FA25: Sensors and Measurements
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
What Arduino feature should be used instead of ‘delay’ function for safety purposes?
internal timer lastMilli = millis();
What is a conflict of interest?
Someone involved in an experiment could have a vested interest in the results.
What steps go into defining an effective experiment?
objective, defining variables, determine static/dynamic characteristics, specific equipment needed, procedure, data analysis, reporting
What are the two main ethical issues that can occur when conducting an experiment?
altering and misrepresenting data
How can you find a functional relationship within data?
graphing the data on linear-linear, linear-log, log-linear, or log-log axis
What is a functional relationship?
the mathematical relationship between the parameter being measured and the control parameters
What is a correlation coefficient?
describes how much better the first-order approximation is when compared to the zeroth-order approximation (R²)
Equation for correlation coefficient:
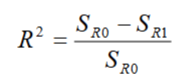
Why did we vary the motor speed slowly in experiment 3?
to accurately compare the speed measured by the two devices
Why did we vary the motor speed quickly in experiment 3?
to see if the ETach measurement lags, leads, or matches the encoder motor speed
What are optical encoders used for?
to measure angular position and clockwise or counterclockwise motion
What is a tunnel in LabView?
used to pass information out of a loop
What is a shift register in LabView?
used to pass information from one iteration of a loop to the next
When defining variables for an experiment, what should be explained?
independent, dependent, parameters, and disturbances
What is a parameter in an experimnet?
non-changing variable or value that sets the boundaries or conditions of an experiment
What is a disturbance in an experiment?
an external or uncontrollable factor that can unexpectedly change the results of the experiment
What is FFT?
mathematical process for determining the dominant frequencies present in a signal
What is signal filtering?
signal conditioning used to remove unwanted frequencies from a signal
What does a low-pass filter do?
removes high frequency content from a signal
What does a high-pass filter do?
removes low frequencies from a signal
What does a band-pass filter do?
removes frequencies below or above specified limits
What does a notch filter do?
removes frequencies within a certain range
What is the cutoff frequency?
the frequency at which the power is one half of its maximum
What does an ADC do?
converts an analog (continuous) signal into a digital (discrete) signal
Why is it important to use ADC?
a necessary step in order to use a computer for acquiring/processing/recording data
What determines the size of the discrete increments in a digital signal?
the number of “bits”
How can you calculate the resolution of an ADC system?
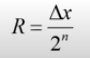
What is a Fourier Series Expansion of a signal?
a signal represented as an infinite series of sines and cosines
Why would we use Fourier Series Expansion?
to plot the approximate amplitude of a signal as a function of frequency
What is Shannon’s Sampling Theorem?
the sampling frequency should be at least two times the highest frequency of interest
What is the Nyquist frequency?
the highest frequency that can be observed for a given sampling rate
How do you determine the Nyquist frequency?
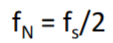
What is strain?
the fraction increase in length caused by an applied load
How is strain calculated?
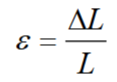
How can you relate stress and strain?
Young’s Modulus
How does a strain gage work?
relates strain to a change in electrical resistance
What is the gage factor?
the principle parameter of strain gage performance
How can you calculate gage factor?
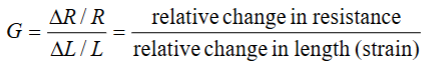
What does a wheatstone bridge do?
relates measured voltage to resistance
What inputs does a wheatstone bridge require?
excitation voltage, three fixed resistors, and variable resistor (being measured)
What is a quarter-bridge arrangement for wheatstone bridge?
when a strain gage serves as one of the resistors
Why do we need a “dummy gage” on a wheatstone bridge arrangement?
to account for the variation of resistance due to temperature (used a strain gage mounted in the transverse direction)
What is a “half-bridge” arrangement for a wheatstone bridge?
replacing another fixed resistor with a second active strain gage (one is in tension while the other is in compression)
Is a strain gage an active or passive device?
passive (active in a wheatstone arrangement)
What type of signal does a strain gage produce?
analog signal
How to calculate outliers in a data set?
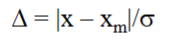
How can you ensure that your data set is normally distributed?
constructing a histogram
How to calculate uncertainty in calculated values each with specified uncertainties?
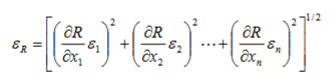
How to calculate an estimated sample size?
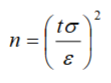
How to calculate uncertainty relating to a specified confidence level?
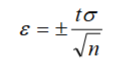
When can we expect a normal distribution?
if a measurement system is affected by random errors
How can we calculate the probability of a value occurring between 0 and a specified value? (assuming normal distribution)
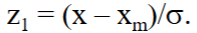
What is a confidence level?
a way of quantifying how confident we are that the actual value of a measurement lies within a certain range
How to calculate confidence interval?
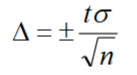
What are the three Rs to keep in mind when selecting a DAQ system?
resolution, range, rate (signal frequency)
What should the axis labels on a graph include?
variable name, symbol, and units
What should be included in an introduction to a technical report?
context, objective, overview
What should be included in the conclusion of a formal report?
summary of results, answers to specific questions, explanation of sources of error
What are two common reasons for developing an experiment?
perform research to understand relationships between dependent and independent variables, to validate
What is a dependent variable?
system characteristic being measured (changing)
What is an independent variable?
system characteristic being varied intentionally
What is the definition of the time constant?
the ratio of capacitance (storage) to diffusivity (dissipation); time required to accomplish 63.2% of the total change in x
What is the time constant used for?
to estimate how quickly a measurement system will respond to sudden changes in the parameter being measured
How can time constant be calculated?
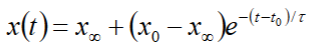
What does RTD stand for?
resistance temperature detector
What does an RTD do?
evaluates a change in temperature by measuring a change in electrical resistance
What is fatigue (in RTD)?
thermally-induced stress caused by repeated expansion and contraction of the resistor
What is lead resistance (RTD)?
additional resistance in the electrical leads of the circuit needed to measure resistance
Why does self-heating occur (RTD)?
current through the resistor element increases the heat
What are some drawbacks of RTDs?
include fragile components, relatively slow response due to bulkiness, expensive
What are some advantages of RTDs?
linear relationship between temperature and resistance, stable and accurate
What does a thermistor do?
relates temperature to a change in electrical resistance, but the material makes a nonlinear relationship
What are some advantages of thermistors?
very accurate, large resistance values, high sensitivity
What are some drawbacks of thermistors?
limited temperature range
How does a thermocouple work?
made by joining two wires of dissimilar materials; relates a voltage difference between the free ends of the wires to the junction temperature (Seebeck effect)
What are some drawbacks of thermocouples?
small voltage output, cold junction compensation is needed
What are some advantages of thermocouples?
fast response time, inexpensive, large temperature range
What is cold junction compensation?
creating a second junction that is maintained at a constant known temperature to account for inaccuracies in thermocouple measurements
What is accuracy?
measure of how close the output of the instrument is to the correct value
What is uncertainty?
the extent to which a reading might be wrong
What is precision?
describes how repeatable the results will be when measuring the same value
What is random error?
moves the measurement away from the correct value in all directions
What is bias error?
moves the measurement away from the correct value in the same direction each time
How can you remove bias errors?
by calibrating your equipment
When is a measurement repeatable?
measurements are the same over a short period of time using the same instrument under the same conditions
When is a measurement reproducible?
measurements are the same even when there are changes to the instrument or measurement conditions
What is the range of an instrument?
the difference between the minimum and maximum values of quantity that the instrument is designed to measure
What is the threshold of an instrument?
the smallest output reading an instrument can produce
What is the resolution of an instrument?
the smallest change in output reading an instrument can produce
What is the nonlinearity of a device?
the maximum deviation of any output reading from the linear best-fit of the measurements
What is the sensitivity of an instrument?
the ratio of the change in output of a transducer to the change in input
What is zero drift of an instrument?
the measure of bias error that occurs due to one or more environmental factors
What is sensitivity drift?
a measure of how much the sensitivity varies as ambient conditions change
What is hysteresis?
occurs if an instrument produces a different result if the measurement point is approached from a different direction
What is a passive instrument?
when the output display or signal is produces only by the quantity being measuredW
What is an active instrument?
when the quantity being measured modulates the magnitude of an external power source, require an external power supply
What is a null-type instrument?
when the instrument itself is adjusted until it is balanced with the system W
What is a deflection-type instrument?
when the measurement displays the difference between the measurand and some reference value
What are the components of a DAQ?
primary sensor, signal processing, secondary sensors, signal transmission, signal presentation/recording
What is a transducer?
a device which converts the aspect of interest into one which is more easily measured