H Anatomy Muscle contractions
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Tendon
Connects muscle to bone
Fascicle
Groups of muscle fibers
Myofibril
Contractile organelles found in muscle fibers - these contain sarcomeres
Sarcomere
Make up myofibrils- where muscle contraction occurs
Actin and Myosin
Myofilaments found in sarcomeres
Sarcolemma
The cell membrane of muscle fibers - it has protein receptors for acetylcholine
Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
Wraps around each sarcomere - stores calcium
T- Tubules
Brings the action potential deeper into the muscle cell to trigger the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium ions
Neuromuscular Junction
The place where a motor neuron connects with a muscle fiber - the axon terminal of the neuron releases acetylcholine to pass on the neuron’s action potential to the muscle fiber
Direct phosphorylation of creatine phosphate
Very quick method of ATP generation that only yields 1 ATP - gives a very quick burst of energy that lasts 15 seconds for very intense exercise (ex. Sprinting or lifting a very heavy weight). Does not require oxygen.
Anaerobic cellular respiration
When your body is doing pretty intense exercise and it needs more oxygen to keep up with the amount of ATP needed, some ATP can be made without oxygen present - 2 ATPs. This provides about 40 seconds of energy
Aerobic cellular respiration
This takes a while to make ATP, but it yields the most ATP - around 32 ATPs per molecule of glucose broken down. This is done when oxygen is present and it can last for hours.
Step 1
Brain sends out a message to tell the muscles to move. This message travels via action potential - an increasing positive charge occurring on the inside of the neurons due to ion channels opening and Na+ ions flowing in
Step 2
At the neuromuscular junction, action potential arrives causing the axon terminal to release acetylcholine
Step 3
When acetylcholine attaches to the receptor proteins on the sarcolemma, that opens voltage gated sodium channels to allow Na+ ions briefly into the muscle fiber cell, the spreading action potential opens up more and more voltage gated sodium ion channels on the sarcolemma, until the action potential reaches a T Tubule
Step 4
Action potential travels down the T Tubule and then triggers the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Step 5
Ca2+ ions bind to troponin, which causes it to change shape. As troponin changes shape, that also makes the position of tropomyosin shift around, thereby exposing the binding sites on actin filaments to myosin heads
Step 6
ATP is used to make the myosin heads pull the actin filaments towards the middle of the sarcomere, like oars rowing a boat
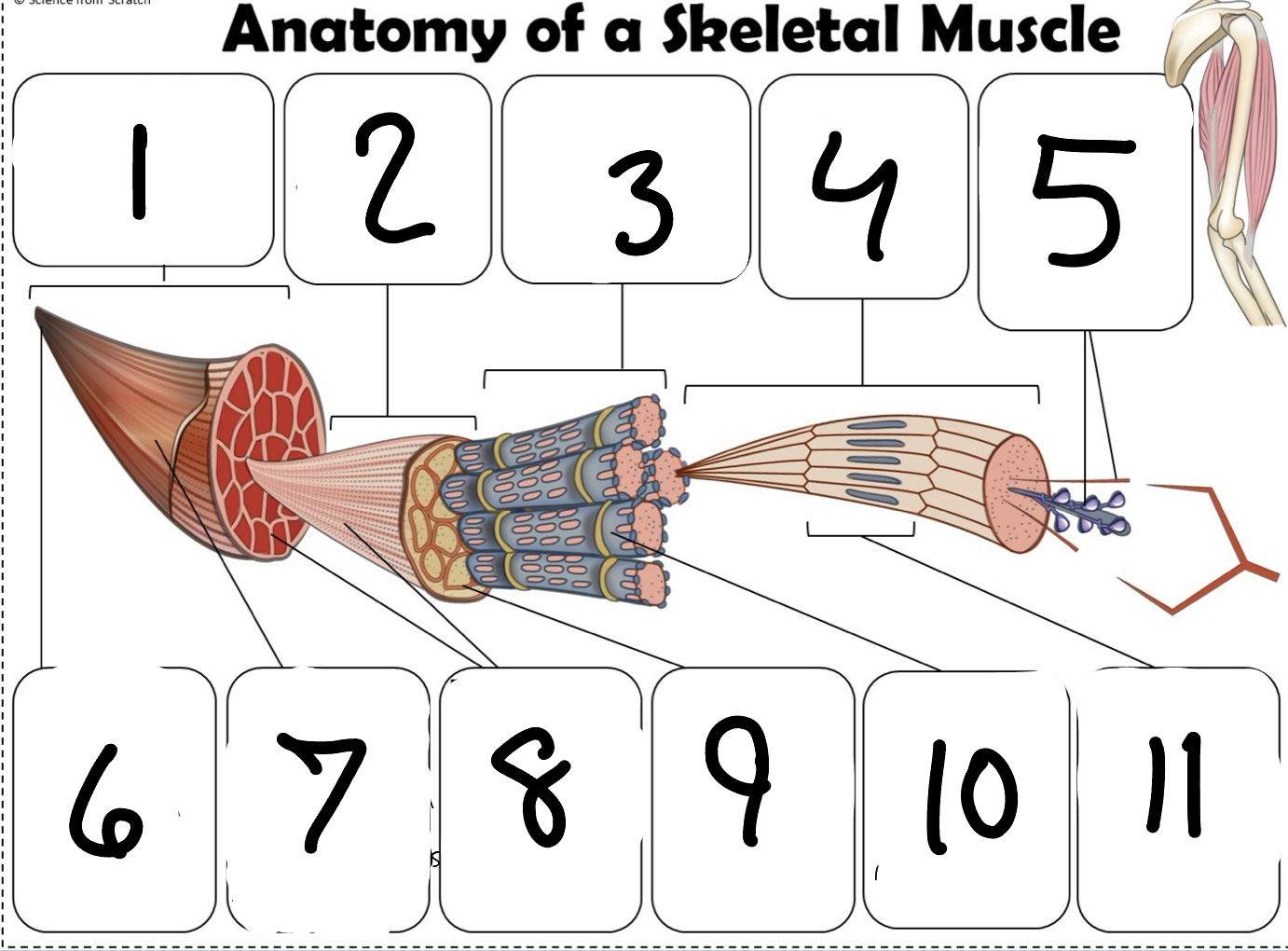
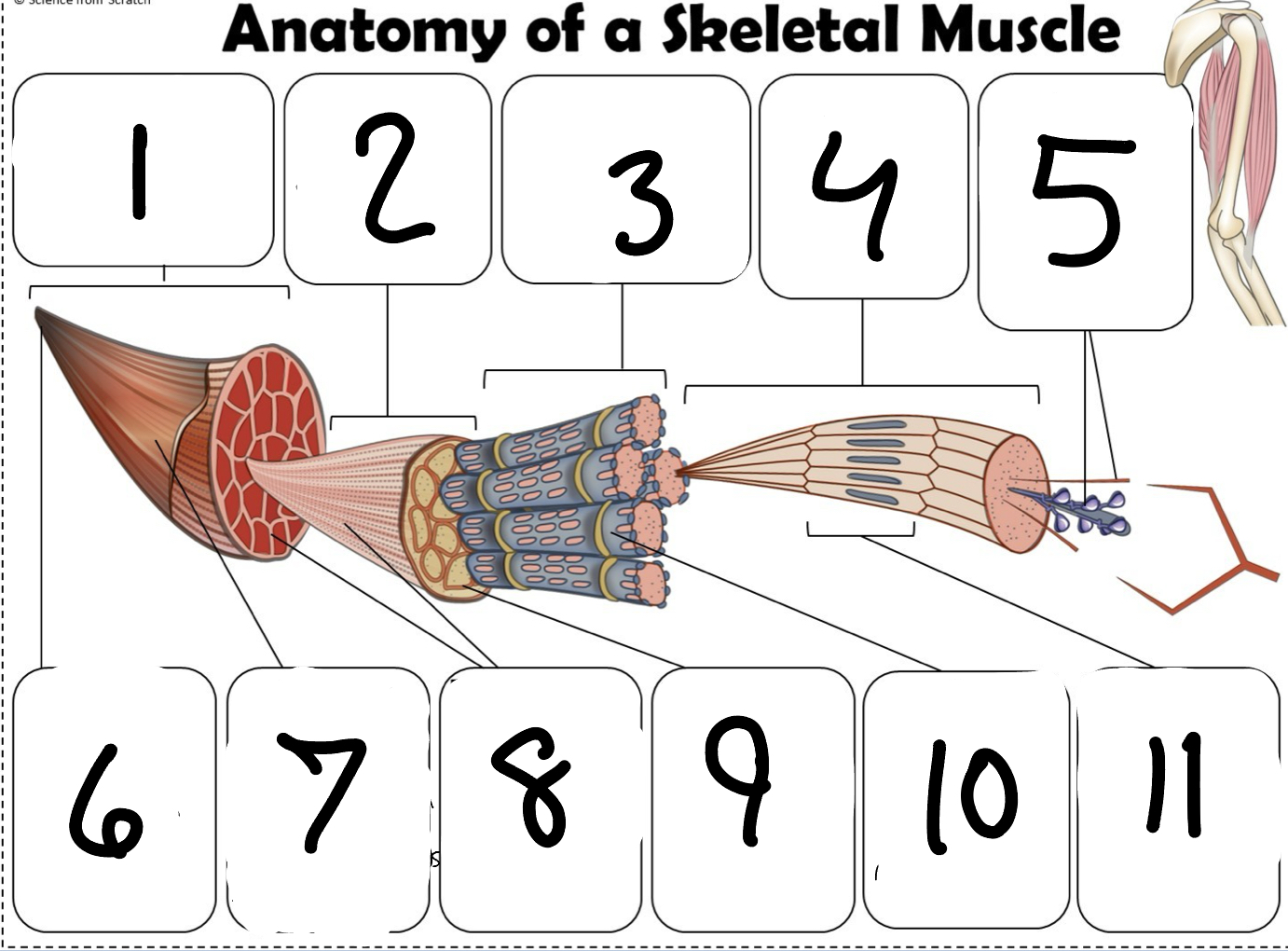
What is #1
Muscle (picture)
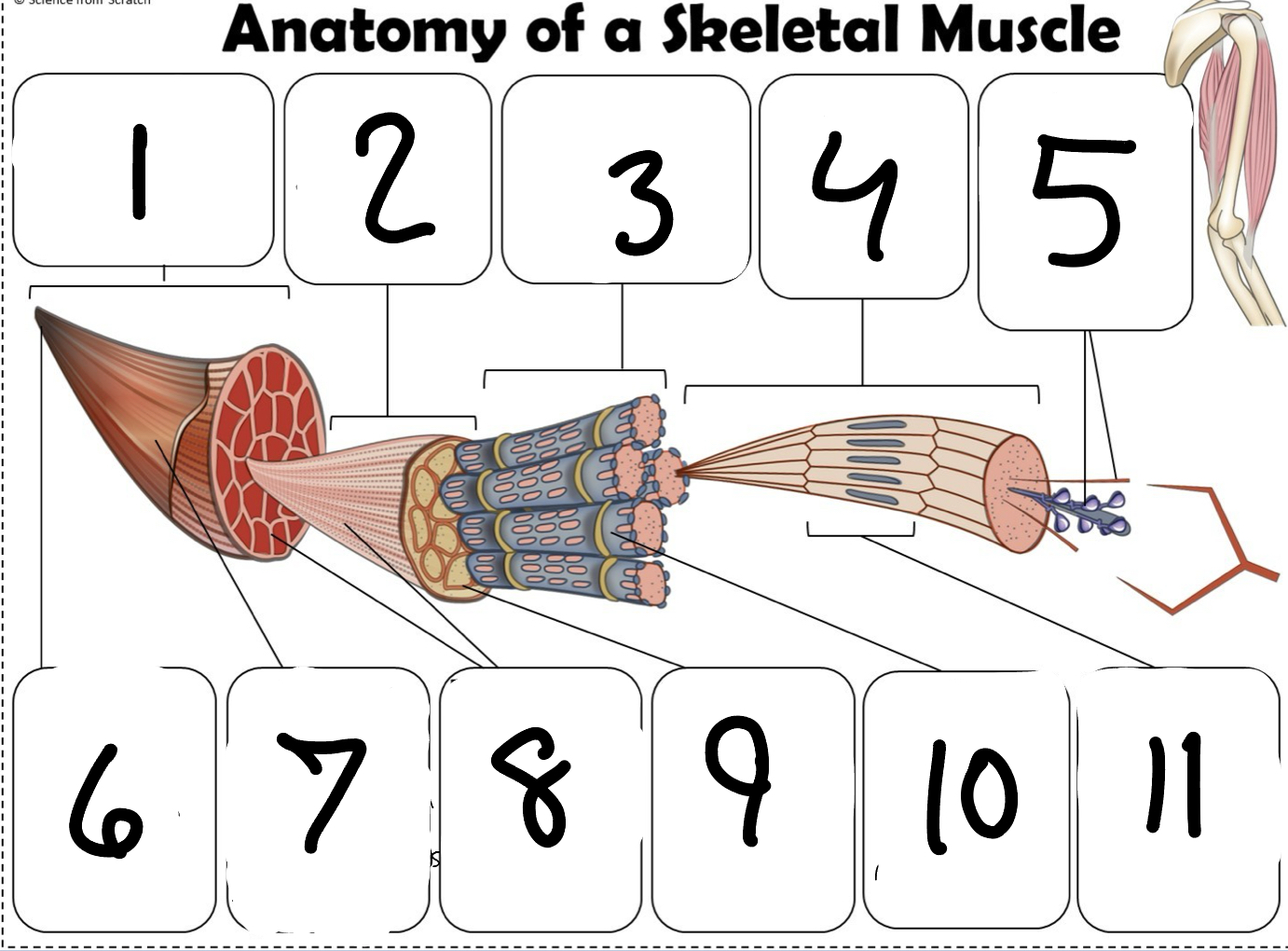
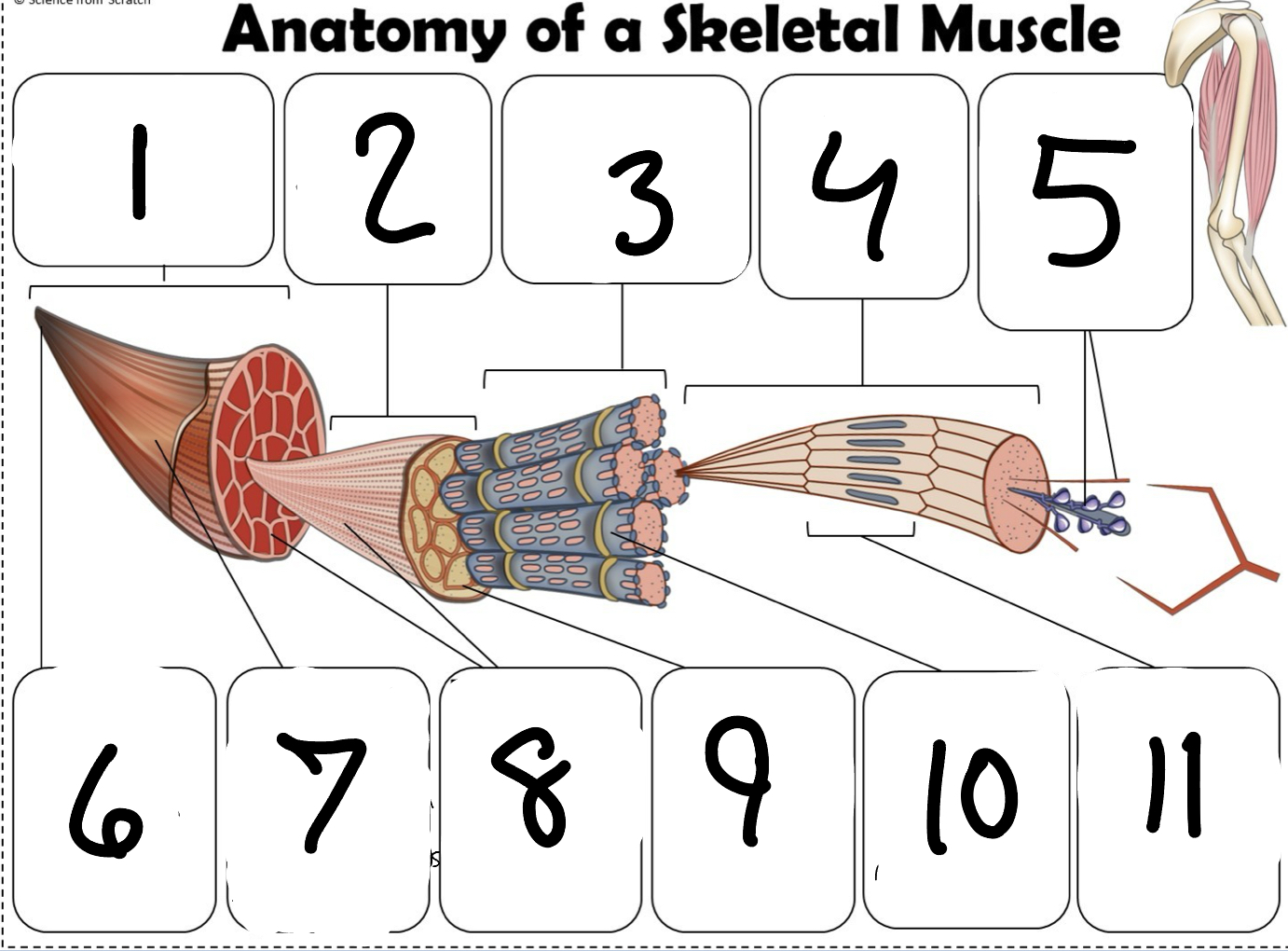
What is #2
Fascicle (picture)
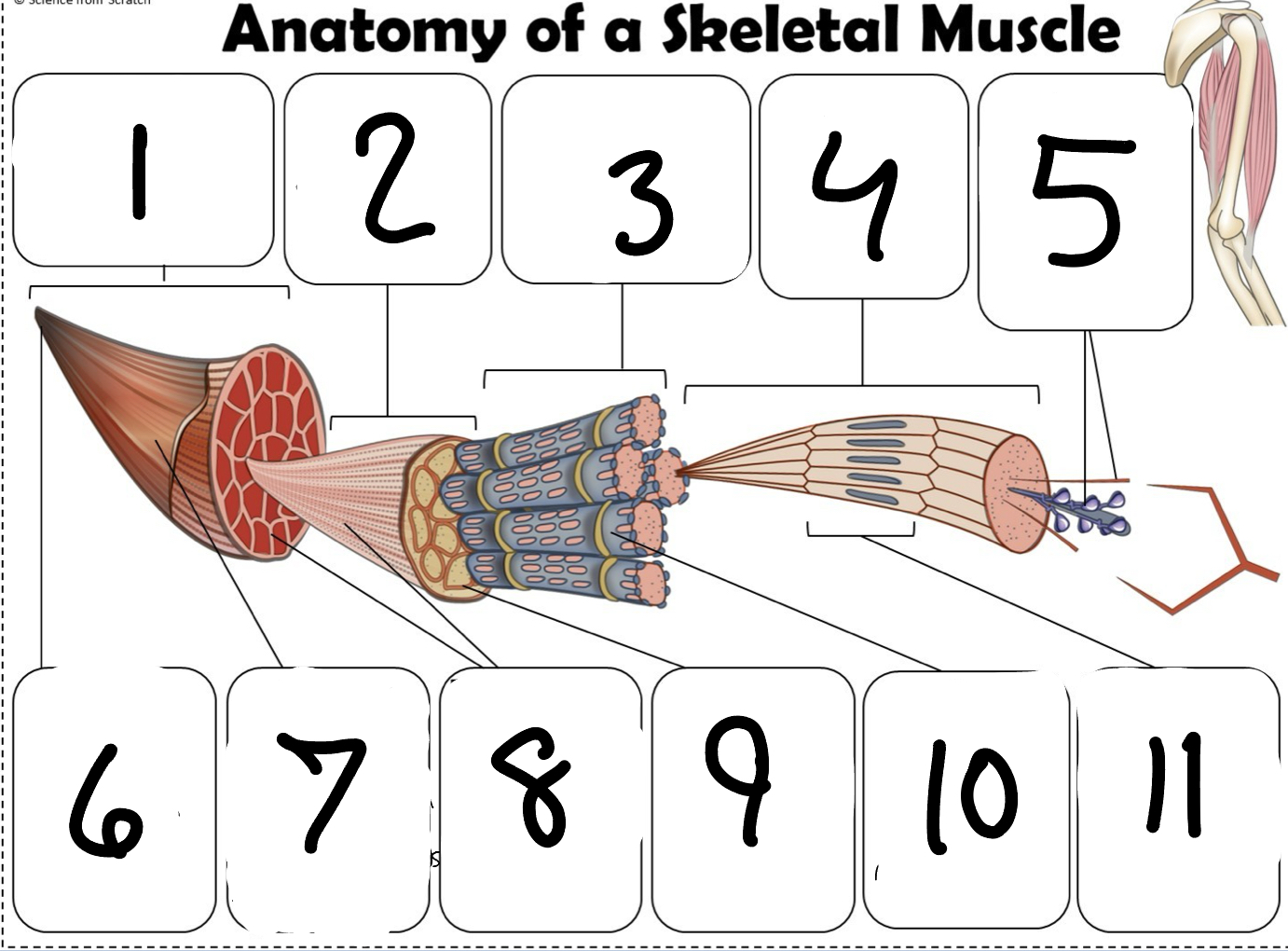
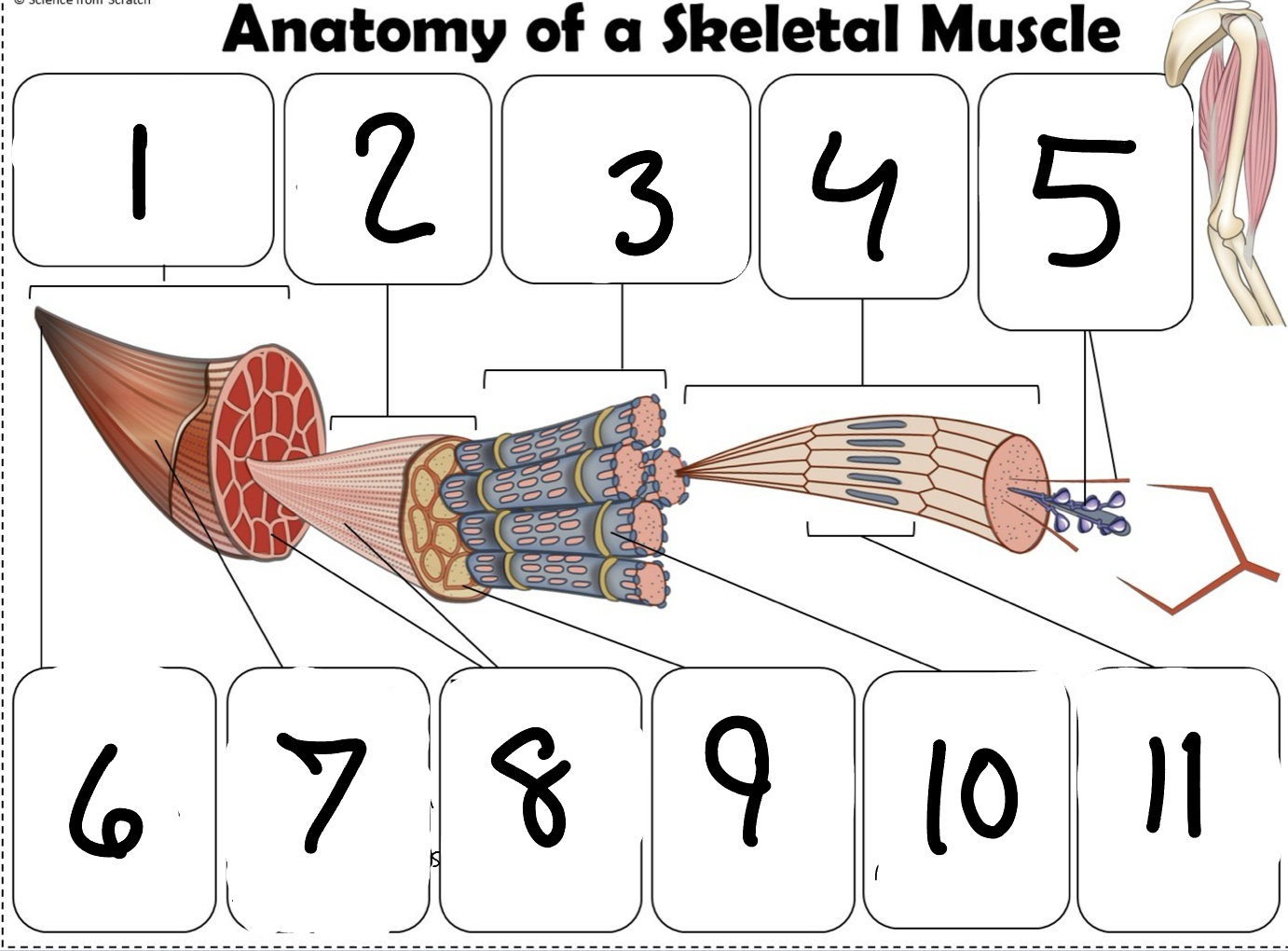
What is #3
Muscle Fiber (picture)
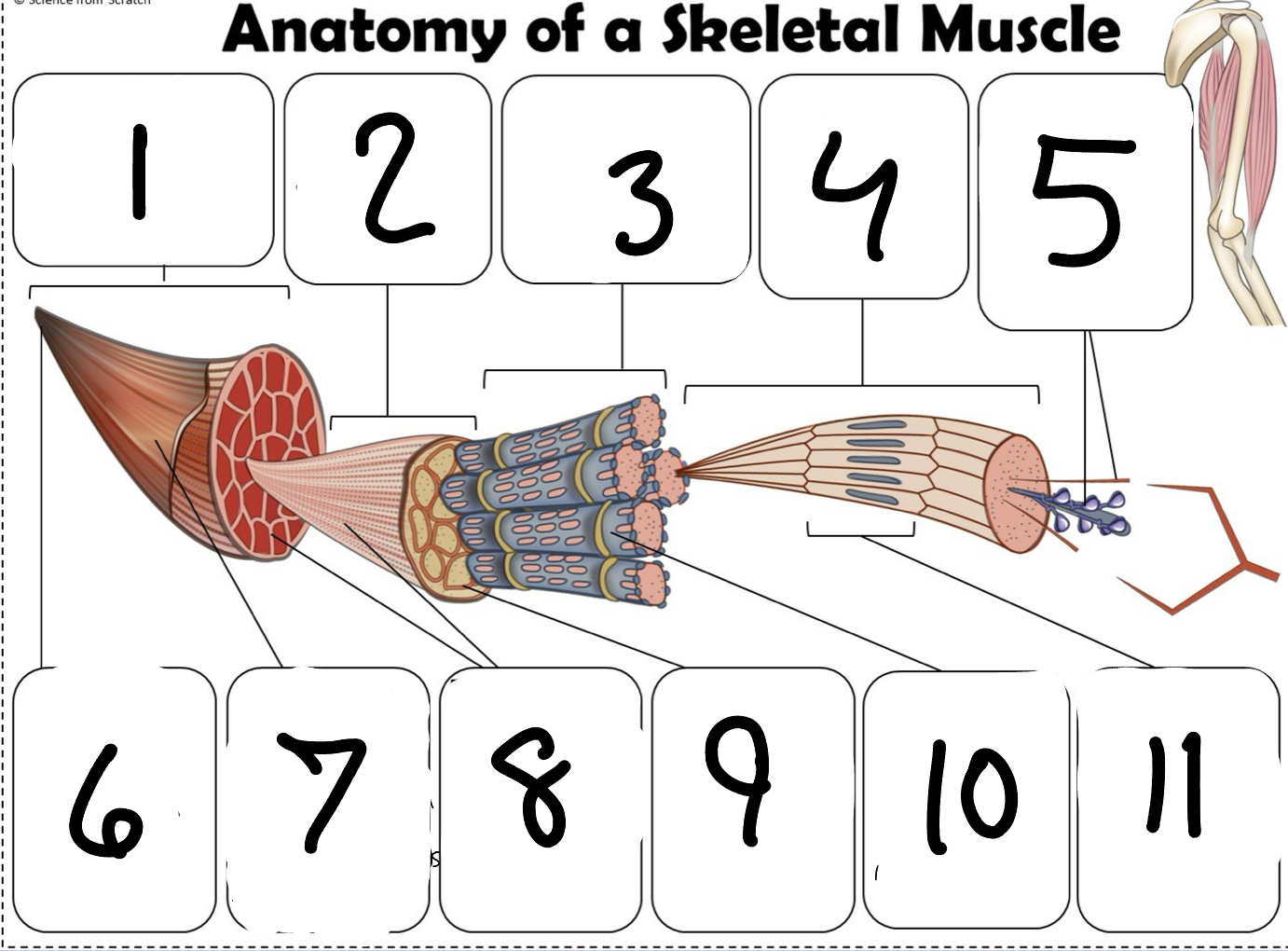
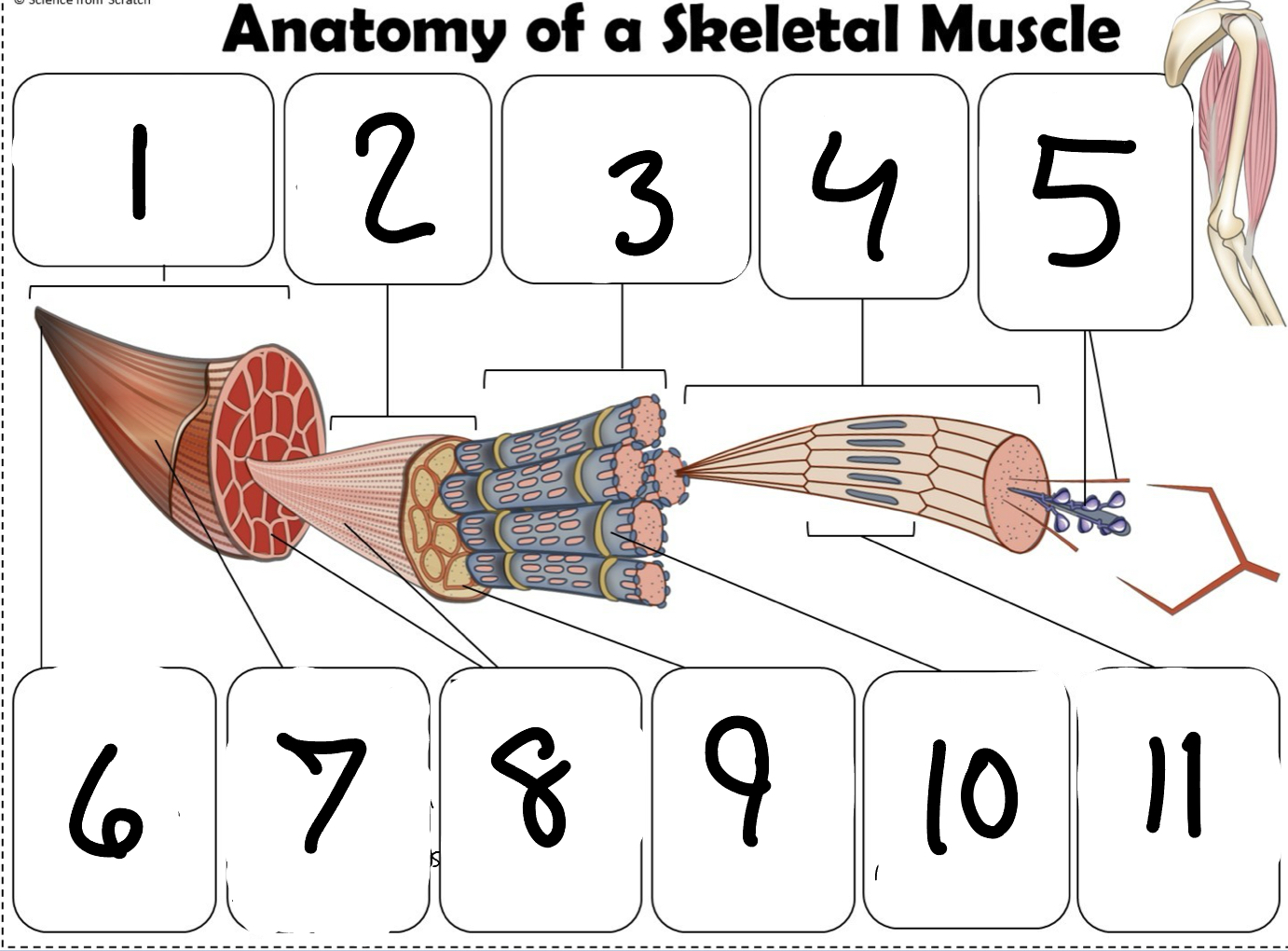
What is #4
Myofibril (picture)
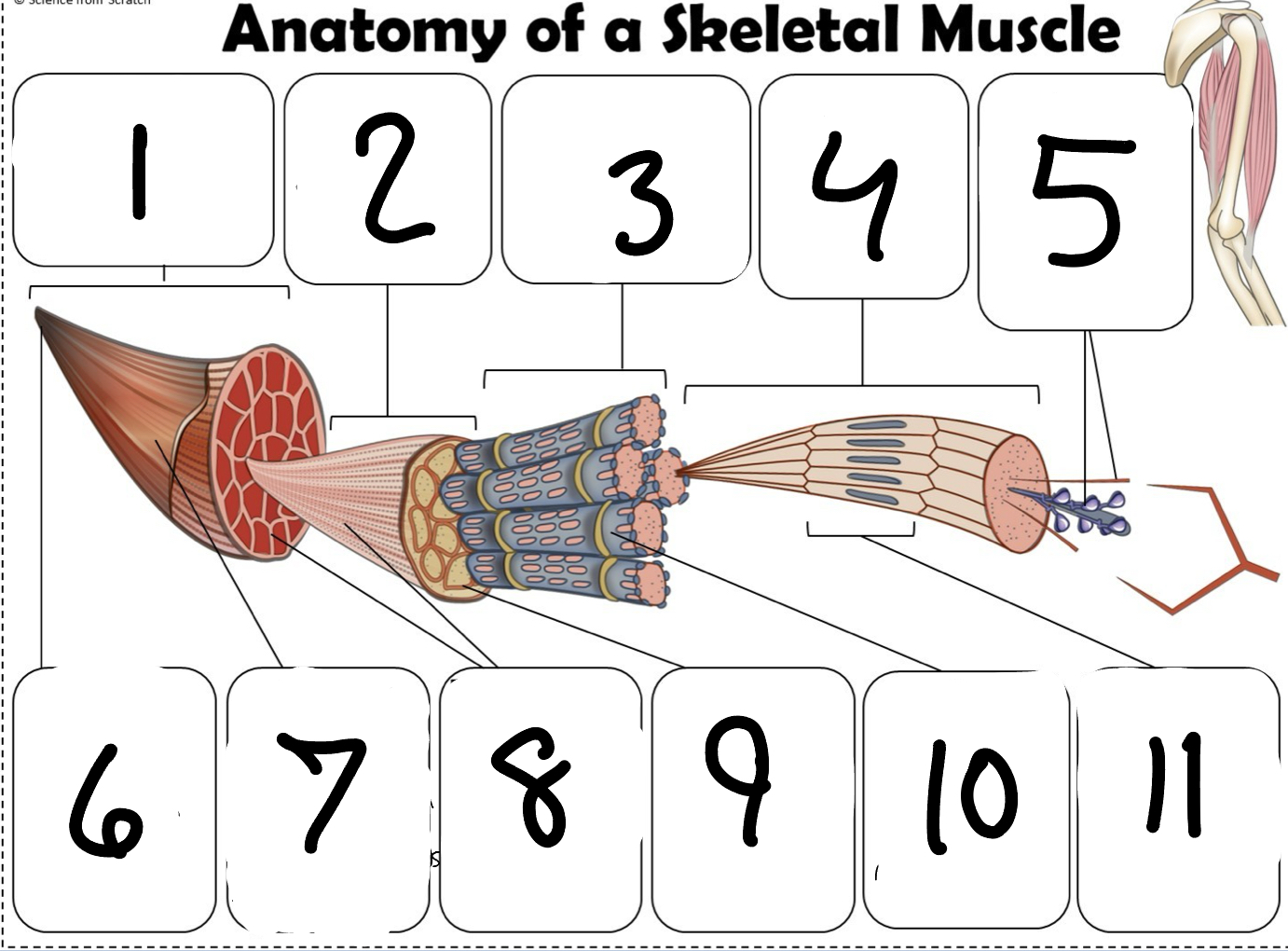
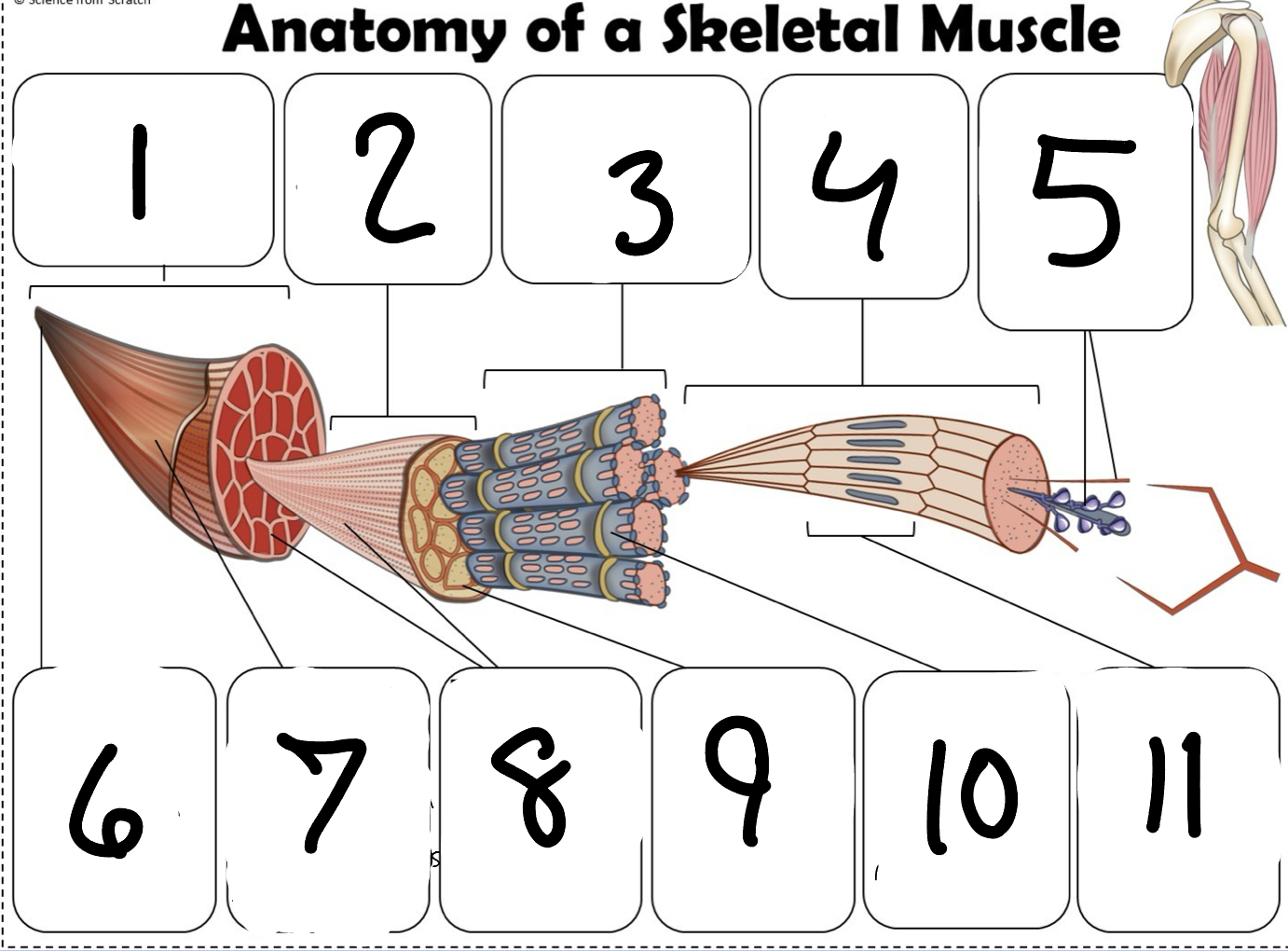
What is #5
Myofilaments (Picture)
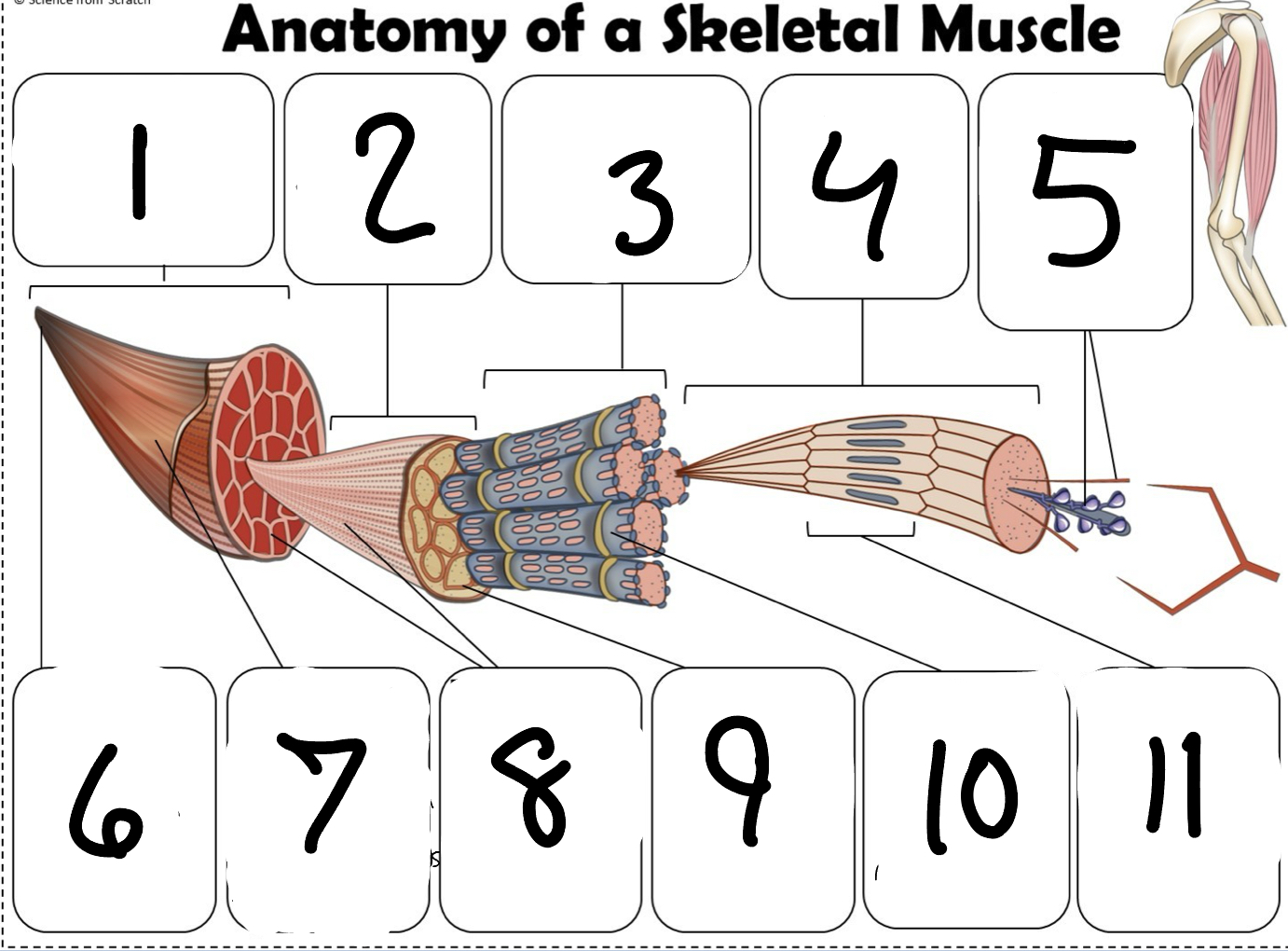
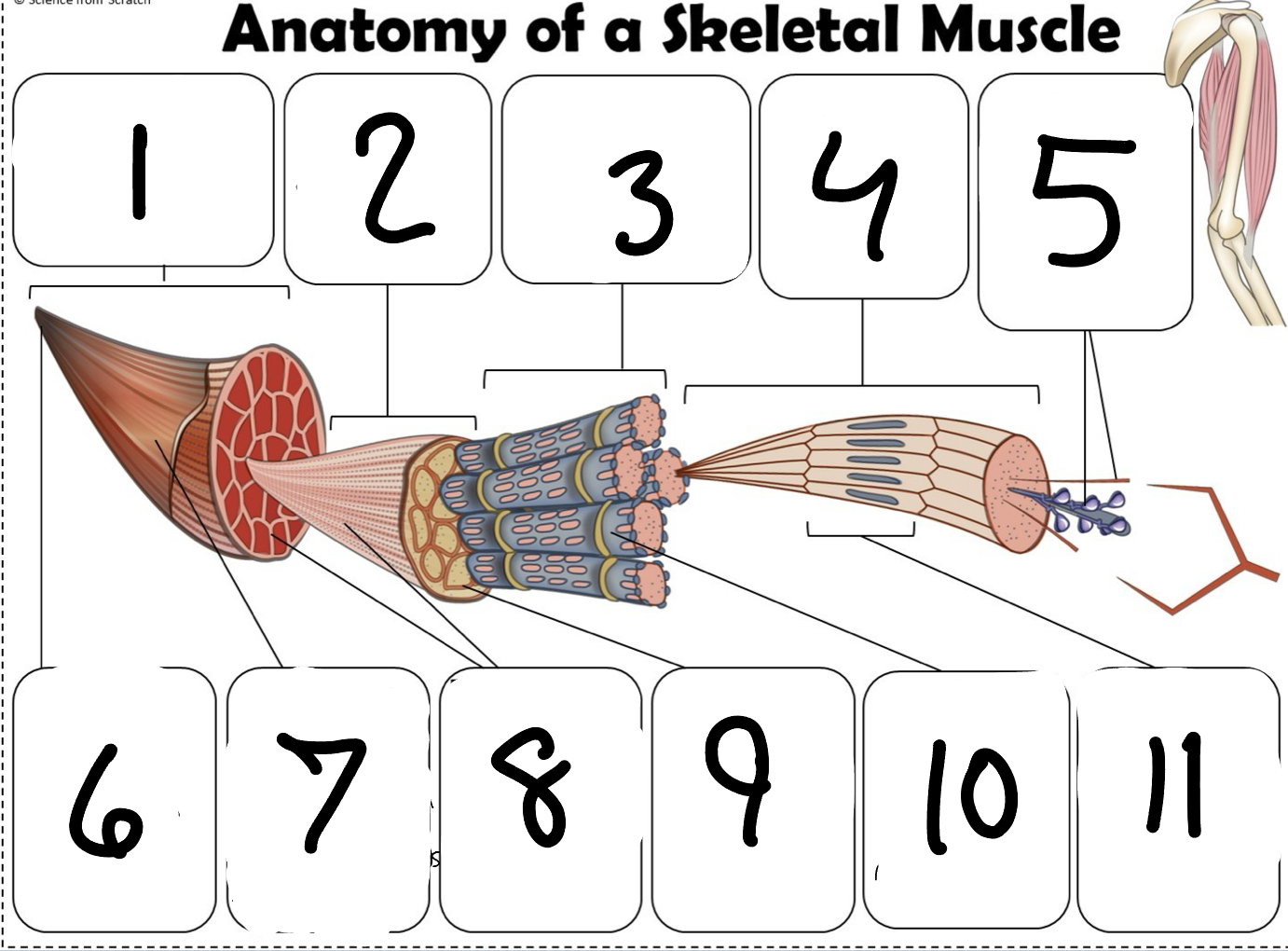
What is #6 pointing to
Tendon (picture)
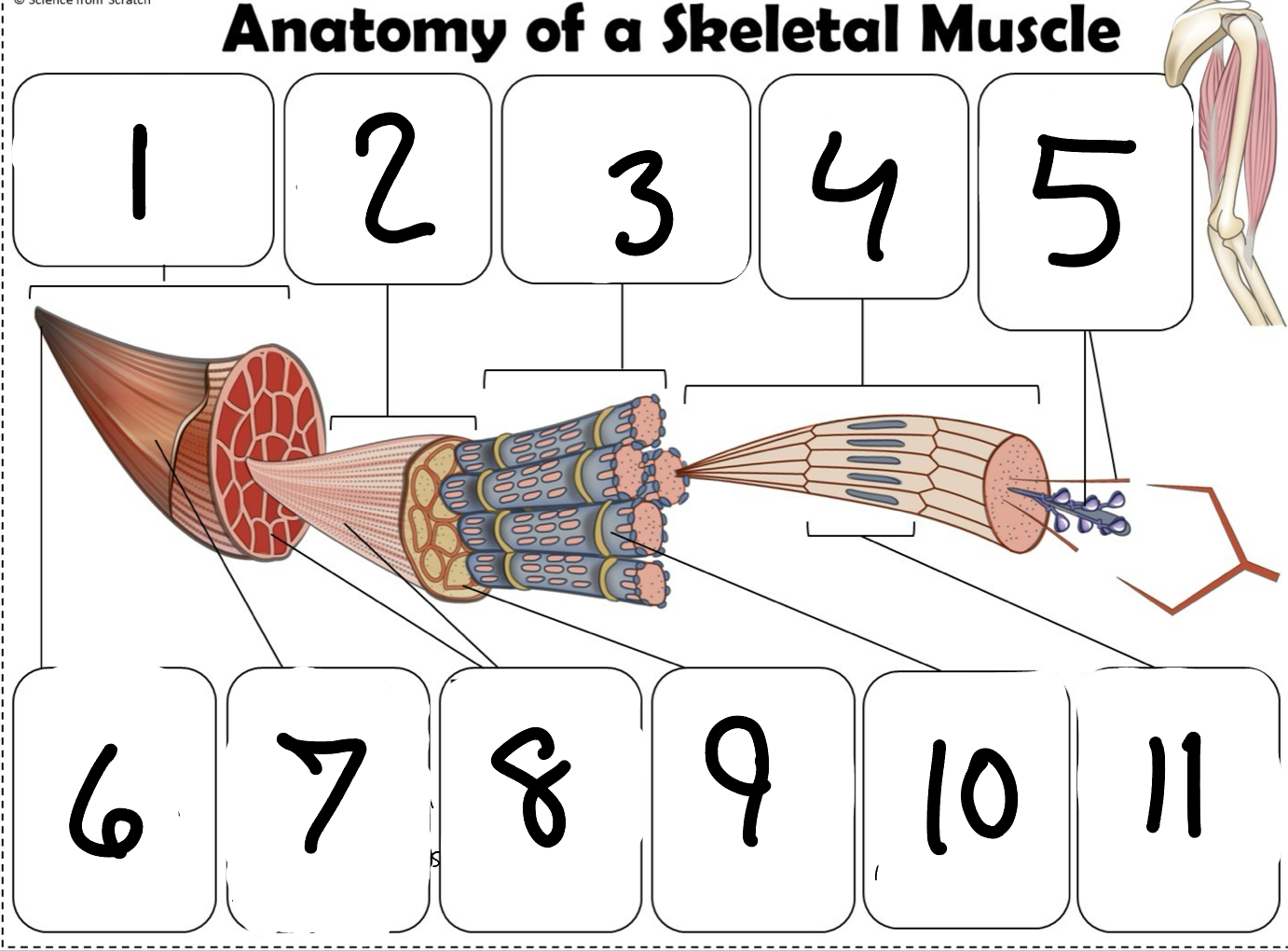
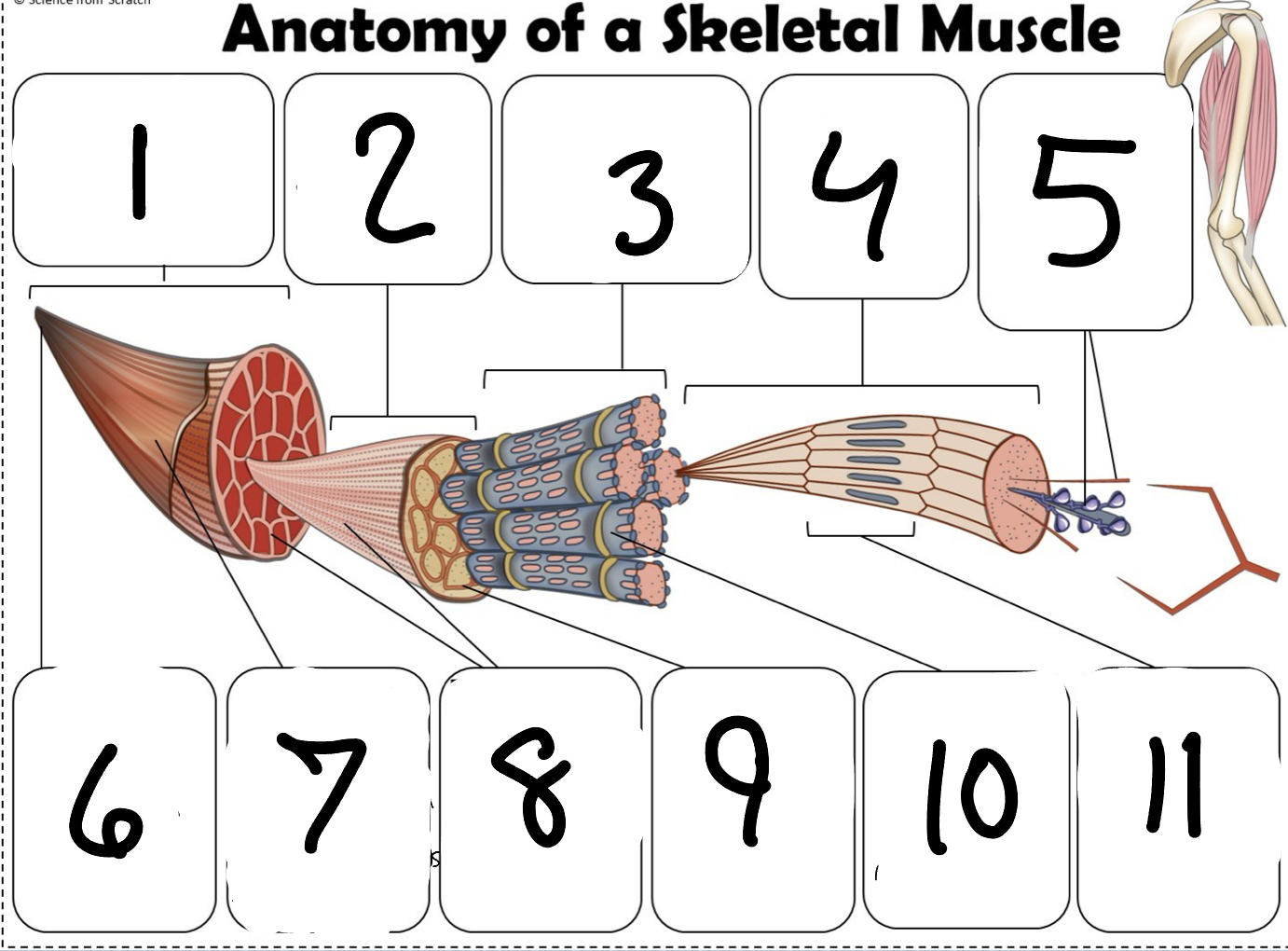
What is #7 pointing to
Epimysium (Picture)
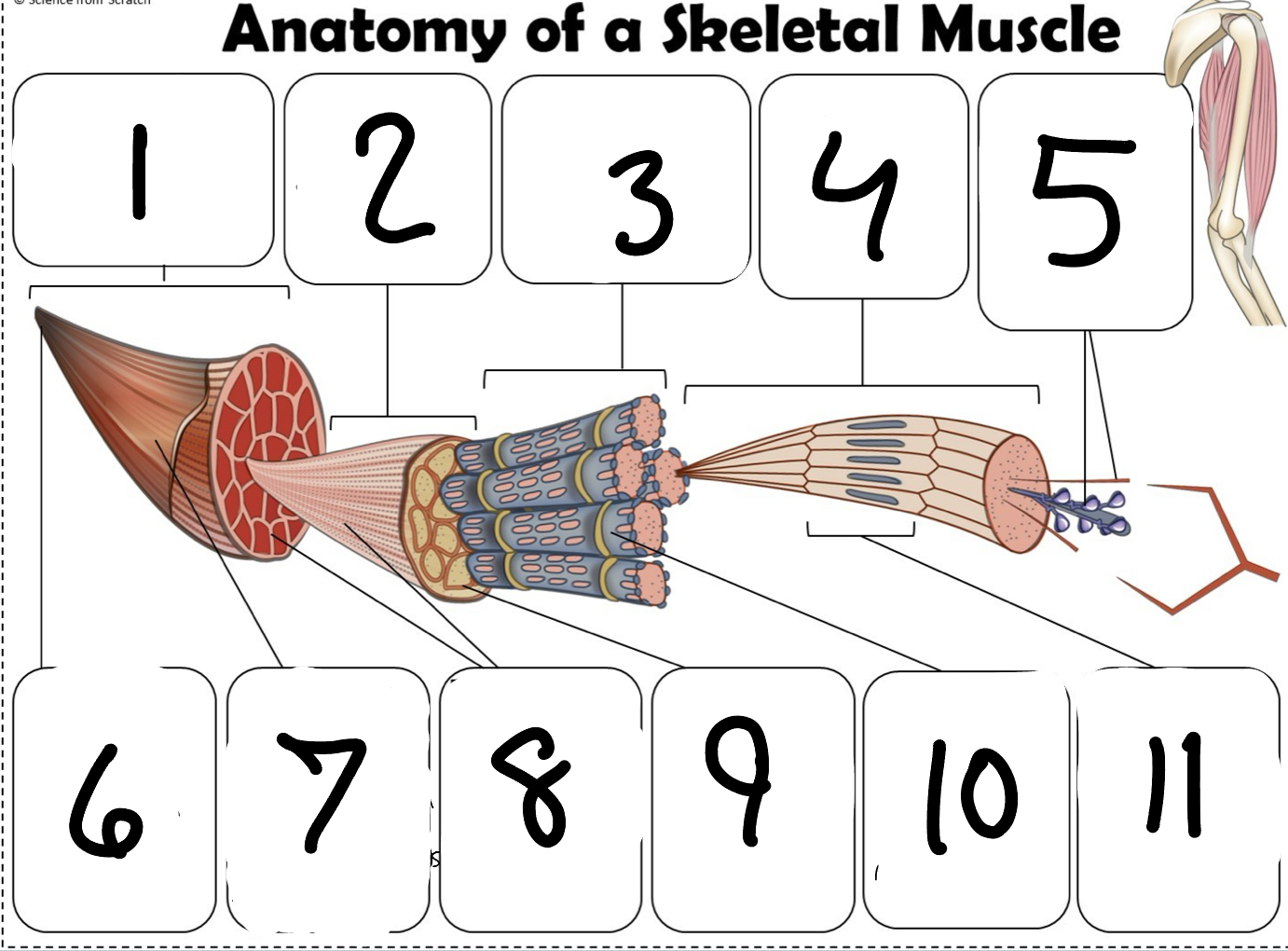
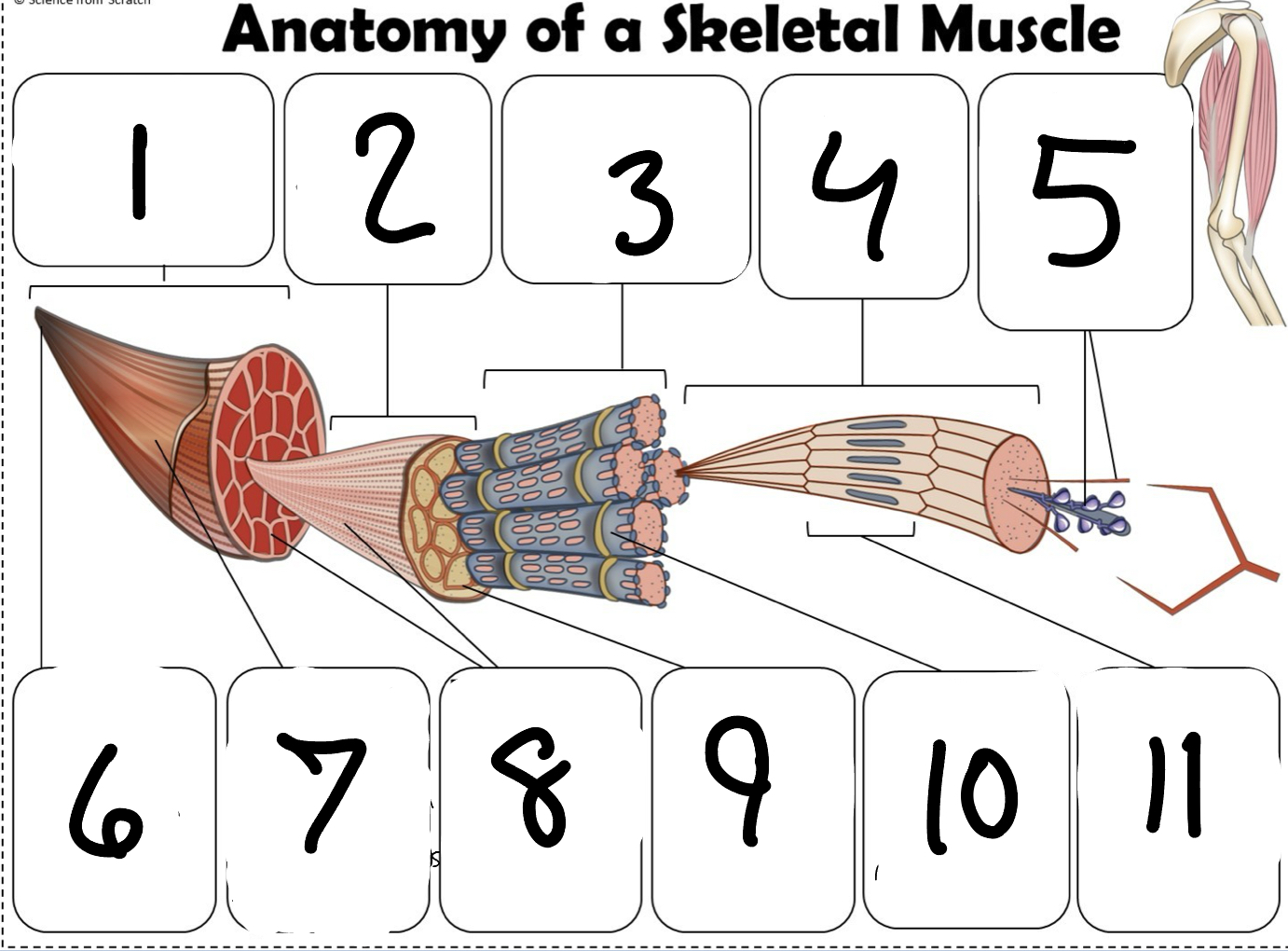
What is #8 pointing to
Perimysium (picture)
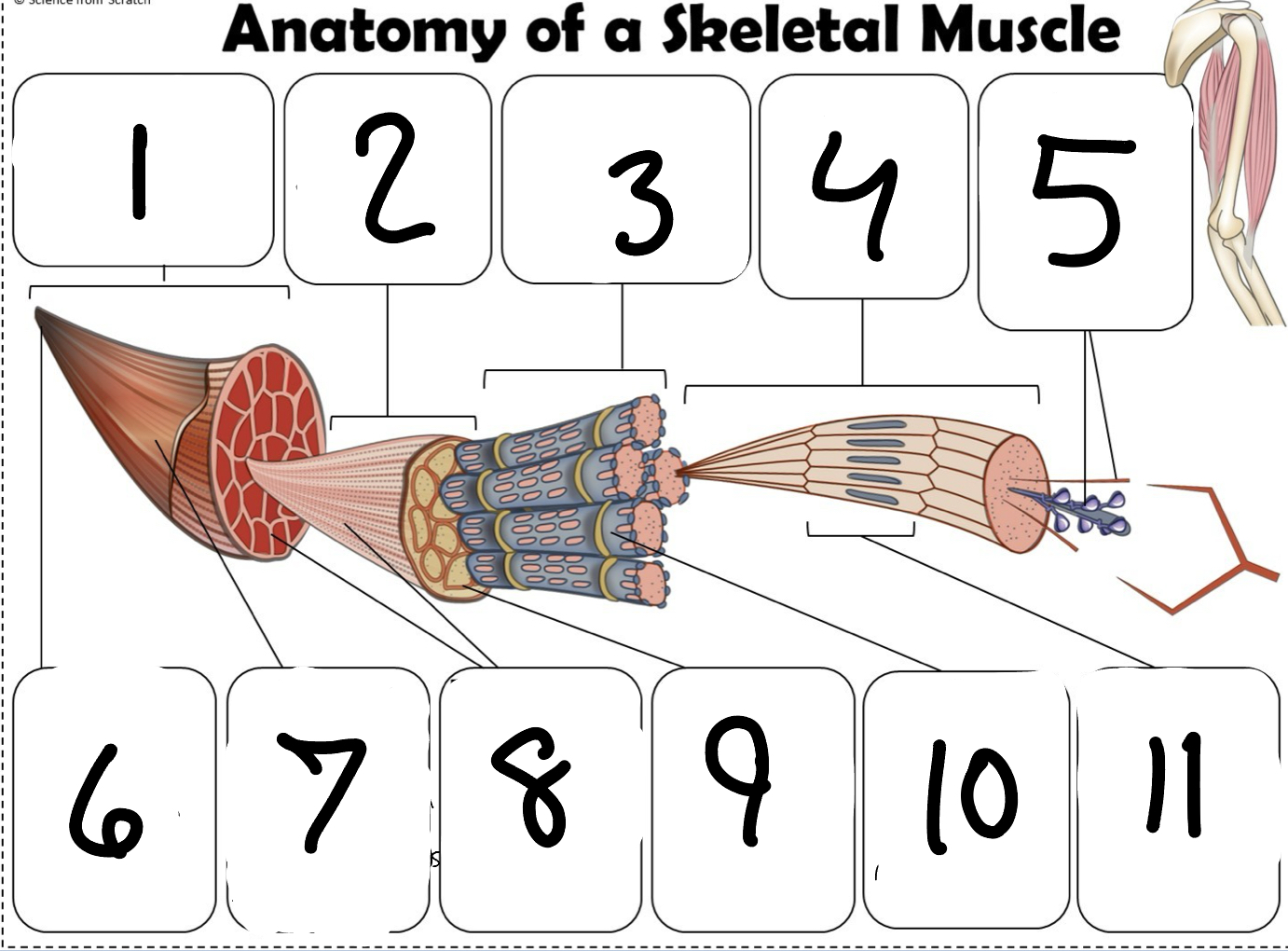
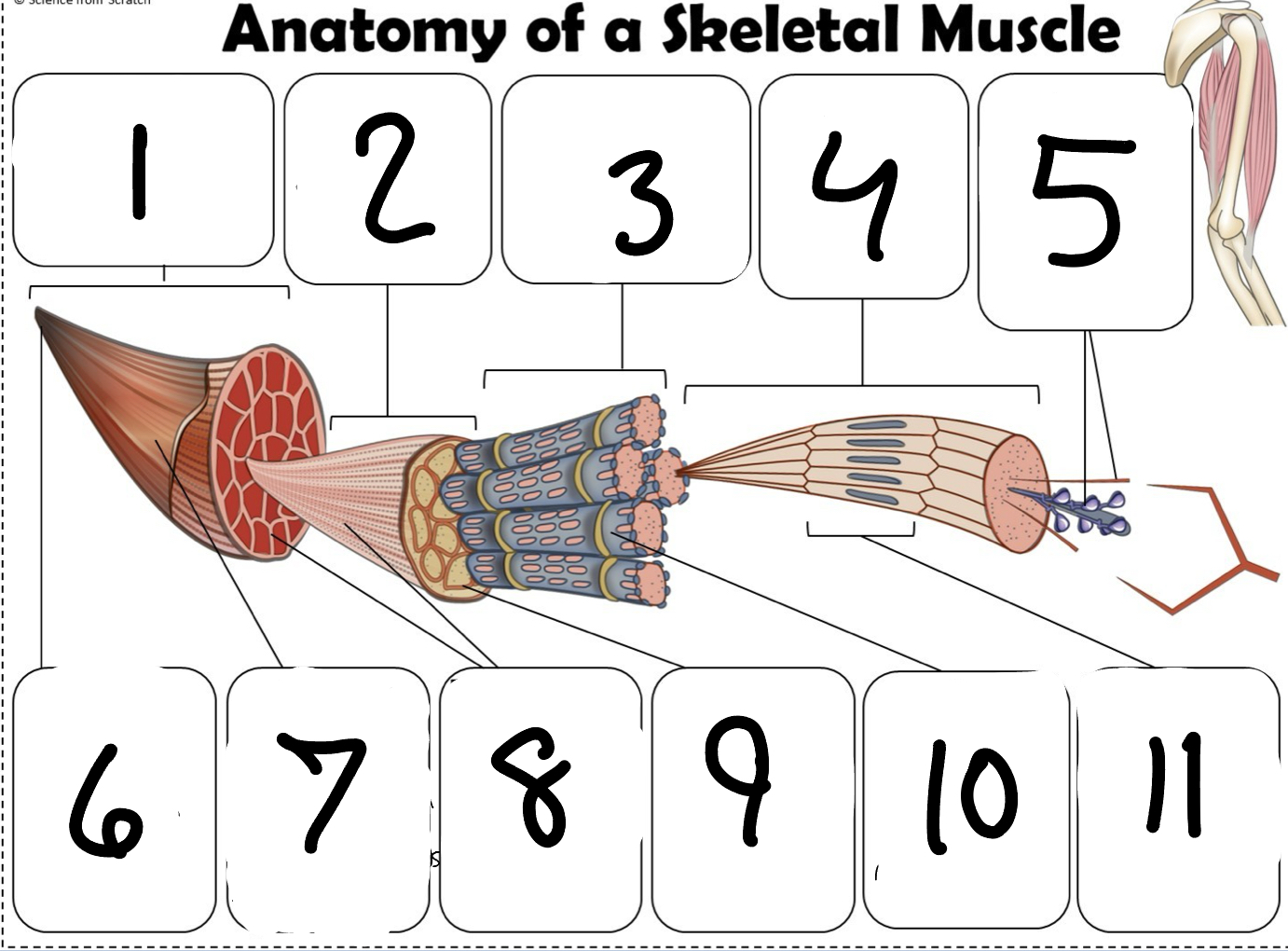
What is #9 pointing to
Endomysium (Picture)
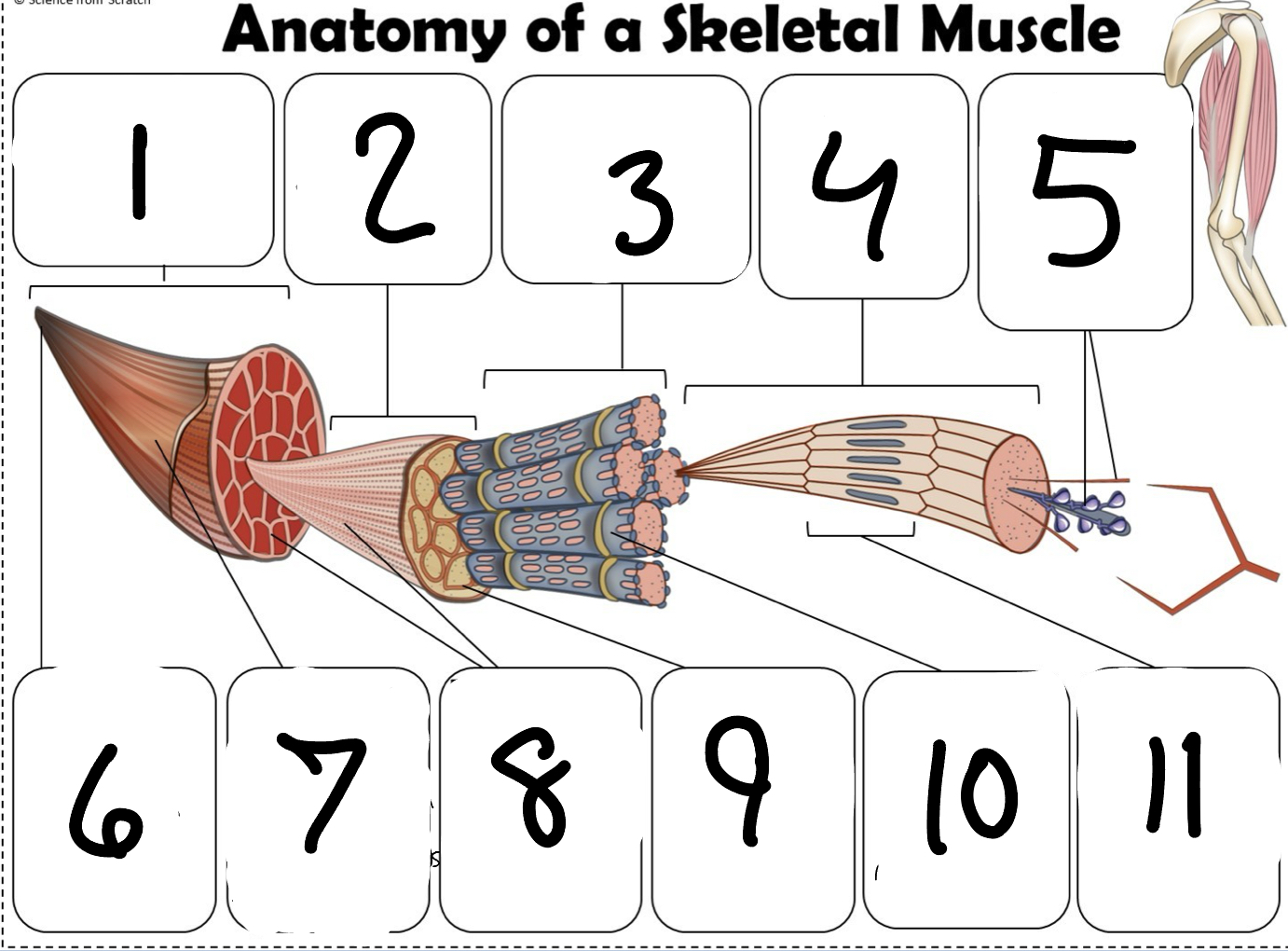
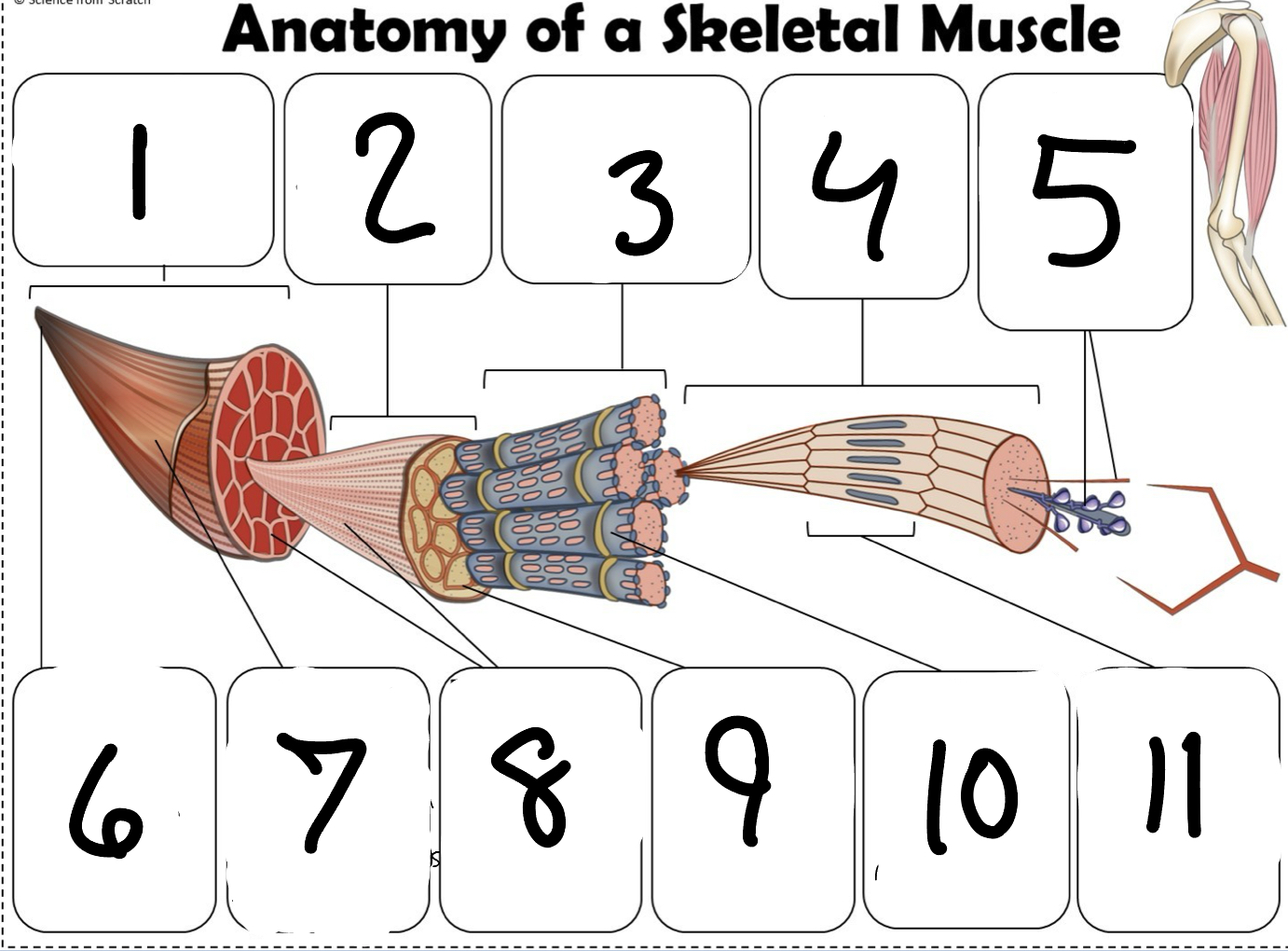
What is #10 pointing to
Sarcolemma (picture)
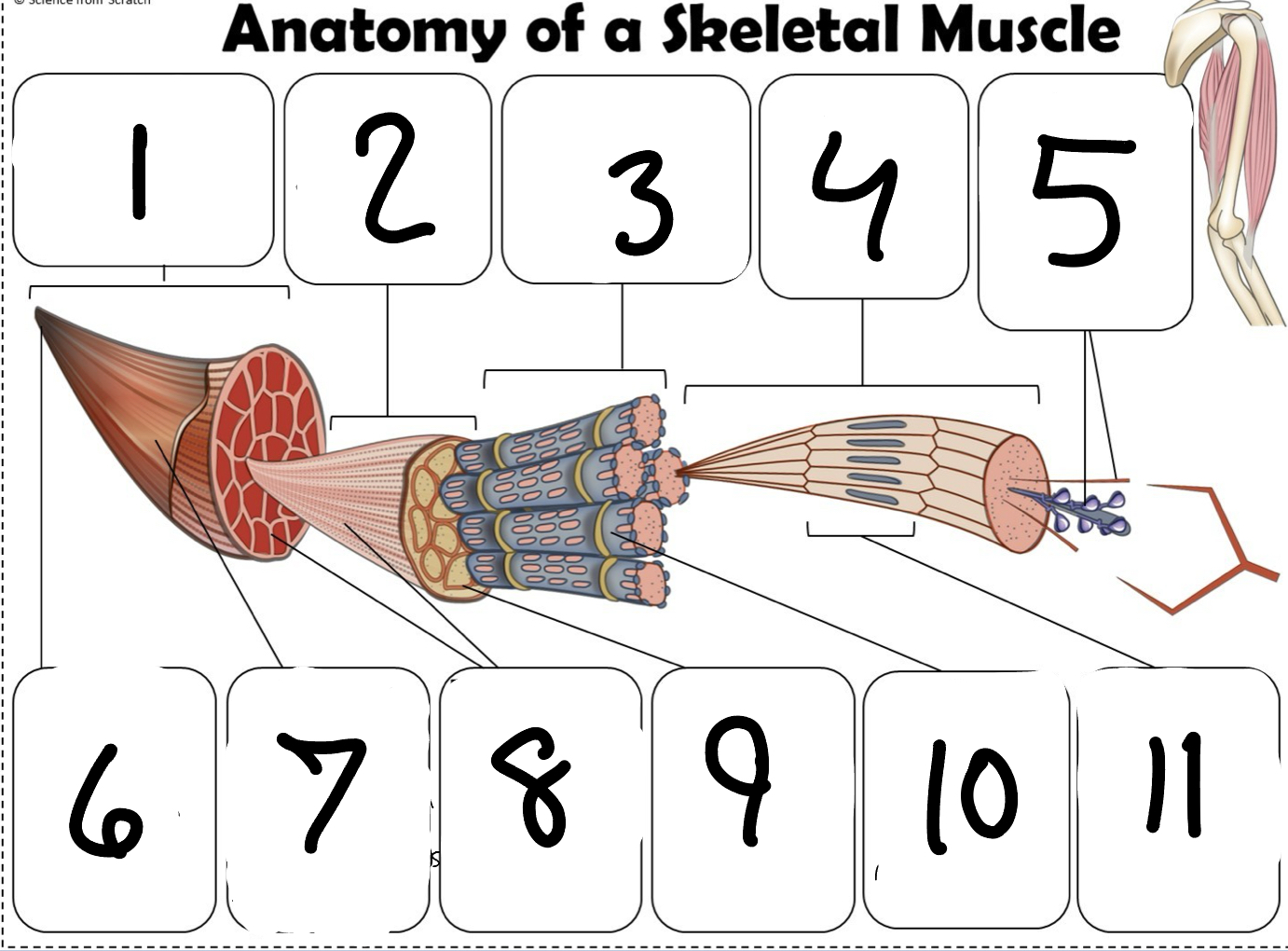
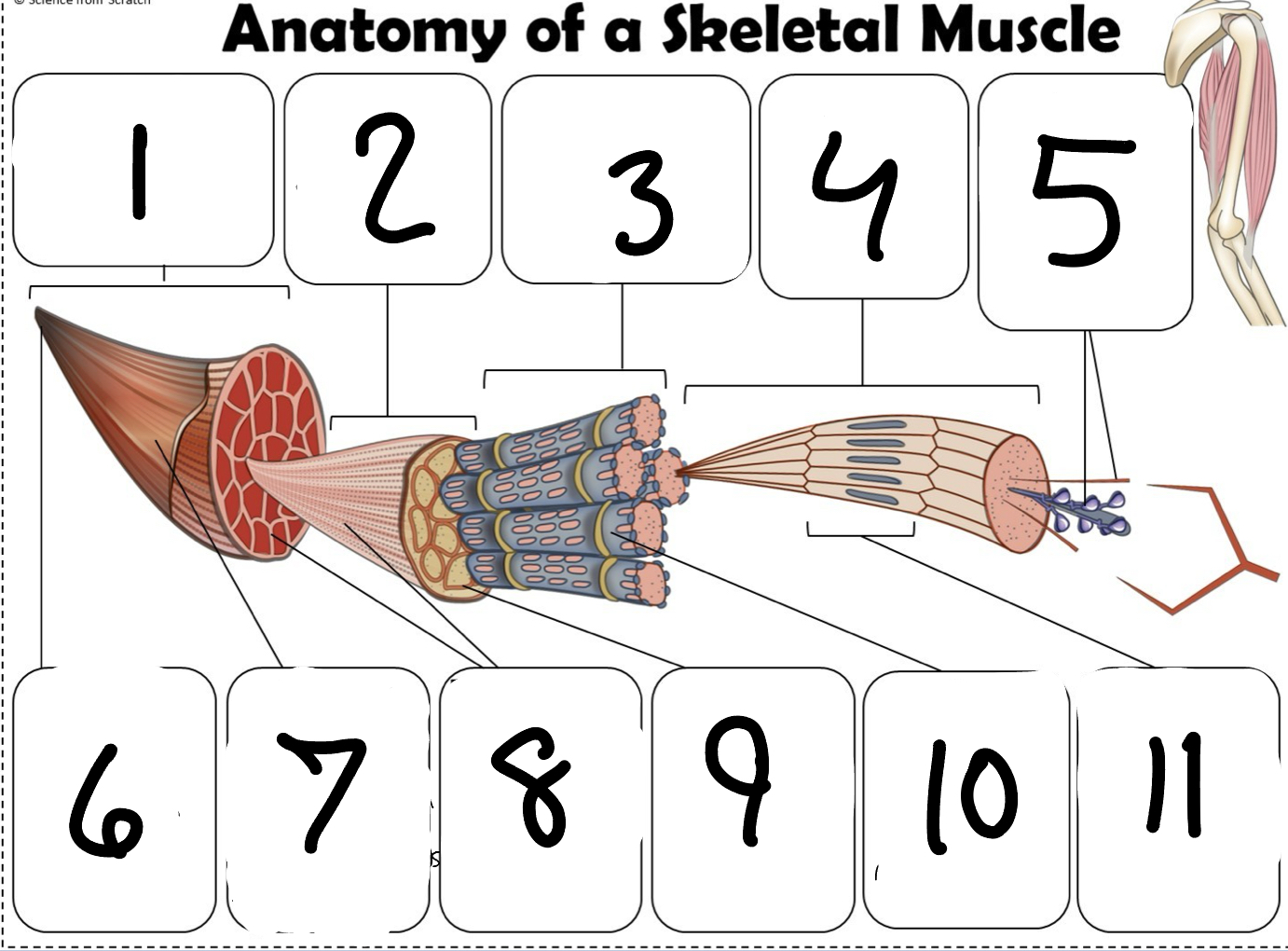
What is #11 pointing to
Sarcomere. (picture)