UNIT 4: Transoceanic Interconnections c. 1450 - 1750
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Unit 4
Transoceanic Interconnections
c. 1450 - 1750
expansion of European maritime empires driven by exploration, trade, and colonization (particularly in the Americas, Africa, and Asia)
Causes of European Expansion
Technological: Maritime Technologies
astrolabe, monsoon winds, magnetic compass, lateen sail
Portuguese Caravel: smaller, faster, can go through shallow waters
allowed for more efficient navigation and travel across Atlantic and Indian oceans
Economic: Trading of Luxury Goods
Mercantilism: an economic system that focused on growing a nation's wealth by exporting easily produced goods in exchange for limited imports (between the mother country and smaller states)
gold and silver
favorable balance of trade: when states organize their economies around exports and avoid imports as much as possible
Political: Growth of State Power
European monarchs were growing stronger than they have before
Goods on the Silk Road were overpriced by the time they got Europe so the alternative to find a new route where they could trade on their own terms was vital (Indian Ocean)
Joint-Stock Company
where multiple investors contribute their resources to fund a project, sharing profits and risks
Dutch East India Company: VOC
the Dutch monopolized the Indian Ocean trade, spreading their influence; allowing it to control trade routes, establish trading posts, and even wage wars
facilitated the spread of goods globally
growth of capitalism and international trade
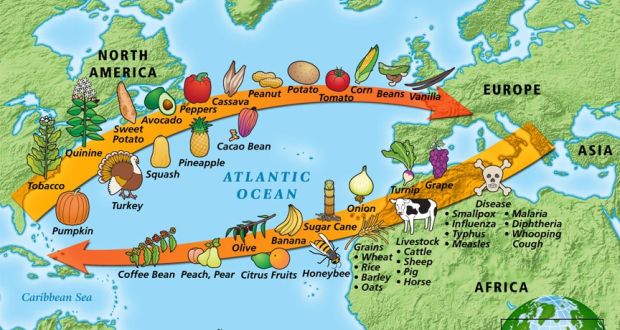
Columbian Exchange
the transfer of new diseases, foods, plants, and animals between the Eastern and Western hemispheres (New World = Americas | Old World = Eurasia & Africa)
Disease:
immunity to certain illness were only apparent to the certain hemispheres; coming into contact with new diseases led to mass sickness
Europeans introduced - smallpox, measles, malaria
indigenous populations were devasted with population decline,
The Great Dying
Food & Plants:
affected populations in both the Old and New Worlds
Old World food when introduced: varied their diets and slowly increased life span - more caloric foods (banana, wheat, corn)
New World food when introduced: varied their diets and increased life span - population expansion
Animals:
animals introduced allowed for more extensive travel and resources
Old World introduced - pigs, sheep, cattle
Horse: allowed for better military defense, leather, land travel
Cash Crops
growing crops to export and make profit
Carribean: Sugarcane
Americas: Corn
Eurasia: Rice
Global Balance of Power
shifting significantly towards the Europeans
Main Motivation of European Imperialism
ways to spread Christianity
Tokugawa Japan
many of the population had converted to Christian faith
Shogun saw this as a threat to the unification of Japan
exiled all Christian missionaries from Japan (brutality and violence)
RESISTANCE TO IMPERIALISM
The Fronde
located in France under the political doctrine of absolutism: all political power under the Monarch
series of rebellions
challenged the growing power of the monarch
Causes:
financial difficulties - increasing taxation was imposed on the people for expansion
resistance to Absolutism - where monarchs wanted to consolidate power and control
Outcome:
a more centralized state
weakened nobility
king who would rule with absolute power (absolutism became stronger)
RESISTANCE TO IMPERIALISM
Asante Empire
West Africa
produced gold, ivory, enslaved people
wealth accumulated allowed them to expand their military and imperialize
Kingdom of the Kongo
Southern Africa
trades with the Portuguese - gold, copper, enslaved people
converted to Christianity - facilitate trade with Christian states
immense expansion of the empire
Indian Ocean Network: CHANGE & CONTINUITY
Change:
European states got introduced into the trading post
increased profits for the powers and merchants
Atlantic system: Africa + Europe + Americas - particularly driven by the transatlantic slave trade and the exchange of goods, labor, and culture
sugar was introduced
silver was a luxury export/import
used to purchase luxury goods from China
coerced labor - indigenous labor
indentured servitude - a labor system where individuals contracted to work for a specific period
Continuity:
Middle East and Asian empires continued using the network
Silk Roads were still controlled entirely by Asian land-based powers
Ming China, Qing, Ottoman Empire
peasant and artisan labor continued to keep producing unique goods
Chattel Slavery
enslaved people are treated as property, with no legal rights or freedoms, in which the purchaser has total ownership over the enslaved person
race based
hereditary
Polygyny
one man marrying more than one woman
Indentured Servitude
contract bounding peasant to work for a particular amount of time (usually 7 years)
Encomienda System
a forced labor system used by the Spanish to distribute indigenous Americans among them
Americans forced to provide labor for the Spanish in exchange for food and protection
Hacienda System
state owners directly employed indigenous people, who had low wages, high taxes, and large debt to landowners
worked on large plantation fields - haciendas
Christianity in the Americas
Jesuits were sent by Catholics to convert the indigenous people
indigenous groups continued to privately practice their own beliefs
syncretism - the blending of some Christian beliefs and practices with indigenous beliefs and practices
Casta System
Spanish imposed social hierarchy:
classify all of the Americas' various races and racial combinations, as well as where Spaniards were born