4.3 - Alcohols and phenols
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
How can alcohols be classified?
Primary
Secondary
Tertiary
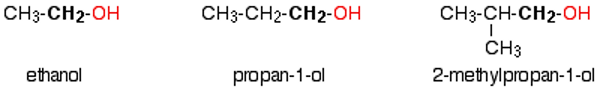
What are primary alcohols?
The carbon which carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group
general formula = RCH2OH
What are secondary alcohols?
The carbon with the -OH group attached is joined directly to two alkyl groups which may be the same or different
general formula = R2CHOH
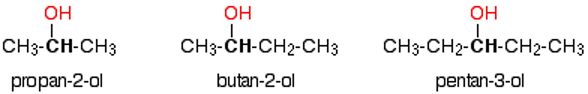
What are tertiary alcohols?
The carbon with the -OH group attached is joined directly to three alkyl groups which may be the same or different
general formula = R3COH
What are the 2 methods of forming primary and secondary alcohols?
From halogenoalkanes by a substitution reaction
By reducing aldehydes, ketones or carboxylic acids
How do you form alcohols from hydrolysis of a halogenoalkane (nucleophilic substitution)?
covalent bond is broke by reaction with water- NaOH is used instead as it reacts more quickly than water
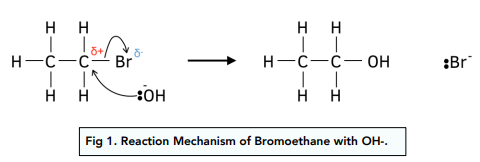
What are the conditions for nucleophilic substitution to form an alcohol?
Heat 1 bromobutane under reflux with aqueous alkali - NaOH
What is a nucelophile?
An electron pair donor
must have at least lone pair of electrons
How is the rate of reaction of hydrolysis of halogenoalkanes affected by different halogens?
The weaker the C-X bond, the faster the reaction
How do you form primary and secondary alcohols from reducing aldehydes and ketones?
Using an aqueous solution of the reducing agent sodium tetrahydridoborate (III) (NaBH4)
Aldehyde —> primary alcohol
R-CHO + 2 [H] → R-CH2OH
CH3-CHO + 2[H] → CH3-CH2OH
Ketone —> secondary alcohol
R1-CO-R2 + 2[H] → R1-CH(OH)-R2
CH3-CO-CH3 + 2[H] → CH3-CH(O)-CH3
What are the conditions for reducing aldehydes and ketones into primary and secondary alcohols?
NaBH4 in aqueous methanol
Room temperature
How do you reduce a carboxylic acid into an alcohol?
Have to use a stronger reducing agent
excess lithium tetrahydridoaluminate (III) (lithium aluminium hydride or lithal) dissolved in ethoxyethane
CH3 + 4 [H] → CH3CH2OH + H2O
When reducing carboxylic acids into alcohols, why must the reaction mixture be removed?
excess reducing agent is used
so reaction mixture must be removed by adding a dilute acid
alcohol then needs to be separated from mixture using separating funnel
if the alcohol dissolves in the aqueous solution it can be extracted using another organic solvent like ethoxyethane (solvent extraction)
What are the reactions of primary and secondary alcohols?
alcohols with hydrogen halides (chlorination, bromination, iodination)
esterification
What is chlorination of alcohols?
HCl gas passed into alcohol in presence of anhydrous zinc chloride - acts as a catalyst
CH3CH2OH + HCl → CH3CH2Cl + H2O
What is a possible issue with the method of chlorination of alcohols?
Separation
How do you prepare Hydrogen bromide for bromination of alcohols?
HBr is prepared in situ by reacting concentrated sulfuric (VI) acid with potassium bromide
H2SO4 + KBr → KHSO4 + HBr
What is the general equation of bromination of alcohols?
ROH + HBr → RBr + H2O
What is the method for the bromination of alcohols?
Concentrated sulfuric acid is added carefully to the alcohol with continuous cooling
Potassium halide is added and mixture is heated in a distillation apparatus
the halogeno compound distils over
e.g. CH3CH2OH + KBr + H2SO4 → CH3CH2Br + KHSO4 + H2O
What is the iodination of alcohols?
Refluxing the alcohol with excess hydroiodic acid
e.g. CH3CH2OH + HI → CH3CH2I + H2O
Describe esters
naturally occuring
found in sweet smelling flowers and fruits
important in cosmetic industry as components of perfume
also used as solvents e.g. nail varnish remover
can be made synthetically
How can esters be made synthetically?
Alcohol with carboxylic acids
Alcohol with ethanoyl chloride
What is the reaction of alcohols with carboxylic acids?
acid + alcohol ⇋ ester + water
RCOOH + ROH ⇋ RCOOR + H2O
e.g. CH3COOH + CH3OH CH3COOCH3 + H2O
ethanoic acid + methanol methyl ethanoate + water
What are the reaction conditions for alcohols with carboxylic acids?
Acid and alcohol refluxed for 10 mins with concentrated sulfuric (VI) acid as catalyst
Sweet smelling ester formed is then distilled off
What is the reaction of alcohols with ethanoyl chloride?
ethanoyl chloride + alcohol → ester + hydrogen chloride
CH3COCl + ROH → CH3COOR + HCl
e.g. CH3COCl + CH3OH → CH3COOCH3 + HCl
ethanoyl chloride + methanol → methyl ethanoate + hydrogen chloride
What condition does ethanoyl chloride need to be in to form an ester?
Has to be completely dry (no water)
or it will turn back into carboxylic acid
What is a phenol?
Aromatic alcohol
Contains OH group directly bonded to a carbon in a benzene ring
White solid
Hydrogen bonding makes boiling point higher
It’s a compound and also a functional group
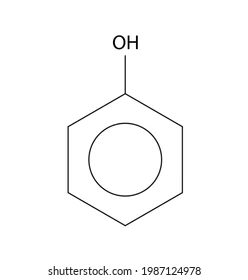
What is the formula of phenol?
C6H5OH
What type of interaction occurs between the delocalised electrons in the benzene ring and the lone pairs on the oxygen atom in phenol?
Interaction between the oxygen’s lone pair (in a p orbital) and the delocalised pi electrons of the benzene ring
Which oxygen lone pair interacts with the benzene ring in phenol?
The lone pair in the p orbital (P2) that can overlap sideways with the ring’s pi system
What does the sideways overlap of p orbitals between oxygen and benzene carbons produce?
A delocalised pi-electron cloud including the oxygen atom
What happens due to the donation of the oxygen’s lone pair into the benzene ring?
Lone pair is now delocalised with the ring pi-electrons, increasing electron density around the ring
How does the donation of the oxygen’s lone pair affect the reactivity of phenol?
It increases electron density in the ring making it easier for phenol to be attacked by an electrophile
How does the donation of the oxygen’s lone pair affect the acidity of phenol compared to alcohols?
The -OH groups How hydrogen becomes more acidic (δ+) than in aliphatic alcohols because the oxygen’s lone pair is party delocalised
How does the donation of the oxygen’s lone pair affect the C-O bond in phenol compared to alcohols?
The C-O bond becomes shorter and stronger than in alcohols
What is the solubility of phenol?
Not very soluble in water due to large non polar aromatic ring
What happens when phenol dissolves in water?
It partially dissociates to form a phenoxide ion and a proton
makes it a weak acid
weaker than carboxylic acids
makes it unlike alcohols which do not form acidic solutions
What are the reactions of phenol?
Phenols with water - acts as an acid
Phenols with hydroxides
Bromination of phenol
nitration of phenol
What functional group in phenol makes it reactive and allows it to act as an acid?
The polar -OH group
Why can phenol act as an acid?
Because the lone pair on the oxygen atom is partially drawn into the benzene ring, making the O-H bond weaker and the hydrogen atoms more δ+ than aliphatic alcohols
What type of reactions can phenol undergo on the benzene ring?
electrophilic substitution reactions
What happens when phenol reacts with water?
It forms an acidic solution
C6H5OH + H2O → C6H5O- + H3O+
What ion is produced when phenol loses a hydrogen ion? (H+)
Phenoxide ion (C6H5O-)
How does phenol react with alkalis?
Reacts to form salts
How do phenols react with hydroxides?
Acidic enough to react with strong bases e.g. NaOH
It is not acidic enough to react with weak bases eg. sodium carbonate
C6H5OH + NaOH → C6H5O-Na+ + H2O
produces sodium phenoxide
What type of reaction does phenol undergo with bromine water?
Electrophilic substitution (bromination)
Why is the benzene ring in phenol more reactive than in benzene itself?
cos of the hydroxyl group attached to it
The donation of the oxygen’s lone pair into the ring increases the electron density around the ring making it easier for phenol to attract an electrophile
What happens when phenol reacts with bromine water?
Decolourises the bromine water
forms a white precipitate of 2,4,6 - tribromophenol in a solution of hydrogen bromide
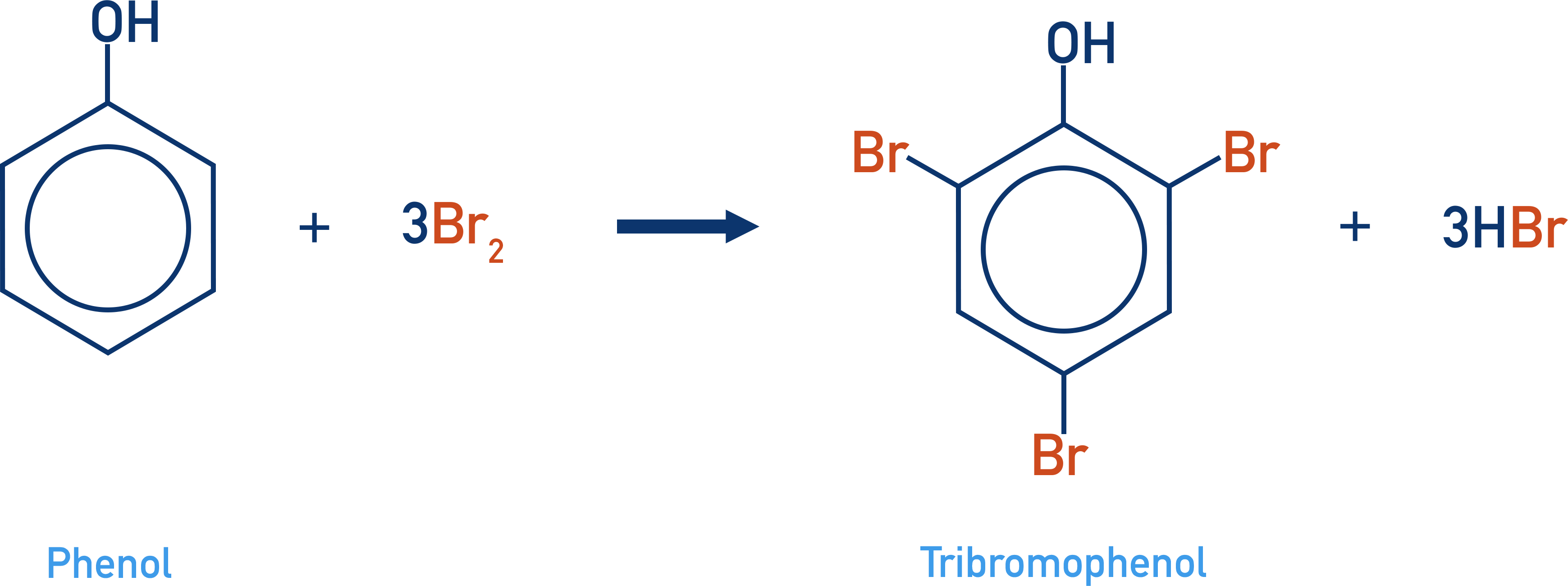
What happens when phenol reacts with dilute nitric acid (nitrification)?
reacts readily at room temperature
forms a mixture of 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol
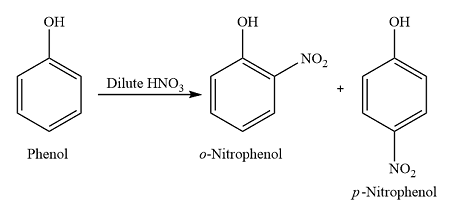
Why is phenol more reactive than benzene?
The -OH group donates a lone pair of electrons into the ring, activating it and making it more attractive to electrophiles
What do activating groups do?
they increase the electron density of the aromatic ring making it more reactive towards electrophiles
What are other activating groups apart from -OH?
-NH2 and -CH3
What do deactivating groups do?
They withdraw electron density away from the ring making it less attractive to electrophiles and therefore less reactive
What are some examples of deactivating groups?
-NO2, -CHO, -CN
How does the presence of an activating group affect the reaction conditions?
The aromatic ring reacts rapidly with electrophiles without needing a catalyst or a high temperature
How does the presence of a deactivating group affect the reaction conditions?
The aromatic ring reacts slowly with an electrophile and requires high temperature and a catalyst
What do directing effects determine?
The position of the second substituent on the benzene ring
What positions do -OH and -NH2 groups direct new substituents to?
Positions 2 or 4
Are positions 2,4 - directing groups activating or deactivating groups?
They are activating groups (except halogens which are deactivating but still 2,4 - directing)
What position does a -NO2 group direct a new substituent to?
Position 3
Are 3-directing groups activating or deactivating?
Deactivating
Why are directing effects important in synthesis?
To ensure substitution occurs at the desired carbon in the ring
What is the reaction of phenol with an acid chloride e.g. ethanoyl chloride?
Forms esters
Phenol + ethanoyl chloride → phenyl ethanoate + hydrogen chloride
What is the equation for the reaction of a phenol with ethanoyl chloride?
Phenol + ethanoyl chloride → phenyl ethanoate + hydrogen chloride
C6H5OH + CH3COCl → CH3COOC6H5 + HCl
How is reacting phenol with ethanoyl chloride different from the esterification of alcohols?
Alcohols form esters with carboxylic acids and acid chlorides, phenols only form esters with acid chlorides
What is the reaction of phenol ethanoyl chloride called?
acylation (specifically ethanoylation)
What other functional group undergoes ethanoylation reactions?
Aminnes (RNH2)
so if a compound undergoes an ethanoylation reaction we know it is an alcohol, phenol, or an amine
What happens when phenol reacts with a solution of iron (III) chloride, FeCl3?
forms a purple (violet) complex
and some other colours
What is the reaction of phenol and iron chloride used for?
To distinguish phenols from alcohols (alcohols do not react)
Why was phenol historically significant?
It was used by Lister as an antiseptic
Why isn’t pure phenol used now?
It is toxic and causes burns
What substituted phenol is used instead of pure phenol?
2,4,6-trichlorophenol (in TCP and Dettol)
What are some other uses of phenol apart from antiseptic?
As the starting material in the manufacture of the analgesics (pain killers) paracetamol and aspirin