Week 2 Semi conductors Exam review
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Simplest part of a semi-conductor component
Anode and Cathode
PN Junction allow current to flow in
One direction
Area at the junction where the electrons and holes are far fewer in number (depleted)
Depletion region
Barrier voltage Silicon
0.7V
Barrier Voltage Germanium
0.3V
Voltage applied to a diode in an electrical circuit
Diode Biasing
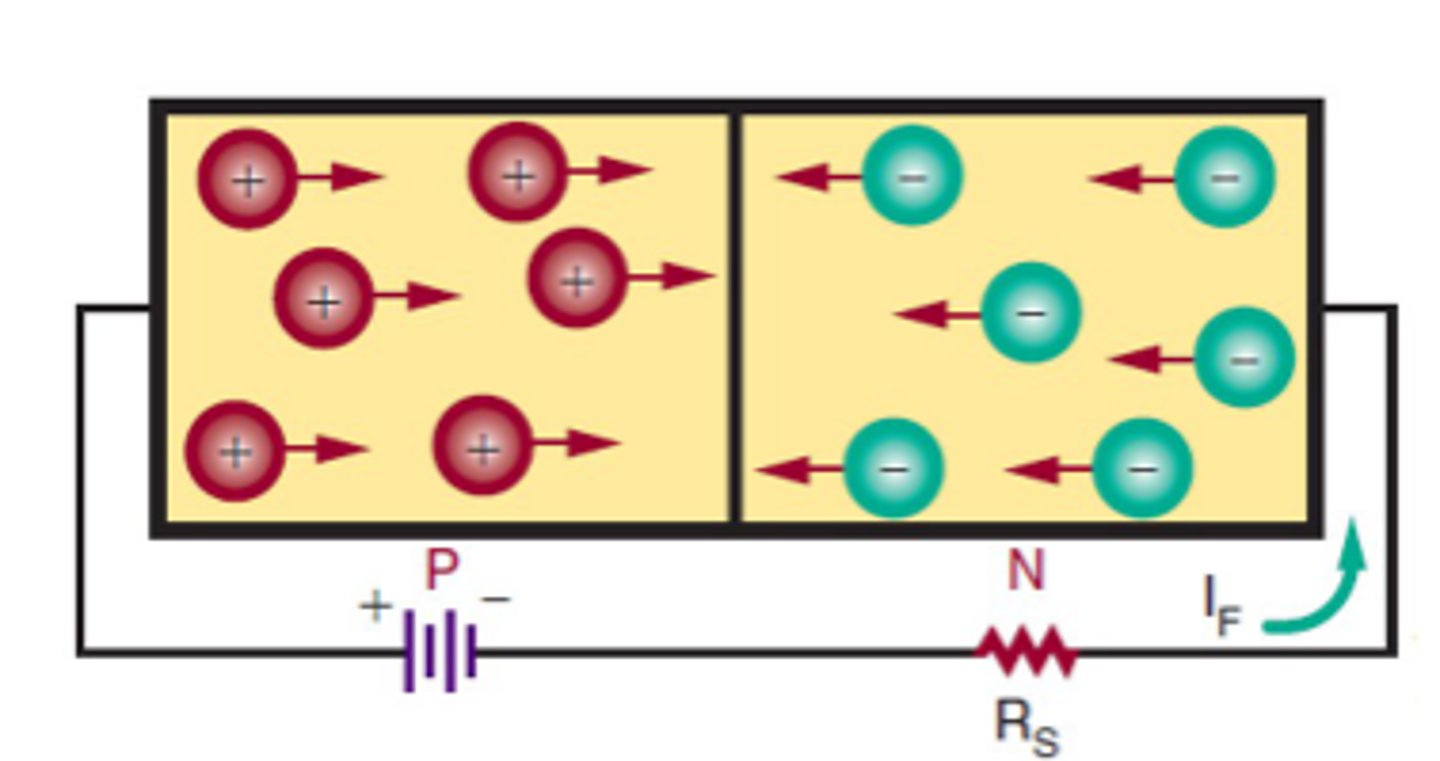
Forward Biasing
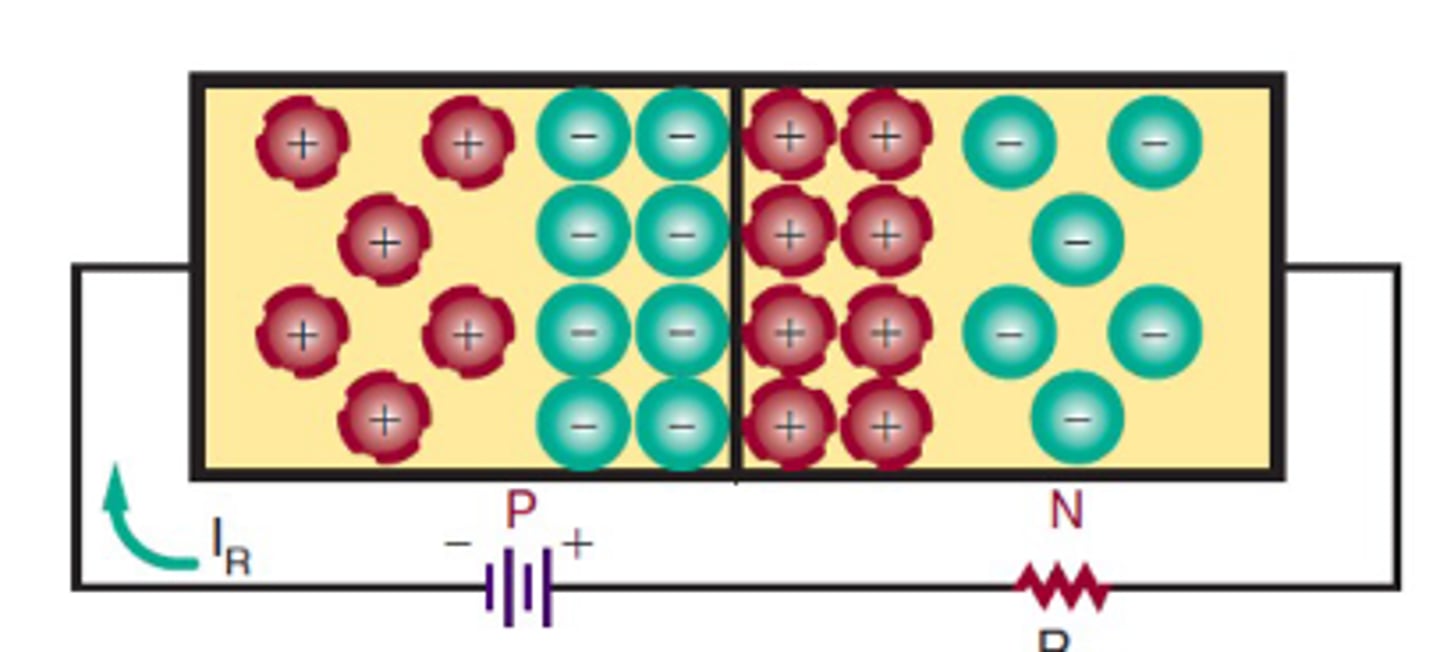
Reverse Biasing
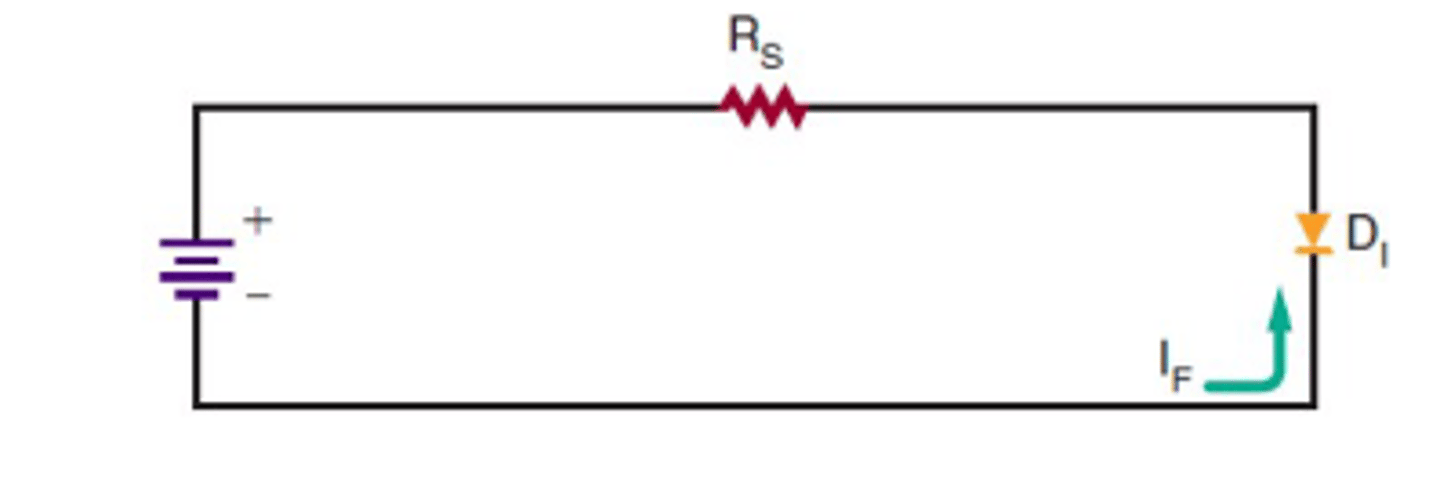
Forward Biasing schematic
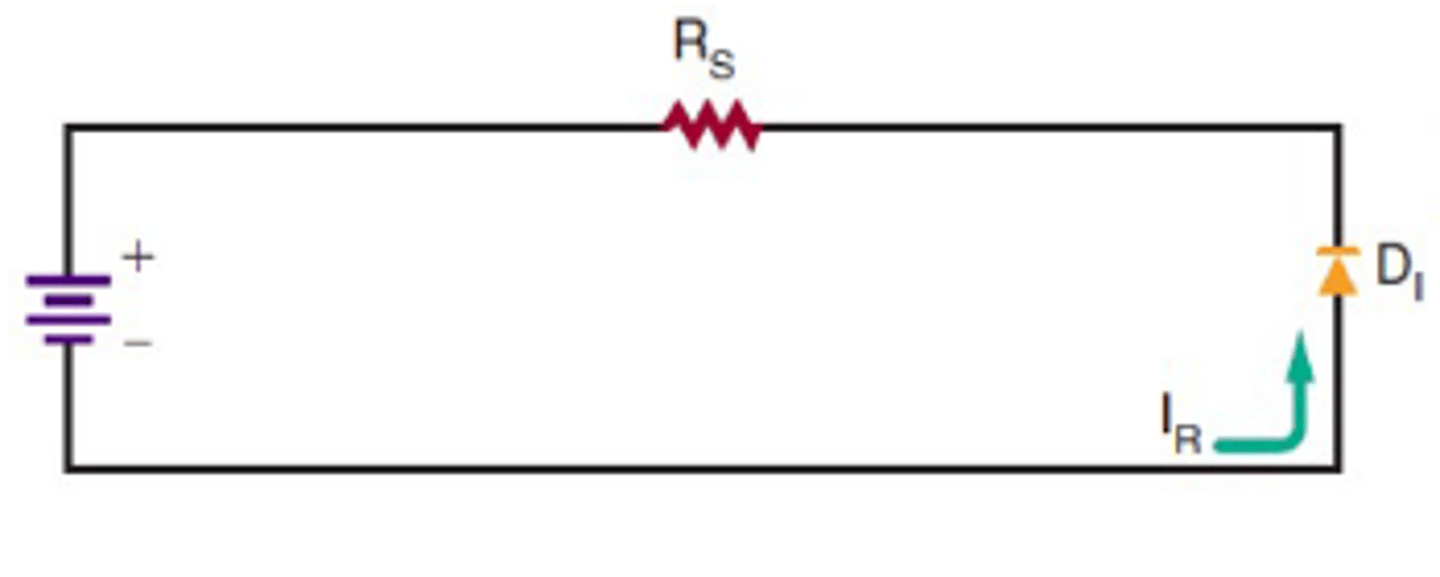
Reverse Biasing Schematic
The maximum safe reverse voltage that can be applied to the diode
PIV/PRV
The maximum forward-biased current that the diode can safely handle
If max
Testing PN Junction diodes can determine
The polarity of a diode's lead and serviceability/qualitive check
, black lead is cathode and red lead anode indicates
Low resistance and forward biasing
black lead is anode and red lead cathode indicates
High resistance and reverse biasing
Using the Diode check reverse biasing shows
.0L
Using the diode check and forward biasing shows
Voltage drop instead of low resistance
Specially constructed to take advantage of reverse current operation
Zener Diodes
Used for regulating voltage in many circuits
Zener Diodes
Zener Diode
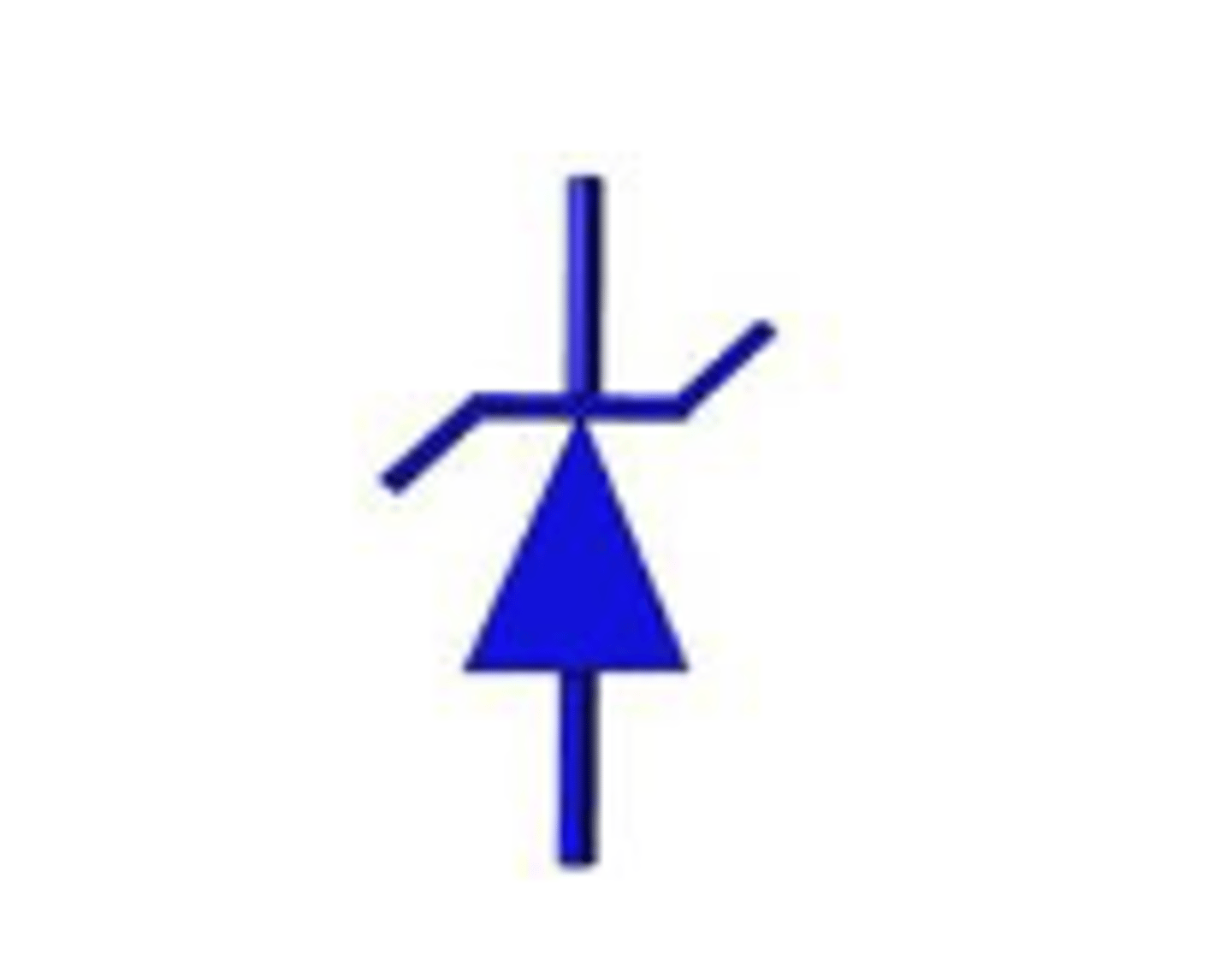
Varicap
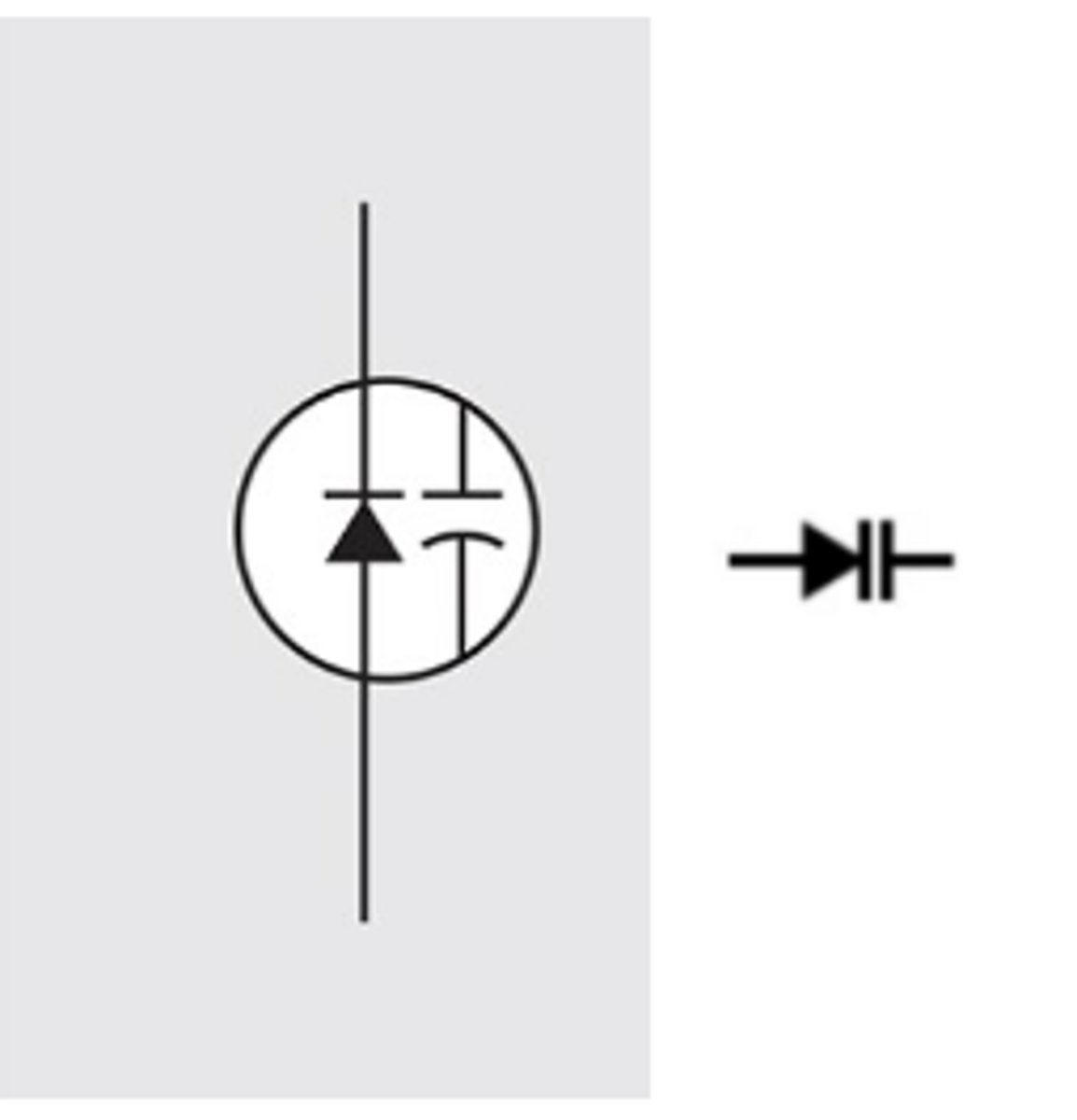
Are primarily used in a resonant circuit where some level of tuning or frequency is desired
Varactor Diode
The capacitance of the diode varies
Inversely with its bias voltage
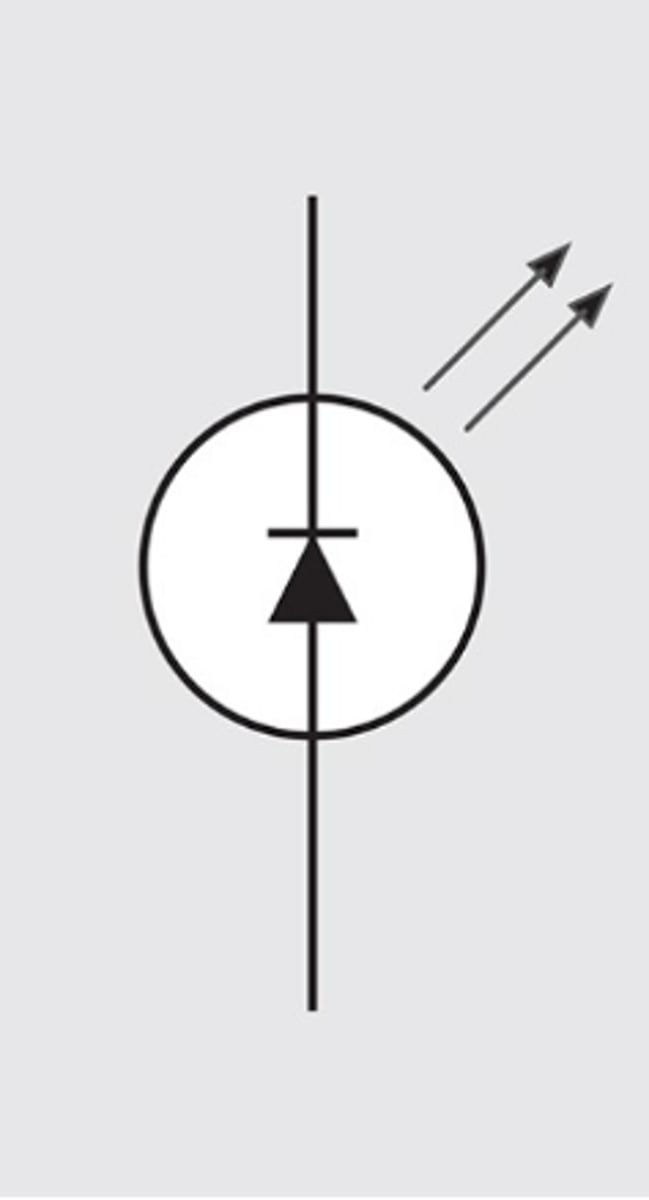
A popular type of optoelectronic semiconductor device
Light Emitting Diode
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
What segments are used to make a 5
A,F,G,C,D
3 multiple choice options
Which way does conventional current flow on a diode
Anode to Cathode
LED Wavelength and colour of light emitted is determining on the
band gap energy
Light is produced when
free electrons combine with holes