly resistant to stains.
Enamel
Dentin is produced by___
Ondontoblasts
The tooth is held into the alveolus by the _____
Periodontal ligament
In the dental formulas, the primary teeth are indicated by _____
Lower case letters
A class _____ occlusion is said to occur when the mandible is shorter than normal.
II
Inflammation of the gingiva is called _____
gingivitis
Maxillary brachygnathism is caused by a ______ maxilla
Shortened
_____ will normally resist staining, but _____ will stain easily due to it being porous
Enamel, dentin
(T/F) A slab fracture is the most common fracture of the 4th premolar
True
Select the choice that includes ONLY types of hand instruments. (What are the hand instruments?)
Explorers, periodontal probes, calculus removal forceps, curettes
T or F Scalers have 2 sharp sides and a sharp tip?
False
Scalers should not be used __________ because they could damage the gingiva and the periodontal ligaments.
Subgingivally
SLOB Rule
Same Lingual, Opposite Buccal
Which tooth has 3 roots and is imaged using the SLOB rule?
Maxillary 4th premolar
Nasopalatine duct is responsible for the conduction of ___________ from the mouth to the nasal cavity, thereby assisting in communication and breeding
pheromones
(T/F) The cutting edge is the working portion of the scaler.
True
A _____________ blade will not reflect light, and a ____________ blade will reflect light.
Sharp, dull
(T/F) Used burs do not have to be treated as sharps.
False
An acquired pellicle is classified as...
An acellular film composed of salivary glycoproteins that closely and firmly adheres to the oral cavity.
(T/F) The amount of plaque and calculus will always correspond to the degree of periodontal disease that is present in a patient.
False
Stage 4 periodontal disease is classified by:
Probing and radiographic signs of attachment loss >50%, Severe pocket depth or recession, Bleeds easily on probing, Pus, bone loss, mobility, Advanced breakdown
What are the systemic effects of periodontal disease?
bacteria introduced into the blood stream
Mesaticephic
Medium head breeds
brachycephalic
short wide heads
dolichocephalic heads
long narrow heads
the fibrous connective tissue that surrounds the root of a tooth, separating it from and attaching it to the alveolar bone, and serving to hold the tooth in its socket
peridonatal ligament
The transformation of energy from a painful stimulus into nerve impulses by pain receptors.
Transduction
The movement of nerve impulses to the spinal cord and then to the brain. This process can be inhibited by use of local anesthetics, opioids, and alpha-2 agonists.
Transmission
The transmission of the painful stimulus at the spinal cord to be transmitted to the brain as pain or to inhibit further transmission to the brain
Modulation
When tissue is injured, the painful response is recognized by the central nervous system through a process called
Nociception
What is the goal of preemptive analgesia?
What does local anesthesia do?
decreases the depth of general anesthesia
It also helps with post-op pain control, minimizes complications (ie: hypoventilation, hypotension, bradycardia
What instruments level abnormally uneven occlusal surface
Files and rasps (floats)
The materials needed for regional nerve blocks in the oral cavity are a _______________________________ and a local anesthetic agent
1 cc tuberculin syringe,
25 to 27 gauge
¾ to 1 inch needle
If regional anesthesia is being performed on a 10lb cat (4.6kgs) with all 4 quadrants being blocked, the cat would receive 0.4mls total (0.1ml per site).
0.4mls X 5 mg/ml (concentration of bupivacaine) = 2mg (total)
The max total dose for this patient would be 9.2 mgs.
4.6 kg X 2 mg/kg= 9.2 mgs
In dental radiography the kVp and MA is usally fixed and the time can be adjusted.
True
Bupivacaine at a concentration of _____ is the drug of choice
0.5%
What is the total dose of lidocaine in feline and canine patients?
feline: 2.5mg/kg
canine: 5.0mg/kg
Which drugs onset is faster?
Lidocaine
Why is epi used with bupivacaine?
decreases the chance of toxicity and counteract vasodilation when added to bupivacaine.
Which of the following is true about bupivacaine?
Shown to effectively double the analgesic duration when combined with bupivacaine
What are the nerve block rules?
- ALWAYS ASPIRATE
- DO NOT GO IV!!!!!!
- INJECT SLOWLY
This is used to block the nerves that innervate the canine and incisor teeth.
In addition, the first three premolar teeth, as well as the maxillary bone and surrounding soft tissue, are affected
Cranial Infraorbital or Rostral Maxillary Nerve Block
This block will anesthetize the upper molars and PM4, caudal cheek teeth and associated bone and soft tissue (basically blocks the entire maxillary quadrant and surrounding bone/soft tissue)
The soft palatal mucosa, hard palatal mucosa and bone will also be affected by this block
This may be preferred over infraorbital nerve blocks
Caudal Maxillary Nerve Block
For the Mental or Rostral Mandibular Nerve Block the landmark for infiltration is the ?
mandibular labial frenulum
This block anesthetized include the incisors, the canine and the first three premolars.
The adjacent bone and soft tissue also are also affected
mental or rostral mandibular nerve block
Which block imposes a threat to tongues caused by mastication?
Caudal Mandibular/Inferior Alveolar block
This nerve block affects the oral side of the hard palate.The areas affected are bone and soft tissue of the hard and soft palate and the palatal aspect of the gingiva surrounding the maxillary arcade.
major palatine nerve block
What are the complications of nerve blocks?
hemtoma, tachycardia, dysrhythmia, bronchospasm, broken needle, tongue and lip chewing, damage to the nerve, allergic reaction
What are the indications for exodontics?
tooth cannot be salvaged or the client is unwilling or unable to perform home care
This instrument is used for used for cutting the periodontal ligament and expanding the alveolus (tooth socket
Luxator
This instrument is used to elevate canine and feline teeth (raise them from the socket)
Elevators
This instrument is used for used for elevating and extracting retained root tips?
Root tip picks
Used to elevate gingival tissue and periosteum from the bone in periodontal surgery
Periosteal elevators
Extractions are surgical procedure with the instrument entering tissue instruments must be ?
Sterilized
What is the recommended method for exodontic procedures?
rotate/stretch/tear
What are the single rooted teeth in the dog?
incisors, canines, first pre-molars, and mandibular 3rd molar
What are the single rooted teeth in the cat?
incisor, canines, and maxillary second pre-molar
What are the complications of extractions?
trauma, hemorrhage, slippage, loss of function, root tips stuck in mandibular canal
Power-driven periotome with foot pedal operation that cuts the periodontal ligament like a luxator
VetTome Powertome