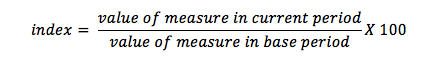Macro Chapter 6, The measurement of macroeconomic performance
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:37 PM on 5/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
1
New cards
What is macroeconomics? 6.1
The study of the economy as a whole
2
New cards
What are the four main objectives of a government's macroeconomic policy? 6.1
Create and maintain full employment or low unemployment.
Limit or control inflation, or to achieve some measure of price stability.
Achieve economic growth and improve the living standards and levels of economic welfare.
Attain a satisfactory balance of payments, defined usually as the avoidance of an external deficit, which could cause an exchange rate crisis.
Limit or control inflation, or to achieve some measure of price stability.
Achieve economic growth and improve the living standards and levels of economic welfare.
Attain a satisfactory balance of payments, defined usually as the avoidance of an external deficit, which could cause an exchange rate crisis.
3
New cards
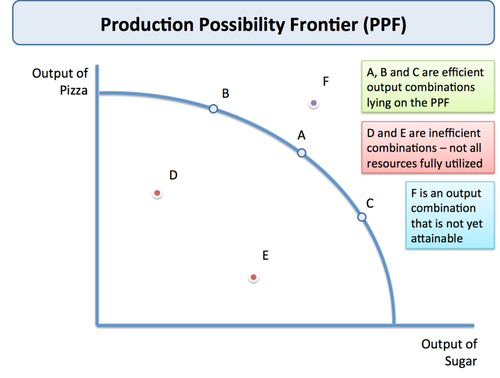
What is short-run economic growth? 6.1
Growth of real output resulting from using idle resources, including labour, thereby taking up the slack in the economy.
4
New cards
What is long-run economic growth? 6.1
An increase in the economy's potential level of real output, represented by an outward shift of the economy's production possibility curve.
5
New cards
What are gross domestic products? 6.1
The sum of all goods and services, adjusted for price change and inflation.
6
New cards
What is nominal GDP? 6.1
the production of goods and services valued at current prices.
7
New cards
Explain short-run economic growth to long-run economic growth through the PPF graph? (draw and label) 6.1
8
New cards
What are the two methods used to measure unemployment? 6.1
The Claimant Count and Labour Force survey.
9
New cards
What is meant by 'full employment' 6.1
Full employment means 5% or less of the labour force unemployed.
10
New cards
What is a recession? 6.1
A fall in real GDP for two quarters or more. (6 months)
11
New cards
What is inflation? 6.1
a general increase in prices and fall in the purchasing value of money.
12
New cards
What is deflation? 6.1
a decrease in the general level of prices
13
New cards
What is disinflation defined as? 6.1
A fall in the rate of inflation, but still positive.
14
New cards
What is the Consumer prices index (CPI) 6.1
The official measure used to calculate the rate of consumer price inflation in the UK. It calculates the average price increase of a basket of 700 different consumer good or services.
15
New cards
What is the Retail prices index (RPI) 6.1
It is the old measure used to calculate the rate of consumer price inflation in the UK.
16
New cards
What equation can be used to calculate the 'rate of increase of real GDP' 6.1
rate of increase of real GDP\= rate of increase of nominal GDP - rate of price inflation
17
New cards
What is the balance of payments? 6.1
A record of all the currency flows into and out of a country in a particular time period.
18
New cards
What is the current account of the balance of payments? 6.1
Measures all the currency that flows into and out of a country in a particular time period in payments for exports and imports, together with income and transfer flows.
19
New cards
What is the balance of trade? 6.1
The difference between the money value of a country's imports and its exports. Balance of trade is the largest component of a country's balance of payments on current account.
20
New cards
What is a balance of trade deficit 6.1
The money value of a country's imports exceeds the money value of its exports. M \> X
21
New cards
What is a balance of trade surplus 6.1
The money value of a country's exports exceeds the money value of its imports. X \> M
22
New cards
What is a balanced budget 6.1
when government spending equals government revenue, which is mostly tax revenue
23
New cards
What is a balanced deficit 6.1
When government spending is greater than government revenue.
24
New cards
Who are Keynesian economists? 6.1
Followers of John Maynard Keynes, who generally believes that governments should manage the economy, particularly through the use of fiscal policy.
25
New cards
What is fiscal policy? 6.1
the means by which a government adjusts its spending levels and tax rates to monitor and influence a nation's economy
26
New cards
What is monetary policy? 6.1
Policies that control the supply of money, the price of money, and the availability of credit.
27
New cards
Who are pro-free market economists 6.1
Opponents of Keynesian economists, who dislike government intervention in the economy and whom much prefer the operation of free markets.
28
New cards
What is a performance indicator 6.2
Provides information for judging the success or failure of a particular type of government failure.
29
New cards
What are lead indicators? 6.2
performance measures that predict future performance
30
New cards
What are lag indicators? 6.2
performance indicators that reveal the results of past actions and decisions
31
New cards
What are index numbers 6.3
A number used in an index, such as the consumer prices index, to enable accurate comparisons over time to be made.
32
New cards
What is the base year index number 6.3
100
33
New cards
How to calculate percentage increase (index number) 6.3