Lab #3 | Fischer Esterification and Structure Elucidation
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Is the C=O in carbonyls electrophilic or nucleophilic?
Electrophilic and they react with nucleophiles
Fischer esterification
A nucleophilic alcohol attacks the C=O bond of a carboxylic acid to produce a new ester product (esterification)
different than aldehydes and ketone (who spontaneously react with nucleophiles) as a strong acid is needed like Nafion resin 417
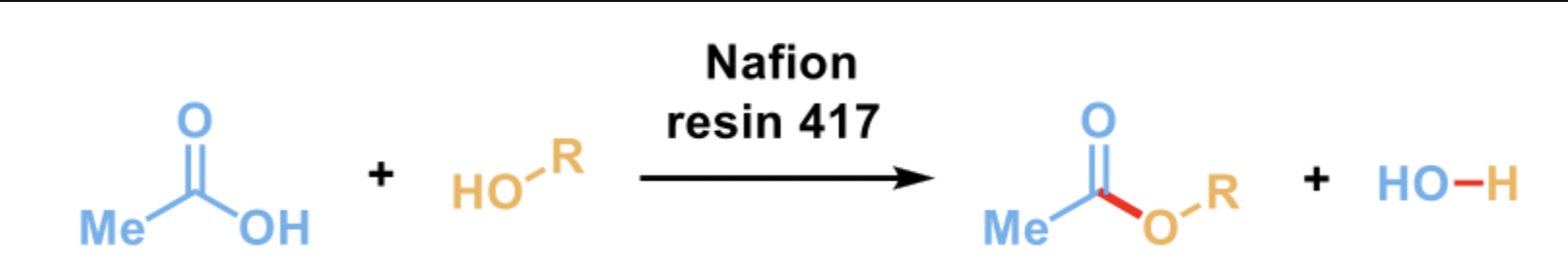
Nafion resin 417
A solid synthetic polymer with a sulfuric group that acts as a super acid catalyst. It can be removed through filtration
protonates the oxygen of the carboxylic acid to form an oxonium ion (c=o → c-oh), which is highly electrophilic species
Why is structure elucidation difficult?
Sometimes unexpected products can occur, meaning multiple characteristic techniques need to be used to determine outcome
Molecular ion peak in mass spec
Represents the ionized molecule that has yet to fragment, meaning its value corresponds to the molecular weight of the molecule
Peek furthest on the x axis
Rule of 13 in mass spec
M+/13= whole number N + (remainder R/ 13)
Reslting formula is CnHn+r and plug in
For every oxygen added, subtract one carbon and 4 hydrogen
Degrees of unsaturation (DOU)
The presence of a π bond or ring in the chemical structure
rings= 1 DOU
DOU equation
X= number of halogens
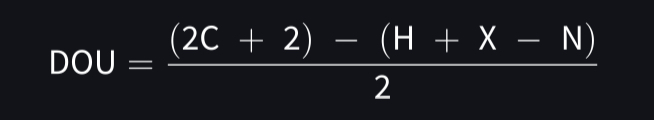
CNMR of δ77.16
Arises from CDCl3 solvent
Common chemical shifts
δ 220-165: carbonyls
δ 150-100: alkenes and aromatic rings
δ 100-70: Alkynes
δ 70-50: C-O in alcohols or ethers
δ <50: Alkyl groups
Glacial acetic acid
Acetic acid that contains minimal water
Why is Nafion needed?
Carboxylic acids are less electrophilic compared to other carbonyl compounds
So, they will not react spontaneously with nucleophiles and a strong acid catalyst like Nafion can promote the esterification
How can mass spec help with characterization?
Mass spec allows the viewer to determine molecular structure
Useful peaks: M+ (molecular ion peak)
Q1: What is true about Nafion?
Protonates carboxylic acid
It is a solid that can be conveniently removed by filtration
It is a super acid
Q2: The molecular ion, M+, is
the ionized form of the molecule with a mass that corresponds to the molecular weight of the molecule
Q3: The molecular ion for an unknown carboxylic acid has m/z = 122. Using the Rule of 13, determine a possible molecular formula. Hint: consider how many oxygen atoms a carboxylic acid should have.
122/13= 9 +5/13
C9H(9+5)= C9H14
2 oxygens, so - 2C and 8H
C7H6O2
Note if hydrogen number is too small, take off one carbon and replace with 12 hydrogens
Q4: Which of the following molecules has 4 degrees of unsaturations?
Benzene
Q5: How many degrees of unsaturation does the compound with molecular formula C6H12O6 have?
1
Q6: Which signal in the above 13C NMR spectrum is characteristic of the ester carbonyl carbon?
171
Q9: When extracting water with diethyl ether, which of the follow statement(s) are correct?
Diethyl ether is less dense than water
The organic and aqueous layers are completely immiscible
Diethyl ether is the top layer
Q10: What important information can be derived from IR spectroscopy?
Key functional groups present in the sample
Why is glacial used over vinegar?
Glacial acetic acid is used over vinegar is because glacial acetic acid contains minimal water. In using vinegar, more water will be introduced into the reaction. This would cause hydrolysis of the newly formed ester, as esters decompose back into the original reagents of carboxylic acid and alcohol. Therefore, in using vinegar, the yield of the desired ester will be lower than using glacial acetic acid, as the ester will decompose back to the original reagents.