NST 103 MT 1 - KLATT
1/225
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
226 Terms
absorption of lipid digestion products by enterocytes
occurs mostly in the duodenum and jejunum
passive diffusion
lipid digestion pdts dissolve in the lipids of the brush border membrane
absorbed lipid digestion products are rapidly bound by fatty acid binding proteins and re-esterified
carrier mediated uptake
intestinal fatty transport
proteins in brush border membrane for carrier-mediated lipid transport
CD36
Fatty Acid Binding Protein-plasma membrane (FABPpm)
GPR109A, GPR120
MCT1 (SCFA)
proteins can compensate for knockout of other proteins
CD36 transport of fatty acids
abundant in duodenal and jejunal brush border membrane
palmitoylated and glycosylated, facilitating membrane localization
directly binds fatty acids
positively charged lysine interacts with fatty acid carboxylic acid group
acyl chain is fed through a tunnel that facilitates passage by the phospholipid head groups
cholesterol absorption
dietary cholesterol enters the body’s cholesterol pool
absorption: NPC1L1 transports cholesterol from lumen into enterocyte
excretion: ATP Casette Binding Protein family members facilitate transintestinal cholesterol excretion (TICE)
ABCA1a/b
ABCG5/8 (also exports plant sterols)
targets nuclear receptor (transcription factor) - Liver X Receptor (LXR)
NPC1L1 transport of cholesterol
NPC1L1 binds extracellular cholesterol and deposits cholesterol into the surrounding plasma membrane
high concentrations of cholesterol induce endocytosis of this microdomain
internalized cholesterol is directed towards intraclllular compartments
cholesterol efflux transporter dysfunction
β-sitosterolemia: disease caused by inactivating mutations in ABCG5/8
high levels of cholesterol and plant sterols
characterized by abnormal cholesterol/lipid deposits (xanthomas) and atherosclerosis
treatment: reducing dietary plant sterols, ezetimibe
lipid processing once inside the intestine
similar to pre-micellization, the individual lipid species are liberated from micelles in an aqueous intracellular environment
lipids get..
bound and trafficked by intracellular storage proteins
most lipids are to be regenerated to their storage form to be exported in lipoproteins (chylomicrons) —> lymph —> blood stream —> peripheral tissues
fatty acid binding proteins (FABPs)
intracellular transport of lipids
reduce concentration of molecules in free form, promoting transport across apical membrane via simple and facilitated diffusion
direct lipid molecules to organelle (ER for metabolism)
I-FABP/FABP2 (intestinal): binds FFA
L-FABP/FABP1 (liver): Binds LCFA, MAG, lysophosphatidylcholine, retinoids
SCP-1, SCP-2: sterols & cholesterol
chylomicrons
large TAG rich lipoprotein particles (vehicle for fat transport)
main emulsifier: phosphatidylcholine
apo B-48: proteins synthesized by enterocyte and incorporated
apoE, apo C: proteins synthesized by liver and added to chylomicrons in circulation
secreted from basolateral membrane via exocytosis
chylomicron formation
the Microsomal Transport Protein (MTP) transports lipids to the ER
ER heterodimeric protein (transfers triglycerids & cholesteryl esters to apoB) forms pre chylomicrons
pre-chylomicron transport vessel (PCTV) shuttles to golgi to facilitate final lipidation
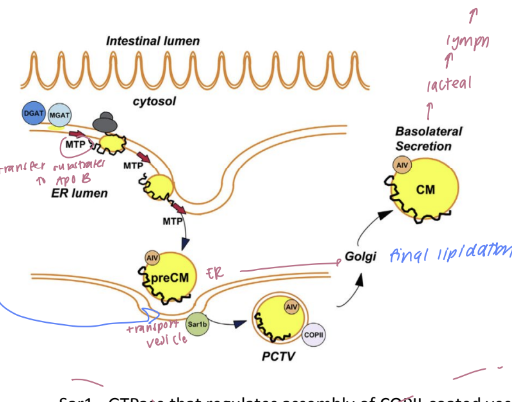
genetic defects in MTP
results in abetalipoproteinemia
life threatening autosomal recessive condition
failure to thrive, diarrhea, fat, malabsorption
absence/low LDL-C, TG, ApoB
treated with low fat diets and supplementation
Formation and secretion of chylomicrons from enteryocytes
formation of mixed micelles in lumen
dissociation of micelles in enterocyte
FABP associates with lipids
smooth ER
TAG re-esterification
phospholipid reacylation
Rough ER
Apoprotein synthesis and packaging
Golgi: glycosylation & storage
chlyomicrons in vesicles
vesicles fuse with basolateral membrane - exocytosis into extracellular space (lymph)
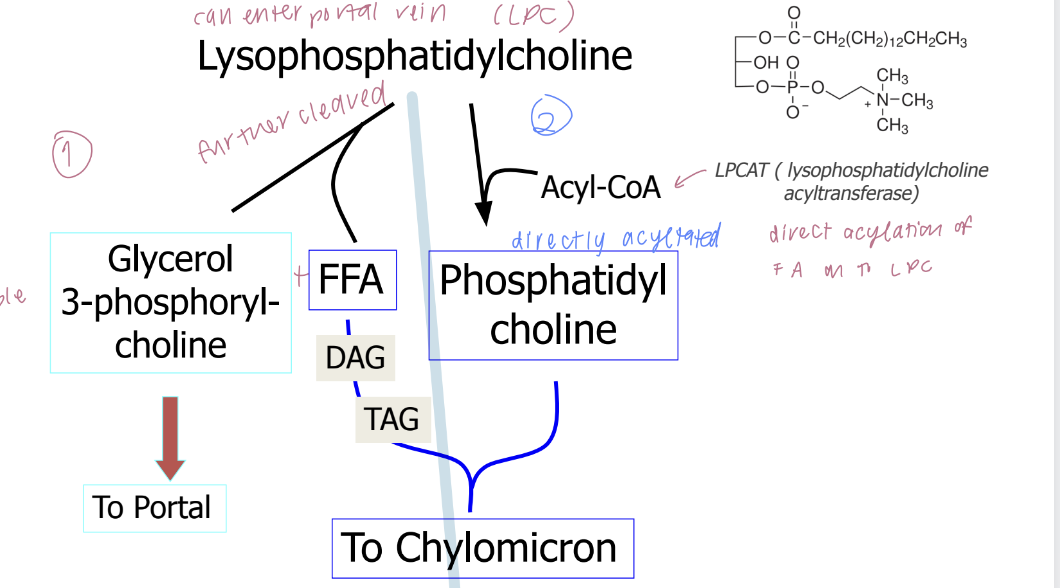
fate of lipid constituents
TAG —> SCFA
Phosphatidylcholine —> MCFA
cholesteryl esters —> glycerol 3-phosphorylchline
Re-esterification at cystolic surface of ER
MAG -(Acetyl CoA)-→ DAG -(Acetyl CoA)-→ TAG
MGAT and DGAT intermediates
G3P —(2xAcetyl CoA + glycerol 3P)-→ phosphatidic acid -(Acetyl CoA)-→ TAG
cholesterol -(Acyl CoA)-→ Cholesteryl Ester —> chylomicron
facilitated by Acyl CoA: cholesterol acyl transferase (ACAT)
Phospholipid metabolism in enterocytes
fate of bile acids
bile acids released from their lipid load at the UWL of proximal small intestine
reabsorption:
passive transport in proximal small intestine
active transport in terminal ileum
apical sodium dependent bile acid transporter ASBT
Essential Nutrient
A component of food deemed essential for life and physiological functions
inadequate intake can lead to dysfunction, impaired growth, and organismal demise.
Metabolism
The chemical conversions that occur within cells, associated with changes in energy
Nutrition
how organisms acquire adequate nutrient intakes to facilitate physiological function, encompassing aspects like feeding behavior, food composition, digestion, and absorption.
Humoral Theory
theory popularized by Hippocrates and Galen
suggests that the human body is a chemical system made of four humors (blood, phlegm, yellow bile, black bile), and disease results from their imbalance.
Chylous
The substance produced in the stomach after digestion, which is converted in the liver to chymous.
Chymous
Chylous is converted into chymous in the liber
made up of 4 humors and circulates in the body
Essential nutrients
required for life
energy
fatty acids
amino acids
minerals
Non-essential-compounds
some influence physiology & health
some may be inert, toxins
Why do we need energy?
various endergonic reactions
muscle contraction
glandular secretions
generation of electrochemical gradients
Na/K ATPase pump
synthesis/growth
Macromoleculars
lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates
cannot be synthesized - food provides the raw materials
Micronutrients
Accessory factors (vitamins and minerals) required in smaller amounts for metabolic reactions and homeostasis.
cofactors, substrates, signaling molecules
Why care about GI Tract Anatomy and Function?
digestive anatomy and physiology changes across life-stages and in disease
understand the norm to assess functional degree of change
medical assessment, diagnosis, and intervention of diseases
digestive physiology as a model for other biomedical fields
ecology & immunotolerance: digestive tract is extracellular
cell proliferation: digestive tract rapidly turns over, maintaining high proliferative capacity
neurobiology: vagus nerves allows coordination between brain and gut
Parts of the Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract
oral cavity
esophagus
stomach
small intestine
large intestine
anus
Functions of the GI system
digestion: reduce size & repackage to facilitate absorption
absorption: movement from GI tract to blood/lymph
secretion: movement into GI tract lumen
motility: perstalsis
storage & elimination: stomach, anus
barrier: between external and internal environment
Common layers of the GI tract
mucosa
submucosa
muscularis
adevntitia (esophagus) or serosa (stomach, intesntine)
common tissue types of the GI tract
epithelia: hormone + enzyme secretion
connective: supportive structure for tissues, facilitate storage, transport, and signaling
vascular: absorption & transport
lymphatic: transports lipids, interstitial fluid + facilitates immune function
muscle: smooth & striated to process + move food along GI tract
nerve: neural and glial cells grouped into plexuses to coordinate various gut functions
oral cavity functions
chewing
initiate digestion (salivary glands)
swallowing
goal: food bolus
saliva functions
water moistens food
glycoproteins (mucin) lubricate and prevent abrasion
salivary amylase inititates digestion of starch
antimicrobial agents reduce risk of infection
acts as pH butter
inadequate saliva production results in..
dry mouth (xerostomia)
causes discomfort, can impact swallowing capacity
causes: medications, autoimmune diseases, radiation exposure, nerve damage
Peristalsis
The rhythmic contraction of smooth muscle cells in the GI tract that facilitates the movement of food through the digestive system.
contraction controlled by input from mechanical, chemical, and electrical stimuli
functions of the stomach
goal: form chyme (food + secretions)
accept bolus from esophageal sphincter
mechanoreceptors sense food presence
mix by peristalsis + mucus
digest: acid, pepsinogen, gastric lipase
empty: antral peristalisis induced by gastrin, blocked by CCK
store food
kill bacteria
some metabolism of ethanol
Types of gastric Juices
HCl + intrinsic factor (parietal cells)
pepsinogen + gastric lipase (chief cells)
mucus (goblet cells)
water, electrolytes, bicarbonate
pepsinogen
inactive precursor to pepsin (protease with low pH)
activated by HCl
phases of gastric secretions
cephalic: prior to food entering stomach
gastric: foods presence in stomach
intestinal: food moves into duodenum
production of stomach acid
Parietal cells secrete H+ and Cl- separately
H2O dissociates into H+ and OH- in the cell
H+ exported via H+/K+ ATPase pump
Cl- diffuses into stomach lumen OR exchanged with HCO3 (formed when OH- condense with CO2 from metabolism)
How is HCl production and secretion regulated
G cells secrete gastrin hormone that is released in response to stomach stretching & peptides/AAs
gastrin = positive regulator
facilitates H+/K+ ATPase
synthesis of histamine
histadine is converted to histamine via histidine carboxylase, which is vitamin B6 depedent
histadine is an essential AA
pyridoxal phosphate is an essential vitamin, acts as coenzyme to facilitate decarboxylation
What does gastrin do?
regulates histidine decarboxylase synthesis in the ECL cell
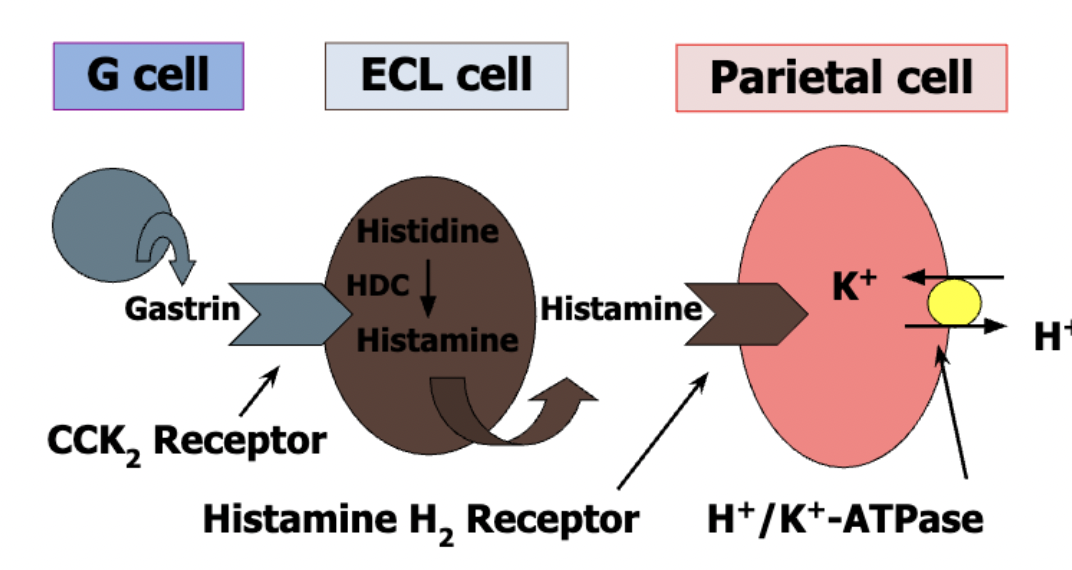
how is HCl production inhibited?
somatostatin: negative regulator
produced by D-cells of stomach, duodenum, pancrease
positive regulation of stomach acidification
vagal nerve: acetylcholine
ECL cells: histamine
G-cells: gastrin
negative regulation of stomach acidification
D-cells: somatostatin
gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
relaxed lower esophageal sphincter leads to inflamed esophagus
HCl: antacids
H+: proton pump inhibitor
H2: H2 blocker
gastric cells & functions: chief cells
pepsinogen: proenzyme
gastric lipase: enzyme
gastric cells & functions: goblet cells
mucous mucin: lubricant & buffer
gastric cells & functions: parietal cells
HCl: protein denaturing
intrinsic factor: absorb B12
gastric cells & functions: D-Cells
somatostain: positive regulator hormone
gastric cells & functions: ECL cells
histamine: positive regulator hormone
serotonin: hormone
gastric cells & functions: G-cells
gastrin: hormone
process of gastric emptying
food leaves pylorus
circular muscle wall around pylrous (pyloric sphincter) is thick, stays contracted (fluids can pass)
pyloric contraction controlled by nervous and hormonal signals
emptying takes around 2-4 hours
factors that influence rate of gastric emptying
nervous reflexes sensitive to distension of duodenum and the composition, osmolaity, and acidity of duodenal chyme
hormonal
stomach stretching
peptides/AA that stimulate gastrin
intestine-derive CCK (fat
secretin (acid)
GLP-1 & GIP (nutrients)
functions of small intestine
main site of nutrient digestion and absorption
package lipids in a form that can be asborbed
absorb macronutrient components, vitamins, minerals
reabsorb bile
barrier
small intestine structure
mucosa (absorptive / secretory layer)
submucosa (vascular connective tissue)
muscularis (peristalsis)
serosa (protective)
nutrients are absorbed into what two circulatory systems
Blood: absorption of water-soluble constituents (carbohydrates, AA)
lymphatics: absorption of lipid soluble constituents (fats)
types of cells in intestinal mucosa
undifferentiated stem cells
enterocytes (absorptive epithelial cells)
goblet cells (mucin)
endocrine cells
paneth cells (lysozyme, antimicrobial peptides)
caveolated cells (chemoreceptors)
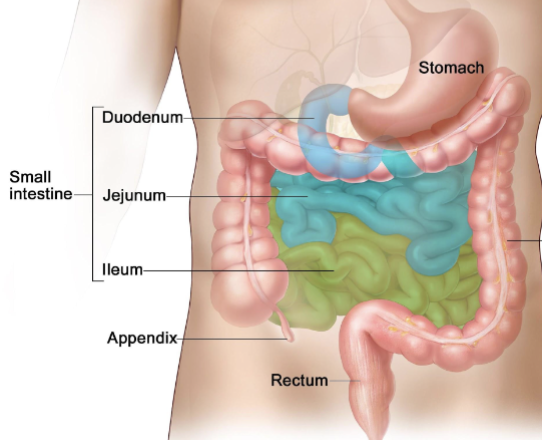
what is absorbed in the duodenum & jejunum?
carbs
lipids
AA
calcium, iron
what is absorbed in the illeum?
bile salts
vitamin B12
H2O
electrolytes
small intestine parts
upper: duodenum, jejunum
lower: illeum
Enterohepatic Circulation
The recycling process of bile salts between the intestine and the liver, essential for lipid absorption.
Exocrine Pancreas
The part of the pancreas that secretes digestive enzymes into the pancreatic duct for digestion.
medical intervention in stomach and small intestine for weight loss
gastric sleeve: remove large portion of stomach
gastric bypass: bypass stomach, ileum, jejunum
secretions from accessory organs into small intestine
liver & galbladder: bile
pancrease: “juice” (bicarbonate ions and digestive enzymes)
liver functions
bile production: bile salts, phospholipids, cholesterol
synthesis, secretion, & storage of glucose: gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, glycogen synthesis, ketogenesis
detoxification: urea production, alteration of drugs, excretion
protein production: albumin, globulin, clotting factors (fibrinogen, prothrombin)
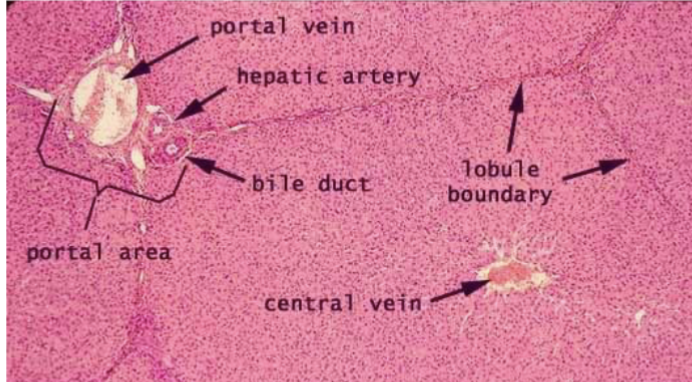
blood & bile movement in liver
blood enters liver through portal triad, passes through sinusoids, exits through central vein
bile produced by hepatocytes & secreted into bile caniculi, which carry bile to hepatic duct
blood and bile never mix
liver structures
Pancrease endocrine functions
secretes hormones like insulin and glucagon into the bloodstream to regulate glucose levels.
insulin: glucose uptake (beta cell)
glucagon: glycogen breakdown (alpha cell)
pancreas anatomy and function
acini cells: exocrine functions, secrete enzymes into pancreatic duct
beta/alpha cells: endocrine functions, secrete hormones into blod
pancreas exocrine functions
water, salts, bicarbonate
trypsin and chymotrypsin: protein digestion
pancreatic amylase: carb breakdown
pancreatic lipase: fat breakdown
pancrease and weight gain
exocrine function of pancreas can be compromised due to medical conditions (CF, exocrine pancreas insufficiency (EPI))
results in malabsorption, malnutrition
treatment: pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT)
anatomy and function of large intestine
absorb water, electrolytes (proximal half)
microbial fermentation
formation and storage of feces (distal half)
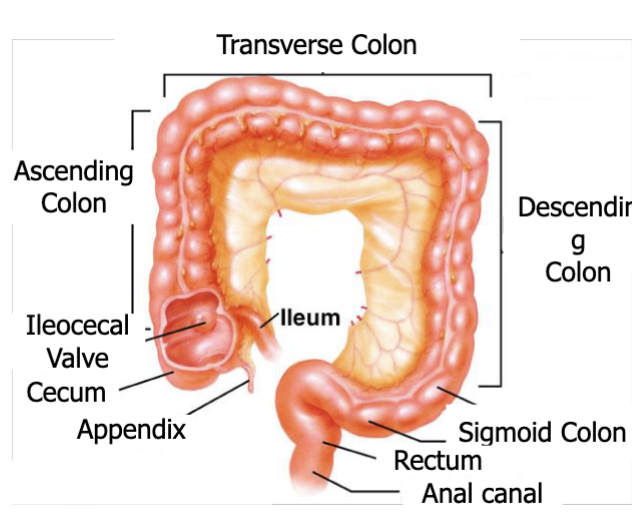
large intestine differences from small intestine
no villi
epithelial cells do not secrete digestive enzymes (secrete alkaline mucus instead)
absorption limited to salts, water, vitamins, microbial byproducts due to tighter junctions
site of microbial metabolism: conversion of carbs to gases & short chain fatty acids
Villi
Small, finger-like projections in the small intestine that increase the surface area for absorption of nutrients.
Microvilli
Tiny hair-like structures on the surface of epithelial cells in the small intestine that further amplify the absorptive surface area.
Somatostatin
A hormone produced by D-cells in the stomach and pancreas that inhibits gastric acid secretion and regulates other hormones.
Gastrin
A hormone secreted by G-cells in the stomach that stimulates the secretion of gastric acid and aids in digestion.
CCK (Cholecystokinin)
A hormone released by the small intestine that stimulates the release of bile from the gallbladder and digestive enzymes from the pancreas.
history of carbohydrates consumption in human diets
varying carb content diets throughout history
hominids consumed diverse carb quantities: fruits, vegetation, honey
humans recently introduced carb-rich foods: grains, tubers, and legumes
contain amyloplast organelle where starch granules are synthesized and stored
minimally digestible without further processing
history of carbohydrate processing
cooking allowed for introduction of tubers, legumes, grains by breaking down plant cell microstructure to release starch granules, available to contact digestive enzymes + inactivate toxic components
fermentation: bacteria contain enzymes to digest carbs that are indigestible to humans
grain and grape fermentation for beer and wine in acient babylon & egypt
dairy fermenting to break down lactose
carbohydrates in human nutrition
not essential for human population - plasma glucose maintained through de novo synthesis in the absence of dietary carbohydrates
source of rapidly digestible energy (4 kcal/g)
types of carbohydrates in human diet
available carbs: humans produce enzymes capable of cleaving bonds so they can be absorbed
unavailable carbs: digestibility dependent on type of glycosidic bond, food microparticle sturtcure, and dose of carbohydrate
can be naturally occuring or added to foods during processing
carbs for food processing
flavor
preservative
water retention
browning
energy for microorganisms (yeast)
thickening agent
reduce glycemic responses (sugar alcohols)
chemical variation of carbohydrates
# of carbons in monosaccharide: tetrose, pentose, hexose
aldose (carbonyl at the end of carbon chain) vs ketose (carbonyl within)
stereochemistry: enantiomers (D/L, differ at all chiral centers), epimers (differ at 1 chiral center)
degree of polymerization: mono-, di-, poly-, fused by glycosidic bonds, alpha/beta
hemiacetal
aldehyde reacting with OH
hemiketal
ketone reacting with OH