APhug Final exam terms
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
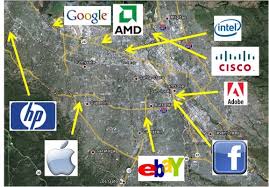
Agglomeration
the clustering of industries in one area for mutual benefit; e.g., Silicon Valley's concentration of tech companies
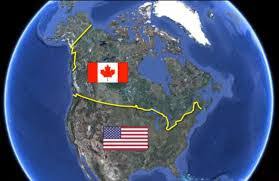
Antecedent boundary
a boundary established before the cultural landscape developed; e.g., the US-Canada border established by treaty in 1846
Break-of-Bulk points
locations where goods are transferred between transportation modes; e.g., the Port of Los Angeles where goods move from ship to truck

Bulk-Gaining Industry
industry where the final product weighs more or has more volume than the inputs; e.g., soda bottling, where water is added to syrup

Cartogram map
a map where size of regions is distorted to show a specific variable; e.g., a population cartogram where India and China appear enlarged
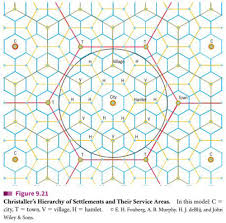
Central Place Theory
theory explaining the distribution of services based on settlements serving as market centers; e.g., hexagonal trade areas in rural Germany
Circulation
short-term, repetitive movements that recur regularly; e.g., commuting daily from home to work
Combine
a machine that reaps, threshes, and cleans grain while moving over a field; e.g., used in Iowa wheat farming

Commercial Agriculture
large-scale farming with the goal of selling crops for profit; e.g., corn farming in the US Midwest

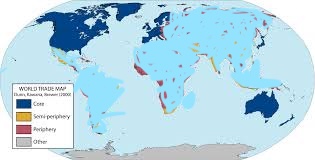
Core countries
economically dominant, high-income countries with strong institutions; e.g., the United States or Germany
Cottage industry
small-scale production done in homes before industrialization; e.g., textile weaving in 18th-century England

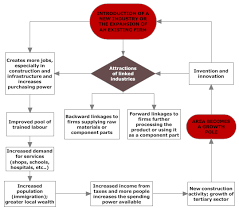
Cumulative Causation
process where economic growth in one area spurs growth in nearby areas; e.g., growth of tech startups around Austin, Texas
Deglomeration
the dispersal of industries from an agglomerated area due to rising costs; e.g., factories leaving New York City for cheaper land
Denomination
a recognized autonomous branch within a religion; e.g., Baptists within Christianity
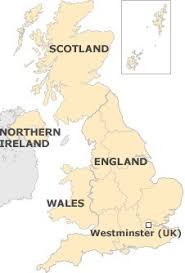
Devolution
the transfer of power from a central government to regional governments; e.g., Scotland gaining its own parliament in the UK
Distribution
the spatial arrangement of a phenomenon over an area; e.g., the distribution of fast food restaurants in a city

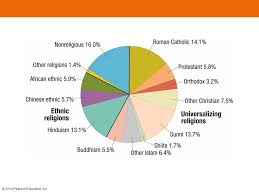
Ethnic religion
religion tied to a particular ethnic group, not seeking converts; e.g., Judaism

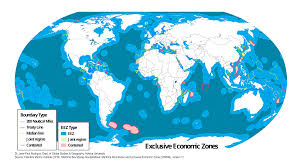
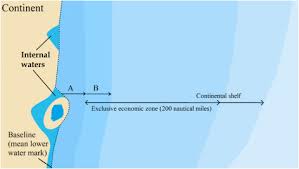
Exclusive Economic Zone
sea zone extending 200 nautical miles where a state controls resource use; e.g., oil drilling in Norway’s North Sea EEZ
Feedlot
area where livestock are fed and fattened before slaughter; e.g., cattle feedlots in Texas

Fordist production
mass production with each worker assigned a specific task; e.g., automobile assembly lines in the early 20th century

Formal region
a geographical area where everyone shares one or more distinctive traits; e.g., the Corn Belt based on corn production
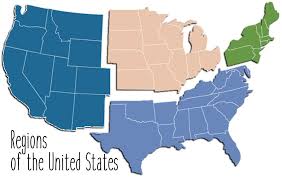
Functional region
area organized around a central node; e.g., the delivery area of a local newspaper
Geopolitics
the study of power relationships and geographic space; e.g., Russia’s interest in controlling access to the Black Sea
GMOs
organisms genetically modified for desired traits; e.g., herbicide-resistant soybeans

Gravity model
model predicting interaction based on population size and distance; e.g., trade between New York and Los Angeles being stronger than with smaller cities
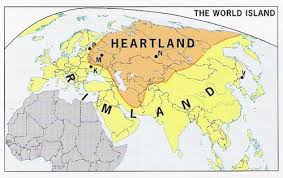
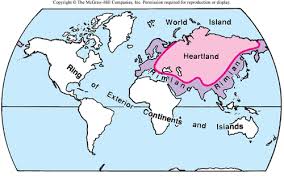
Heartland theory
idea that control of Eastern Europe leads to global power; e.g., used to justify Soviet control over Eastern Europe during the Cold War
Hinduism
an ethnic religion practiced mainly in India characterized by belief in reincarnation and a caste system; e.g., worship at temples in Varanasi

Infrastructure
basic physical systems needed for a society; e.g., roads, bridges, water supply

Intervening Obstacles
barriers to migration or travel; e.g., deserts or immigration laws

Intraregional migration
movement within one region; e.g., moving from a city center to a suburb in Chicago
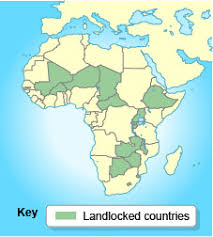
Landlocked state
a state with no direct access to the ocean; e.g., Bolivia
International Law of the Sea
defines nations' rights concerning the use of oceans; e.g., granting 12 nautical miles of territorial sea
Least Cost Theory
theory that businesses locate to minimize transportation, labor, and agglomeration costs; e.g., a factory built near both resources and markets
Maquiladoras
factories in Mexico near the US border that export goods to the US; e.g., electronics plants in Tijuana

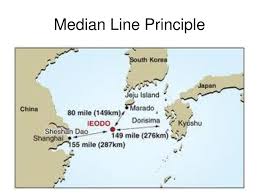
Median-line principle
dividing and creating boundaries at the mid-point between two places; e.g., maritime boundary between the US and Canada in the Great Lakes
Megacity
a city with over 10 million people; e.g., Tokyo

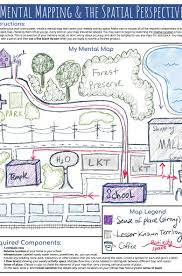
Mental maps
internal representations of places we’ve experienced; e.g., your idea of how to get from school to home
Missionary
someone who spreads a universalizing religion; e.g., Christian missionaries in Sub-Saharan Africa

Monotheism
belief in a single god; e.g., Islam

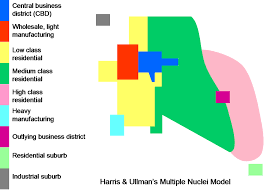
Multiple Nuclei model
urban model suggesting cities have multiple centers for different activities; e.g., Los Angeles with distinct hubs like Hollywood and Downtown
New International Division of Labor
shift of manufacturing jobs to developing countries due to cheaper labor; e.g., clothing production moving to Bangladesh
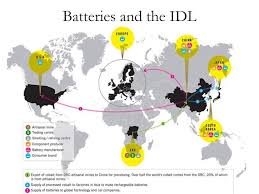
Outsourcing
contracting jobs to external or foreign providers; e.g., customer service call centers in the Philippines

Physical boundary
natural barrier that separates regions; e.g., the Andes Mountains dividing Chile and Argentina
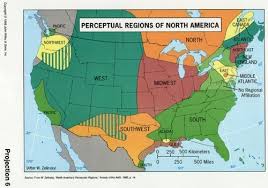
Region
broad geographical area distinguished by similar features; e.g., the Middle East
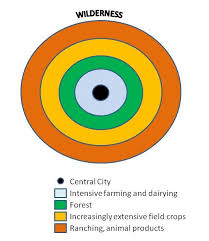
Von Thunen’s Model
model explaining agricultural land use in rings around a city based on cost; e.g., dairy farms near cities, grain farther away