UNIT 1: The Global Tapestry c. 1200 - c. 1450
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Unit 1
The Global Tapestry
c. 1200 - 1450
various civilizations around the world and how they are maintaining and building their power
State
a territory that is politically organized under a single government
Song Dynasty (CHINA)
Neo-Confucianism (previously from the Tang Dynasty)
Imperial Bureaucracy
Neo-Confucianism
got rid of the Buddhist influence on Confucianism
Confucianism
hierarchical society (proper order of conduct)
filial piety (extreme respect for elders)
women were stripped of legal and social rights
foot binding
Bureaucracy
a government that is politically arranged hierarchically, that carries out the orders of the elite/emperor
Imperial Bureaucracy in the Song Dynasty
Civil Service Exam (jobs earned on merit and skill rather than hierarchy)
legitimacy of the emperor’s rule
focus on education
Song Dynasty’s Influence on Neighboring Regions
Korea + Japan + Vietnam
each influenced by Chinese traditions and ideals
tactics used by China influenced neighboring states
Buddhism
originated in India and spread to China (before the Song Dynasty)
Four Noble Truths
Theravada Buddhism - individual enlightenment (Nirvana)
Mahayana Buddhism - collective enlightenment, helping all people achieve liberation
Buddhism and Hinduism
cycle of life and death to reincarnation
become one with the universe
achieving nirvana
Song Dynasty’s Economy
prosperity and population growth steadily increased
commercialization - manufacturers and artisans produced more to sell in markets (from China to across Eurasia)
porcelain & silk
champa rice - resisted drought, matured early, could be harvested multiple times per year
Grand Canal - facilitated trade and communication in China
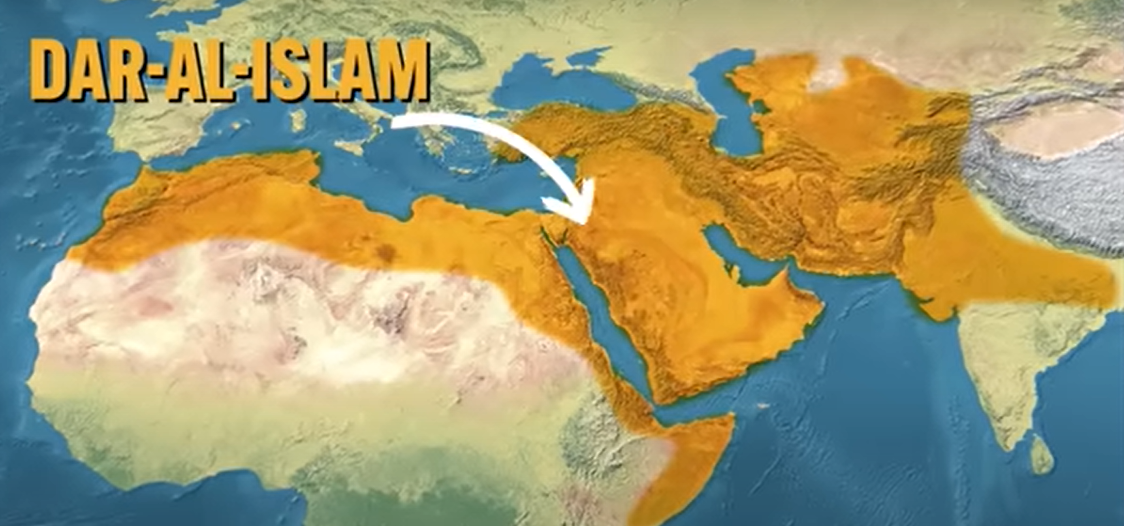
Dar-Al Islam
“House of Islam” - refers to all the places in the world where Islamic faith was the principal religion
Monotheistic Religions
Judaism - ethnic religion of the Jews
Christianity - centered on Jesus Christ
Islam - centered on “Allah”
the practice of these religions shaped their societies
Prophet Muhammad
final prophet of God’s messengers
preached that salvation would be found in righteous action
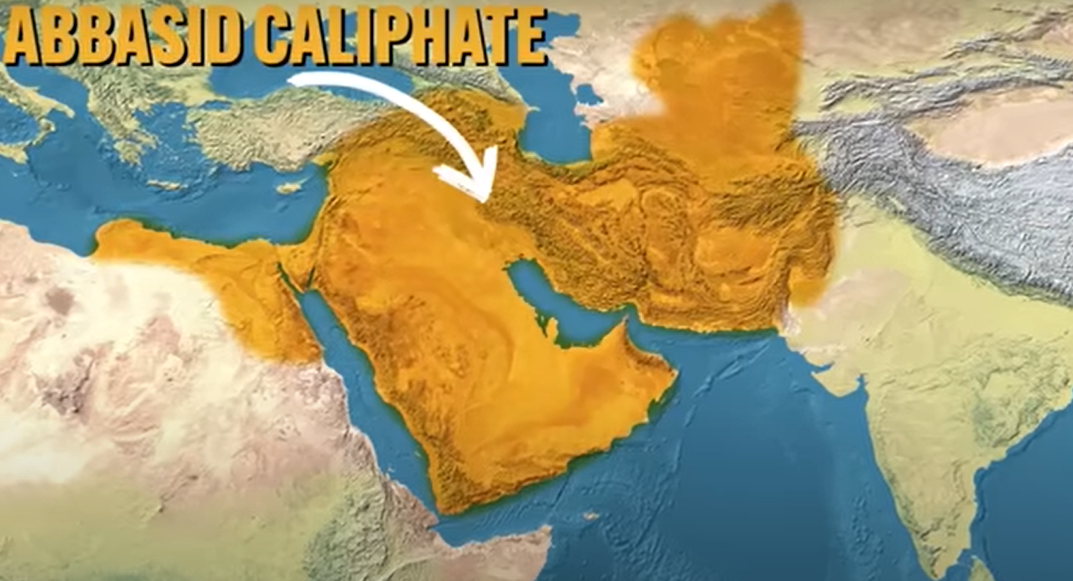
Abbasid Caliphate
located in Baghdad and ethnically Arab
began to break up and lose power allowing political entities to arise
dominated by Turkic people (ethnic Turks - NOT Arabs)
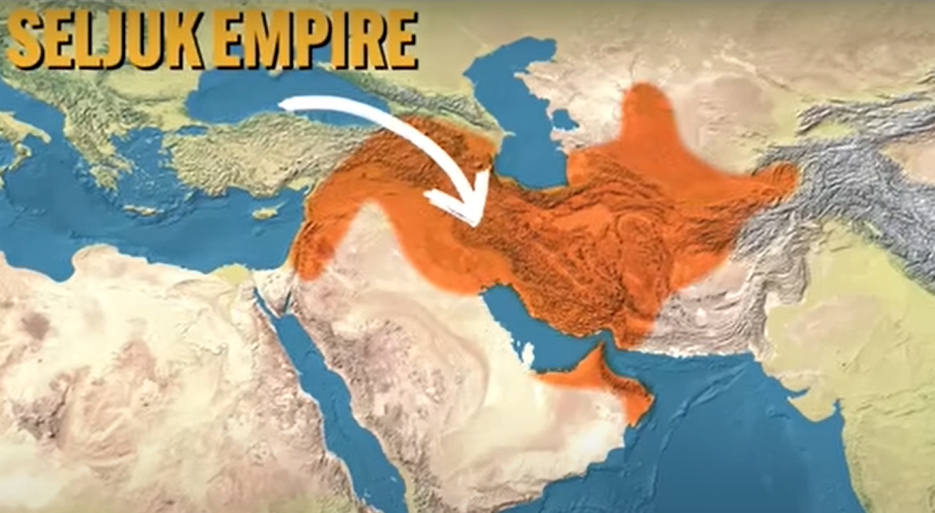
Seljuk Empire
established in the 11th century and located in Central Asia
Seljuk fought the Abbasid regime through weaknesses
Seljuks claimed most of the power in the region
Dominance of Arabs VS. Turks
During c. 1200 - 1450: the dominance of …
Arab Muslim DECREASED
Turkic Muslim INCREASED
Turkic Empires: CONTINUITY
(some practices were still continued from former empires)
military administered their states
Sharia Law - governed various aspects of a Muslim's life, including moral, ethical, and legal matters
The Qur'an
Scientific Innovations: Muslim World
NASIR AL-DIN AL-TUSI: invented trigonometry
translation of ancient Greek morals and philosophies like Plato and Aristotle
House of Wisdom
intellectual center in Baghdad during the Islamic Golden Age
established under the Abbasid Empire
held scholarly works and preserved manuscripts
Dar-Al Islam & Song China
represented the center of the world’s scholarship and wealth during c. 1200 - 1450
Expansion of Muslim Rule
Military Expansion:
establishment of new empires (Seljuk Empire, Delhi Sultanate, etc.)
Muslim Merchants:
stimulated trade and the movement of Islam ideals to other region - resulting in conversion (e.g. West African Empire of Mali)
Muslim Missionaries:
Sufis - represented a new sect of Islam which was more open to adapting themselves to local beliefs (allowing a faster spread of religion)
South & Southeast Asia’s Belief Systems
Hinduism + Buddhism + Islam

South Asia: Prominent Belief Systems
Buddhism was born here, but declined and reduced to monastic communities in Nepal and Tibet (individuals live in a community, often in a monastery, dedicating their lives to spiritual development and following a set of rules and vows)
Hinduism became the most widespread religion in India, followed by Islam with the establishment of the Delhi Sultanate

Bhakti Movement
South Asia
an innovation on Hinduism (polytheistic)
devotion to ONE of the Hindu gods was emphasized
this version of Hinduism became much more appealing to believers, without the need for complex hierarchies and sacrifices
challenged some social and gender norms present in India

Southeast Asia: Prominent Belief Systems
Buddhism + Islam were against each other for dominance
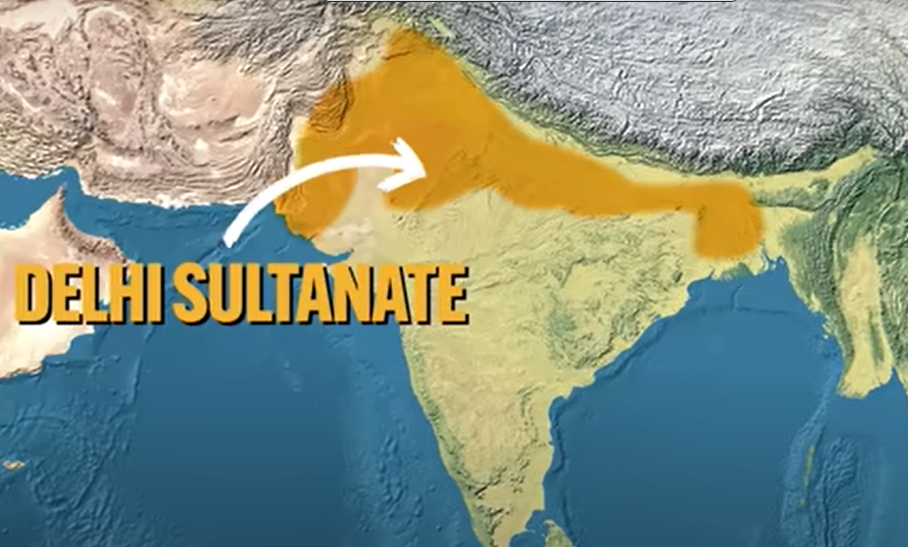
Delhi Sultanate: State Building Attempts (South Asia)
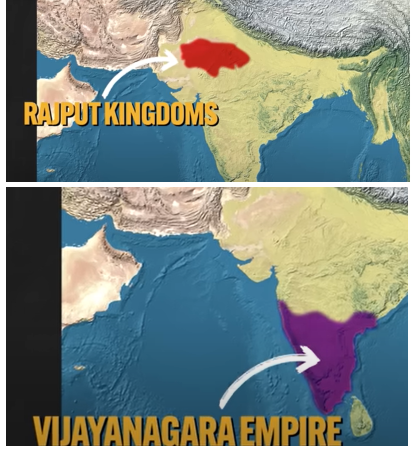
Rajput Kingdoms:
South Asia - ruled Northern India
there was difficulty imposing a total Muslim state on a majority Hindu population
Hindu resistance led to RAJPUT KINDOMS (a collection of rival/warring Hindu kingdoms that existed before Muslim rule) where Muslim rule was controlled
Vijayanagara Empire:
South Asia - ruled Southern India
established due to a failed attempt of the Delhi Sultanate extending Muslim rule
missionaries sent by the Sultanate were former Hindus who converted to Islam under pressure
they created a rival empire with majority Hindu status
Majapahit Kingdom
Southeast Asia - sea based kingdom
Buddhist
most powerful state
immense naval power and control over sea routes for trade
began to decline through the supporting of its trading rival: The Sultanate of Malacca
Khmer Empire
Southeast Asia
converted from Hindu to Buddhist
the blending of these two belief systems is displayed by the structure: Angkor Wat: Hindu temple the underwent Buddhist changes and elements

Americas’ Civilizations
Mesoamerica + Andean Civilizations
Aztec Empire
Mesoamerica - founded by Meshika people
capital city: Tenochtitlan: largest city in the Americas before the Europeans
entered an alliance with two other Mesoamerican states and established an empire with rapid expansionism
Aztec Administration:
tribute states: people that were conquered had to provide labor for the Aztecs and contributions
enslaved people: human sacrifice and coerced labor
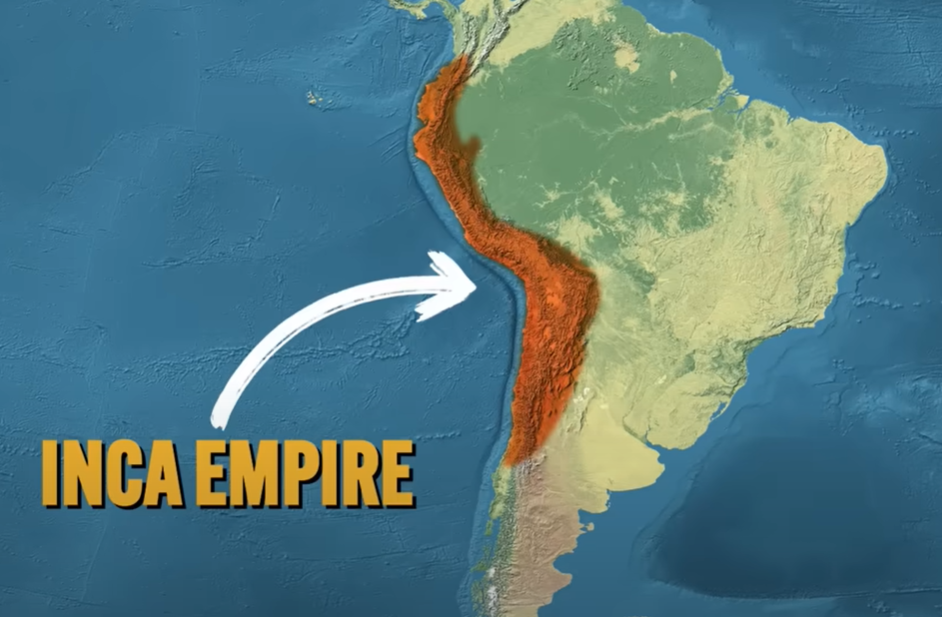
Inca Empire
Andean Civilization - over the Andean Mountain Range
elaborate bureaucracy
rigid social hierarchy of officials
Mit’a System: all people under their rule needed to provide labor on state projects
Centralization of the Aztecs VS. the Inca
Aztecs were mostly DECENTRALIZED
Inca was highly CENTRALIZED
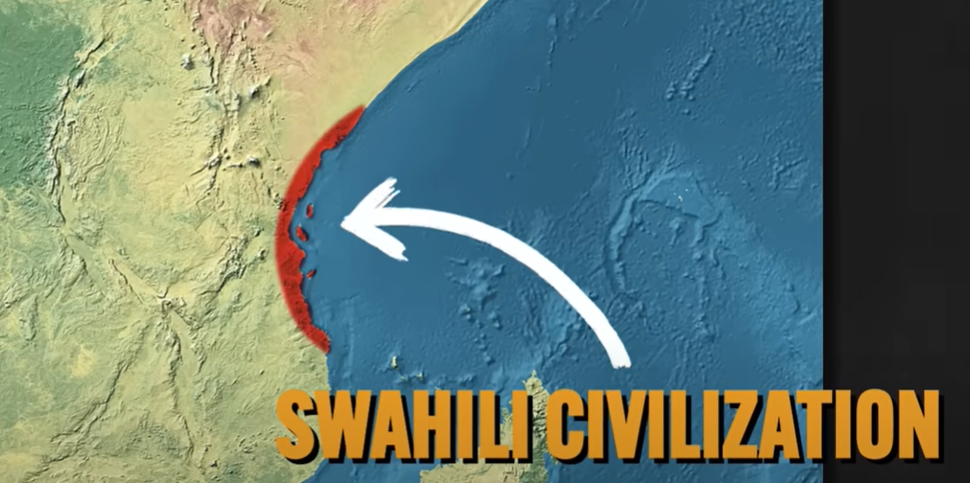
Swahili Civilization
East Africa
series of cities organized around commerce and trade (Indian Ocean)
social hierarchy - elites over commoners
Muslim Traders: settled in the states and fostered trade and the spread of Islam
new language emerged - indigenous African Bantu and Arabic scripts (represents the cooperating and intermingling of various cultures)
Islam: as a result of Muslim influence
the Swahili States became Islamic which increased their integration into the Islamic world of trade
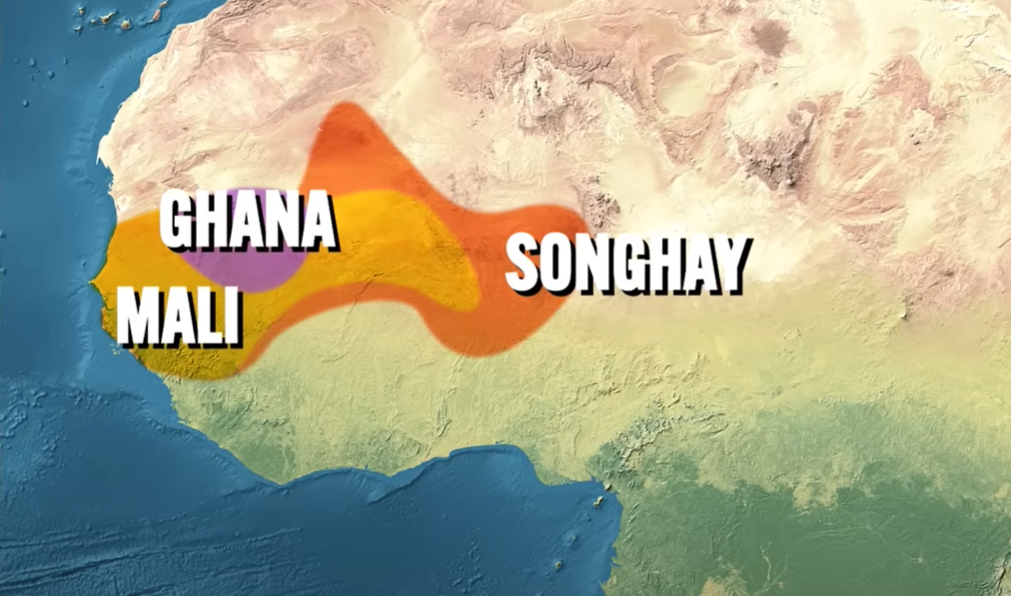
West Africa’s Civilizations
Ghana + Mali + Songhay

Great Zimbabwe
Southern Africa
large populations and structures occurred
farming and cattle herding
participated in international trade which increased wealth - shifted to gold exports
Rulers never converted - maintained their indigenous religion
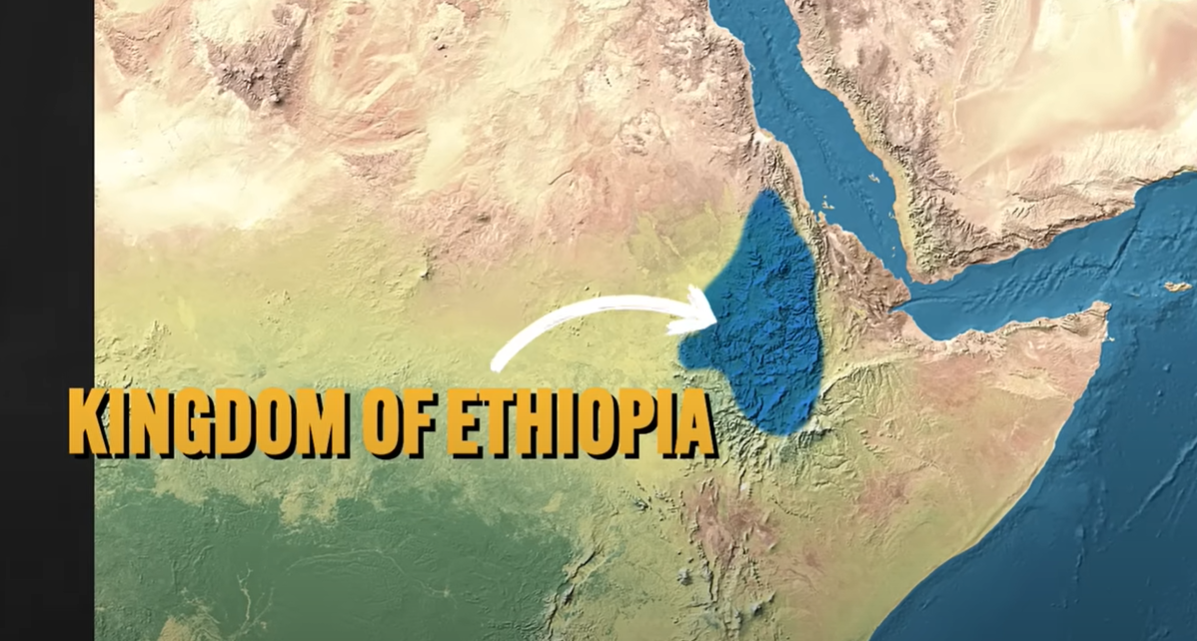
Kingdom of Ethiopia
Northeast Africa
flourished through trade (access to the Mediterranean and Arabian Peninsula)
Christianity - one state in a world of Islamic domination
hierarchical social structure
Europe’s Prominent Religion
Christianity: Eastern Orthodox + Roman Catholicism
European Systems/Beliefs
Feudalism:
system where nobles gave land to vassals (less powerful) in exchange for service, like military support or labor, and protection
Manorialism:
MANOR: piece of land owned by an elite, which is then rented out to a peasant who works the land
peasants were bound to a piece of land in exchange for protection from the elite
SERFS: working peasants