Cornell Veterinary Medicine - Week One
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
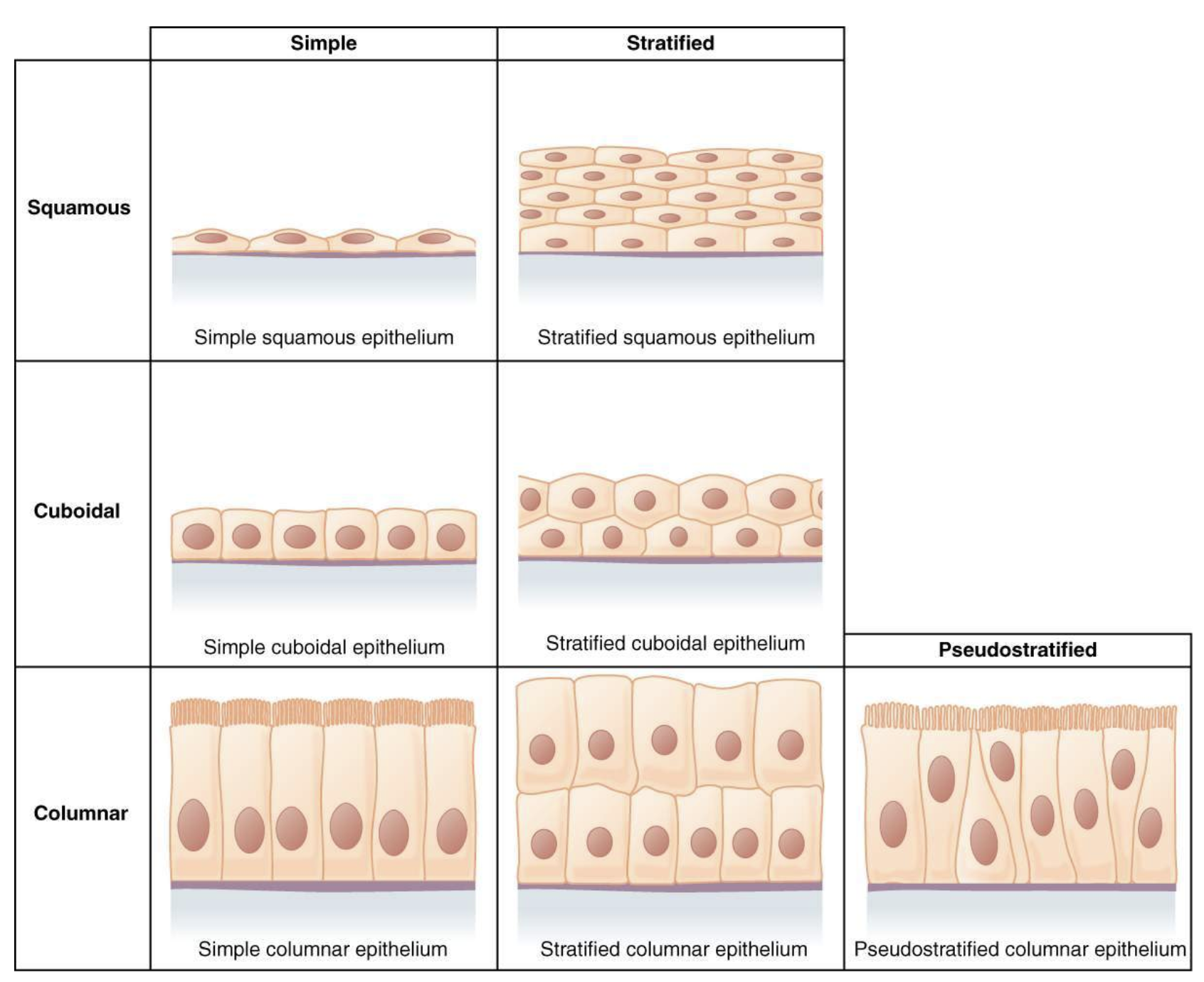
epithelial tissue
adhere closely to one another to form continuous sheets that cover body surfaces
role: protection, absorption, secretion
connective tissue
Cells do not adhere to each other as they are surrounded externally by an extracellular matrix, which provides support and structure to organs and other tissues.
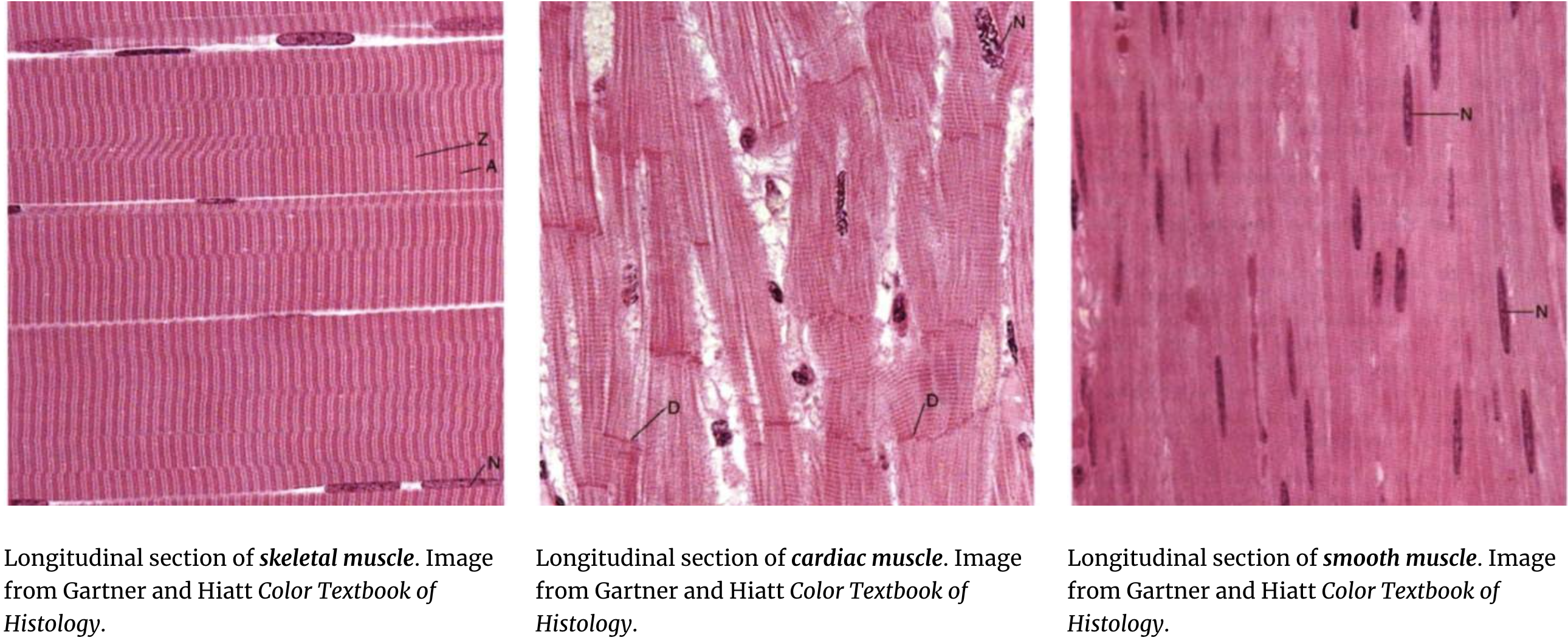
muscle tissue
tissue composed of cells that can contract and are responsible for movement of the body and its organs.
nervous tissue
specialized tissue that transmits electrical impulses throughout the body, facilitating communication between different body parts.
central axis
passes through the head, neck, trunk + divides the body into symmetric left/right halves
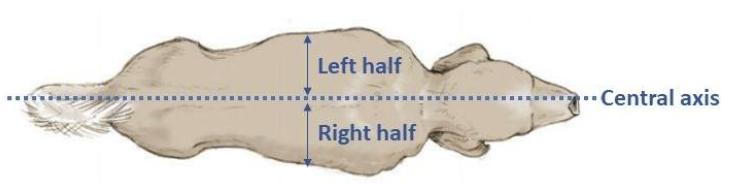
median plane (whole body)
a plane extending along the central axis that divides the body into left and right parts.
sagittal plane (whole body)
parallel to the median plane
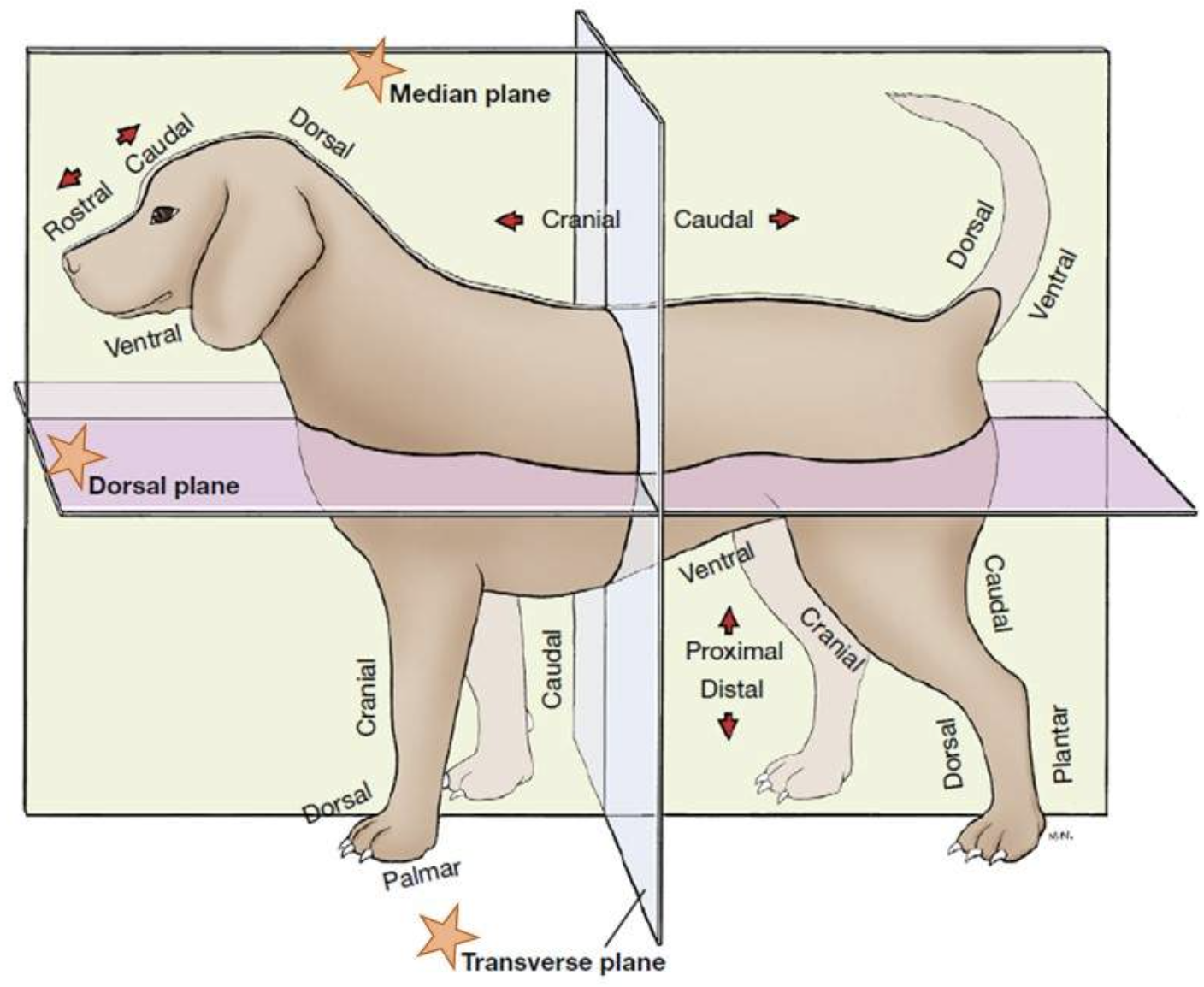
transverse plane (whole body)
a plane that divides the body into cranial and caudal parts, perpendicular to the median and sagittal planes.
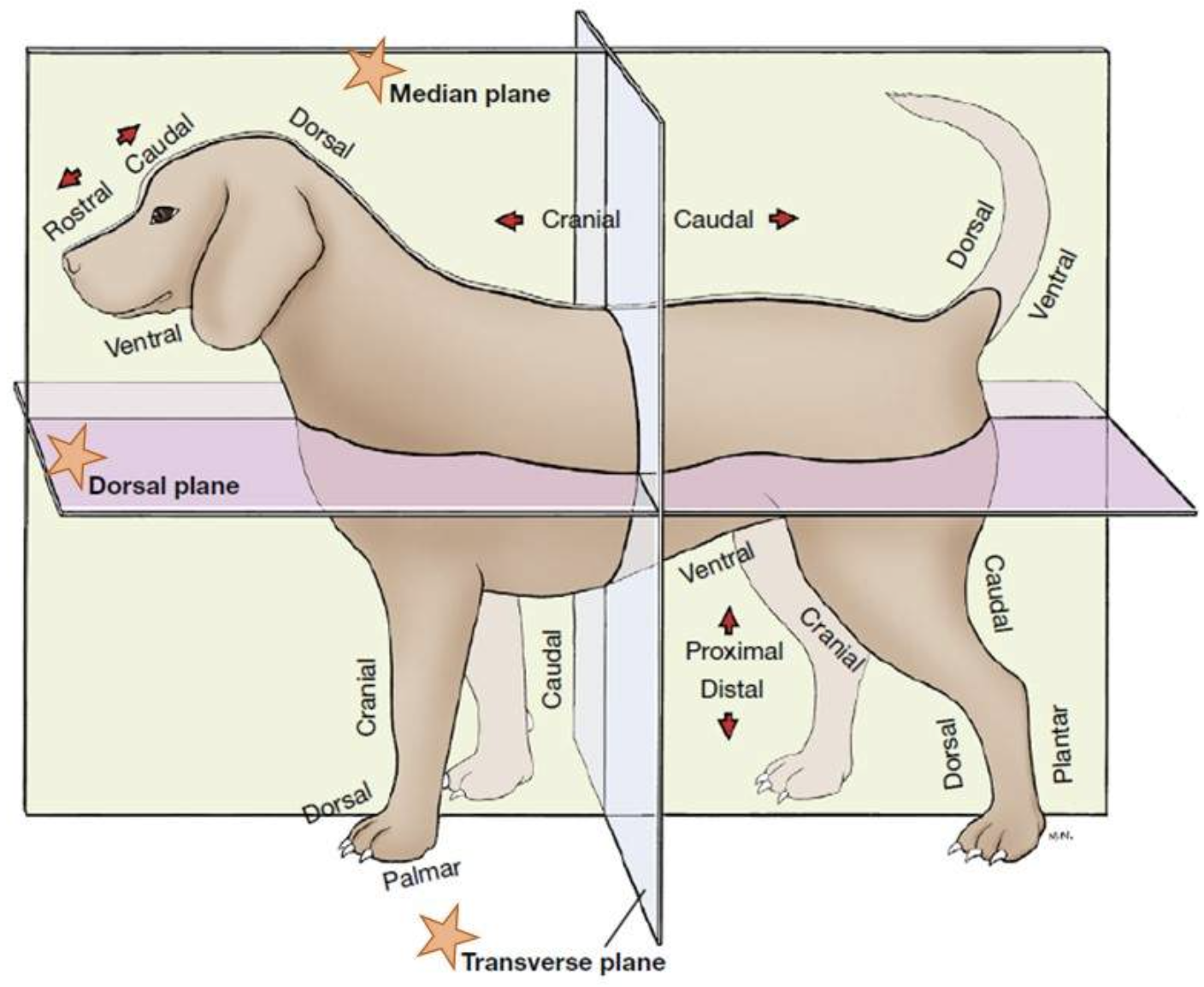
dorsal plane (whole body)
a plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal parts, perpendicular to the median and transverse planes.
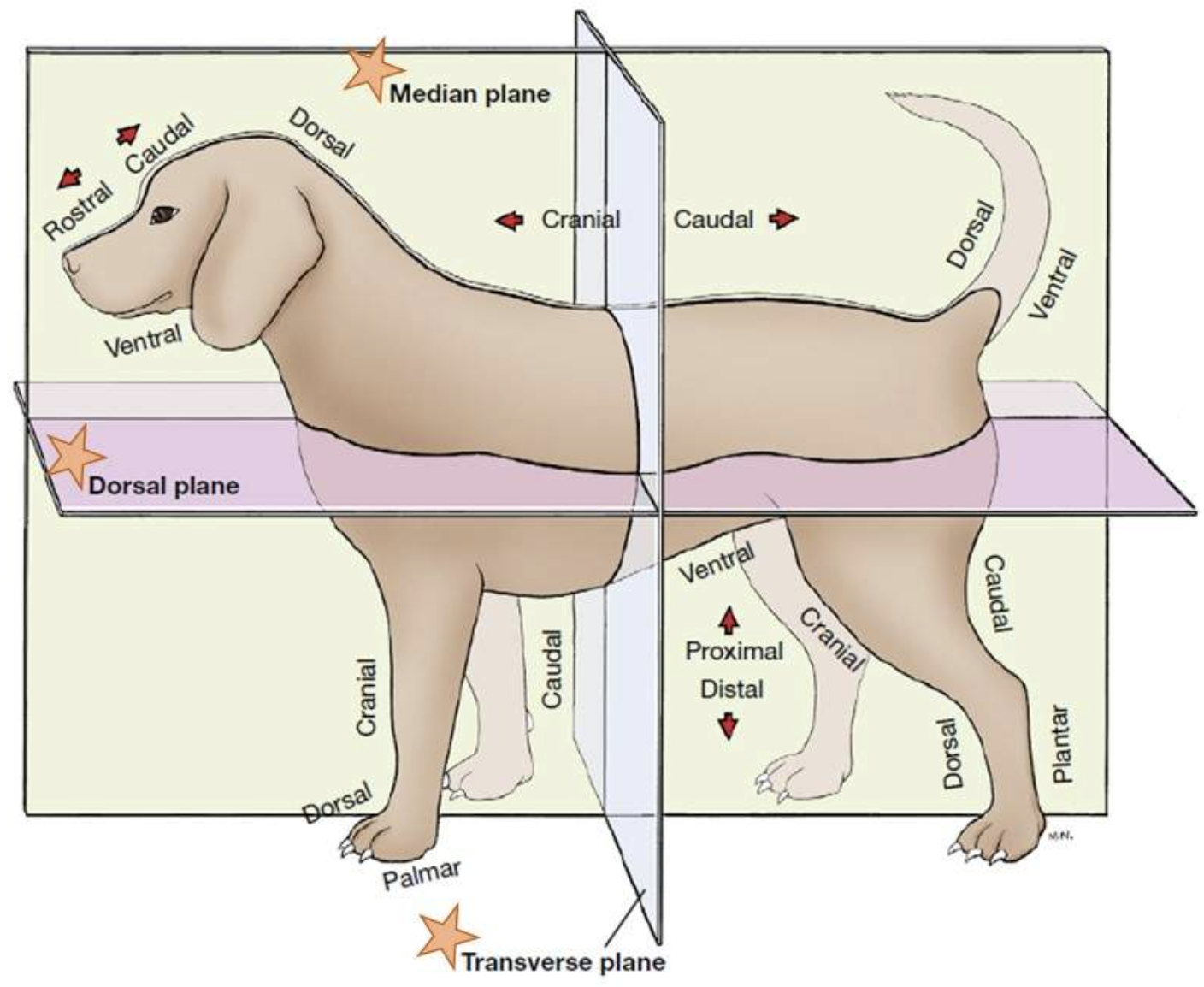
transverse plane (limbs)
a plane that divides a limb into proximal and distal parts
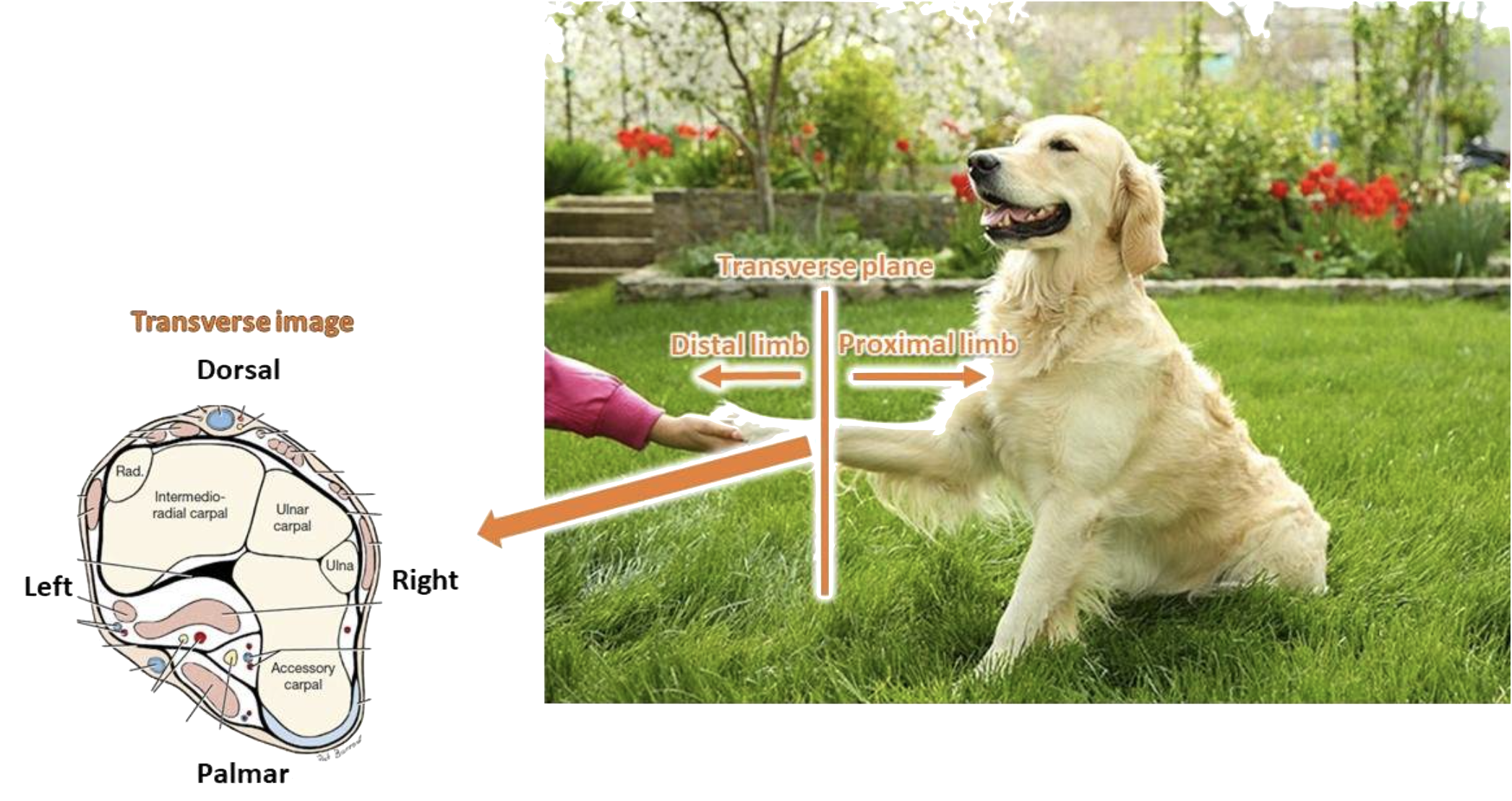
sagittal plane (limbs)
a plane that divides a limb into left and right parts, parallel to the median plane.
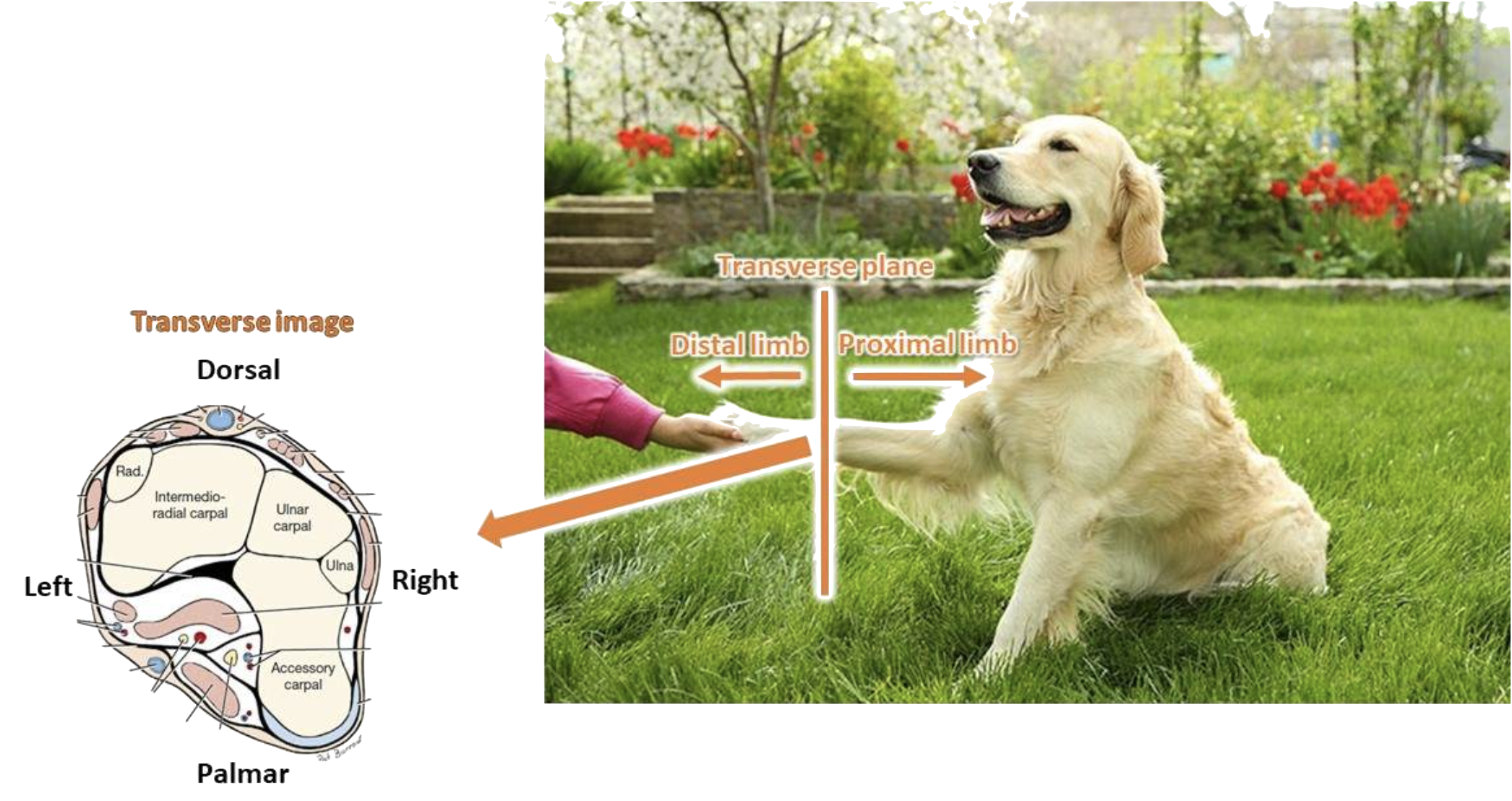
dorsal plane (limb)
a plane that divides a limb into dorsal and palmar (or plantar) parts
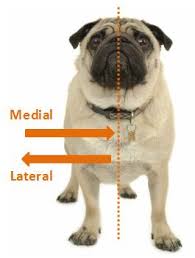
medial
closer to the median plane
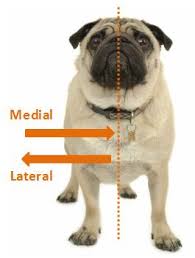
lateral
further from the median plane
intermediate
between medial and lateral
sagittal
relating to a plane that divides the body into left and right portions
transverse
relating to a plane that divides the body into upper and lower portions
cranial
relating to the skull or head region
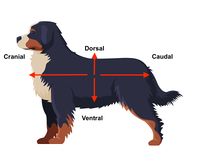
caudal
relating to the tail or lower part
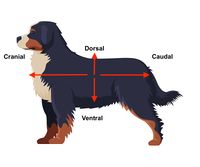
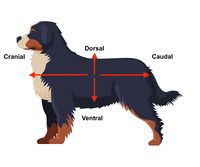
dorsal
closer to the dorsum (back) + corresponding surface of the head
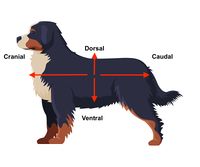
ventral
closer to the ground (if the animal is standing)
proximal
closer to the body
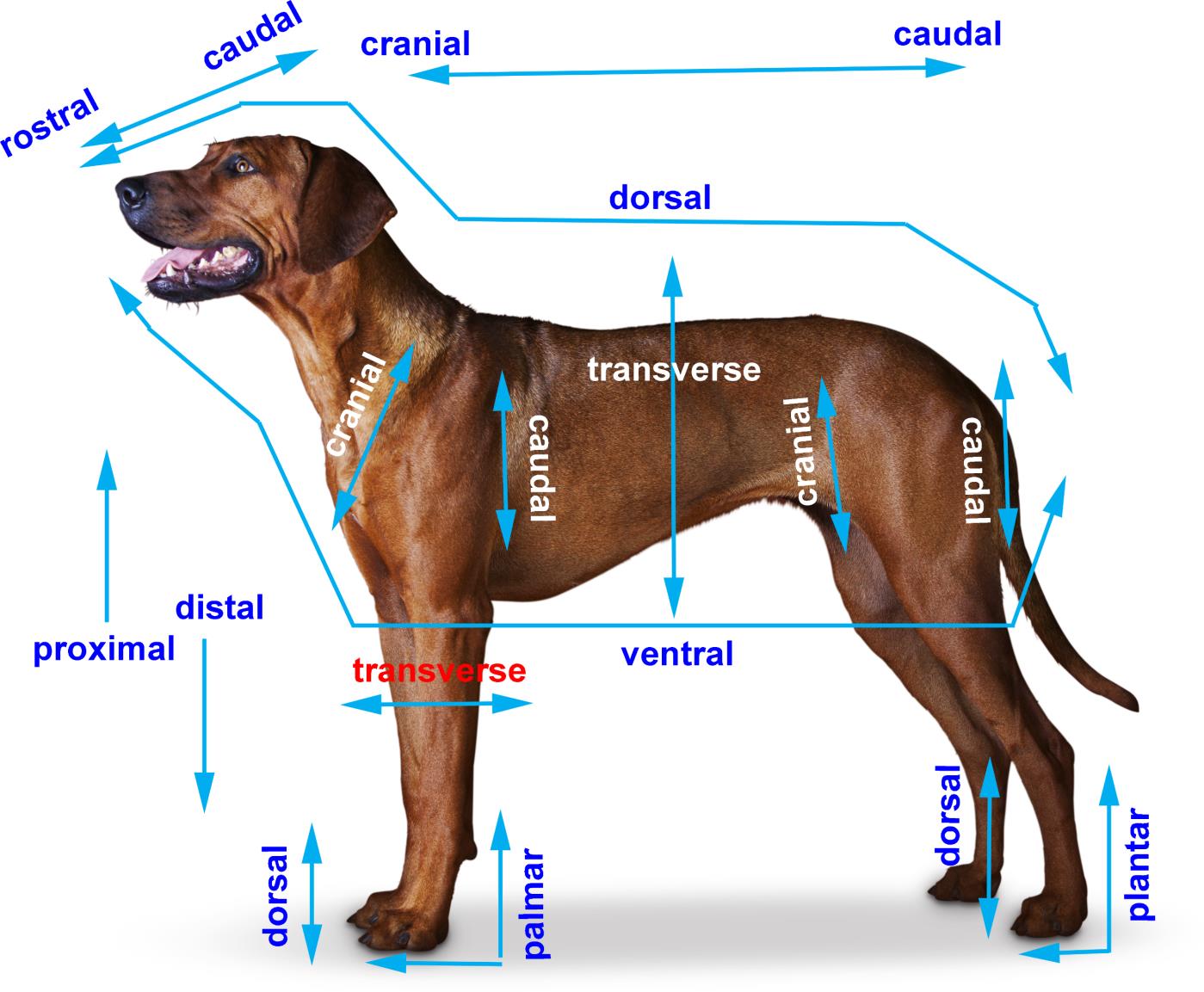
distal
further from the body
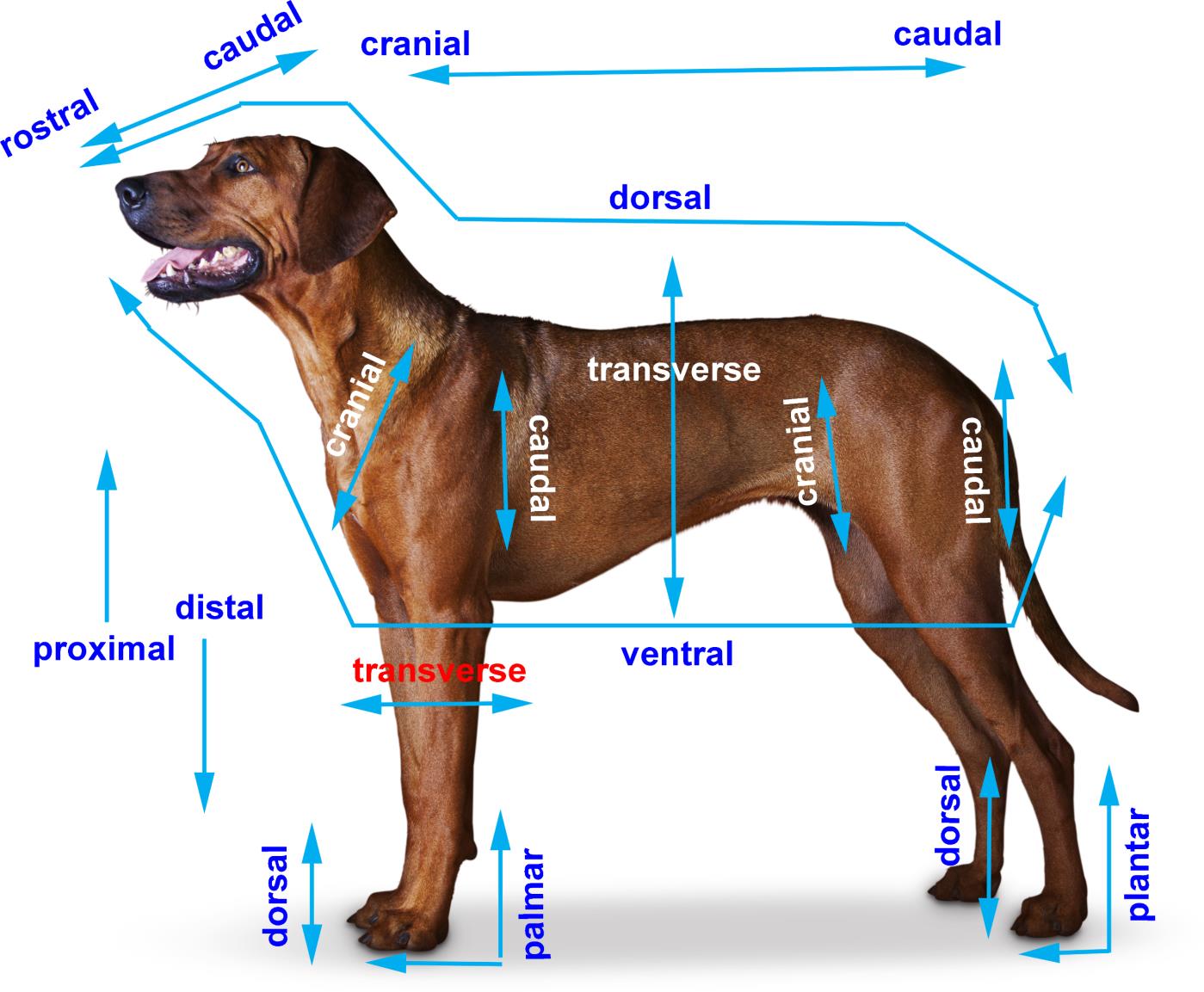
palmer
the part of the front paw (manus/carpus) that contacts the ground
plantar
the part of the hind paw (pedis/tarus) that contacts the ground
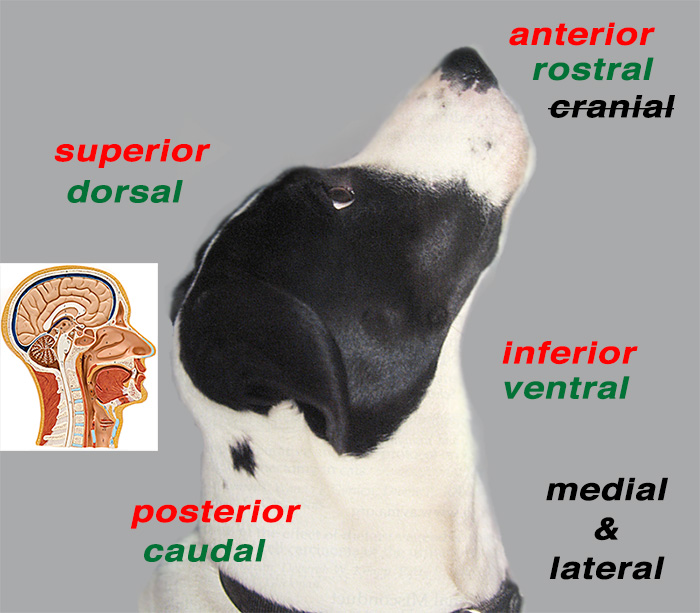
rostral
closer to the muzzle (nose) use when talking about head
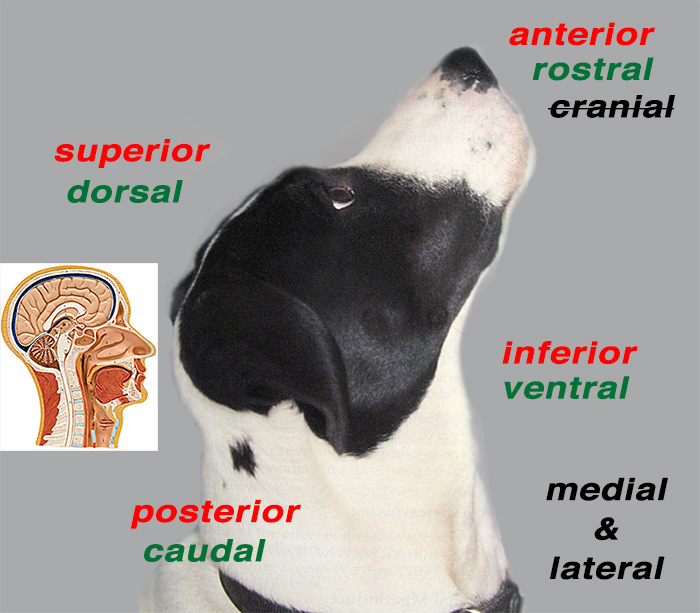
posterior
closer to the tail
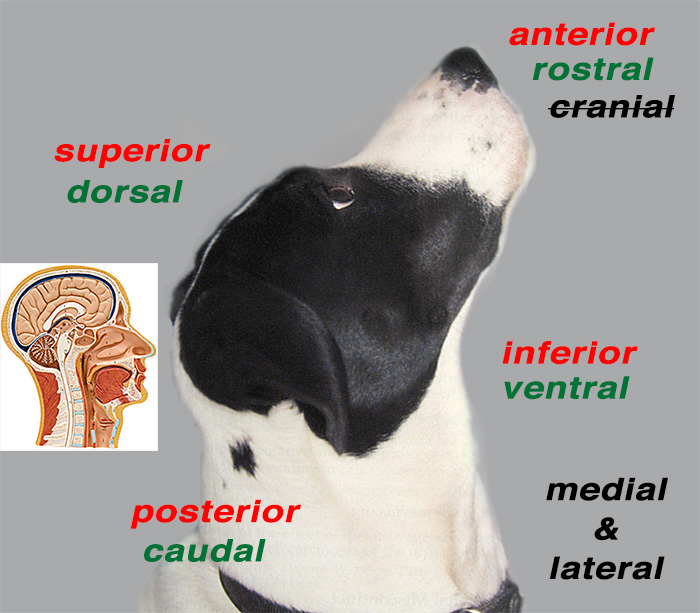
superior
further from the ground
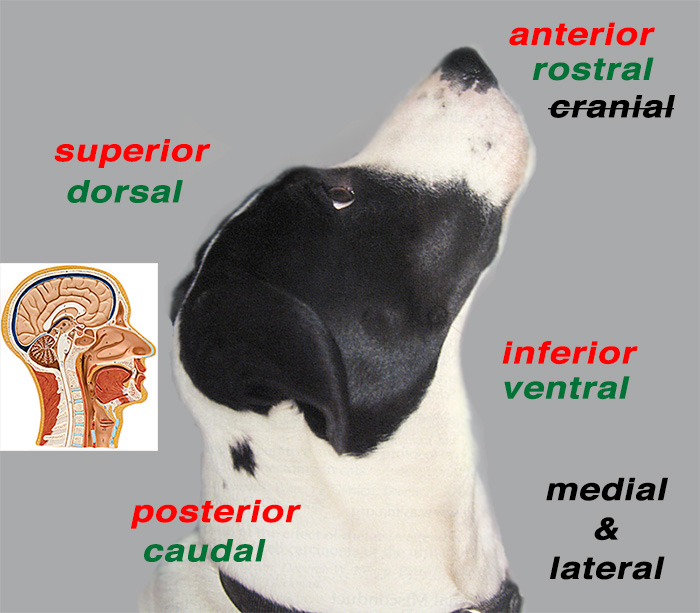
inferior
closer to the ground
lateral rotation
angular motion in the transversal plane to the left/right (ex. turning head to say “no”
flexion
angular motion in the median (sagittal) plane that brings structures closer together
extension
motion that brings structures further apart
lateral flexion
angular motion in the dorsal plane to the left/right that bring structures closer together (bringing ear closer to the shoulder)
circumduction
complex movement of a part of the body when outlining the surface of a cone (ex. drawing a circle)
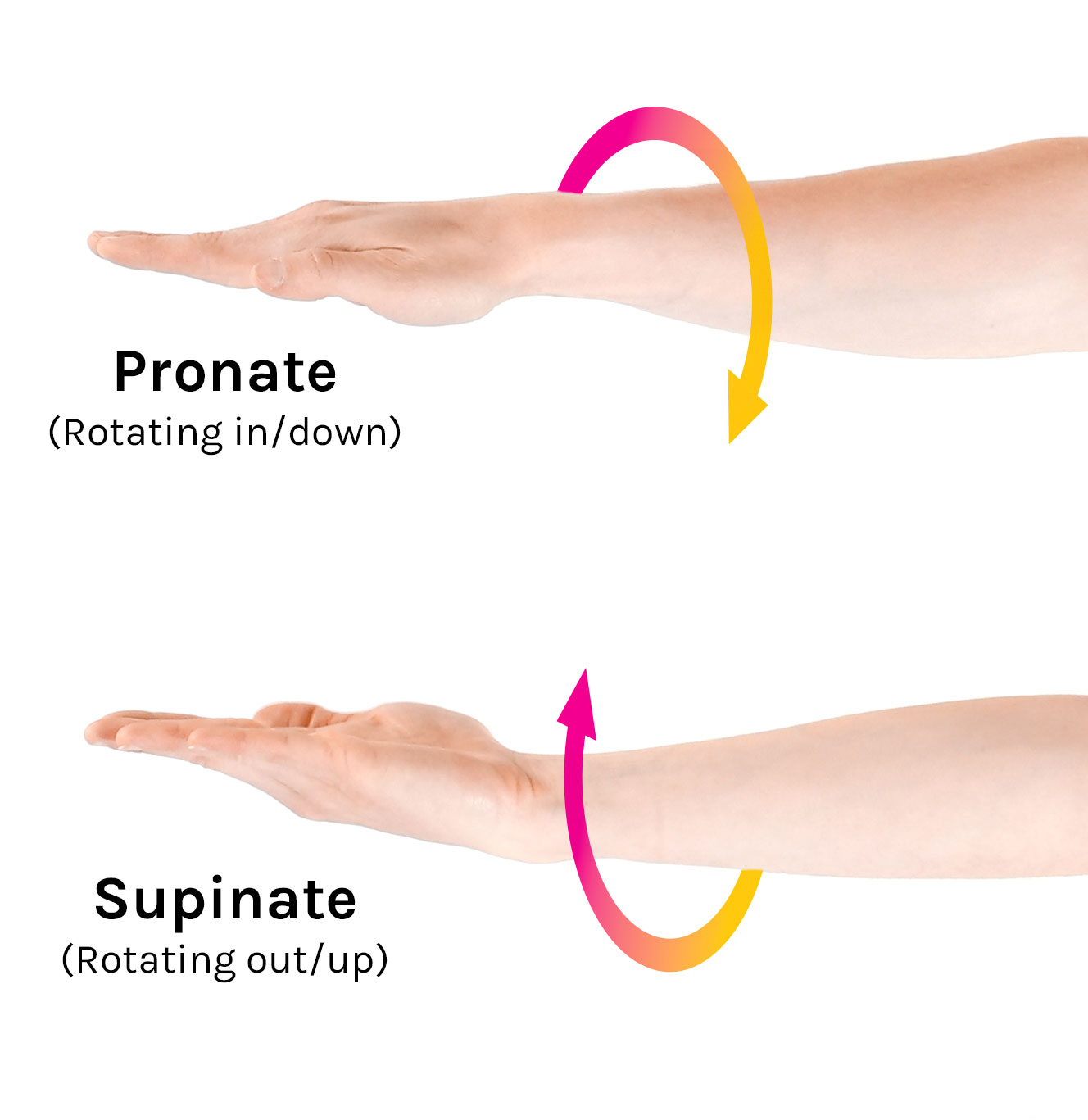
pronation
medial rotation of the appendage from the supine position, so that the palmer/plantar surface will face the substrate (opposite of supination
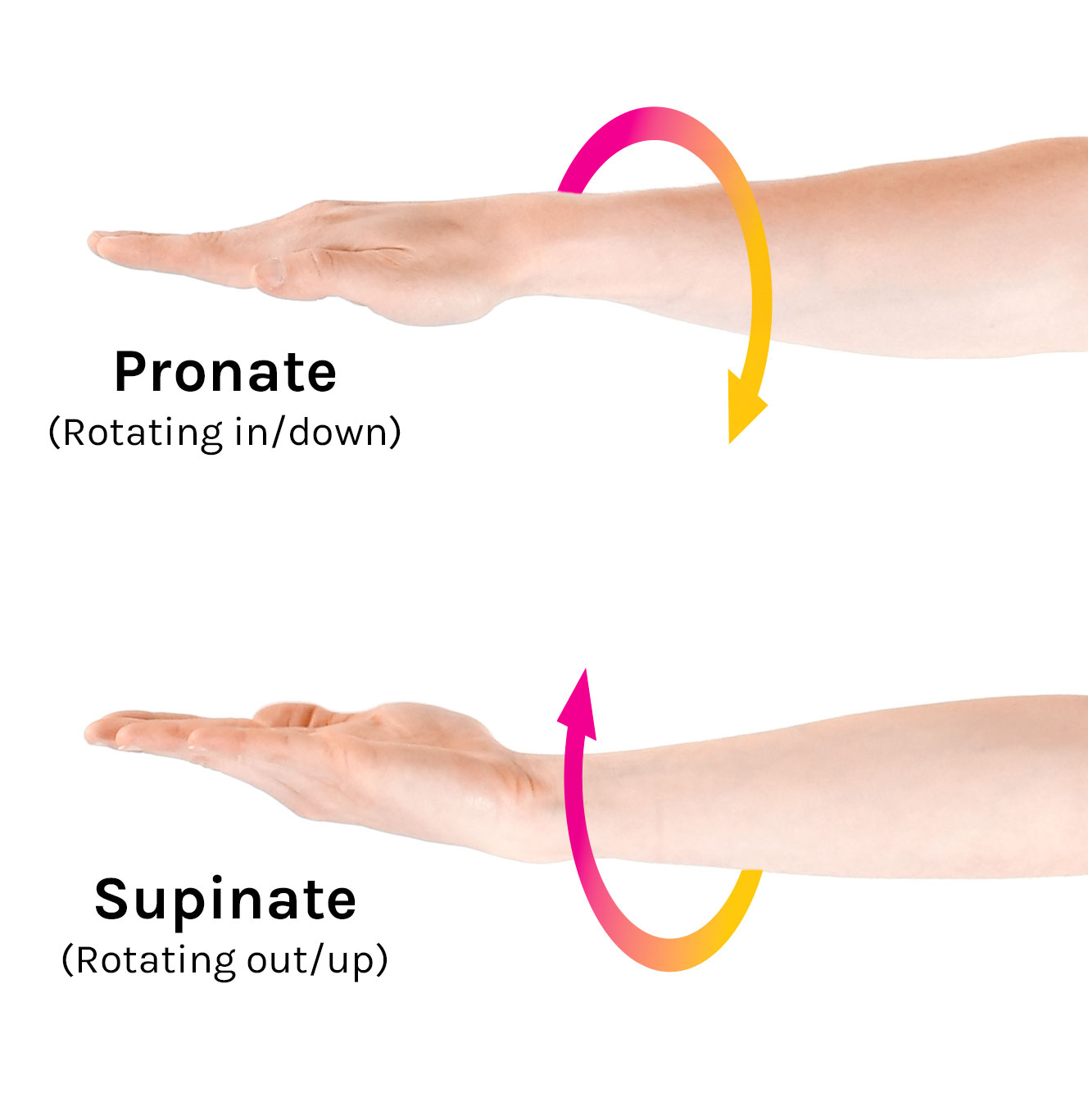
supination
lateral rotation of the appendage so that the palmer/plantar surface of the paw faces medially (scooping soup)
protraction
translatory motion that moves a structure rostrally in a dorsal plane (ex. sticking out the tongue)
retraction
translatory motion that moves a structure caudally in a dorsal plane
abduction
movement of a part of the body away from the median plane
adduction
movement of a part of the body toward median plane
plasma
liquid proportion of blood
makes ~55% of blood
serum
Liquid remaining after blood clots naturally
Does not contain clotting factors
Serum = plasma - clotting factors
red blood cells
Makes up ~45% of the blood
Also called erythrocytes
Function: transport oxygen + carbon dioxide
Principal component: hemoglobin (Hb)
Each molecule of hemoglobin is responsible for carrying molecules of oxygen
Lifespan: 2-4 months
Mature in the bone marrow from reticulocytes (larger and contains less hemoglobin
buffy
Makes up ~1% of blood
White blood cells
Platelets
anemia
decrease in red blood cells
Hemorrhage (loss of RBCs)
Hemolysis (destruction of RBCs)
Non-regenerative anemia
hemorrage
loss of RBCs
hemolysis
destruction of RBCs
Non-regenerative anemia
decreased production
Erythrocytosis
increase in red blood cells
Overproduction by the bone marrow
Compensation for chronic hypoxia (low oxygen levels) or high altitudes
white blood cells
Also called leukocytes
Function: Responsible for defending the body against infection
Less numerous than RBCs
Classifications of leukocytes:
Granulocytes (contain granules) → Neutrophils, Basophils, Eosinophils
Agranulocytes (lacks granules) → Lymphocytes, Monocytes
leukocytosis
increase in WBCs
leukopenia
decrease in WBCs
Neutrophils
Most abundant of the leukocytes/white blood cells
Function: fights against disease
Appearance: lobulated nucleus with granulated cytoplasm
Mature: segmented nucleus
Immature: “band” nucleus
Lifespan: 5-10 hours
neutrophilia
increase in neutrophils
neutropenia
decrease in neutrophils
Eosinophils
Function: Parasite defense, allergic reactions, enzyme inactivate histamine
Appearance: lobulated nucleus with eosinophilic (pink) granules
Lifespan: minutes to hours
Migrate into tissue → survive for weeks
eosinophilia
increase in eosinophils
eosinopenia
decrease in eosinophils
Basophils
Function: parasite defence, regulate allergic reactions (release histamine → pro-inflammatory)
Appearance: lobulated nucleus with basophilic (purple) granules
Lifespan: ~ 6 hours
Migrate into tissue → survive for weeks
basophilia
increase in basophils
basopenia
decrease in basophils
Monocytes
Largest of all leukocytes
Function: Phagocytic cells that kill microorganisms, ingest foreign material, and remove dead cells
Appearance: variable morphology
Lifespan: 12-24 hours
Migrate into the tissues → mature into macrophages OR dendritic cells
monocytosis
increase in monocytes
monocytopenia
decrease in monocytes
Lymphocytes
Second most common type of leukocyte
Function: Main cell type of the immune system (B and T cells)
Appearance: Round nucleus with little cytoplasm
Lifespan: hours to years
B-Cells
Plasma cells → antibody production
T-Cells
cytotoxic T cells kill infected cells; helper T cells recognize infected cells and recruit other cells
lymphocytosis
increase of lymphocytes
lymphopenia (seen w stress)
decrease of lymphocytes
Platelets
Also called thrombocytes
Function: formatted of blood clots, prevents bleeding out after vessel injury, Aggregate to the site of injury and form a “platelet plug”
Appearance: very small, disc-shaped
A nucleated cell fragments
Lifespan: 1-2 weeks
Produced in the bone marrow
thrombocytosis
increase in platelets/thrombocytes
thrombocytopenia
decrease in platelets/thrombocytes
Can lead to increased bleeding and bruising
Purple Top (blood tubes)
Contains EDTA (anticoagulant) + used for complete blood count (CBC)
green top (blood tube)
Contains heparin (anticoagulant) + used for chemistry panels
blue top (blood tube)
Contains citrate (anticoagulant) + used for coagulation panels
red top (blood tube)
No additives + used for chemistry panels
CBC test
Analyzes the number and types of blood cells (complete blood count)
Chemistry Panel
Analyzes the non-cellular component of blood (protein, electrolytes, minerals)
Blood smear
Show morphology of blood cells
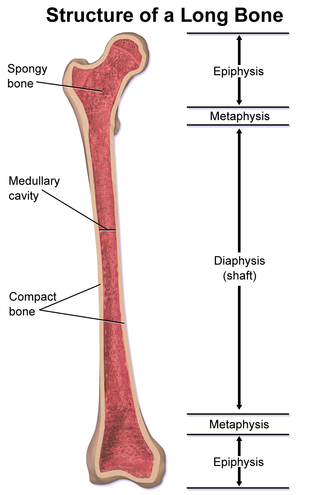
epiphysis
Each end of the long bone + covered by articular cartilage
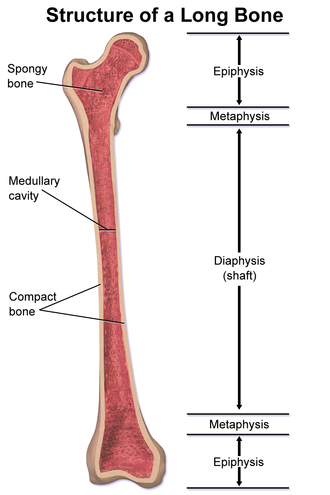
diaphysis
central shaft of the long bone
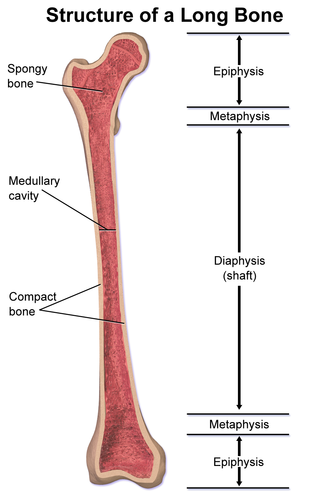
metaphysis
flared area between the diaphysis and epiphys
Cranial cruciate ligament rupture
can be a partial or complete tear of the ligament
osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a chronic and degenerative disease of synovial joint